Abstract
A lithopedion is one of the rare complications of ectopic pregnancy, which manifests as a calcified mass in a part of the abdominal or pelvic cavity. We present a 52-year-old woman admitted to the emergency department after an accident, and a lithopedion was observed in imaging examinations. Immediately, surgery was performed, and the calcified mass was removed.
Keywords: Lithopedion, Ectopic pregnancy, CT-scan
Introduction
The term “lithopedion” is derived from 2 Greek words, “lithos” (stone) and “payion” (child), which was first described in the 10th century by Albucasis, a pioneer of modern surgery [1,2]. It is a rare phenomenon in 1.5%-2% of ectopic pregnancies and accounts for 0.0054% of all pregnancies. The patient's age ranges from 30 to 100 years, while the duration of lithopedion retention ranges from 4 to 60 years [3]. A lithopedion is an extremely rare consequence of ectopic pregnancy. This mass may remain asymptomatic in the mother's body for years until it is discovered incidentally following imaging or surgery [3,4].
Case presentation
We present a 52-year-old woman diagnosed with a lithopedion. She was referred to the emergency department after an accident. After taking a pelvic X-ray, we noticed an area with a large mass-like ossification in the pelvic region. Next, a computed tomography (CT) scan was requested from the abdominal and pelvic area, in which a calcified mass was identified in the shape of a fetus with flexion; in addition, the ribs, vertebral column, arm, and skull were recognizable to some extent (Figs. 1 and 2). The patient was operated on by a surgeon, and the calcified mass was removed. The sample was sent for histopathological examination. Pathological observations show fibroconnective tissue with cystic changes, necrotic, calcified, and Ossified tissue.
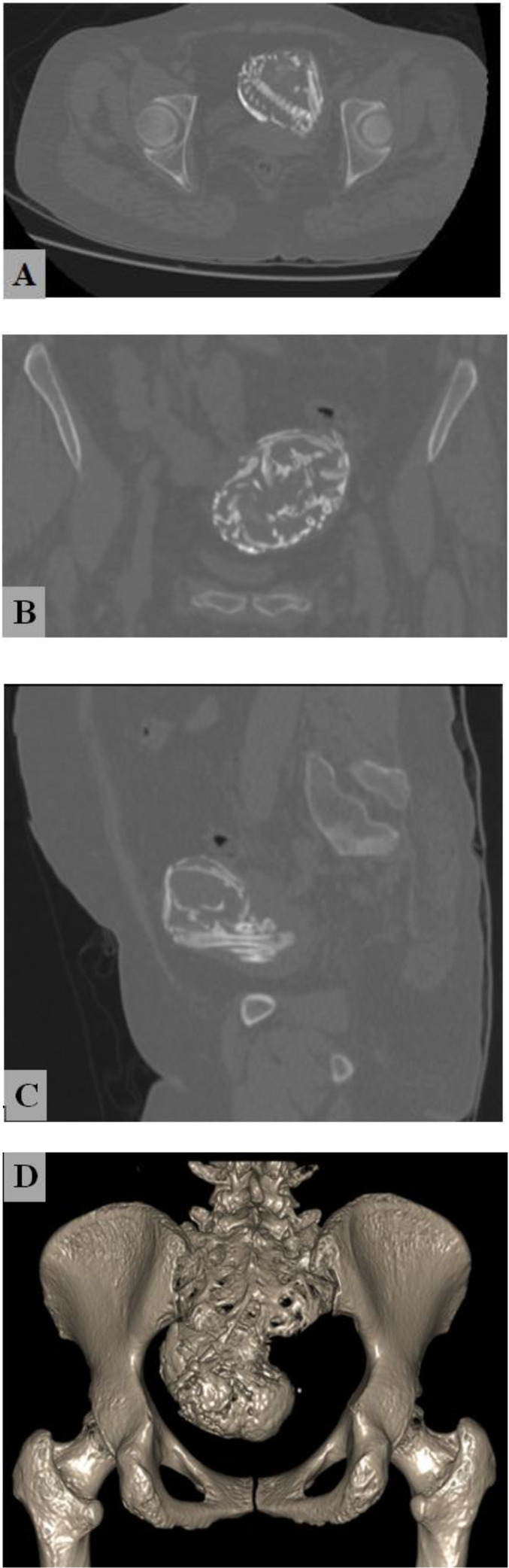
Fig 2.
