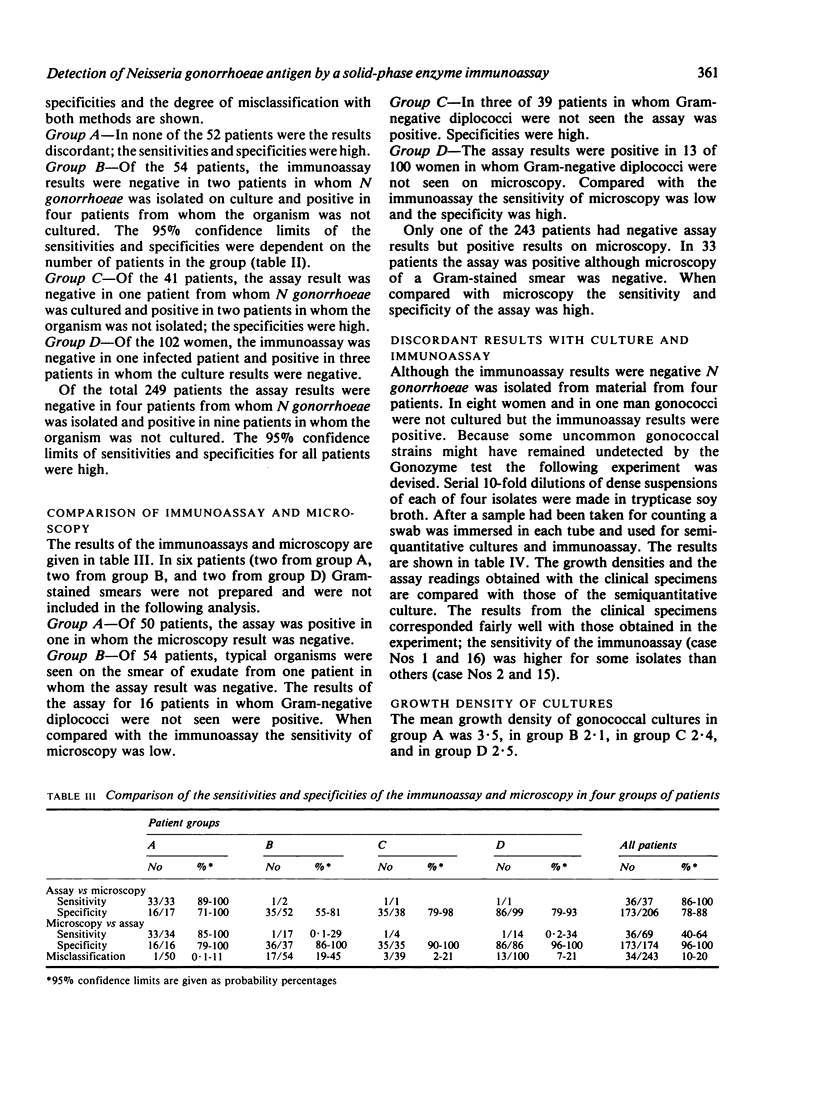
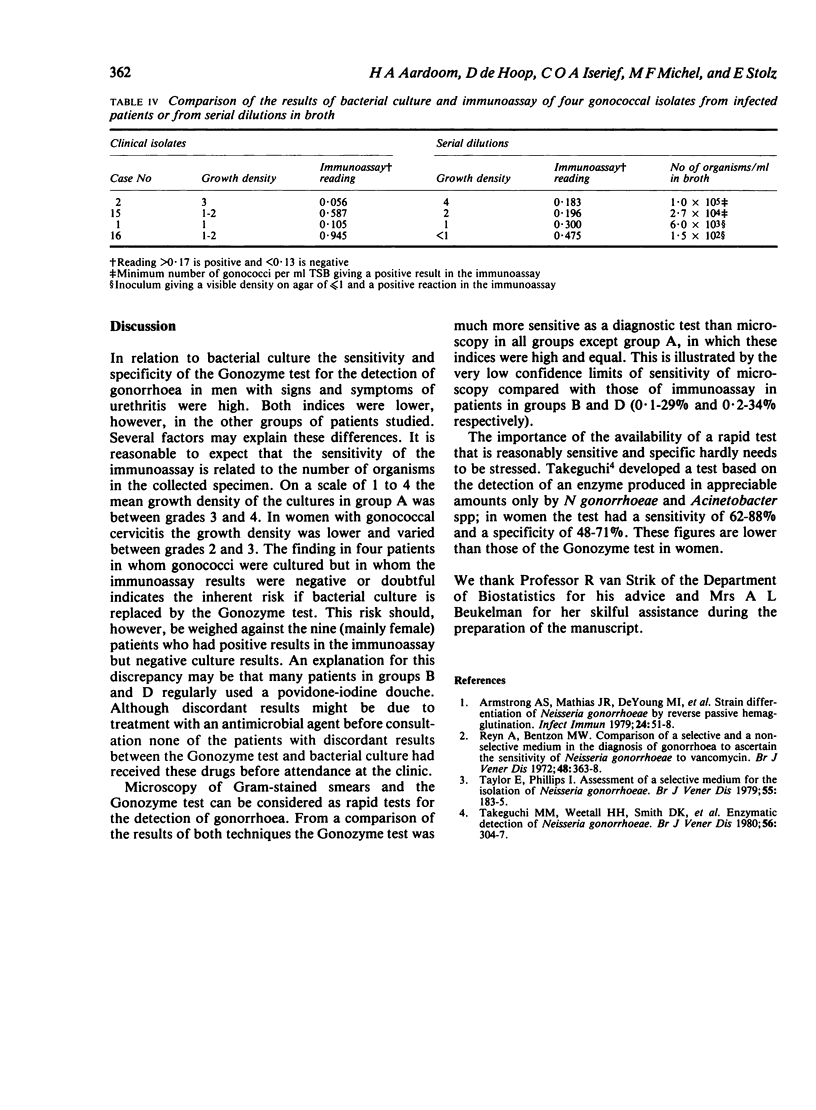
Abstract
The Gonozyme test (Abbott Laboratories) is a new enzyme immunoassay for detecting Neisseria gonorrhoeae antigens in specimens from the urethra in men and the endocervix in women. To evaluate the usefulness of the assay 249 patients were investigated. The results obtained with the immunoassay were compared with those of culture and microscopy of Gram-stained smears. The sensitivity and specificity of the test were high in men with urethritis and acceptable in different groups of women. As the sensitivity of the Gonozyme test was much higher than that of microscopy for endocervical specimens it might be useful as a rapid screening test for the detection of gonorrhoea in women.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong A. S., Mathias J. R., DeYoung M. I., Hirata A. A. Strain differentiation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by reverse passive hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):51–58. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.51-58.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyn A., Bentzon M. W. Comparison of a selective and a non-selective medium in the diagnosis of gonorrhoea to ascertain the sensitivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to vancomycin. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Oct;48(5):363–368. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.5.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeguchi M. M., Weetall H. H., Smith D. K., McDonald H. C., Livsey K. A., Detar C. C., Chapel T. A. Enzymatic detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1980 Oct;56(5):304–307. doi: 10.1136/sti.56.5.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor E., Phillips I. Assessment of a selective medium for the isolation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1979 Jun;55(3):183–185. doi: 10.1136/sti.55.3.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


