Abstract
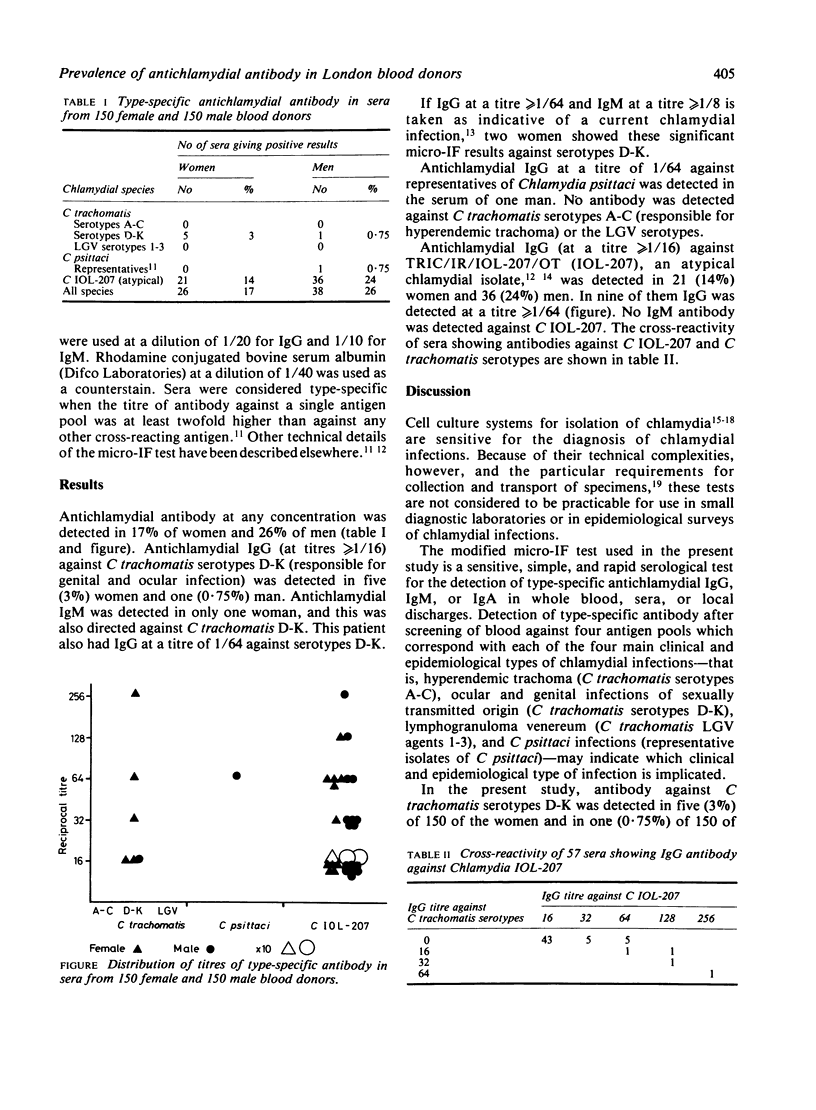
The prevalence of type-specific antichlamydial antibody in a population of blood donors in London was studied using a microimmunofluorescence test. Twenty-six (17%) of 150 women and 38 (26%) of 150 men had antichlamydial antibody (IgG at greater than or equal to 1/16 or IgM greater than or equal to 1/8 or both). Of these, five (3%) women had one (0.75%) man had this antibody directed against Chlamydia trachomatis serotypes D-K, responsible for genital infections, and one man had antibody to Chlamydia psittaci agents. The remaining 57 men and women had antibody against an atypical chlamydial isolate designated Chlamydia IOL-207, which is iodine-negative and serologically distinct from both C trachomatis and C psittaci. The nature and location of infection by this agent are obscure. The results of this study suggest that the prevalence of sexually transmitted infection with C trachomatis serotypes D-K in a normal adult population in London is very low.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani M. D., Darougar S., Burns D. C., Thin R. N., Dunn H. Isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis from the male urethra. Br J Vener Dis. 1977 Apr;53(2):88–92. doi: 10.1136/sti.53.2.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beem M. O., Saxon E. M. Respiratory-tract colonization and a distinctive pneumonia syndrome in infants infected with Chlamydia trachomatis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 10;296(6):306–310. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702102960604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darougar S., Jones B. R., Kinnison J. R., Vaughan-Jackson J. D., Dunlop E. M. Chlamydial infection. Advances in the diagnostic isolation of Chlamydia, including TRIC agent, from the eye, genital tract, and rectum. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):416–420. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer R. S., Treharne J. D., Jones B. R., Herring J. Chlamydial infection. Results of micro-immunofluorescence tests for the detection of type-specific antibody in certain chlamydial infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Dec;48(6):452–459. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.6.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton A. L., Richmond S. J., Milne J. D., Hindley F., Clarke S. K. Chlamydia A in the female genital tract. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Feb;50(1):1–10. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C., Wang S., Wentworth B. B., Grayston J. T. Primary isolation of TRIC organisms in HeLa 229 cells treated with DEAE-dextran. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jun;125(6):665–668. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Ripa T., Svensson L., Weström L. Chilamydia trachomatis infection in patients with acute salpingitis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 16;296(24):1377–1379. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706162962403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Schoop J. W., Wang S. P., Munzinger J., Schläpfer H. U., Knoblauch M., Tammann R. W. Chlamydia trachomatis as possible cause of peritonitis and perihepatitis in young women. Br Med J. 1978 Apr 22;1(6119):1022–1024. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6119.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J. Chlamydial infections (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 2;298(9):490–495. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803022980905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treharne J. D., Darougar S., Jones B. R. Modification of the microimmunofluorescence test to provide a routine serodiagnostic test for chlamydial infection. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jun;30(6):510–517. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.6.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treharne J. D., Ripa K. T., Mårdh P. A., Svensson L., Weström L., Darougar S. Antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis in acute salpingitis. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Feb;55(1):26–29. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., Alexander E. R. Isolation of Chlamydia trachomatis by use of 5-iodo-2-deoxyuridine-treated cells. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):912–916. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.912-916.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Bel-Kahn J. M., Watanakunakorn C., Menefee M. G., Long H. D., Dicter R. Chlamydia trachomatis endocarditis. Am Heart J. 1978 May;95(5):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(78)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


