Abstract
Background
Macrosomia (birthweight ≥ 4 kg or ≥ 4.5 kg) is strongly associated with a predisposition to childhood obesity, which in turn is linked with adverse cardiometabolic health. Despite this, there is a lack of longitudinal investigation on the impact of high birthweight on cardiometabolic outcomes in youth. The preteen period represents an important window of opportunity to further explore this link, to potentially prevent cardiometabolic profiles worsening during puberty.
Methods
This is a secondary analysis of 9–11-year-olds (n = 405) born to mothers in the ROLO longitudinal birth cohort study, who previously delivered an infant with macrosomia. Preteens were dichotomised into those born with and without macrosomia, using two common cut-off criteria (birthweight ≥ 4 kg (n = 208) and < 4 kg; ≥ 4.5 kg (n = 65) and < 4.5 kg). Cardiometabolic health was assessed using anthropometry, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, blood pressure, heart rate, cardiorespiratory endurance (20-m shuttle run test), and non-fasting serum biomarkers for a subgroup (n = 213). Statistical comparisons between the two groups were explored using independent t-tests, Mann–Whitney U tests, and Chi-square tests. Crude and adjusted linear regression models investigated associations between macrosomia and preteen cardiometabolic outcomes.
Results
In total, 29.3% (n = 119) of preteens had overweight/obesity based on their BMI z-score. Preteens born ≥ 4 kg had lower median (IQR) C3 concentrations (1.38 (1.22, 1.52) g/L vs. 1.4 (1.26, 1.6) g/L, p = 0.043) and lower median (IQR) ICAM-1 concentrations (345.39 (290.34, 394.91) ng/mL vs. 387.44 (312.91, 441.83) ng/mL, p = 0.040), than those born < 4 kg. Those born ≥ 4.5 kg had higher mean (SD) BMI z-scores (0.71 (0.99) vs. 0.36 (1.09), p = 0.016), and higher median (IQR) lean mass (24.76 (23.28, 28.51) kg vs. 23.87 (21.9, 26.79) kg, p = 0.021), than those born < 4.5 kg. Adjusted linear regression analyses revealed birthweight ≥ 4 kg was negatively associated with C3 concentration (g/L) (B = − 0.095, 95% CI = − 0.162, − 0.029, p = 0.005) and birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg was positively associated with weight z-score (B = 0.325, 95% CI = 0.018, 0.633, p = 0.038), height z-score (B = 0.391, 95% CI = 0.079, 0.703, p = 0.014), lean mass (kg) (B = 1.353, 95% CI = 0.264, 2.442, p = 0.015) and cardiorespiratory endurance (B = 0.407, 95% CI = 0.006, 0.808, p = 0.047).
Conclusion
This study found no strong evidence to suggest that macrosomia is associated with adverse preteen cardiometabolic health. Macrosomia alone may not be a long-term cardiometabolic risk factor.
Trial registration ISRCTN54392969 registered at www.isrctn.com.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12986-023-00759-8.
Keywords: Birthweight, Macrosomia, ROLO, Cardiometabolic health, Birth cohort, Childhood obesity, Preteen
Introduction
Cardiometabolic diseases represent a major cause of death in adults and the greatest financial burden in healthcare globally [1]. Early signs of cardiometabolic dysfunction can appear in the first decade of life [2, 3]. High rates of overweight and obesity are associated with increasing prevalence of chronic inflammation, immune dysregulation, and cardiovascular comorbidities in school-aged youth [4, 5]. The pubertal transition is linked with significant progression of cardiometabolic risk factors that become more challenging to reverse [6].
The developmental origins of health and disease paradigm supports a link between birthweight extremities, particularly low birthweight and long-term health [7]. High birthweight, or macrosomia, represents a challenging perinatal issue with lasting health implications [8]. The definition of macrosomia varies in the literature, usually referred to as a birthweight ≥ 4 kg or ≥ 4.5 kg [8]. Fetal overnutrition promotes hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinemia, leading to extra fat accumulation that persists postnatally [9]. Thus, high birthweight has been highlighted as a reliable predictor of obesity in childhood and adolescence [10–13]. Several studies also support this phenomenon by linking high birthweight to excess fat mass in youth [14–16].
Observations in adults with high birthweight report increased blood pressure, triglycerides, and altered glucose metabolism [17, 18]. It is unclear if adverse cardiometabolic manifestations of high birthweight become apparent earlier in life. Few retrospective observations in youth include positive correlations between birthweight with blood pressure, unfavourable lipids, and poor glycaemic control [19–22]. The availability of robust evidence is further weakened by the ambiguity of results from few birth cohort studies that have examined high birthweight in relation to cardiometabolic disease risk [2, 15, 23–25].
To address potential inaccuracies arising from cardiometabolic assessment in early childhood, international clinical guidelines endorse preteen ages (9–11 years) as a more stable time point for cardiometabolic screening in both sexes as most will not have commenced puberty [3]. High birthweight individuals are more likely to deliver high birthweight offspring and this harmful pattern may contribute to an ongoing cycle of adverse maternal and offspring health [7, 9]. Thus, a case can be made for further longitudinal investigation of cardiometabolic health determinants in preteens, to enable greater impact for early intervention strategies in the prevention of later disease.
The aim of this study is to examine associations between macrosomia and cardiometabolic health at 9–11 years of age in preteens born to mothers in the ROLO (Randomised cOntrol trial of a LOw glycaemic index diet in pregnancy to prevent macrosomia) longitudinal birth cohort, who previously delivered an infant with macrosomia. We hypothesise that macrosomia may increase cardiometabolic risk in the preteen period, compared to preteens born without macrosomia.
Methods
The ROLO longitudinal birth cohort
The ROLO study was a randomised control trial of a low glycaemic diet in pregnancy to prevent the recurrence of macrosomia in secundigravida women [26]. The study was conducted in the National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland (2007–2011) and ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of the National Maternity Hospital (GEN/279/12). Detailed description of the methodology and results of the ROLO pregnancy study have been published previously [26]. The intervention involved the delivery of low glycaemic index dietary advice by a research dietitian, while those randomised to the control group received routine antenatal care which did not include any formal dietary advice. The primary outcome was birthweight, and no differences were noted in birthweight, though infants from the intervention group showed slightly lower thigh skinfolds [27]. The 759 mothers and children born into the pregnancy study have since been followed-up at multiple timepoints, with the most recent follow-up period taking place at 9–11 years postpartum. Written and informed consent was obtained from all eligible individuals prior to study participation.
The ROLO preteen follow-up
Participants born into the ROLO pregnancy study who had available data on birthweight and attended a ROLO Preteen follow-up appointment between 9.0 and 11.9 years of age were eligible for inclusion. Once the study child became eligible for follow-up, mothers were phoned or emailed by the research team and invited to attend a follow-up visit at the Institute for Sport and Health in University College Dublin. At the 9–11 year follow-up, preteens in which a body mass index (BMI) z-score had been obtained were included, leading to a total sample of 405 preteens. This parameter was chosen to set the sample size to maximise power, and complete data for other variables varied depending on data collection at the time of follow-up.
Exposure
The primary exposure of interest for this analysis was macrosomia, using two common definitions. Preteens were dichotomised as those who were born ≥ 4 kg (n = 208) and those born < 4 kg (n = 197). Subsequently, preteens were dichotomised into those born ≥ 4.5 kg (n = 65) and those born < 4.5 kg (n = 340) to further tease apart potential differences. The secondary exposure of interest for this analysis was birthweight centile, using the cut-off for “large-for-gestational-age”. At delivery, the Gestation Network’s Bulk Calculator version 6.2.3 UK was used to calculate birthweight centiles [28]. Preteens were dichotomised as those who were born with a birthweight ≥ 90th centile (n = 159) and those born < 90th centile (n = 245).
Outcomes
Anthropometry and body composition
At 9–11 years of age, weight and height were assessed by a trained research nutritionist/dietitian with participants dressed in light clothing and shoes removed. Weight was measured using the calibrated SECA model flat, mobile weighing scales, to the nearest 0.1 kg (SECA GmbH & co. Kg. Germany). Height was measured using the SECA 123 portable stadiometer, to the nearest 0.1 cm (SECA GmbH & co. Kg. Germany). BMI was calculated as kg/m2 and values were converted to z-scores in line with the 1990 UK reference data [29, 30]. BMI z-scores were categorised according to World Health Organization cut-offs; “underweight” (BMI z-score < − 2.0); “healthy weight” (BMI z-score > − 2.0 and ≤ 1.0); “overweight” (BMI z-score > 1.0); “obesity” (BMI z-score > 2.0) [31]. Circumferences were measured at the mid-upper arm and waist (at the point of the umbilicus), using the SECA 201 ergonomic circumference measuring tape, to the nearest 0.1 cm (SECA GmbH & co. Kg. Germany). Skinfold thickness were assessed at three sites (biceps, triceps, and subscapular) using a Holtain Tanner/Whitehouse skinfold calipers, to the nearest 0.2 mm (Holtain Ltd, Crymych, UK). The sum of three skinfolds and subscapular/triceps ratio were calculated as proxy measures of adiposity. Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) was performed for 348 participants using the Lunar iDXA™ scanner (GE Healthcare, Madison WI) with enCORE™ v.18.0 software. Measurements included total lean mass (kg) and percentage body fat.
