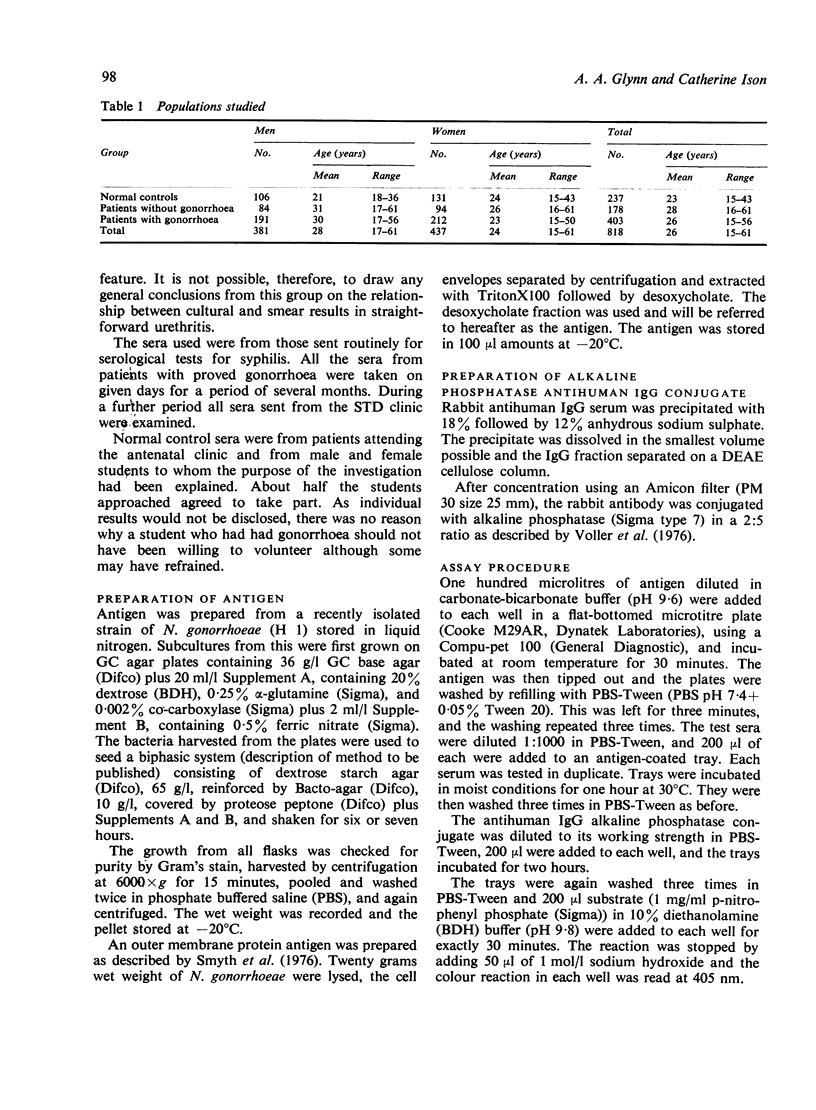
Abstract
IgG antibody to an outer membrane protein extracted from Neisseria gonorrhoeae was measured in patients with gonorrhoea. The level in such patients was significantly higher than in normal controls or in patients with other conditions who were attending the clinic for sexually transmitted diseases. Significantly higher antibody levels were detectable in half the patients within a few days of infection and in a similar proportion of carriers--both male and female. Men with rectal gonorrhoea had particularly high antibody levels. Sixteen per cent of presumptively normal men and 11% of normal women gave positive results but the actual false positive rate could be lower.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchanan T. M., Swanson J., Holmes K. K., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Quantitative determination of antibody to gonococcal pili. Changes in antibody levels with gonococcal infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2896–2909. doi: 10.1172/JCI107486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Kellogg D. S., Jr, Norins L. C. Serum antibody response in experimental human gonorrhoea. Immunoglobulins G, A, and M. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Dec;45(4):325–327. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.4.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Ward M. E. Nature and Heterogeneity of the Antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Involved in the Serum Bactericidal Reaction. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.162-168.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A., Larsen B. Human serum antibodies reacting with endotoxin from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Aug;47(4):269–272. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.4.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oates S. A., Falkler W. A., Jr, Joseph J. M., Warfel L. E. Asymptomatic females: detection of antibody activity to gonococcal pili antigen by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jan;5(1):26–30. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.1.26-30.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., Daoust V. The lipopolysaccharides of Neisseria gonorrhoeae colony types 1 and 4. Can J Biochem. 1975 May;53(5):623–629. doi: 10.1139/o75-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Friedman-Kien A. E., Salton M. R. Antigenic analysis of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1273–1288. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1273-1288.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead A., Main J. S., Ward M. E., Watt P. J. Studies on lipopolysaccharides isolated from strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):123–131. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Glynn A. A. Human antibody response to lipopolysaccharides from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):56–59. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. J., Ward M. E., Glynn A. A. A comparison of serological tests for the diagnosis of gonorrhoea. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Dec;47(6):448–451. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.6.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


