Fig. 6. Schematic representation of SMAD4-I500V disrupting TGFβ and BMP signaling.
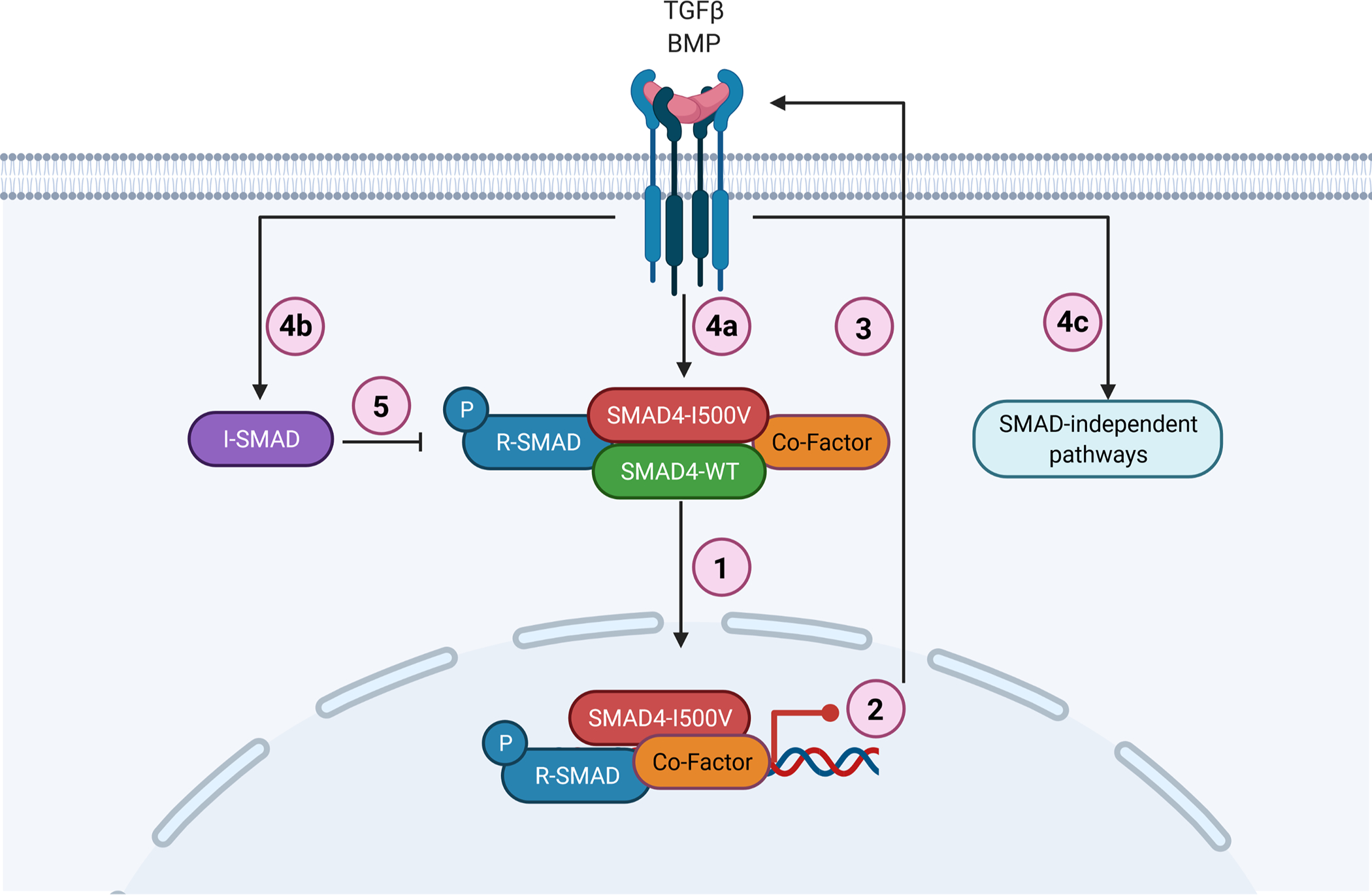
(1) SMAD4-I500V binds to SMAD4, R-SMADs, and co-factors such as NKX2–5. (2) SMAD4-I500V has reduced transcriptional activity and expression of downstream target genes is perturbed. (3) Loss of SMAD4 function activates TGF/BMP signaling. (4a) Active TGF/BMP signaling leads to increased phosphorylation of R-SMADs and buildup of SMAD4-I500V-R-SMADs. (4b) Activation of TGF/BMP signaling leads to increased I-SMADs. (4c) Activation of TGF/BMP signaling leads to initiation of SMAD-independent pathways. (5) Increased I-SMADs lead to further inhibition of SMAD-mediated transcriptional regulation. Image created with BioRender.
