Abstract
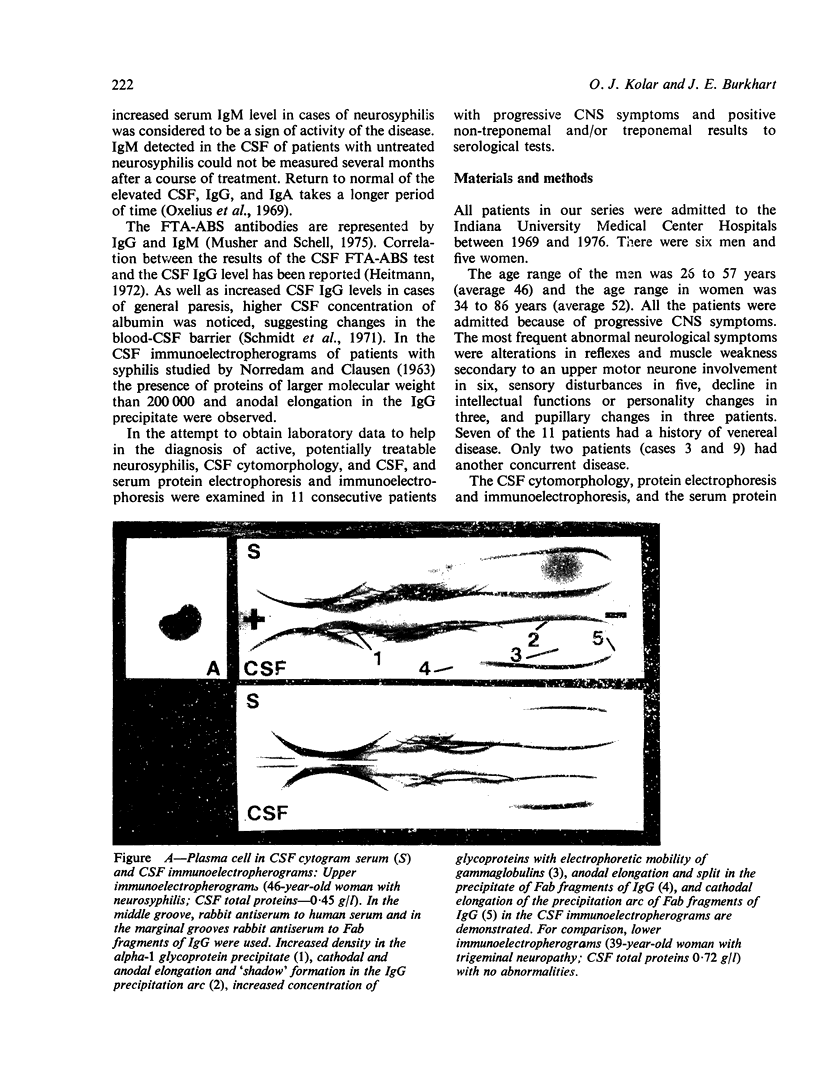
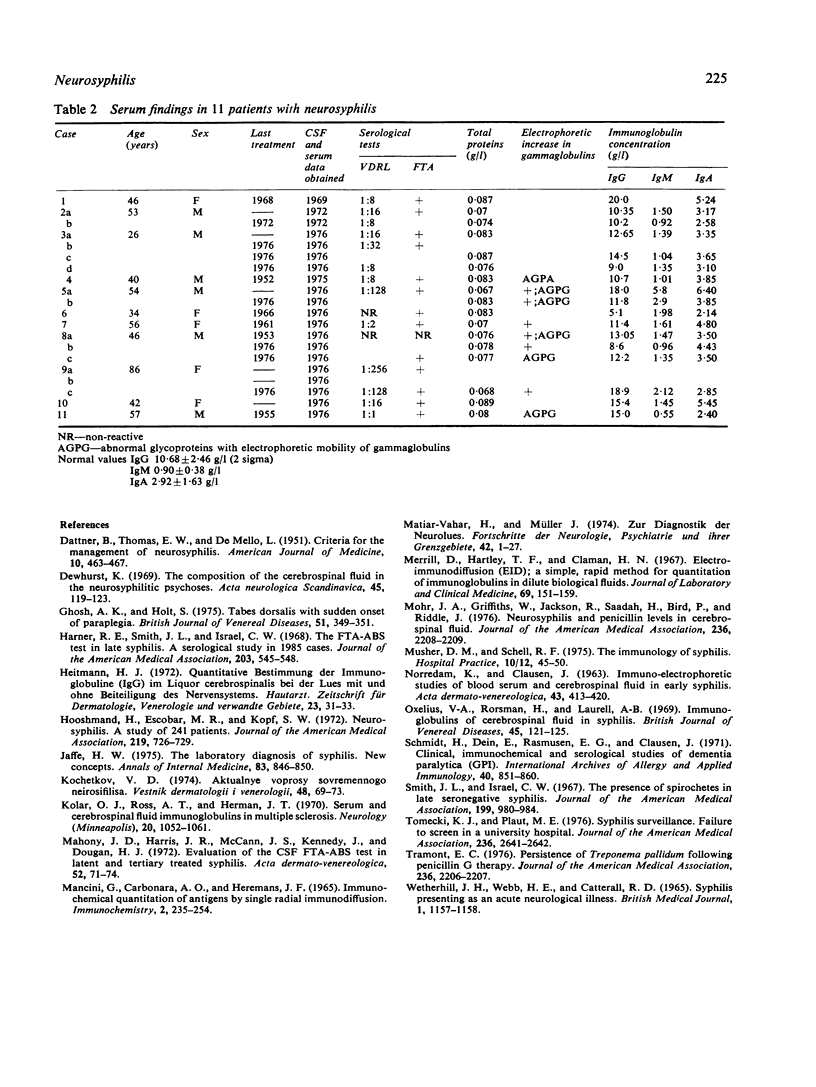
In patients with abnormal neuropsychiatric symptoms and a reactive fluorescent treponemal antibody absoption (FTA-ABS) test in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or serum, a normal CSF cell count and total protein concentration does not exlude late syphilis involving the central nervous system. In these patients, the presence of plasma cells in the CSF cytogram, increased concentration of CSF immunoglobulin G (IgG), immunoelectrophoretic abnormalities in the precipitates of the IgG and of the Fab fragments of IgG in the CSF immunoelectropherogram, and an increased serum level of immunoglobulin M (IgM) suggest an active, potentially treatable neurosyphilis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DATTNER B., THOMAS E. W., DE MELLO L. Criteria for the management of neurosyphilis. Am J Med. 1951 Apr;10(4):463–467. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90292-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst K. The composition of the cerebro-spinal fluid in the neurosyphilitic psychoses. Acta Neurol Scand. 1969;45(1):119–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1969.tb01226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. K., Holt S. Tabes dorsalis with sudden onset of paraplegia. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Oct;51(5):349–351. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.5.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harner R. E., Smith J. L., Israel C. W. The FTA-ABS test in late syphilis. A serological study in 1,985 cases. JAMA. 1968 Feb 19;203(8):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitmann H. J. Quantitatve Bestimmung der Immunoglobuline (IgG) im Liquor cerebrospinalis bei der Lues mit und ohne Beiteiligung des Nervensystems. Hautarzt. 1972 Jan;23(1):31–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooshmand H., Escobar M. R., Kopf S. W. Neurosyphilis. A study of 241 patients. JAMA. 1972 Feb;219(6):726–729. doi: 10.1001/jama.219.6.726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe H. W. The laboratory diagnosis of syphilis. New concepts. Ann Intern Med. 1975 Dec;83(6):846–850. