Abstract
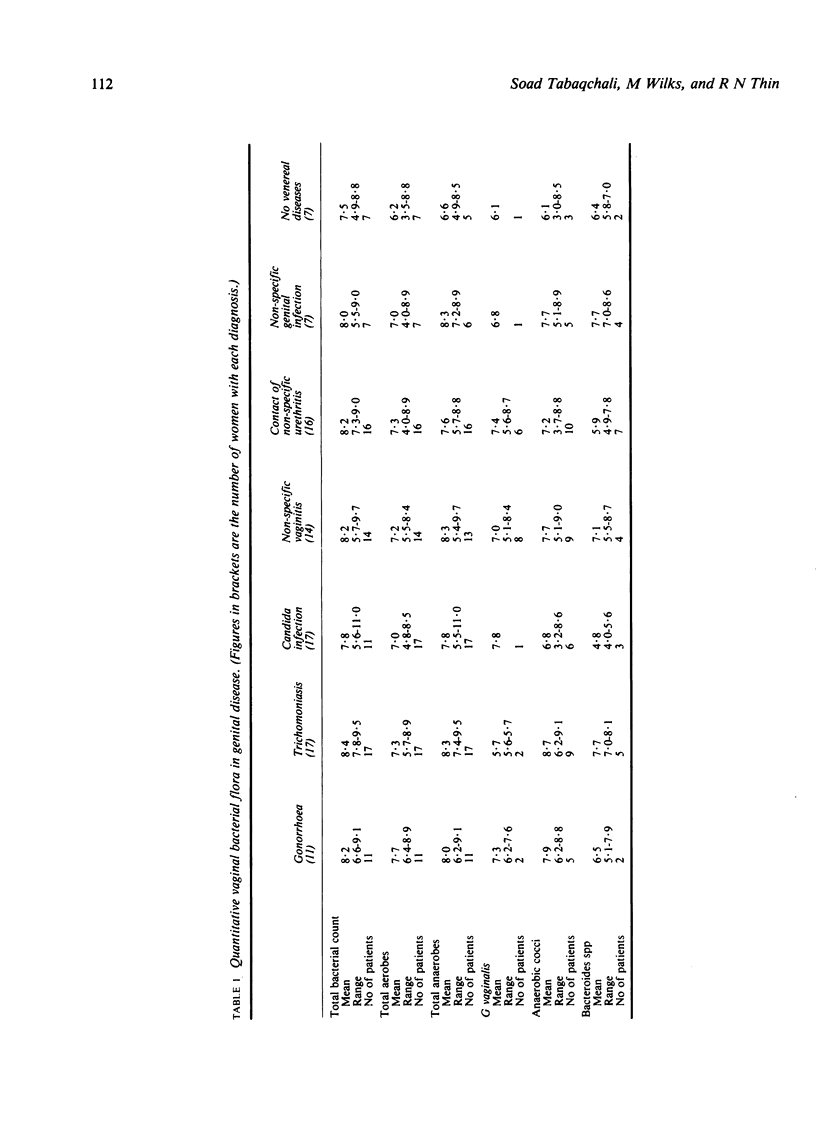
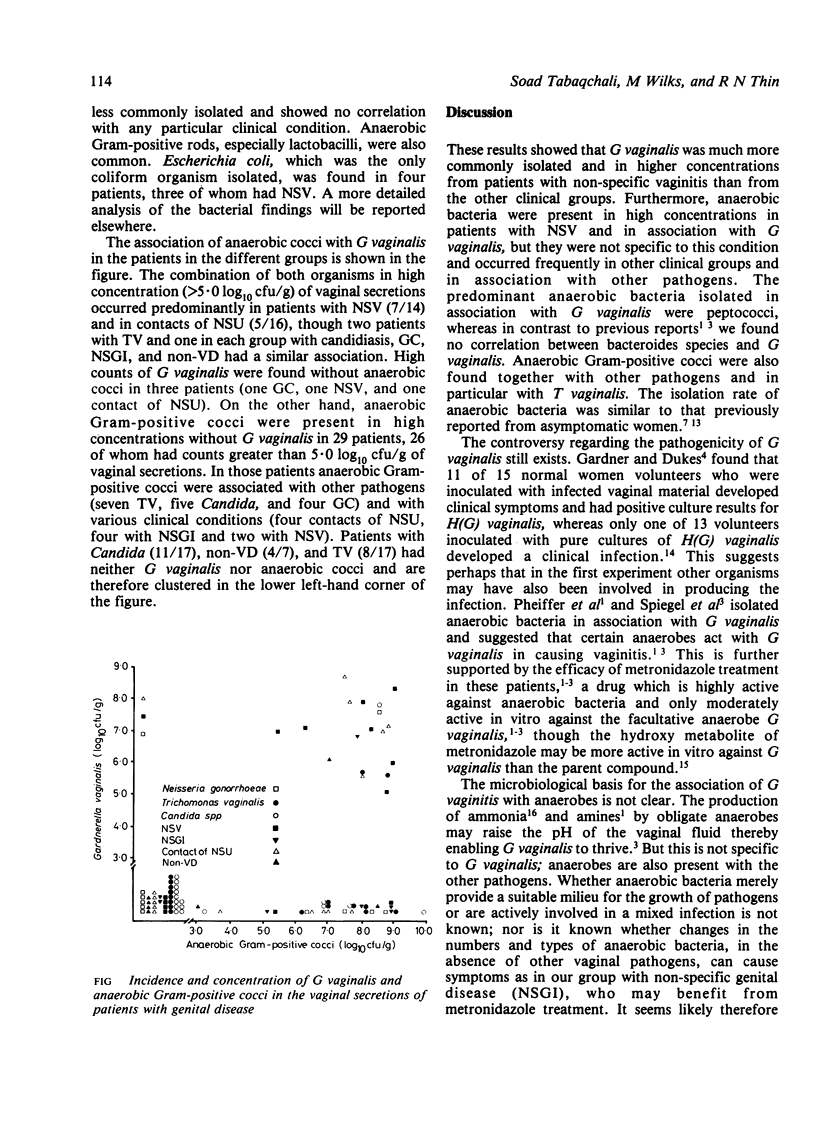
In a study of Gardnerella vaginalis and anaerobic bacteria in non-specific vaginitis (NSV) and other genital disease 89 patients attending a genital medicine clinic had vaginal samples examined for conventional pathogens and for quantitative analysis of G vaginalis and aerobic and anaerobic bacterial flora. The overall incidence of G vaginalis was 20%; G vaginalis (mean concentration 7.0 log10/g of secretion) occurred predominantly in patients with NSV (57%) but also in sexual contacts of non-specific urethritis (NSU) (37.5%) and in patients with other conditions (11.8%). G vaginalis is therefore a relatively common isolate in patients with vaginal discharge. The concentration of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria ranged from 4.9-11.0 log10/g of secretion with an anaerobe-to-aerobe ratio of 10:1. Anaerobic bacteria, particularly anaerobic Gram-positive cocci (mean concentrations 7.7 log10/g), were present in patients with NSV and in association with G vaginalis, but they also occurred in other clinical groups and with other pathogens, particularly Trichomonas vaginalis. Anaerobic bacteria may therefore play an important role in the pathogenesis of vaginal infections.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey R. K., Voss J. L., Smith R. F. Factors affecting isolation and identification of Haemophilus vaginalis (Corynebacterium vaginale). J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):65–71. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.65-71.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsdon M. J., Taylor G. E., Pead L., Maskell R. Corynebacterium vaginale and vaginitis: a controlled trial of treatment. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):501–503. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Onderdonk A. B., Drude E., Goldstein C., Anderka M., Alpert S., McCormack W. M. Quantitative bacteriology of the vaginal flora. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):271–277. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramley H. M., Dixon R. A., Jones B. M. Haemophilus vaginalis (Corynebacterium vaginale, Gardnerella vaginalis) in a family planning clinic population. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Feb;57(1):62–66. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. C., Forsyth P. S., Buchanan T. M., Holmes K. K. Amine content of vaginal fluid from untreated and treated patients with nonspecific vaginitis. