Abstract
Sera from various groups were tested for syphilis by cardiolipin, fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorbed (FTA-ABS), and treponemal haemagglutination (TPHA) tests. The proportion of positive results, 12.7%, obtained from an unselected urban population suggested that the prevalence of the disease had declined since 1953. The probable explanation is the widespread use of penicillin. Late manifestations of syphilis are much rarer in Ethiopia than would be predicted from the high incidence at the infectious stage and, if present, they affect the cardiovascular system. These findings confirm old observations. Llymphocytes from Ethiopians with early syphilis did not proliferate when cultured with Treponema pallidum in vitro, in contrast with cells from patients with cardiovascular syphilis. These findings differed from observations made previously on patients in England with early syphilis.
Full text
PDF

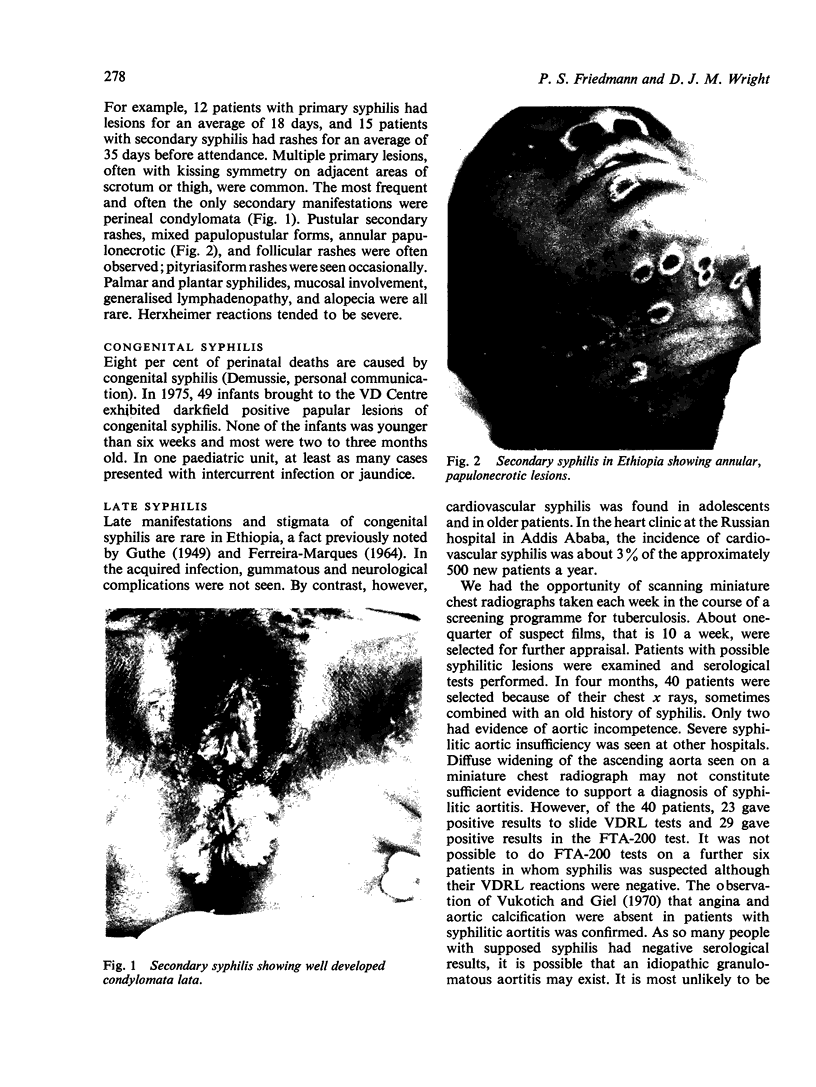


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUCK A. A., SPRUYT D. J. SEROREACTIVITY IN THE VENEREAL DISEASE RESEARCH LABORATORY SLIDE TEST AND THE FLUORESCENT TREPONEMAL ANTIBODY TEST. A STUDY OF PATTERNS IN SELECTED DISEASE AND CONTROL GROUPS IN ETHIOPIA. Am J Hyg. 1964 Jul;80:91–102. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjune G., Barnetson R. S., Ridley D. S., Kronvall G. Lymphocyte transformation test in leprosy; correlation of the response with inflammation of lesions. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jul;25(1):85–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERREIRA-MARQUES J. CONTRIBUTION A L'ETUDE DES MALADIES VENERIENNES ET CUTANEES A ADDIS-ABABA. Dermatol Trop Ecol Geogr. 1964 Jul-Sep;30:139–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton W. F. Estimate of annual incidence of undiscovered syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1973 Jun;49(3):249–255. doi: 10.1136/sti.49.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleer A., van der Hart M., Blok-Schut B. J., Schellekens P. T. Correlation of PPD and BCG-induced leukocyte migration inhibition, delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity, lymphocyte transformation in vitro and humoral antibodies to PPD in man. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACSON C. An idiopathic aortitis in young Africans. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:69–79. doi: 10.1002/path.1700810109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston N. A. Treponema pallidum haemagglutination test for syphilis. Evaluation of a modified micro-method. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):474–478. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankhurst R. Old-time Ethiopian cures for syphilis, seventeenth to twentieth centuries. J Hist Med Allied Sci. 1975 Jul;30(3):199–216. doi: 10.1093/jhmas/xxx.3.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reggiardo Z., Middlebrook G. Delayed-type hypersensitivity and immunity against aerogenic tuberculosis in guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):815–820. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.815-820.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro C. D., Harding G. E., Smith D. W. Relationship of delayed-type hypersensitivity and acquired cellular resistance in experimental airborne tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jul;130(1):8–15. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.1.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha D. P., Bang F. B. Protein and calorie malnutrition, cell-mediated immunity, and B.C.G. vaccination in children from rural West Bengal. Lancet. 1976 Sep 11;2(7985):531–534. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91791-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIVOLET J., SIMERAY A., ROLLAND M., CHALLUT F. Etude de l'intradermoréaction aux suspensions de Tréponèmes formolées souche Nichols pathogène chez les syphilitiques et les sujets normaux. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1953 Jul;85(1):23–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vukotich D., Giel R. Cardiovascular and neurological findings in Ethiopians with syphilitic heart disease. Trop Geogr Med. 1970 Mar;22(1):45–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




