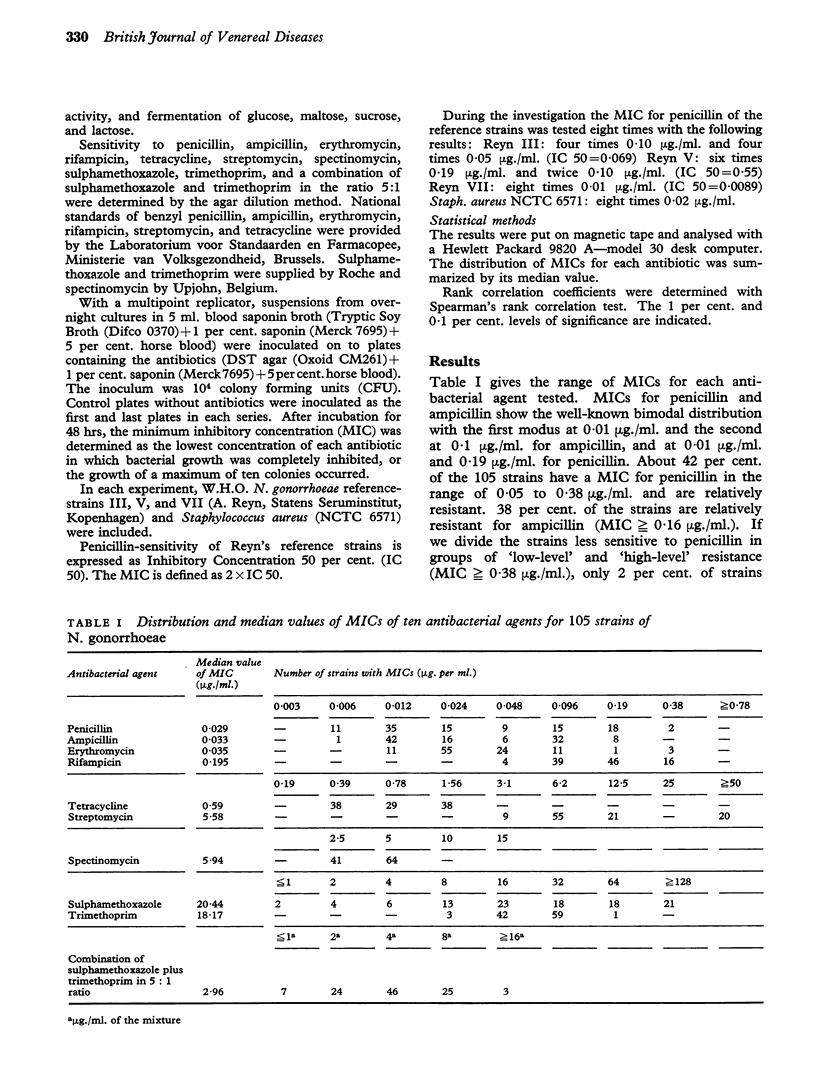
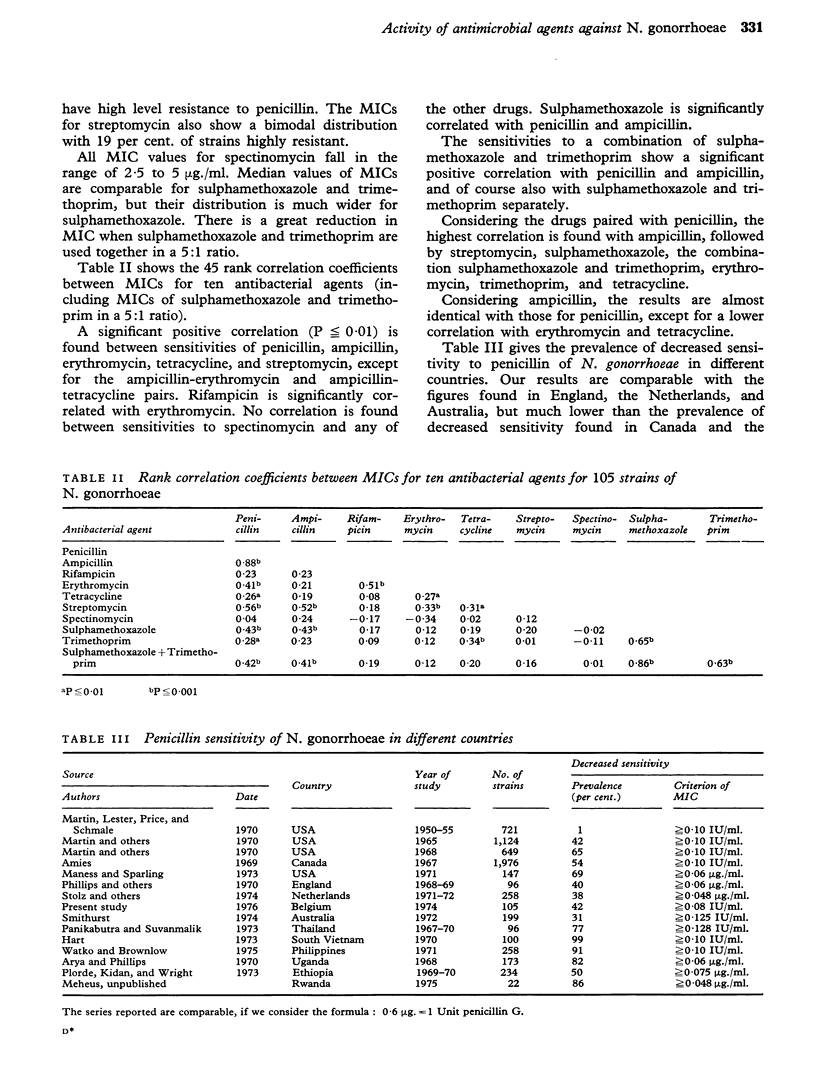
Abstract
105 Belgian strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae were tested for their sensitivity to penicillin, ampicillin, rifampicin, erythromycin, tetracycline, streptomycin, spectinomycin, sulphamethoxazole, trimethroprim, and a combination of sulphamethoxazole and trimethroprim in a 5:1 ratio. Distribution and median values of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are given and discussed. 42 per cent. of strains were relatively resistant to penicillin (MIC greater than or equal to 0-04 mug/ml.), but only 2 per cent. showed high-level resistance (MIC greater than or equal to 0-38 mug/ml.), which is comparable with the prevalence of decreased sensitivity found in other European countries. A significant positive correlation (P less than or equal to 0-01, rank correlation coefficient) is found between the sensitivities to penicillin, ampicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, and streptomycin, except for the ampicillin-erythromycin and ampicillin-tetracycline pairs. Rifampicin is correlated with tetracycline. No correlation is found between the sensitivities to spectinomycin and any of the other drugs. The combination of sulphamethoxazole and trimethoprim in a 5:1 ratio also shows a significant positive correlation with penicillin and ampicillin and with sulphamethoxazole and trimethoprim separately.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amies C. R. Sensitivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to penicillin and other antibiotics. Studies carried out in Toronto during the period 1961 to 1968. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Sep;45(3):216–222. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.3.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya O. P., Phillips I. Antibiotic sensitivity of gonococci and treatment of gonorrhoea in Uganda. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Apr;46(2):149–152. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.2.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. Penicillin resistance of gonococci in South Vietnam. Med J Aust. 1973 Sep 29;2(13):638–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousa M., Lassus A., Järveläinen R., Renkonen O. V. Spectinomycin hydrochloride in the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhoea in males and females. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Aug;50(4):291–293. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.4.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier T. W., Beilstein H. R., Zubrzycki L. Multiple antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jul;6(1):22–28. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness M. J., Sparling P. F. Multiple antibiotic resistance due to a single mutation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):321–330. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. E., Jr, Lester A., Price E. V., Schmale J. D. Comparative study of gonococcal susceptibility to penicillin in the United States, 1955-1969. J Infect Dis. 1970 Nov;122(5):459–461. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.5.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meheus A. Z., De Brauwere D., Muganza F. Treatment of gonorrhoea with spectinomycin hydrochloride (trobicin) in African males. