Abstract
1,223 ambulant patients with gonorrhoea were each treated with a single dose of eight tablets of cotrimoxazole. 1,069 patients were followed up (794 males and 275 females). Of these, only 46 (4%) failed to respond. Cotrimoxazole in the dosage used was well tolerated by all the patients, with very few side-effects. There was clear evidence that cotrimoxazole did not mask concomitant syphilitic infections; neither did it produce a gonococcal carrier state. The incidence of post-gonococcal non-specific urethritis was 6 per cent. At present cotrimoxazole seems to be the most useful alternative to penicillin in the treatment of gonorrhoea.
Full text
PDF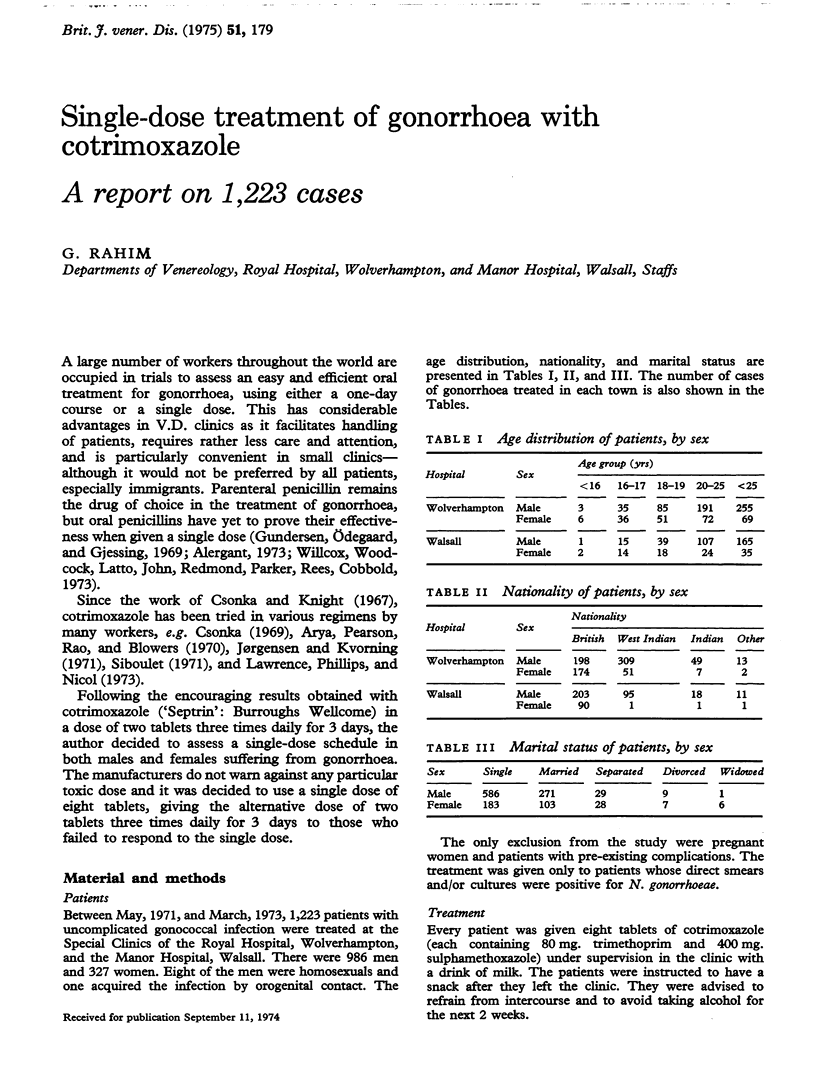



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alergant C. D. Treatment of gonorrhoea with amoxycillin. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Jun;49(3):274–276. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.3.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya O. P., Pearson C. H., Rao S. K., Blowers R. Treatment of gonorrhoea with trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole in Uganda. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Jun;46(3):214–216. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.3.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka G. W., Knight G. J. Therapeutic trial of trimethoprim as a potentiator of sulphonamides in gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1967 Sep;43(3):161–165. doi: 10.1136/sti.43.3.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrell J. H., Garrod L. P., Waterworth P. M. Trimethoprim: laboratory and clinical studies. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Mar;21(2):202–209. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.2.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen T., Odegaard K., Gjessing H. C. Treatment of gonorrhoea by one oral dose of ampicillin and probenecid combined. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Sep;45(3):235–237. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.3.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen B. L., Kvorning S. A. Ukompliceret gonoré behandlet med Trimethoprim og sulfametoksazol. Ugeskr Laeger. 1971 Jul 2;133(26):1259–1260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keys D. Treatment of gonorrhoea. S Afr Med J. 1972 Jul 8;46(28):984–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloosman W. L. A comparative study of three drugs in the treatment of gonorrhoea. S Afr Med J. 1972 May 6;46(19):584–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigfield A. S., Selkon J. B., Rich G. E. Single-session treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhoea in men, using penicillin combined with cotrimoxazole. Controlled trial comparing four different treatment schedules with observations on antibiotic sensitivities of gonococci and a review of the literature. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Jun;49(3):277–290. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.3.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox R. R., Woodcock K. R., Latto D., John J., Redmond A., Parker R. B., Rees G. D., Cobbold R. J. Treatment of gonorrhoea with single oral doses of ampicillin plus probenecid. I. Comparison with procaine penicillin. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Jun;49(3):263–267. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