Cardiovascular health
Cardiovascular health parameters were assessed using blood pressure and heart rate at rest. A validated electronic sphygmomanometer (Omron M6 HEM-7211-E8(V)) was used to assess systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and resting heart rate. Values were measured twice with a 1-min interval between each reading and an average was determined. If the difference between the first two readings was > 10%, a third measurement was taken and the mean of three measurements was used. SBP and DBP percentiles were calculated for each participant according to sex, age, and height-specific reference data [32].
Cardiorespiratory endurance
Preteens completed the validated 20-m shuttle run test which followed previously described protocols [33]. A pre-recorded sound signal was emitted that had a starting speed of 8.5 km h−1 and increased by 0.5 km h−1 every 60 s. Participants ran in consecutive stages back and forth to measured end-points on a linear 20 m indoor track. Preteens were instructed to reach the endpoints before the sound was emitted and the test ended once they could no longer follow the pace of the bleep by failing to reach the end lines on two consecutive occasions. The last stage number was used to predict cardiorespiratory endurance from the score obtained.
Cardiometabolic biomarkers
Non-fasting blood samples were obtained from 213 preteens. We analysed several traditional and non-traditional biomarkers that have been previously associated with adverse cardiometabolic functioning in youth [4, 34, 35]. Serum concentrations of glucose, insulin, total cholesterol, triglycerides, high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), c-reactive protein, and C3 complement protein (C3) were all analysed on the Cobas c701/702 module of the Roche Cobas 8000 analyser (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Penzburg, Germany). Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) index was calculated using the standard formula (glucose (mmol/L) x insulin (mIU/L) / 22.5) [10]. Low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) was calculated using the Friedewald equation [36]. Serum concentrations of intracellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), tumour necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), soluble cluster of differentiation factor 163 (sCD163), leptin, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-17A (IL-17A) were all quantified using the benchtop automated ELISA platform ProteinSimple Ella™ (Bio-Techne) following the manufacturer’s instructions. For all biomarkers, outliers more than 5 standard deviations from the mean were excluded.
Covariates
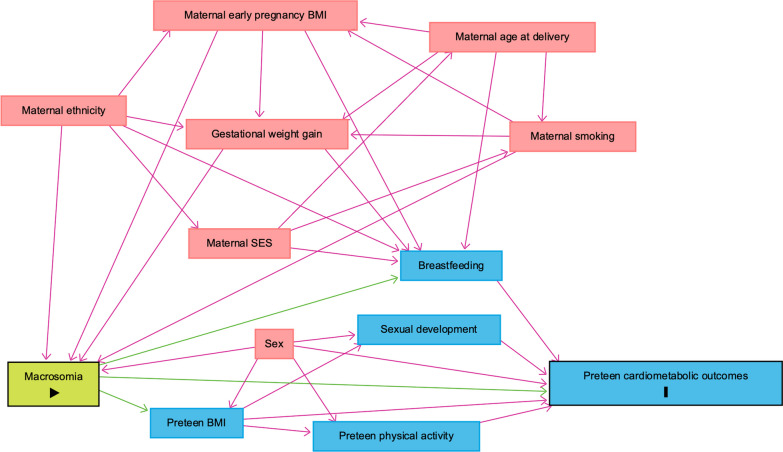
The a priori selection of potential confounding factors to include in multiple linear regression models was informed by the literature [37–40] and by a directed acyclic graph (DAG) (Fig. 1). Study group allocation and age at the time of the 9–11 year follow-up were controlled for to account for differences within the sample population. The ROLO pregnancy study collected data on maternal characteristics which have been described previously [41, 42]. Information included ethnicity, smoking status in pregnancy, early pregnancy BMI (obtained at the first antenatal appointment), gestational weight gain (adherence to 2009 Institute of Medicine guidelines), age at delivery, and socio-economic status using the Pobal Hasse and Pratschke Deprivation Index (HP index). Information on breastfeeding exposure and duration was obtained at 6 months and 2, 5, and 9–11 year postnatal follow up visits. Mothers reported estimates of their preteens’ sexual development using standardised Tanner staging figures (from Stage 1 to 5) [43]. At 9–11 years, self-reported physical activity was assessed using the validated Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children (PAQ-C), with calculated mean scores ranging from 1 (low physical activity levels) to 5 (high physical activity levels) [44].
Fig. 1.
Directed acyclic graph of preteen cardiometabolic outcomes. Abbreviations: BMI Body mass index, SES Socio-economic status
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were carried out using the IBM Statistical Package for the Social Sciences Statistics for Mac Version 27.0 (Macintosh, Armonk, NY). Normality was assessed for all continuous variables using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov tests and visual inspection of simple histograms. Normally distributed variables were reported as mean (standard deviation (SD)), non-normally distributed variables were reported as median (interquartile range 25th–75th percentile (IQR)), and categorical variables were reported as n (%). Non-normal data was log transformed prior to analysis. Differences between those born with macrosomia and those without were investigated using independent t-tests, Mann–Whitney U tests, and Chi-square tests as appropriate.
Crude and adjusted multiple linear regression models were created to examine associations between birthweight ≥ 4 kg (yes/no); birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg (yes/no); birthweight ≥ 90th centile (yes/no); and cardiometabolic outcomes at 9–11 years of age using a forced entry approach. Model 1 presents crude results; Model 2 was adjusted for confounders informed by the DAG (maternal ethnicity (White Irish, yes/no), HP index, maternal age at delivery (years), smoking in pregnancy (yes/no), early pregnancy BMI (kg/m2), adherence to gestational weight gain guidelines (inadequate/adequate/excessive), and child sex (male, yes/no)), along with study group allocation (intervention, yes/no) and age of the preteen at the time of follow-up (years); Model 3 was additionally adjusted for breastfeeding exposure (never breastfed/breastfed < 2 months/breastfed ≥ 2 and < 4 months/breastfed ≥ 4 months) for all outcomes and preteen BMI (kg/m2) for outcomes of cardiovascular health, fitness, and laboratory biomarkers only.
Sensitivity analyses were performed to examine the additional effect of preteen lifestyle and biological factors on the outcomes of interest based on previous literature [45, 46]. Linear regression models were repeated and further adjusted for sexual development (Tanner stage 1, yes/no) and preteen physical activity level (PAQ-C score) for all outcomes. All analyses were performed with pairwise deletion of missing data. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant for all analyses. Correction for multiple testing was not applied due to the exploratory design of this analysis [47].
Results
Maternal and child characteristics in the ROLO longitudinal birth cohort
A total of 405 preteens were included in this analysis and the cohort were evenly distributed by sex; 50.1% (n = 203) were male. The mean (SD) birthweight was 4.03 (0.46) kg and ranged from 2.66 to 5.35 kg. The median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) birthweight centile was 86.32 (72.24, 95.68) and 39.4% (n = 159) were born ≥ 90th centile. 51.4% (n = 208) of preteens were born with macrosomia and 16% (n = 65) were born ≥ 4.5 kg. The median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) age of follow-up was 9.83 (9.24, 10.27) years. Further details of cohort characteristics are displayed in Table 1. There were no significant differences in baseline maternal and infant characteristics between the follow-up cohort at 9–11 years and the original ROLO pregnancy cohort (Additional file 1: Table 1).
Table 1.