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 1974 Oct;16(10):1091–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panikabutra K., Suvanmalik S. Sensitivity to penicillin of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Bangkok. Relation to the results of treatment. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Apr;49(2):209–212. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Ridley M., Rimmer D., Lynn R. In-vitro activity of twelve antibacterial agents against Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Lancet. 1970 Feb 7;1(7641):263–265. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90635-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plorde J. J., Kidan T. G., Wright L. J. Penicillin sensitivity of gonococci in Ethiopia. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Jun;49(3):260–262. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.3.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter I. A., Wood W. J. Spectinomycin: minimum inhibitory concentrations for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Aug;50(4):289–290. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.4.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyn A., Benzon M. W. A study of the relationships between the sensitivities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to sodium penicillin G, four semi-synthetic penicillins, spiramycin, and fusidic acid. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Jun;44(2):140–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.2.140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyn A., Schmidt H., Trier M., Bentzon M. W. Spectinomycin hydrochloride (Trobicin) in the treatment of gonorrhoea. Observation of resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Feb;49(1):54–59. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Genetic mapping of linked antibiotic resistance loci in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1284-1292.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithurst B. A. Resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to penicillin in 199 gonococcal infections in women and the response of those infections to penicillin treatment. Med J Aust. 1974 Apr 13;1(15):585–586. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb50883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Med Clin North Am. 1972 Sep;56(5):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolz E., Zwart H. G., Michel M. F. Sensitivity to ampicillin, penicillin, and tetracyline of gonococci in Rotterdam. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Jun;50(3):202–207. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.3.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. K., Seth A. D. Ampicillin plus probenecid compared with procaine penicillin plus probenecid in the treatment of gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Jun;51(3):183–187. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.3.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer J. D., Martin J. E., Jr Improved medium selective for cultivation of N. gonorrhoeae and N. meningitidis. Public Health Rep. 1966 Jun;81(6):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


