Abstract
Urethral specimens from 477 men were collected with endourethral swabs and examined for Chlamydia trachomatis by cell culture on McCoy cells pretreated with idoxuridine. Of these men, 141 had gonococcal urethritis, 262 non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU), and 74 showed no evidence of urethritis. Of 118 men with heterosexually acquired gonococcal urethritis, thirty (25 per cent.), and of 23 men with homosexually acquired gonococcal urethritis, five (22 per cent.), yielded C. trachomatis from the urethra. Urethral specimens from 240 heterosexual men with NGU were examined, and 118 (49 per cent.) yielded C. trachomatis. Of these 240 men, 140 gave a past history of gonococcal or nongonococcal urethritis and 67 (48 per cent.) of these were positive for C. trachomatis; no past history was given by 100 men, of whom 51 were positive for C. trachomatis. Of the 240 heterosexual men with NGU, 81 had had symptoms for 7 days or more before examination, of whom 48 (59 per cent.) yielded isolates of C. trachomatis, and 145 had had symptoms for less than 7 days, of whom 59 (41 per cent.) yielded isolates. Of fourteen asymptomatic men, three were positive for C. trachomatis. Of 22 homosexual men with NGU, seven (32 per cent.) yielded C. trachomatis. C. trachomatis was recovered from the urethra in three (5 per cent.) of sixty heterosexual men without urethritis, and none of fourteen homosexual men without urethritis yielded C. trachomatis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOYD J. T., CSONKA G. W., OATES J. K. Epidemiology of non-specific urethritis. Br J Vener Dis. 1958 Mar;34(1):40–43. doi: 10.1136/sti.34.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
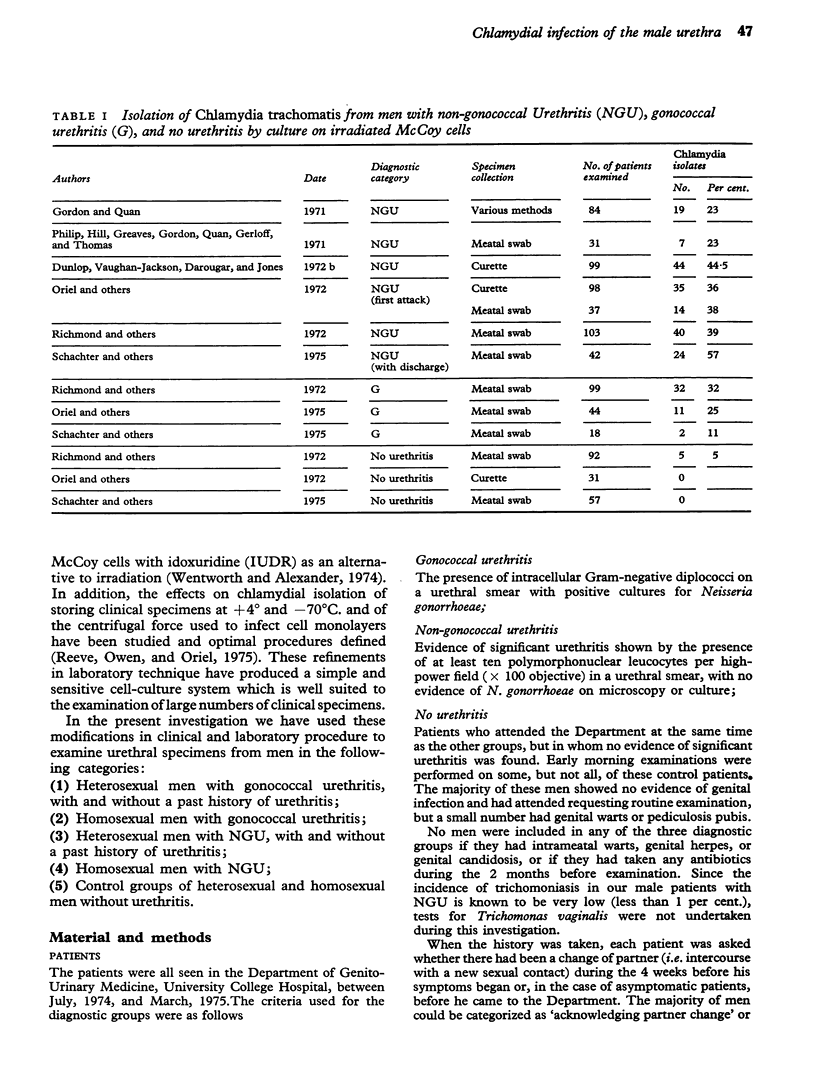
- Dunlop E. M., Vaughan-Jackson J. D., Darougar S. Chlamydial infection. Improved methods of collection of material for culture from the urogenital tract and rectum. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):421–424. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriel J. D., Reeve P., Powis P., Miller A., Nicol C. S. Chlamydial infection. Isolation of Chlamydia from patients with non-specific genital infection. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):429–436. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriel J. D., Reeve P., Thomas B. J., Nicol C. S. Infection with Chlamydia group A in men with urethritis due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):376–382. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Hill D. A., Greaves A. B., Gordon F. B., Quan A. L., Gerloff R. K., Thomas L. A. Study of Chlamydiae in patients with lymphogranuloma venereum and urethritis attending a veneral diseases clinic. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Apr;47(2):114–121. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.2.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve P., Owen J., Oriel J. D. Laboratory procedures for the isolation of chlamydia trachomatis from the human genital tract. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Nov;28(11):910–914. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.11.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond S. J., Hilton A. L., Clarke S. K. Chlamydial infection. Role of Chlamydia subgroup A in non-gonococcal and post-gonococcal urethritis. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):437–444. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Hanna L., Hill E. C., Massad S., Sheppard C. W., Conte J. E., Jr, Cohen S. N., Meyer K. F. Are chlamydial infections the most prevalent venereal disease? JAMA. 1975 Mar 24;231(12):1252–1255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., Alexander E. R. Isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis by use of 5-iodo-2-deoxyuridine-treated cells. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):912–916. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.912-916.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