Maternal, infant, and preteen characteristics of the ROLO longitudinal birth cohort study
| Total (n = 405) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean/Median/n | SD/(IQR)/% | |
| Maternal characteristics | |||
| Age at delivery (years) | 404 | 33.17 | (30.5, 35.47) |
| Early pregnancy BMI (kg/m2) | 401 | 25.46 | (23.3, 27.96) |
| HP index | 405 | 7.5 | (1.1, 12.5) |
| Gestational weight gain | |||
| Inadequate, n (%) | 333 | 52 | 15.6 |
| Adequate, n (%) | 333 | 127 | 38.1 |
| Excessive, n (%) | 333 | 154 | 46.2 |
| Ethnicity (White Irish), n (%) | 405 | 372 | 91.9 |
| Smoking in pregnancy, n (%) | 405 | 12 | 3.2 |
| RCT group (intervention), n (%) | 405 | 203 | 50.1 |
| Infant characteristics | |||
| Child sex (male), n (%) | 405 | 203 | 50.1 |
| Birthweight (kg) | 405 | 4.03 | 0.46 |
| Birthweight centile | 404 | 86.32 | (72.24, 95.68) |
| Gestational age at delivery (days) | 404 | 283.0 | (277.0, 288.0) |
| Birthweight ≥ 4 kg, n (%) | 405 | 208 | 51.4 |
| Birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg, n (%) | 405 | 65 | 16.0 |
| Birthweight ≥ 90th centile, n (%) | 404 | 159 | 39.4 |
| Breastfeeding exposure and duration | |||
| Never breastfed, n (%) | 360 | 133 | 36.9 |
| Breastfed < 2 months, n (%) | 360 | 46 | 12.8 |
| Breastfed ≥ 2 and < 4 months, n (%) | 360 | 39 | 10.8 |
| Breastfed ≥ 4 months, n (%) | 360 | 142 | 39.4 |
| Preteen characteristics | |||
| Age at follow-up (years) | 405 | 9.83 | (9.24, 10.27) |
| Pubic hair distribution (Tanner stage I), n (%) | 320 | 283 | 88.4 |
| Breast development (Tanner stage I), n (%) | 163 | 128 | 78.5 |
| Physical activity level (PAQ-C score) | 370 | 2.48 | 0.66 |
Results presented as mean (SD) for normally distributed variables and median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) for non-normally distributed variables. N = total population with available data; n = frequency. ROLO Randomised cOntrol trial of LOw glycaemic index diet in pregnancy versus no dietary intervention to prevent recurrence of macrosomia, SD Standard deviation, IQR Interquartile range, BMI Body mass index, HP Hasse and Pratschke Deprivation index, RCT Randomised control trial, PAQ-C Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children
Anthropometry and body composition at the 9–11 year follow-up
At 9–11 years of age, the median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) BMI was 17.3 (15.85, 19.55) kg/m2. Based on BMI z-score classification, 21.2% (n = 86) of preteens had overweight and 8.1% (n = 33) had obesity (Table 2). No significant differences were found in any of the anthropometric measurements between preteens born ≥ 4 kg and < 4 kg (Table 3). When dichotomised into preteens born ≥ 4.5 kg and < 4.5 kg, preteens born ≥ 4.5 kg had higher mean (SD) weight z-scores (0.88 (0.88) vs. 0.48 (0.99), p = 0.003), higher mean (SD) height z-scores (0.81 (0.86) vs. 0.46 (0.96), p = 0.007), higher mean (SD) BMI z-scores (0.71 (0.99) vs. 0.36 (1.09), p = 0.016), and higher median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) lean mass (24.76 (23.28, 28.51) kg vs. 23.87 (21.9, 26.79) kg, p = 0.021), compared to preteens born < 4.5 kg (Table 4). Preteens born with a birthweight ≥ 90th centile had higher mean (SD) weight z-scores (0.7 (0.92) vs. 0.44 (1.01), p = 0.010), higher median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) height (141.4 (136.8, 145.8) cm vs. 139.1 (134.4, 146.6) cm, p = 0.028), higher mean (SD) height z-scores (0.73 (0.91) vs. 0.38 (0.96), p < 0.001), lower median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) subscapular/triceps ratio (0.57 (0.47, 0.67) vs. 0.6 (0.51, 0.75), p = 0.004), and higher median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) lean mass (24.56 (22.95, 27.23) kg vs. 23.7 (21.75, 26.89) kg, p = 0.015), than those born < 90th centile (Additional file 2: Table 2).
Table 2.
Descriptive cardiometabolic outcomes of preteens
| Total (n = 405) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean/Median/n | SD/(IQR)/% | |
| Anthropometry and body composition | |||
| Weight (kg) | 405 | 33.8 | (30.4, 39.9) |
| Weight z-score | 405 | 0.55 | 0.98 |
| Height (cm) | 405 | 140.1 | (135.5, 146.3) |
| Height z-score | 405 | 0.52 | 0.96 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 405 | 17.3 | (15.85, 19.55) |
| BMI z-score | 405 | 0.41 | 1.08 |
| Overweight, n (%) | 405 | 86 | 21.2 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 405 | 33 | 8.1 |
| MUAC (cm) | 401 | 21.0 | (19.1, 23.2) |
| WC (cm) | 405 | 62.3 | (58.7, 68.0) |
| Sum of skinfolds (mm) | 366 | 28.28 | (21.58, 36.84) |
| Subscapular/triceps ratio | 375 | 0.59 | (0.49, 0.72) |
| Lean mass (kg) | 348 | 24.14 | (22.02, 26.91) |
| Body fat (%) | 348 | 26.3 | (20.9, 31.97) |
| Cardiovascular health and cardiorespiratory endurance | |||
| SBP (mmHg) | 380 | 111.0 | (104.0, 117.0) |
| SBP percentile | 380 | 88.0 | (68.0, 96.0) |
| DBP (mmHg) | 380 | 67.0 | (61.75, 72.0) |
| DBP percentile | 380 | 73.5 | (53.0, 87.0) |
| Resting heart rate (bpm) | 377 | 79.07 | 12.66 |
| 20-M SRT score | 378 | 3.55 | (3.1, 4.52) |
| Cardiometabolic biomarkers | |||
| HOMA-IR | 210 | 2.46 | (1.38, 5.11) |
| TC (mmol/L) | 212 | 4.15 | 0.69 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 213 | 0.88 | (0.69, 1.29) |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 212 | 2.41 | 0.55 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 213 | 1.24 | (0.96, 1.5) |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 202 | 0.25 | (0.12, 0.46) |
| C3 complement (g/L) | 213 | 1.39 | (1.23, 1.57) |
| ICAM-1 (ng/mL) | 163 | 357.24 | (297.6, 419.04) |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 163 | 8.64 | 2.71 |
| GDF-15 (ng/mL) | 163 | 0.29 | (0.24, 0.35) |
| sCD163 (ng/mL) | 163 | 429.53 | (338.42, 554.93) |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 162 | 4.53 | (1.72, 8.81) |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 162 | 0.74 | (0.49, 1.09) |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | 163 | 1.27 | (0.84, 2.13) |
Results presented as mean (SD) for normally distributed variables, median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) for non-normally distributed variables, and n (%) for categorical variables. N = total population with available data; n = frequency. ROLO Randomised cOntrol trial of LOw glycaemic index diet in pregnancy versus no dietary intervention to prevent recurrence of macrosomia, SD Standard deviation, IQR Interquartile range, BMI Body mass index, MUAC Mid-upper arm circumference, WC Waist circumference, SBP Systolic blood pressure, DBP Diastolic blood pressure, 20-M SRT 20-m shuttle run test, HOMA-IR Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance, TC Total cholesterol, LDL-C Low density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C High density lipoprotein cholesterol, ICAM-1 Intracellular adhesion molecule 1, TNF-α Tumour necrosis factor alpha, GDF-15 Growth differentiation factor 15, sCD163 Soluble cluster of differentiation factor 163, IL Interleukin
Table 3.
Comparison of cardiometabolic health in 9–11-year-old preteens born ≥ 4 kg and < 4 kg
| Birthweight ≥ 4 kg | Birthweight < 4 kg | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean/Median/n | SD/(IQR)/% | N | Mean/Median/n | SD/(IQR)/% | ||
| Anthropometry and body composition | |||||||
| Weight (kg) | 208 | 34.4 | (30.45, 40.15) | 197 | 33.6 | (30.3, 39.6) | 0.598 |
| Weight z-score | 208 | 0.63 | 0.94 | 197 | 0.45 | 1.01 | 0.064 |
| Height (cm) | 208 | 141.06 | 7.37 | 197 | 140.98 | 7.98 | 0.911 |
| Height z-score | 208 | 0.61 | 0.91 | 197 | 0.43 | 1.33 | 0.059 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 208 | 17.38 | (16.03, 19.48) | 197 | 17.14 | (15.62, 19.66) | 0.409 |
| BMI z-score | 208 | 0.48 | 1.03 | 197 | 0.34 | 1.13 | 0.169 |
| Overweight, n (%) | 208 | 51 | 24.5 | 197 | 35 | 17.8 | 0.141 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 208 | 14 | 6.7 | 197 | 19 | 9.6 | |
| MUAC (cm) | 206 | 21.0 | (19.1, 23.0) | 196 | 21.0 | (19.2, 23.6) | 0.977 |
| WC (cm) | 208 | 62.35 | (58.42, 67.42) | 197 | 62.0 | (58.8, 68.05) | 0.752 |
| Sum of skinfolds (mm) | 192 | 27.06 | (21.2, 36.5) | 188 | 29.5 | (22.3, 37.83) | 0.167a |
| Subscapular/triceps ratio | 189 | 0.58 | (0.48, 0.7) | 186 | 0.6 | (0.51, 0.74) | 0.098 |
| Lean mass (kg) | 178 | 24.4 | (22.3, 27.14) | 170 | 23.77 | (21.87, 26.38) | 0.063 |
| Body fat (%) | 178 | 25.3 | (20.42, 31.9) | 170 | 26.5 | (21.8, 32.1) | 0.218a |
| Cardiovascular health and cardiorespiratory endurance | |||||||
| SBP percentile | 194 | 86.5 | (70.25, 96.0) | 186 | 89.5 | (66.75, 96.0) | 0.747 |
| DBP percentile | 194 | 73.0 | (50.0, 86.0) | 186 | 74.0 | (55.0, 88.0) | 0.380 |
| Resting heart rate (bpm) | 192 | 79.42 | 12.25 | 185 | 78.7 | 13.1 | 0.579 |
| 20-M SRT score | 193 | 3.7 | (3.1, 5.05) | 185 | 3.5 | (3.1, 4.4) | 0.165 |
| Cardiometabolic biomarkers | |||||||
| HOMA-IR | 104 | 2.23 | (1.18, 5.06) | 106 | 2.63 | (1.55, 5.15) | 0.169a |
| TC (mmol/L) | 104 | 4.09 | 0.72 | 108 | 4.22 | 0.66 | 0.171 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 105 | 0.83 | (0.67, 1.16) | 108 | 0.91 | (0.69, 1.49) | 0.243 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 104 | 2.39 | 0.59 | 108 | 2.42 | 0.53 | 0.723 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 105 | 1.22 | 0.38 | 108 | 1.26 | 0.37 | 0.426 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 98 | 0.23 | (0.11, 0.42) | 104 | 0.26 | (0.13, 0.54) | 0.335a |
| C3 complement (g/L) | 105 | 1.38 | (1.22, 1.52) | 108 | 1.4 | (1.26, 1.6) | 0.043a |
| ICAM-1 (ng/mL) | 79 | 345.39 | (290.34, 394.91) | 84 | 387.44 | (312.91, 441.83) | 0.040a |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 79 | 8.37 | 2.75 | 84 | 8.9 | 2.67 | 0.220 |
| GDF-15 (ng/mL) | 79 | 0.29 | (0.24, 0.33) | 84 | 0.3 | (0.25, 0.38) | 0.214 |
| sCD163 (ng/mL) | 79 | 398.61 | (332.86, 510.87) | 84 | 452.41 | (340.26, 574.09) | 0.143a |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 79 | 4.38 | (1.58, 9.03) | 83 | 4.86 | (1.76, 8.52) | 0.672a |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 78 | 0.7 | (0.46, 1.11) | 84 | 0.76 | (0.51, 1.05) | 0.315a |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | 79 | 1.18 | (0.83, 1.84) | 84 | 1.32 | (0.94, 2.2) | 0.177 |
Results presented as mean (SD) for normally distributed variables, median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) for non-normally distributed variables, and n (%) for categorical variables. N = total population with available data; n = frequency. alog10 transformed data was used. SD Standard deviation; IQR Interquartile range, BMI Body mass index, MUAC Mid-upper arm circumference, WC Waist circumference, SBP Systolic blood pressure, DBP Diastolic blood pressure, 20-M SRT 20-m shuttle run test, HOMA-IR Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance, TC Total cholesterol, LDL-C Low density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C High density lipoprotein cholesterol, ICAM-1 Intracellular adhesion molecule 1, TNF-α Tumour necrosis factor alpha, GDF-15 Growth differentiation factor 15, sCD163 Soluble cluster of differentiation factor 163, IL Interleukin. P values determined using independent t-tests for normally distributed variables; Mann–Whitney U tests for non-normally distributed variables; Chi square tests for categorical variables
Table 4.