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):828–835. doi: 10.1172/JCI109382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Malkasian K. L., Marshall J. R., Guze L. B. The bacteriology of acute pelvic inflammatory disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Aug 1;122(7):876–879. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90731-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criswell B. S., Ladwig C. L., Gardner H. L., Dukes C. D. Haemophilus vaginalis: vaginitis by inoculation from culture. Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Feb;33(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkelberg W. E. Corynebacterium vaginale. Sex Transm Dis. 1977 Apr-Jun;4(2):69–75. doi: 10.1097/00007435-197704000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Ison C. A., Kaye C. M., Timewell R. M., Dawson S. G. Pharmacokinetics of metronidazole and its principal metabolites and their activity against Gardnerella vaginalis. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Aug;58(4):246–249. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.4.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER H. L., DUKES C. D. Haemophilus vaginalis vaginitis: a newly defined specific infection previously classified non-specific vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1955 May;69(5):962–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood J. R., Pickett M. J. Salient features of Haemophilus vaginalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):200–204. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.200-204.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pheifer T. A., Forsyth P. S., Durfee M. A., Pollock H. M., Holmes K. K. Nonspecific vaginitis: role of Haemophilus vaginalis and treatment with metronidazole. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jun 29;298(26):1429–1434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197806292982601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel C. A., Amsel R., Eschenbach D., Schoenknecht F., Holmes K. K. Anaerobic bacteria in nonspecific vaginitis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 11;303(11):601–607. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009113031102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks M., Thin R. N., Tabaqchali S. Quantitative methods for studies on vaginal flora. J Med Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(1):141–147. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-1-141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



