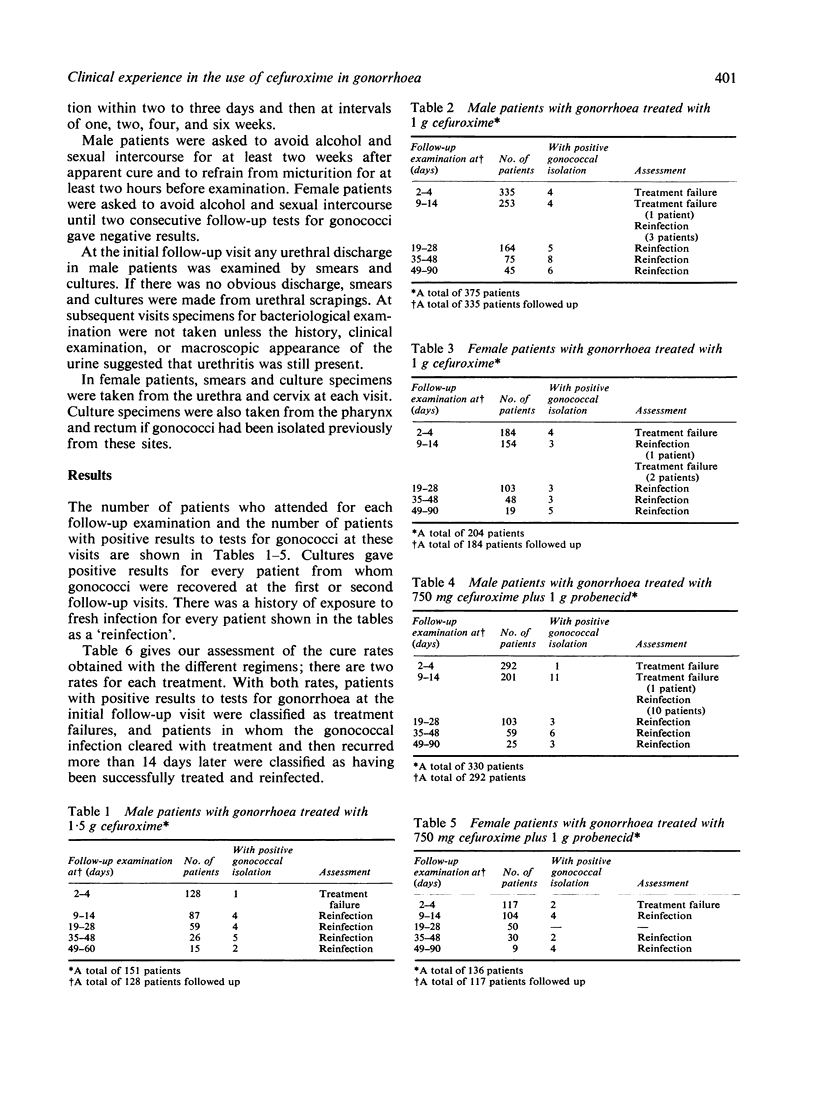
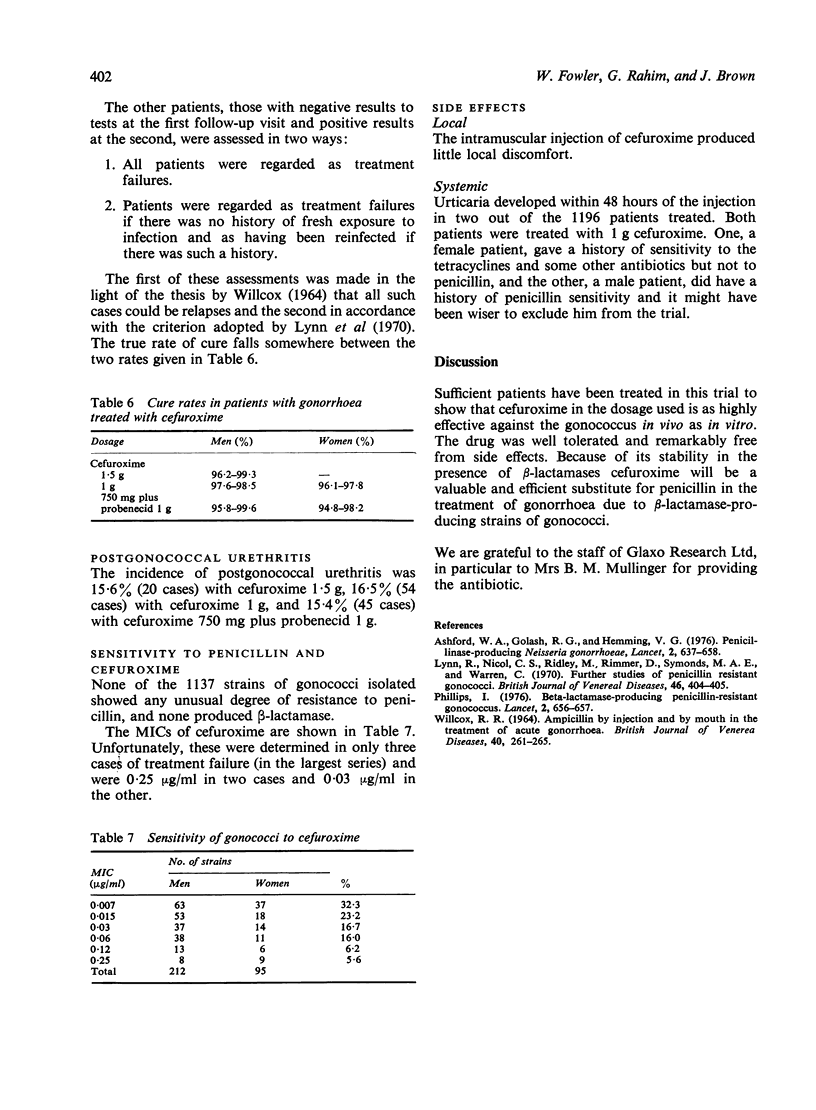
Abstract
Cefuroxime, a new antibiotic derived from cephalosporin-C which is very stable in the presence of beta-lactamases produced by Gram-negative organisms, was used to treat 856 male patients and 340 female patients with uncomplicated gonorrhoea. In men the drug was used in three different doses, 1.5 g, 1 g, and 750 mg plus 1 g probenecid; in women 1 g and 750 mg cefuroxime plus 1 g probenecid was used. Cure rates ranged from 94.8% to 99.3%. The antibiotic was well tolerated and was free from side effects. Cefuroxime would be a valuable and efficient substitute for penicillin in the treatment of gonorrhoea due to beta-lactamase-producing strains of gonococci.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford W. A., Golash R. G., Hemming V. G. Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):657–658. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92467-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn R., Nicol C. S., Ridley M., Rimmer D., Symonds M. A., Warren C. Further studies of penicillin resistant gonococci. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Oct;46(5):404–405. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.5.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I. Beta-lactamase-producing, penicillin-resistant gonococcus. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):656–657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92466-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLCOX R. R. AMPICILLIN BY INJECTION AND BY MOUTH IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE GONORRHOEA. Br J Vener Dis. 1964 Dec;40:261–265. doi: 10.1136/sti.40.4.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