Comparison of cardiometabolic health in 9–11-year-old preteens born ≥ 4.5 kg and < 4.5 kg
| Birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg | Birthweight < 4.5 kg | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean/Median/n | SD/(IQR)/% | N | Mean/Median/n | SD/(IQR)/% | ||
| Anthropometry and body composition | |||||||
| Weight (kg) | 65 | 35.6 | (31.6, 40.5) | 340 | 33.8 | (30.0, 39.75) | 0.111 |
| Weight z-score | 65 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 340 | 0.48 | 0.99 | 0.003 |
| Height (cm) | 65 | 142.05 | 6.82 | 340 | 140.82 | 7.81 | 0.237 |
| Height z-score | 65 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 340 | 0.46 | 0.96 | 0.007 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 65 | 17.86 | (16.36, 19.43) | 340 | 17.12 | (15.69, 19.64) | 0.068 |
| BMI z-score | 65 | 0.71 | 0.99 | 340 | 0.36 | 1.09 | 0.016 |
| Overweight, n (%) | 65 | 18 | 27.7 | 340 | 68 | 20.0 | 0.464 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 65 | 6 | 9.2 | 340 | 27 | 7.9 | |
| MUAC (cm) | 65 | 21.1 | (19.55, 23.5) | 336 | 21.0 | (19.1, 23.2) | 0.447 |
| WC (cm) | 65 | 63.2 | (59.7, 68.1) | 340 | 62.0 | (58.25, 68.0) | 0.159 |
| Sum of skinfolds (mm) | 60 | 26.53 | (21.51, 37.48) | 306 | 28.43 | (21.58, 36.48) | 0.808 |
| Subscapular/triceps ratio | 61 | 0.58 | (0.46, 0.69) | 314 | 0.59 | (0.5, 0.72) | 0.157 |
| Lean mass (kg) | 57 | 24.76 | (23.28, 28.51) | 291 | 23.87 | (21.9, 26.79) | 0.021 |
| Body fat (%) | 57 | 25.3 | (20.35, 31.85) | 291 | 26.4 | (20.9, 32.1) | 0.604 |
| Cardiovascular health and cardiorespiratory endurance | |||||||
| SBP percentile | 60 | 86.0 | (72.25, 95.75) | 320 | 88.5 | (67.0, 96.0) | 0.723 |
| DBP percentile | 60 | 64.5 | (46.25, 81.75) | 320 | 74.0 | (54.0, 88.0) | 0.038 |
| Resting heart rate (bpm) | 60 | 78.45 | 13.23 | 317 | 79.18 | 12.57 | 0.682 |
| 20-M SRT score | 61 | 3.8 | (3.1, 5.15) | 317 | 3.5 | (3.1, 4.5) | 0.333 |
| Cardiometabolic biomarkers | |||||||
| HOMA-IR | 35 | 2.48 | (1.56, 6.07) | 175 | 2.45 | (1.36, 4.6) | 0.413a |
| TC (mmol/L) | 35 | 4.03 | 0.65 | 177 | 4.18 | 0.7 | 0.264 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 36 | 0.92 | (0.68, 1.58) | 177 | 0.88 | (0.69, 1.24) | 0.352 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | 35 | 2.26 | 0.53 | 177 | 2.44 | 0.56 | 0.082 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | 36 | 1.21 | 0.39 | 177 | 1.25 | 0.37 | 0.623 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 35 | 0.22 | (0.11, 0.42) | 167 | 0.25 | (0.13, 0.49) | 0.779a |
| C3 complement (g/L) | 36 | 1.38 | (1.2, 1.56) | 177 | 1.39 | (1.24, 1.58) | 0.486a |
| ICAM-1 (ng/mL) | 22 | 322.19 | (291.97, 390.87) | 141 | 358.2 | (300.91, 426.82) | 0.106 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 22 | 8.53 | 2.09 | 141 | 8.66 | 2.81 | 0.842 |
| GDF-15 (ng/mL) | 22 | 0.29 | (0.23, 0.33) | 141 | 0.29 | (0.25, 0.35) | 0.436 |
| sCD163 (ng/mL) | 22 | 394.95 | (344.01, 544.07) | 141 | 430.66 | (335.64, 556.24) | 0.720a |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 22 | 2.52 | (1.53, 10.38) | 140 | 4.9 | (1.76, 8.73) | 0.625 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 21 | 0.62 | (0.44, 1.14) | 141 | 0.75 | (0.5, 1.07) | 0.278a |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | 22 | 1.01 | (0.76, 1.78) | 141 | 1.3 | (0.87, 2.13) | 0.254 |
Results presented as mean (SD) for normally distributed variables, median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) for non-normally distributed variables, and n (%) for categorical variables. N = total population with available data; n = frequency. alog10 transformed data was used. SD Standard deviation, IQR Interquartile range, BMI Body mass index, MUAC Mid-upper arm circumference, WC Waist circumference, SBP Systolic blood pressure, DBP Diastolic blood pressure, 20-M SRT 20-m shuttle run test, HOMA-IR Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance, TC Total cholesterol, LDL-C Low density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C High density lipoprotein cholesterol, ICAM-1 Intracellular adhesion molecule 1, TNF-α Tumour necrosis factor alpha, GDF-15 Growth differentiation factor 15, sCD163 Soluble cluster of differentiation factor 163, IL Interleukin. P values determined using independent t-tests for normally distributed variables; Mann–Whitney U tests for non-normally distributed variables; Chi square tests for categorical variables
Cardiovascular health and cardiorespiratory endurance at the 9–11 year follow-up
No significant differences were found in cardiovascular health parameters and cardiorespiratory endurance between preteens born ≥ 4 kg and < 4 kg (Table 3) and those born with a birthweight ≥ 90th and < 90th centile (Additional file 2: Table 2). When dichotomised into preteens born ≥ 4.5 kg and < 4.5 kg, preteens born ≥ 4.5 kg had lower median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) diastolic blood pressure percentile (64.5 (46.25, 81.75) vs. 74.0 (54.0, 88.0), p = 0.038), compared to those born < 4.5 kg (Table 4).
