Abstract
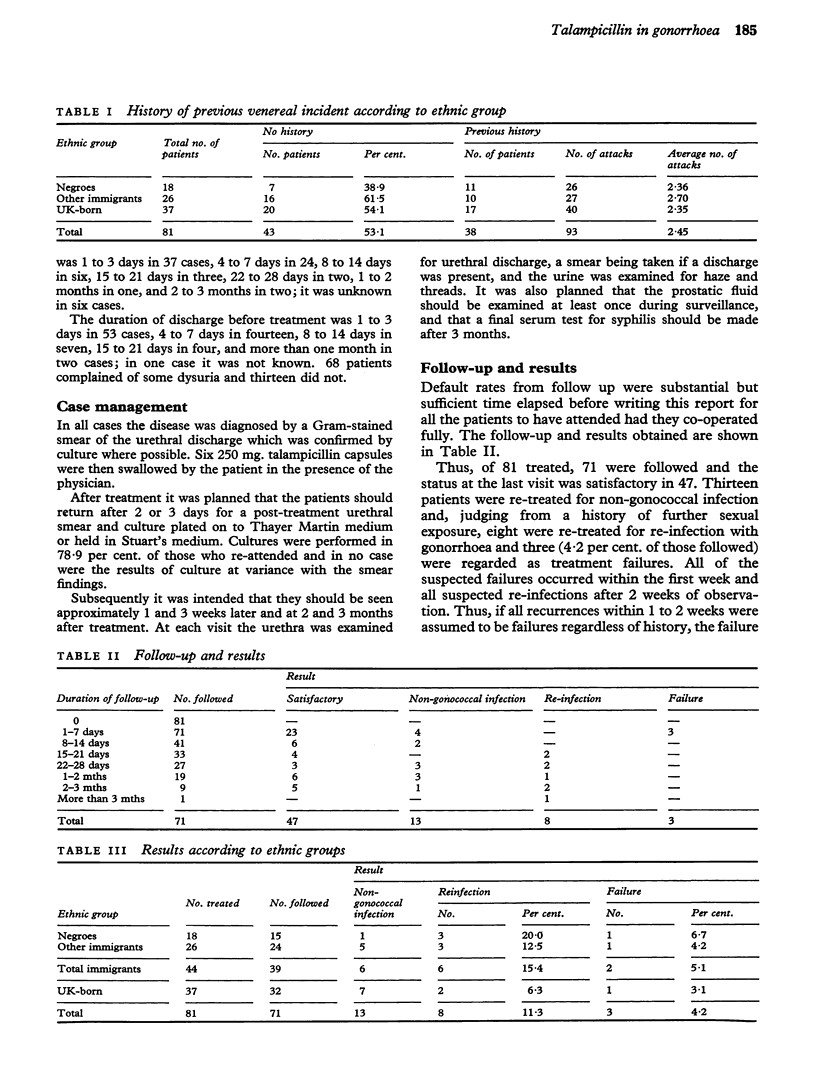
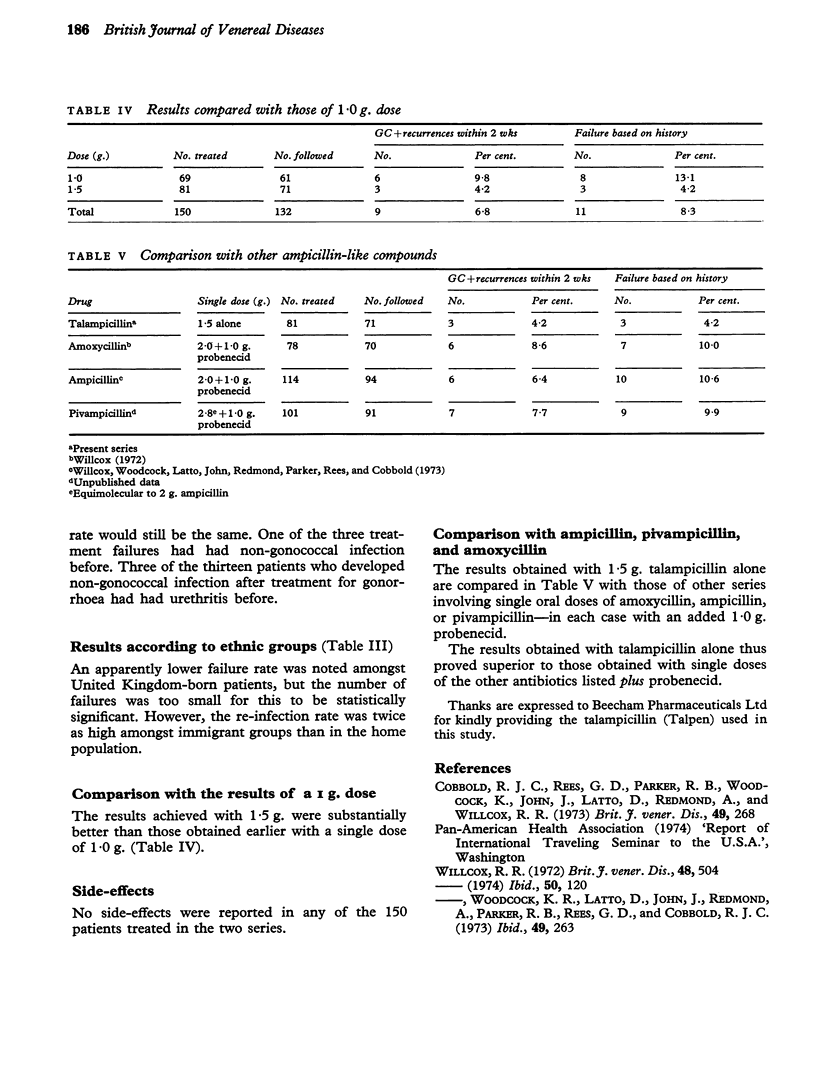
81 patients have been treated with single oral doses of 1-5 g. (6 tablets) of talampicillin without probenecid. The failure rate amongst those followed was only 4-2 per cent. No side-effects were reported. These results were superior to those obtained with 2-0g. or equivalent of ampicillin, amoxycillin, or pivampicillin with probenecid. Talampicillin is thus the most potent ampicillin-like antibiotic so far available for the treatment of gonorrhoea and is capable of curing the disease with a smaller single dose without probenecid than is necessary for other preparations.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cobbold R. J., Rees G. D., Parker R. B., Woodcock K. R., John J., Latto D., Redmond A., Willcox R. R. Treatment of gonorrhoea with single oral doses of ampicillin plus probenecid. II. Comparison of results in London and Wales. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Jun;49(3):268–270. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.3.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox R. R. Amoxycillin in the treatment of gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):504–509. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox R. R., Woodcock K. R., Latto D., John J., Redmond A., Parker R. B., Rees G. D., Cobbold R. J. Treatment of gonorrhoea with single oral doses of ampicillin plus probenecid. I. Comparison with procaine penicillin. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Jun;49(3):263–267. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