A pelvic CT scan shows a calcified mass in the pelvic cavity. In these images, the ribs, vertebral column, humerus, and skull are defined to some extent. Bone window of CT-scan, Axial (aA) Coronal (bB) Sagittal (cC) Bone three-dimensional reconstruction (dD).
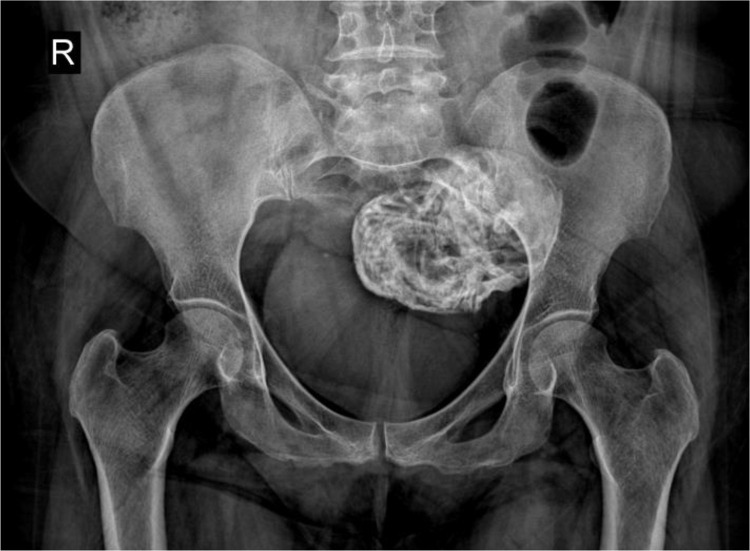
Fig 1.
A pelvic X-ray shows a calcified mass in the pelvic cavity.
Discussion
A lithopedion, or a stone baby, is a rare finding that results from an undiagnosed and untreated advanced ectopic pregnancy [5]. A lithopedion is a very rare consequence of ectopic pregnancy (only 0.0054% of all gestations) [3,4]. Lithopedions cannot develop unless the fetus survives for more than 3 months because, before this time, the bones are still cartilaginous, and the absorption will be fast and complete. Also, other factors are necessary for its occurrence, such as a sterile fetus, failure in medical diagnosis, and the presence of favorable conditions for calcium deposition [5]. The mother's immune system eventually recognizes the fetus as a foreign body and covers it with a calcified substance to protect it from infection [6]. For the calcified fetus inside the mother's abdomen, different forms are considered: (1) lithokelyphos (litho = rock, kelyphos = shell): the membrane of the egg is calcified, but the embryo can be decomposed in different stages, (2) lithokelyphopedion: both the embryo and the egg membrane are disintegrated, (3) lithopedion: only the fetus is calcified [4]. Lithopedions are often asymptomatic, and the patient is unaware of her condition in most cases [5]. Obscure abdominal pain, chronic constipation, cecal volvulus, intestinal obstruction, fistula formation, obstructive uropathy, and pelvic abscess are among the side effects of a lithopedion that may occur [[3], [4], [5], [6], [7]]. In our case, the patient did not present any clinical signs in favor of abdominal mass. The diagnosis of calcified mass was made only based on the imaging of the abdomen and pelvis to rule out injury due to the accident. A report in 2000 presented the first case of lithopedion as a pelvic abscess. Despite the difficult diagnosis of lithopedions, they are sometimes identified as palpable abdominal or pelvic masses on physical examination. However, in most cases, the diagnosis occurs during surgery, autopsy, or imaging of the abdomen and pelvis [7]. In sonographic examinations, it is possible to observe an empty uterine cavity and a calcified abdominal mass with nonspecific features. Also, CT and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans can make a definitive diagnosis [8]. Observing a calcified mass in the pelvis can indicate a variety of pathologies, such as ovarian tumors, uterine fibroids, bladder stones, calcified neoplasms, calcified aneurysms, inflammatory masses, dystrophic soft tissue calcification, lithopedion, and foreign bodies [[8], [9], [10]]. However, it is necessary to remove any dead abdominal fetus or lithopedion as soon as it is detected [10]. A 2019 report presented a 50-year-old woman with abdominal swelling for 15 years and suspected uterine fibroids. In her fibroid surgery, a calcified fetus and a large uterine fibroid were observed and removed from the body [4]. Various studies consider the low socio-economic status and lack of care during pregnancy to be related to the occurrence of this phenomenon [[5], [6], [7], [8], [9], [10], [11]]. Therefore, most recent case reports of lithopedions are from parts of the world where the level of medical care is far from the standard level of first-world countries [2]. Recently, lithopedions have decreased due to increased prenatal care and better paraclinical techniques that accurately determine pregnancy. Because by using diagnostic protocols, it is possible to distinguish ectopic pregnancies from intrauterine types [1]. A 2010 report also described a 74-year-old woman who did not seek medical care due to poverty. Two years later, she became pregnant for the second time and gave birth to an alive and well boy. An abdominopelvic CT scan showed a calcified mass in the abdomen [12]. Therefore, it is important to identify lithopedions in any young or older woman with a calcified abdominopelvic mass, as it can prevent terrible complications that develop over time [13]. Although lithopedions are not always asymptomatic, and in some cases, they may be accompanied by clinical symptoms (such as pain, swelling, and internal problems), improving the level of pregnancy hygiene can be effective in reducing the occurrence of such complications. By training and providing screening services, it is possible to diagnose all types of ectopic pregnancies with high accuracy and prevent the occurrence of acute or chronic complications.
