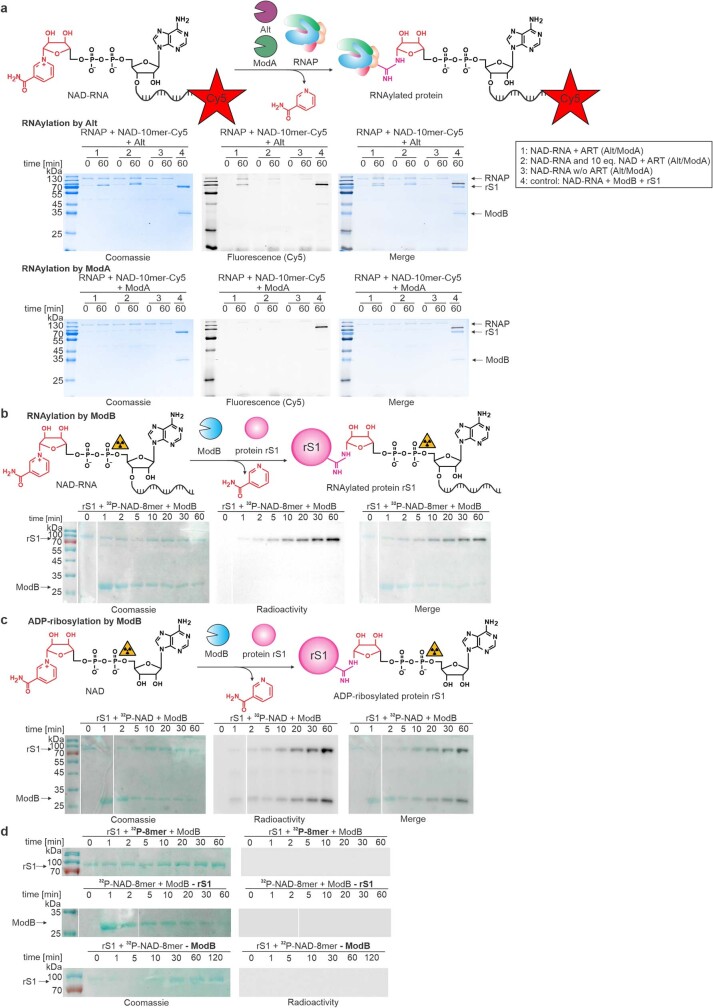
Extended Data Fig. 1. ADP-ribosylation and RNAylation by T4 ARTs.
a, Characterisation of RNAylation of the RNA polymerase (RNAP) by the ARTs Alt or ModA in the presence of NAD-10mer-Cy5 (1), additional 10 equivalents of NAD (2) or in the absence of the respective ART (3) (n = 3). rS1 RNAylated with NAD-10mer-Cy5 by ModB serves as a reference (4). The RNAP is a well-established target protein of Alt and ModA and was thus chosen to assess RNAylation by Alt and ModA. Alt slightly RNAylates the RNAP in vitro which is abolished in the presence of 10 equivalents of NAD relative to NAD-10mer-Cy5. Protein load is visualised by Coomassie staining and RNAylated protein is visualised in the fluorescent Cy5 channel. b,c, Time course analysis of the ModB-mediated RNAylation (b) and ADP-ribosylation (c) of rS1 analysed by SDS-PAGE (n = 3 each). RNAylated or ADP-ribosylated protein is visualised by radioactivity scan and protein load confirmed by Coomassie staining. d, Negative controls for RNAylation of rS1 with ModB analysed by SDS-PAGE. RNAylation assay was performed in the presence of 32P-RNA lacking the NAD-cap (upper panel) and in the absence of either rS1 (- rS1) (middle panel) or ModB (-ModB) (lower panel) (n = 3). In these experiments, no RNAylation was detected in the radioactive scan of the SDS-PAGE gel.