Cardiometabolic biomarkers at the 9–11 year follow-up
Of 405 preteens included in this analysis, a non-fasting blood sample was obtained for 213 preteens (52.5%). Of these, 105 preteens (49.3%) were born ≥ 4 kg. Preteens born ≥ 4 kg had lower median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) C3 concentrations (1.38 (1.22, 1.52) g/L vs. 1.4 (1.26, 1.6) g/L, p = 0.043) and lower median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) ICAM-1 concentrations (345.39 (290.34, 394.91) ng/mL vs. 387.44 (312.91, 441.83) ng/mL, p = 0.040), compared to preteens born < 4 kg (Table 3). Preteens born with a birthweight ≥ 90th centile had lower median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) HOMA-IR index scores (2.0 (1.31, 4.45) vs. 3.06 (1.57, 5.34), p = 0.037) and lower median (IQR 25th–75th percentile) IL-17A concentrations (1.06 (0.73, 2.01) pg/mL vs. 1.33 (0.97, 2.18) pg/mL, p = 0.038), than those born < 90th centile (Additional file 2: Table 2).
Regression between macrosomia and cardiometabolic outcomes at the 9–11 year follow-up
Multiple linear regression analyses examined associations between birthweight ≥ 4 kg; birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg; birthweight ≥ 90th centile; and each cardiometabolic outcome at the 9–11 year follow-up. In the fully adjusted model, birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg (Table 5) and birthweight ≥ 90th centile (Additional file 3: Table 3) were positively associated with weight z-score (B = 0.325, 95% CI = 0.018, 0.633, p = 0.038; B = 0.241, 95% CI = 0.015, 0.467, p = 0.037), height (cm) (B = 2.552, 95% CI = 0.589, 4.516, p = 0.011; B = 2.277, 95% CI = 0.841, 3.713, p = 0.002), height z-score (B = 0.391, 95% CI = 0.079, 0.703, p = 0.014; B = 0.373, 95% CI = 0.145, 0.600, p = 0.001), and lean mass (kg) (B = 1.353, 95% CI = 0.264, 2.442, p = 0.015; B = 1.005, 95% CI = 0.204, 1.805, p = 0.014), respectively. In the fully adjusted model, birthweight ≥ 90th centile was negatively associated with subscapular/triceps ratio (B = − 0.077, 95% CI = − 0.126, − 0.028, p = 0.002) (Additional file 3: Table 3). In the fully adjusted model, birthweight ≥ 4 kg was negatively associated with C3 concentration (g/L) (B = − 0.095, 95% CI = − 0.162, − 0.029, p = 0.005) and birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg was positively associated with cardiorespiratory endurance (20-m shuttle run test score) (B = 0.407, 95% CI = 0.006, 0.808, p = 0.047) (Table 6). There were no significant associations found between birthweight ≥ 90th centile and cardiometabolic outcomes (Additional file 4: Table 4). Sensitivity analyses yielded similar conclusions after further adjustment for preteen physical activity and sexual development in all models (Additional file 5: Table 5 and Additional file 6: Table 6).
Table 5.
Multiple linear regression models between macrosomia and preteen anthropometry and body composition
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 95% CI | R2 adj | p | B | 95% CI | R2 adj | p | B | 95% CI | R2 adj | p | |
| Models for birthweight ≥ 4 kg | ||||||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 0.099 | (1.871, 2.069) | − 0.003 | 0.921 | 0.931 | (− 0.791, 2.653) | 0.292 | 0.288 | 0.732 | (− 0.999, 2.463) | 0.295 | 0.406 |
| Weight z-score | 0.181 | (− 0.044, 0.407) | 0.005 | 0.115 | 0.155 | (− 0.069, 0.380) | 0.090 | 0.175 | 0.128 | (− 0.098, 0.353) | 0.095 | 0.266 |
| Height (cm) | 0.086 | (− 1.676, 1.847) | − 0.003 | 0.924 | 1.135 | (− 0.297, 2.566) | 0.388 | 0.120 | 1.033 | (− 0.412, 2.478) | 0.385 | 0.161 |
| Height z-score | 0.180 | (− 0.039, 0.400) | 0.005 | 0.107 | 0.176 | (− 0.051, 0.404) | 0.017 | 0.128 | 0.162 | (− 0.067, 0.392) | 0.011 | 0.166 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.040 | (− 0.614, 0.695) | − 0.003 | 0.904 | 0.178 | (− 0.441, 0.797) | 0.172 | 0.572 | 0.104 | (− 0.517, 0.726) | 0.176 | 0.742 |
| BMI z-score | 0.148 | (− 0.100, 0.396) | 0.001 | 0.241 | 0.111 | (− 0.133, 0.355) | 0.110 | 0.371 | 0.080 | (− 0.165, 0.324) | 0.117 | 0.520 |
| MUAC (cm) | − 0.033 | (− 0.725, 0.659) | − 0.003 | 0.925 | 0.223 | (− 0.427, 0.873) | 0.183 | 0.500 | 0.148 | (− 0.505, 0.800) | 0.187 | 0.657 |
| WC (cm) | − 0.664 | (− 2.646, 1.317) | − 0.002 | 0.510 | − 0.303 | (− 2.162, 1.556) | 0.186 | 0.748 | − 0.550 | (− 2.413, 1.313) | 0.193 | 0.562 |
| Sum of skinfolds (mm) | − 1.754 | (− 4.799, 1.291) | 0.001 | 0.258 | − 0.283 | (− 3.176, 2.610) | 0.168 | 0.847 | − 0.807 | (− 3.683, 2.069) | 0.189 | 0.581 |
| Subscapular/triceps ratio | − 0.040 | (− 0.088, 0.008) | 0.006 | 0.098 | − 0.040 | (− 0.089, 0.009) | 0.051 | 0.107 | − 0.043 | (− 0.093, 0.006) | 0.046 | 0.084 |
| Lean mass (kg) | 0.504 | (− 0.450, 1.459) | 0.000 | 0.299 | 0.699 | (− 0.095, 1.492) | 0.362 | 0.084 | 0.642 | (− 0.158, 1.442) | 0.360 | 0.115 |
| Body fat (%) | − 0.915 | (− 2.641, 0.811) | 0.000 | 0.298 | 0.105 | (− 1.509, 1.719) | 0.193 | 0.899 | − 0.265 | (− 1.855, 1.324) | 0.228 | 0.743 |
| Models for birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg | ||||||||||||
| Weight (kg) | 1.628 | (− 1.049, 4.304) | 0.001 | 0.232 | 2.236 | (− 0.125, 4.597) | 0.298 | 0.063 | 2.163 | (− 0.196, 4.522) | 0.301 | 0.072 |
| Weight z-score | 0.397 | (0.092, 0.703) | 0.019 | 0.011 | 0.338 | (0.030, 0.646) | 0.098 | 0.032 | 0.325 | (0.018, 0.633) | 0.105 | 0.038 |
| Height (cm) | 1.228 | (− 1.166, 3.623) | 0.000 | 0.313 | 2.586 | (0.630, 4.542) | 0.397 | 0.010 | 2.552 | (0.589, 4.516) | 0.395 | 0.011 |
| Height z-score | 0.351 | (0.053, 0.649) | 0.015 | 0.021 | 0.395 | (0.085, 0.706) | 0.031 | 0.013 | 0.391 | (0.079, 0.703) | 0.026 | 0.014 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.501 | (− 0.388, 1.391) | 0.001 | 0.268 | 0.462 | (− 0.389, 1.313) | 0.175 | 0.286 | 0.432 | (− 0.418, 1.282) | 0.178 | 0.318 |
| BMI z-score | 0.353 | (0.016, 0.689) | 0.011 | 0.040 | 0.230 | (− 0.105, 0.565) | 0.114 | 0.178 | 0.215 | (− 0.119, 0.549) | 0.121 | 0.207 |
| MUAC (cm) | 0.320 | (− 0.622, 1.261) | − 0.002 | 0.505 | 0.393 | (− 0.501, 1.287) | 0.183 | 0.388 | 0.355 | (− 0.538, 1.248) | 0.188 | 0.435 |
| WC (cm) | 0.757 | (− 1.942, 3.455) | − 0.002 | 0.581 | 0.738 | (− 1.820, 3.297) | 0.186 | 0.570 | 0.628 | (− 1.923, 3.180) | 0.193 | 0.628 |
| Sum of skinfolds (mm) | 0.297 | (− 3.858, 4.453) | − 0.003 | 0.888 | 1.613 | (− 2.365, 5.592) | 0.170 | 0.425 | 1.402 | (− 2.535, 5.338) | 0.189 | 0.484 |
| Subscapular/triceps ratio | − 0.040 | (− 0.105, 0.025) | 0.002 | 0.229 | − 0.053 | (− 0.120, 0.015) | 0.050 | 0.124 | − 0.053 | (− 0.121, 0.014) | 0.044 | 0.120 |
| Lean mass (kg) | 1.216 | (− 0.078, 2.510) | 0.008 | 0.065 | 1.354 | (0.267, 2.441) | 0.369 | 0.015 | 1.353 | (0.264, 2.442) | 0.368 | 0.015 |
| Body fat (%) | − 0.296 | (− 2.650, 2.059) | − 0.003 | 0.805 | 0.253 | (− 1.969, 2.474) | 0.193 | 0.823 | 0.132 | (− 2.044, 2.308) | 0.228 | 0.905 |
Models carried out between macrosomia and anthropometry and body composition outcomes at 9–11 years. CI Confidence interval, BMI Body mass index, MUAC Mid-upper arm circumference, WC Waist circumference. Model 1: crude results; Model 2: adjusted for age at follow-up, study group allocation, sex, HP index, maternal age at delivery, maternal ethnicity, maternal early pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, maternal smoking in pregnancy; Model 3: adjusted for breastfeeding exposure
Table 6.