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-83-6-846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochetkov V. D. Aktualnye voprosy sovremennogo neirosifilisa. Vestn Dermatol Venerol. 1974;48(3):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony J. D., Harris J. R., McCann J. S., Kennedy J., Dougan H. J. Evaluation of the C.S.F. F.T.A. ABS test in latent and tertiary treated syphilis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1972;52(1):71–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill D., Hartley T. F., Claman H. N. Electroimmunodiffusion (EID): a simple, rapid method for quantitation of immunoglobulins in dilute biological fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):151–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr J. A., Griffiths W., Jackson R., Saadah H., Bird P., Riddle J. Neurosyphilis and penicillin levels in cerebrospinal fluid. JAMA. 1976 Nov 8;236(19):2208–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORREDAM K., CLAUSEN J. IMMUNO-ELECTROPHORETIC STUDIES OF BLOOD SERUM AND CEREBROSPINAL FLUID IN EARLY SYPHILIS. Acta Derm Venereol. 1963;43:413–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxelius V. A., Rorsman H., Laurell A. B. Immunoglobulins of cerebrospinal fluid in syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Jun;45(2):121–125. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H., Dein E., Rasmusen E. B., Clausen J. Clinical, immunochemical and serological studies of dementia paralytica (GPI). Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(6):851–860. doi: 10.1159/000230468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomecki K. J., Plaut M. E. Syphilis surveillance. Failure to screen in a university hospital. JAMA. 1976 Dec 6;236(23):2641–2642. doi: 10.1001/jama.236.23.2641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Persistence of Treponema pallidum following penicillin G therapy. Report of two cases. JAMA. 1976 Nov 8;236(19):2206–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WETHERILL J. H., WEBB H. E., CATTERALL R. D. SYPHILIS PRESENTING AS AN ACUTE NEUROLOGICAL ILLNESS. Br Med J. 1965 May 1;1(5443):1157–1158. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5443.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



