Abstract
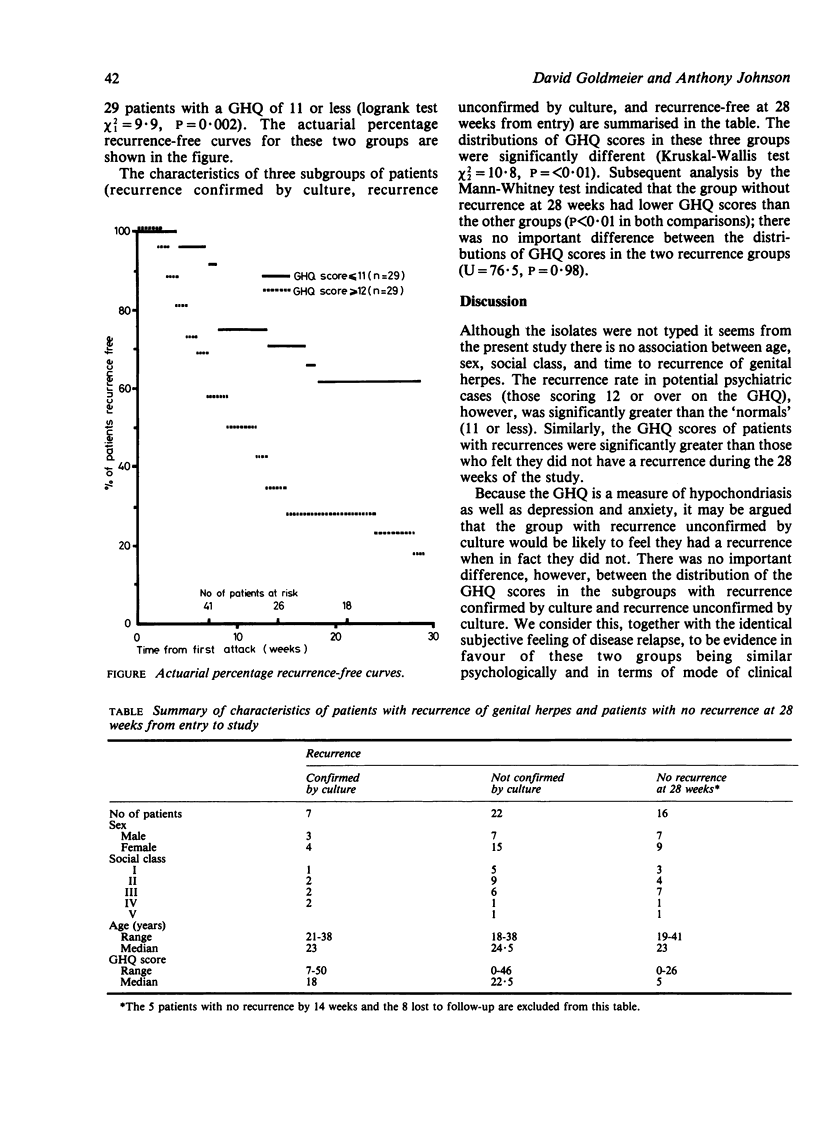
The progress of 58 patients with first attacks of genital herpes was monitored for up to 30 weeks. The effects of sex (gender), age, social class, and non-psychotic psychiatric illness (as measured by the "general health questionnaire," GHQ) on the recurrence rate of herpes was studied. The recurrence rates, measured by the actuarial percentage recurrence-free curves, showed that the 29 patients with GHQ scores above 11 had a significantly higher recurrence rate than those who scored less than 11 (P = 0.002). There were no important differences between recurrence rates according according to sex, age, or social class. These findings suggest that non-psychotic states, such as anxiety or obsessionality resulting in GHQ scores above 12, may possibly cause an excess production of adrenergic substances which encourages reactivation of latent genital herpes. Thus, to lessen the recurrence rate in such patients, a psychological or chemical approach to treatment could be used to modify the autonomic sympathetic response.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Goldberg D. P., Blackwell B. Psychiatric illness in general practice. A detailed study using a new method of case identification. Br Med J. 1970 May 23;1(5707):439–443. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5707.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutfield D. C. Herpes genitalis. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Sep;44(3):241–250. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.3.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juel-Jensen B. E. Herpes simplex and zoster. Br Med J. 1973 Feb 17;1(5850):406–410. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5850.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laibson P. R., Kibrick S. Reactivation of herpetic keratitis by epinephrine in rabbit. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966 Feb;75(2):254–260. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1966.00970050256020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peto R., Pike M. C., Armitage P., Breslow N. E., Cox D. R., Howard S. V., Mantel N., McPherson K., Peto J., Smith P. G. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient. II. analysis and examples. Br J Cancer. 1977 Jan;35(1):1–39. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1977.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