Multiple linear regression models between macrosomia and preteen cardiometabolic outcomes
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 95% CI | R2 adj | p | B | 95% CI | R2 adj | p | B | 95% CI | R2 adj | p | |
| Models for birthweight ≥ 4 kg | ||||||||||||
| SBP percentile | 0.939 | (− 4.336, 6.214) | − 0.003 | 0.726 | 0.746 | (− 4.793, 6.284) | − 0.020 | 0.791 | 0.238 | (− 5.303, 5.779) | − 0.007 | 0.933 |
| DBP percentile | − 1.658 | (− 7.059, 3.742) | − 0.002 | 0.546 | − 0.834 | (− 6.487, 4.819) | − 0.013 | 0.772 | − 1.231 | (− 6.929, 4.466) | − 0.015 | 0.671 |
| Resting heart rate (bpm) | 0.725 | (− 2.184, 3.634) | − 0.003 | 0.624 | 1.520 | (− 1.511, 4.550) | − 0.004 | 0.324 | 1.681 | (− 1.363, 4.725) | 0.001 | 0.278 |
| 20-M SRT score | 0.171 | (− 0.137, 0.478) | 0.001 | 0.275 | 0.170 | (− 0.136, 0.477) | 0.085 | 0.274 | 0.203 | (− 0.090, 0.497) | 0.171 | 0.174 |
| HOMA-IR | − 0.199 | (− 0.984, 0.585) | − 0.004 | 0.617 | − 0.313 | (− 1.117, 0.491) | 0.028 | 0.443 | − 0.356 | (− 1.150, 0.437) | 0.067 | 0.376 |
| TC (mmol/L) | − 0.131 | (− 0.339, 0.077) | 0.003 | 0.214 | − 0.115 | (− 0.333, 0.103) | − 0.010 | 0.297 | − 0.128 | (− 0.346, 0.091) | − 0.002 | 0.250 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | − 0.146 | (− 0.332, 0.040) | 0.008 | 0.123 | − 0.145 | (− 0.339, 0.050) | 0.001 | 0.143 | − 0.150 | (− 0.343, 0.043) | 0.031 | 0.126 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | − 0.027 | (− 0.195, 0.140) | − 0.005 | 0.748 | − 0.024 | (− 0.199, 0.152) | − 0.017 | 0.791 | − 0.034 | (− 0.210, 0.143) | − 0.011 | 0.705 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | − 0.042 | (− 0.155, 0.072) | − 0.003 | 0.470 | − 0.029 | (− 0.147, 0.089) | − 0.004 | 0.631 | − 0.029 | (− 0.147, 0.089) | 0.007 | 0.630 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | − 0.097 | (− 0.468, 0.274) | − 0.004 | 0.607 | − 0.062 | (− 0.455, 0.331) | − 0.037 | 0.757 | − 0.071 | (− 0.453, 0.312) | 0.030 | 0.716 |
| C3 complement (g/L) | − 0.070 | (− 0.145, 0.005) | 0.014 | 0.065 | − 0.080 | (− 0.156, − 0.005) | 0.072 | 0.037 | − 0.095 | (− 0.162, − 0.029) | 0.291 | 0.005 |
| ICAM-1 (pg/mL)a | − 0.044 | (− 0.091, 0.002) | 0.019 | 0.062 | − 0.042 | (− 0.090, 0.007) | 0.021 | 0.093 | − 0.042 | (− 0.091, 0.008) | 0.008 | 0.097 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | − 0.525 | (− 1.453, 0.402) | 0.002 | 0.265 | − 0.624 | (− 1.580, 0.333) | 0.022 | 0.199 | − 0.716 | (− 1.670, 0.238) | 0.041 | 0.140 |
| GDF-15 (pg/mL)a | − 0.041 | (− 0.091, 0.009) | 0.012 | 0.105 | − 0.032 | (− 0.085, 0.021) | − 0.039 | 0.237 | − 0.035 | (− 0.089, 0.019) | − 0.054 | 0.196 |
| sCD163 (pg/mL)a | − 0.037 | (− 0.091, − 0.018) | 0.006 | 0.183 | − 0.041 | (− 0.096, 0.013) | 0.068 | 0.137 | − 0.041 | (− 0.096, 0.014) | 0.080 | 0.143 |
| Leptin (pg/mL)a | − 0.030 | (− 0.186, 0.125) | − 0.006 | 0.701 | 0.005 | (− 0.144, 0.155) | 0.140 | 0.944 | − 0.017 | (− 0.123, 0.089) | 0.573 | 0.751 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | − 0.013 | (− 0.309, 0.283) | − 0.008 | 0.931 | 0.058 | (− 0.238, 0.354) | 0.071 | 0.699 | 0.049 | (− 0.247, 0.346) | 0.079 | 0.743 |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | − 0.239 | (− 0.609, 0.132) | 0.005 | 0.205 | − 0.293 | (− 0.665, 0.079) | 0.072 | 0.122 | − 0.270 | (− 0.648, 0.107) | 0.061 | 0.158 |
| Models for birthweight ≥ 4.5 kg | ||||||||||||
| SBP percentile | 2.585 | (− 4.593, 9.763) | − 0.002 | 0.479 | 2.443 | (− 5.177, 10.063) | − 0.019 | 0.529 | 1.678 | (− 5.919, 9.274) | − 0.007 | 0.664 |
| DBP percentile | − 6.124 | (13.449, 1.200) | 0.006 | 0.101 | − 5.878 | (13.631, 1.875) | − 0.006 | 0.137 | − 6.463 | (− 14.242, 1.315) | − 0.006 | 0.103 |
| Resting heart rate (bpm) | − 0.731 | (− 4.693, 3.231) | − 0.003 | 0.717 | 0.787 | (− 3.391, 4.965) | − 0.007 | 0.711 | 0.578 | (− 3.604, 4.761) | − 0.003 | 0.786 |
| 20-M SRT score | 0.213 | (− 0.206, 0.631) | 0.000 | 0.318 | 0.326 | (− 0.095, 0.747) | 0.089 | 0.128 | 0.407 | (0.006, 0.808) | 0.177 | 0.047 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.560 | (− 0.506, 1.626) | 0.000 | 0.301 | 0.440 | (− 0.667, 1.546) | 0.028 | 0.434 | 0.338 | (− 0.751, 1.428) | 0.064 | 0.541 |
| TC (mmol/L) | − 0.146 | (− 0.430, 0.137) | 0.000 | 0.311 | − 0.058 | (− 0.359, 0.243) | − 0.016 | 0.703 | − 0.069 | (− 0.369, 0.232) | − 0.009 | 0.652 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 0.123 | (− 0.131, 0.377) | 0.000 | 0.340 | 0.144 | (− 0.124, 0.412) | − 0.005 | 0.290 | 0.125 | (− 0.140, 0.390) | 0.022 | 0.354 |
| LDL-C (mmol/L) | − 0.183 | (− 0.410, 0.044) | 0.009 | 0.114 | − 0.143 | (− 0.384, 0.098) | − 0.009 | 0.244 | − 0.149 | (− 0.390, 0.092) | − 0.002 | 0.225 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) | − 0.035 | (− 0.190, 0.120) | − 0.005 | 0.655 | 0.004 | (− 0.59, 0.167) | − 0.006 | 0.964 | 0.008 | (− 0.154, 0.170) | 0.006 | 0.923 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 0.001 | (− 0.505, 0.507) | − 0.006 | 0.996 | − 0.005 | (− 0.546, 0.536) | − 0.038 | 0.986 | − 0.073 | (− 0.598, 0.452) | 0.029 | 0.785 |
| C3 complement (g/L) | − 0.030 | (− 0.133, 0.072) | − 0.004 | 0.560 | − 0.051 | (− 0.156, 0.054) | 0.053 | 0.340 | − 0.074 | (− 0.166, 0.019) | 0.266 | 0.118 |
| ICAM-1 (pg/mL)a | − 0.038 | (− 0.102, 0.026) | 0.003 | 0.240 | − 0.046 | (− 0.114, 0.021) | 0.013 | 0.174 | − 0.049 | (− 0.116, 0.019) | 0.001 | 0.159 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | − 0.116 | (− 1.386, 1.153) | − 0.007 | 0.856 | − 0.098 | (− 1.424, 1.228) | 0.009 | 0.884 | − 0.207 | (− 1.527, 1.113) | 0.024 | 0.757 |
| GDF-15 (pg/mL)a | − 0.020 | (− 0.088, 0.048) | − 0.005 | 0.565 | − 0.004 | (− 0.077, 0.070) | − 0.051 | 0.918 | − 0.005 | (− 0.080, 0.069) | − 0.068 | 0.891 |
| sCD163 (pg/mL)a | − 0.012 | (− 0.087, 0.062) | − 0.007 | 0.744 | − 0.033 | (− 0.109, 0.043) | 0.057 | 0.388 | − 0.035 | (− 0.111, 0.040) | 0.070 | 0.358 |
| Leptin (pg/mL)a | − 0.019 | (− 0.230, 0.193) | − 0.007 | 0.862 | − 0.036 | (− 0.242, 0.170) | 0.141 | 0.731 | − 0.089 | (− 0.234, 0.056) | 0.578 | 0.226 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | − 0.134 | (− 0.536, 0.268) | − 0.004 | 0.510 | − 0.105 | (− 0.512, 0.302) | 0.072 | 0.610 | − 0.136 | (− 0.542, 0.270) | 0.082 | 0.508 |
| IL-17A (pg/mL) | − 0.152 | (− 0.658, 0.355) | − 0.005 | 0.555 | − 0.191 | (− 0.708, 0.325) | 0.057 | 0.465 | − 0.188 | (− 0.709, 0.332) | 0.049 | 0.475 |
Models carried out as macrosomia and cardiometabolic outcomes at 9–11 years. alog10 transformed data was used. CI Confidence interval, SBP Systolic blood pressure, DBP Diastolic blood pressure, 20-M SRT 20-m shuttle run test, HOMA-IR Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance, TC Total cholesterol, LDL-C Low density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C High density lipoprotein cholesterol, ICAM-1 Intracellular adhesion molecule 1, TNF-α Tumour necrosis factor alpha, GDF-15 Growth differentiation factor 15, sCD163 Soluble cluster of differentiation factor 163, IL Interleukin. Model 1: crude results; Model 2: adjusted for age at follow-up, study group allocation, sex, HP index, maternal age at delivery, maternal ethnicity, maternal early pregnancy BMI, gestational weight gain, maternal smoking in pregnancy; Model 3: adjusted for breastfeeding exposure, preteen BMI
Discussion
This exploratory study found no convincing evidence to suggest that macrosomia is linked to the programming of adverse cardiometabolic health at 9–11 years of age. Preteens born with macrosomia had higher weight z-scores, higher BMI z-scores, were taller, and leaner, and had lower diastolic blood pressure percentile and lower inflammation, compared to those born without macrosomia. The results of the adjusted regression analyses revealed that high birthweight was associated with a taller and leaner body composition, along with lower inflammation and higher fitness at 9–11 years of age.
