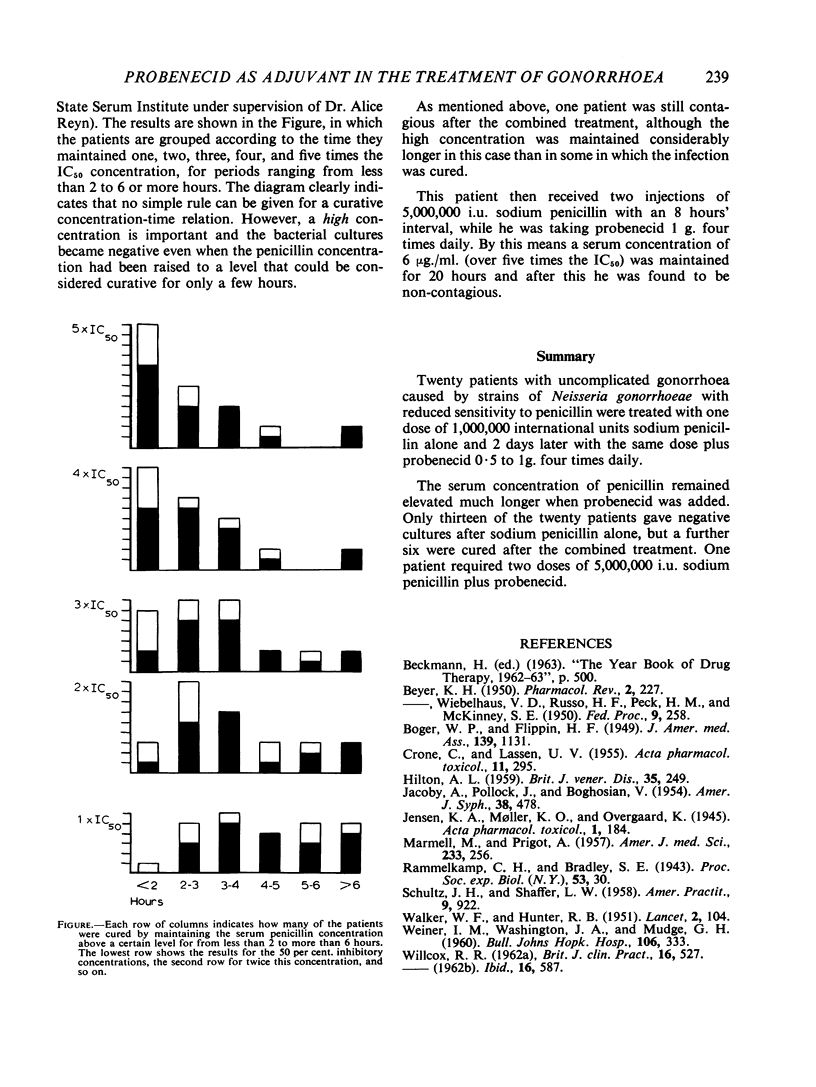
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEYER K. H. Functional characteristics of transport mechanisms. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1950 Aug;99(42):227–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRONE C., LASSEN U. V. The action of probenecid (p-[di-n-propylsulphamyl]-benzoic acid) on uric acid excretion and plasma uric acid level in normal human subjects. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1955;11(3):295–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1955.tb00229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILTON A. L. Treatment of gonorrhoea with P.A.M. and probenecid. Br J Vener Dis. 1959 Dec;35:249–251. doi: 10.1136/sti.35.4.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBY A., POLLOCK J., BOGHOSIAN V. Oral penicillin with and without benemid in the treatment of gonorrhea. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 Sep;38(5):478–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMELL M., PRIGOT A. Oral potassium penicillin G combined with probenecid in the treatment of gonorrhea in the male. Am J Med Sci. 1957 Mar;233(3):256–passim. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195703000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ J. H., SHAFFER L. W. Therapeutic evaluation of oral antibiotic in gonorrhea. Am Pract Dig Treat. 1958 Jun;9(6):922–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER I. M., WASHINGTON J. A., 2nd, MUDGE G. H. On the mechanism of action of probenecid on renal tubular secretion. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1960 Jun;106:333–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