Conclusion
Knowing the types of abdominal masses, etiopathogenesis, and their differentiation from each other is important in preventing and reducing their complications. Ectopic pregnancy is one of the causes of abdominal mass. Proper and timely diagnosis can prevent complications caused by ectopic pregnancies. Improving the health level of society is an important step that can have a significant impact on preventing such pathologies.
Patient consent
The authors confirm that the informed consent form for the publication of this article has been signed by the patient. According to this form, the authors are not allowed to disclose the name of the patient.
Footnotes
Acknowledgments: The authors thank the staff of Shahid Sattari Hospital for their help.
Competing Interests: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- 1.Warfa K., Konya W.P. Lithopedion with seven years of evolution: Case Report. Annals of African Surgery. 2011;7:68–70. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lachman N., Satyapal K.S., Kalideen J.M., Moodley T.R., et al. Lithopedion: a case report. Clinical Anatomy. 2001;14(1):52–54. doi: 10.1002/1098-2353(200101)14:1<52::AID-CA1009>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ede J., Sobnach S., Castillo F., Bhyat A., Corbett J.H. The lithopedion-an unusual cause of an abdominal mass. South African Journal of Surgery. 2011;49(3):140–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sulaiman B., Sani M.T., Binji A.H., Ibrahim R. Lithopedion coexisting with a huge uterine fibroid: A case report. Tropical Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 2019;36(1):144–146. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Santoro G., Laganà A.S., Sturlese E., Giacobbe V., Retto A., Palmara V. Developmental and clinical overview of lithopaidion. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation. 2014;78(4):213–223. doi: 10.1159/000358828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lopez Perez Two Cases of lithopedion in. Ancient Greece.; 2022
- 7.Jain T., Eckert L.O. Abdominal pregnancy with lithopedion formation presenting as a pelvic abscess. Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2000;96(5):808–810. doi: 10.1016/s0029-7844(00)01024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ramos-Andrade D., et al. An unusual cause of intra-abdominal calcification: A lithopedion. European journal of radiology open. 2014;1:60–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2014.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lin S.H., Lo H.L. A calcified tumour in the pelvis. Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore. 2011;40(12):546–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moshiri M., Salari A.A., Mansorian H.R., Shariat R. Lithopedion (stone baby) Annals of Saudi Medicine. 1996;16(1):69–70. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.1996.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chase L.A. Lithopedion. Canadian Medical Association Journal. 1968;99(5):226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sun G., Li M., Lu Y. Unrecognized lithopedion with 35 years' evolution diagnosed on computed tomographic scan. Fertility and sterility. 2010;94(1):341–342. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gueye C., et al. Case report of a lithopedion of tubal location, in a young woman. Radiology Case Reports. 2023;18(4):1552–1555. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.01.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]