The pathophysiology linking high birthweight and cardiometabolic risk in later life remains unknown, highlighting the importance of this research. Based on previous research, we expected that early precursors of obesity and cardiometabolic disease would be evident in youth born with macrosomia at 9–11 years of age [20, 24, 25]. Despite this, the prevalence of overweight and obesity in this preteen cohort did not differ between groups and was similar to an unselected cohort of similar age from the Growing Up in Ireland study [48]. This might, at least in part, account for the lack of long-term impact on cardiometabolic risk factors observed in preteens with a birthweight ≥ 4 kg relative to their counterparts born < 4 kg. This is important, given 1 in 5 neonates weigh greater than 4 kg at birth in some regions and more than 60% of neonates with macrosomia are born to women without identifiable risk factors [49, 50].
We found differences in body composition at 9–11 years of age between those born with and without macrosomia. Those born ≥ 4.5 kg had higher weight and height z-scores, were taller, leaner, and had higher BMI z-scores at 9–11 years compared to those born < 4.5 kg. Similar body composition profiles were observed amongst those born with a birthweight above the 90th centile. Thus, it is plausible those at the upper end of the macrosomic range may have a higher risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome in later life. In adjusted analyses, high birthweight was positively associated with weight and height z-scores, along with lean mass at 9–11 years of age. Previous studies have shown that larger neonates maintain a tall and lean profile into adolescence and adulthood, also displaying higher bone density and muscle mass in old age [16, 51]. This may also explain our finding of a positive association between high birthweight and fitness in adjusted analyses [52]. It is also important to acknowledge the exploratory nature of this study, which may limit the interpretation of our results.
Postnatal growth patterns can independently influence later body composition and those outside the healthy birthweight range tend to return to their genetically determined growth trajectory within the first two years of life [53]. Maternal influence in utero may be compensated by patterns of “catch-up” and “catch-down” growth for low birthweight and high birthweight infants respectively [54]. While the proportion and timing remains unclear, the “catch-down” growth phase has shown protective effects on body composition in 8-year-old children exposed to excess intrauterine fetal growth [55]. Despite this, an estimated 20% of high birthweight infants who do not enter “catch-down” growth represent a high-risk subgroup and maintain higher subcutaneous fat and BMI in later childhood [53]. Lurbe et al. [2] also found that weight gain in early life may also override the effects of high birthweight on obesity and metabolic risk at 10-years of age. Earlier adiposity rebound in children born with high birthweight is another potential risk factor for obesity [9]. Therefore, postnatal growth may be a critical factor in determining the long-term risks associated with macrosomia in our high birthweight cohort beyond infancy [54]. Additionally, the time point of our investigation may influence the differences observed between the groups, because the preteen period can be a transitional phase for body composition profiles in both sexes [56].
The assessment of cardiometabolic health in children is challenging and our novel study included a broad range of cardiometabolic indicators to provide greater insight into metabolic and inflammatory processes. In adjusted analyses, there was only a weak association between macrosomia and lower inflammation (C3 complement protein). Our findings are consistent with results from a small study (n = 90) which found high birthweight was not related to blood pressure or lipid profiles [25]. Sparano et al. [10] also reported no significant impact of macrosomia on blood pressure, lipids, glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR, and HbA1c in 7-year-old European children. Significant associations have been found in adolescent and adult cohorts [18, 20, 21]. It is possible that the high variability of metabolic parameters in children < 10 years of age may limit the ability to detect consequences of macrosomia on biochemical parameters. Alternative assessment by echocardiography may also provide clearer results. Recently, Yapicioglu et al. [24] found 8–9-year-olds born with macrosomia have higher carotid intima-media thickness levels than those born without macrosomia.
Our findings of no relationship between macrosomia and increased cardiometabolic risk in preteens may be explained by the role of the postnatal lifestyle and biological factors that can modify or add to the risks established during intrauterine development [40, 42, 45, 46, 57], many of these we were able to control for within our analyses. It is challenging to establish causality linking fetal life with preteen cardiometabolic health, and various factors after birth may play a role. Correlated aspects of the postnatal environment are often overlooked in studies that focus on birthweight. This study attempted to further tease apart the possible effects of postnatal lifestyle and biological factors in sensitivity analyses, however, preteen physical activity and sexual maturity had minimal effects. The weak influence of different intrauterine factors including maternal glycaemia and metabolic parameters on child adiposity was also shown in the ROLO cohort up to 5-years of age [58, 59]. In contrast, other analyses in the ROLO cohort have reported associations between possible programming of early childhood health and several maternal dietary exposures in utero [60–63]. Therefore, additional research is needed to elucidate the perinatal etiology of cardiometabolic diseases to prevent negative consequences manifesting in childhood. Further research may also explore associations between perinatal exposures and composite cardiometabolic risk scores in youth. Rather than examining risk factors individually, a combined approach may better reflect metabolic patterns and have greater potential to translate to a larger public health impact [64].
This study is strengthened by the longitudinal design and unique Irish cohort who were born to mothers that previously delivered an infant with macrosomia and over half were born with recurrent macrosomia. Additional strengths include a large sample size of preteens with 53.3% follow-up (n = 405) of the original 759 ROLO mother-child dyads, which has been steadily maintained since the 5-year follow-up [59]. Detailed measures of adiposity, cardiovascular health, and cardiorespiratory endurance enables a thorough assessment of preteen cardiometabolic health. In addition, complete data is available for a large proportion of the cohort. The inclusion of traditional and non-traditional serum biomarkers for a subgroup of preteens provides valuable insight into endothelial, metabolic, and inflammatory processes. Majority of research in children and adults rely on BMI, and our analysis contributes to a gap in our understanding of the programming of fat and fat-free mass by including DXA measures [11, 13, 49, 65].
This analysis has several limitations. The serum samples were obtained in a non-fasting state which may not provide an accurate reflection of metabolism. In the literature, the criteria defining high birthweight criteria can vary, which may also complicate direct comparison between studies. The 9–11 year follow-up was conducted over a 6-year period resulting in differences in age and pubertal status, however, this was addressed by including these factors in adjusted analyses. Differences in blood pressure results may have been more apparent with the use of 24 h blood pressure monitoring. Primary sexual development in girls was accounted for by self-report of breast development, however, only self-report of adrenarche was sought in boys rather than testicular volume. This exploratory study is also unable to account for factors that were not included as potential confounders which may impact the interpretation of findings. Given the large number of statistical tests run for this analysis, significant results may be chance findings and should be interpreted with caution. One avenue of future research that we did not explore in detail should focus on potential sex-specific effects of programming on preteen cardiometabolic indicators, given the strong genetic influence on cardiometabolic risk between males and females [66].
Conclusion
Our novel longitudinal study found no convincing evidence to suggest that macrosomia is associated with adverse preteen cardiometabolic outcomes, minimising the potential longitudinal impact of this risk factor. Additional longitudinal research may further explore the influence of postnatal factors such as growth, early feeding, and lifestyle in relation to size at birth to better understand the early life origins of obesity and metabolic disease.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Differences in baseline characteristics between the original ROLO pregnancy cohort and the follow-up cohort at 9–11 years
Additional file 2. Comparison of cardiometabolic health in 9–11-year-old preteens born with a birthweight ≥90th and <90th centile
Additional file 3. Multiple linear regression models between birthweight centile and preteen anthropometry and body composition
Additional file 4. Multiple linear regression models between birthweight centile and preteen cardiometabolic outcomes
Additional file 5. Sensitivity analyses between macrosomia and preteen anthropometry and body composition
Additional file 6. Sensitivity analyses between macrosomia and preteen cardiometabolic outcomes
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the parents and children of the ROLO study for their continued support. Thank you also to the staff of the National Maternity Hospital for facilitating our research.
Abbreviations
- ROLO
Randomised cOntrol trial of a LOw glycaemic index diet in pregnancy to prevent macrosomia
- BMI
Body mass index
- DXA
Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry
- HDL-C
High density lipoprotein cholesterol
- C3
Complement protein
- HOMA-IR
Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance
- LDL-C
Low density lipoprotein cholesterol
- ICAM-1
Intracellular adhesion molecule 1
- TNF-α
Tumour necrosis factor alpha
- GDF-15
Growth differentiation factor 15
- sCD163
Soluble cluster of differentiation factor 163
- IL
Interleukin
- PAQ-C
Physical Activity Questionnaire for Older Children
- SD
Standard deviation
- IQR
Interquartile range
Author contributions
SC designed the study, analysed the data, and drafted the initial manuscript. SLK designed the study, advised on statistical analysis, and contributed to the manuscript preparation. AD, NC, RC, conducted the research, collected the data, and contributed to the manuscript preparation. MJMcK, RKC, PJT, MTK, CMMcD, CMP, and DC contributed to the manuscript preparation. FMMcA designed the study, advised on statistical analysis, contributed to the manuscript preparation, and had primary responsibility for the final content. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
The ROLO study was funded by the Health Research Board Ireland, the Health Research Centre for Health and Diet Research, The National Maternity Hospital Medical Fund and the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013), project Early Nutrition under grant agreement no. 289346. The ROLO Preteen study was funded by the National Children’s Research Centre Ireland at Children’s Health Ireland, grant number PRPG/H/18/325. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The ROLO and ROLO Kids studies were carried out in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 as revised in 1983. Institutional ethical approval was obtained from the National Maternity Hospital in November 2006 for the original ROLO study, REC reference: GEN/279/12. Ethical approval for the ROLO Preteen follow-up was obtained from the University College Dublin, Office of Research Ethics Committee, Dublin, Ireland in February 2015 (LS-15-06-Geraghty-McAuliffe). Written and informed consent was obtained from all eligible individuals prior to study participation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests relevant to this article.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Lopez-Jimenez F, Almahmeed W, Bays H, Cuevas A, Di Angelantonio E, le Roux CW, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: mechanistic insights and management strategies. A joint position paper by the World Heart Federation and World Obesity Federation. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2022;29(17):2218–37. doi: 10.1093/eurjpc/zwac187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lurbe E, Aguilar F, Álvarez J, Redon P, Torró MI, Redon J. Determinants of cardiometabolic risk factors in the first decade of life: a longitudinal study starting at birth. Hypertension. 2018;71(3):437–443. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Steinberger J, Daniels SR, Hagberg N, Isasi CR, Kelly AS, Lloyd-Jones D, et al. Cardiovascular health promotion in children: challenges and opportunities for 2020 and beyond: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;134(12):e236–e255. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Carolan E, Hogan AE, Corrigan M, Gaotswe G, O'Connell J, Foley N, et al. The impact of childhood obesity on inflammation, innate immune cell frequency, and metabolic microRNA expression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(3):E474–E478. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hampl SE, Hassink SG, Skinner AC, Armstrong SC, Barlow SE, Bolling CF, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and treatment of children and adolescents with obesity. Pediatrics. 2023;151(2):e2022060640. doi: 10.1542/peds.2022-060640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vukovic R, Dos Santos TJ, Ybarra M, Atar M. Children with metabolically healthy obesity: a review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2019;10:865. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lurbe E, Ingelfinger J. Developmental and early life origins of cardiometabolic risk factors: novel findings and implications. Hypertension. 2021;77(2):308–318. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.14592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Beta J, Khan N, Khalil A, Fiolna M, Ramadan G, Akolekar R. Maternal and neonatal complications of fetal macrosomia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019;54(3):308–318. doi: 10.1002/uog.20279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hong YH, Lee JE. Large for gestational age and obesity-related comorbidities. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2021;30(2):124–131. doi: 10.7570/jomes20130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sparano S, Ahrens W, De Henauw S, Marild S, Molnar D, Moreno LA, et al. Being macrosomic at birth is an independent predictor of overweight in children: results from the IDEFICS study. Matern Child Health J. 2013;17(8):1373–1381. doi: 10.1007/s10995-012-1136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Evensen E, Emaus N, Kokkvoll A, Wilsgaard T, Furberg AS, Skeie G. The relation between birthweight, childhood body mass index, and overweight and obesity in late adolescence: a longitudinal cohort study from Norway, The Tromsø Study, Fit Futures. BMJ Open. 2017;7(6):e015576. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yang Z, Dong B, Song Y, Wang X, Dong Y, Gao D, et al. Association between birth weight and risk of abdominal obesity in children and adolescents: a school-based epidemiology survey in China. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09456-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gu S, An X, Fang L, Zhang X, Zhang C, Wang J, et al. Risk factors and long-term health consequences of macrosomia: a prospective study in Jiangsu Province, China. J Biomed Res. 2012;26(4):235–240. doi: 10.7555/JBR.26.20120037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kang M, Yoo JE, Kim K, Choi S, Park SM. Associations between birth weight, obesity, fat mass and lean mass in Korean adolescents: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. BMJ Open. 2018;8(2):e018039. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-018039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Perng W, Hajj H, Belfort MB, Rifas-Shiman SL, Kramer MS, Gillman MW, et al. Birth size, early life weight gain, and midchildhood cardiometabolic health. J Pediatr. 2016;173:122–30.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu J, Au Yeung SL, He B, Kwok MK, Leung GM, Schooling CM. The effect of birth weight on body composition: evidence from a birth cohort and a Mendelian randomization study. PLoS One. 2019;14(9):e0222141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Johnsson IW, Haglund B, Ahlsson F, Gustafsson J. A high birth weight is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Pediatr Obes. 2015;10(2):77–83. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Knop MR, Geng TT, Gorny AW, Ding R, Li C, Ley SH, et al. Birth weight and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, and hypertension in adults: a meta-analysis of 7 646 267 participants from 135 studies. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(23):e008870. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dong Y, Zou Z, Yang Z, Wang Z, Jing J, Luo J, et al. Association between high birth weight and hypertension in children and adolescents: a cross-sectional study in China. J Hum Hypertens. 2017;31(11):737–743. doi: 10.1038/jhh.2017.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kuciene R, Dulskiene V, Medzioniene J. Associations between high birth weight, being large for gestational age, and high blood pressure among adolescents: a cross-sectional study. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(1):373–381. doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1372-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Badeli H, Dalili H, Rad AH, Medghalchi A, Dalili S, Koohmanaee S. Birth weight as a cardio metabolic risk factor in Iranian adolescents. Int J Prev Med. 2017;8:72. doi: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_48_16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kuhle S, Maguire B, Ata N, MacInnis N, Dodds L. Birth weight for gestational age, anthropometric measures, and cardiovascular disease markers in children. J Pediatr. 2017;182:99–106. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.11.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Evagelidou EN, Kiortsis DN, Bairaktari ET, Giapros VI, Cholevas VK, Tzallas CS, et al. Lipid profile, glucose homeostasis, blood pressure, and obesity-anthropometric markers in macrosomic offspring of nondiabetic mothers. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(6):1197–1201. doi: 10.2337/dc05-2401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yapicioglu H, Seckin SC, Yontem A, Yildizdas D. Infants with macrosomia and infants of diabetic mothers have increased carotid artery intima-media thickness in childhood. Eur J Pediatr. 2023;182(1):203–211. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04653-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chiavaroli V, Marcovecchio ML, de Giorgis T, Diesse L, Chiarelli F, Mohn A. Progression of cardio-metabolic risk factors in subjects born small and large for gestational age. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e104278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Walsh JM, McGowan CA, Mahony R, Foley ME, McAuliffe FM. Low glycaemic index diet in pregnancy to prevent macrosomia (ROLO study): randomised control trial. BMJ. 2012;345:e5605. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Donnelly JM, Walsh JM, Byrne J, Molloy E, McAuliffe F. Impact of maternal diet on neonatal anthropometry: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatr Obes. 2015;10(1):52–56. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2013.00216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gestation Network. GROW customised centile calculators. 2007. Available at: www.gestation.net/birthweight_centiles/birthweight_centiles.htm.
- 29.Cole TJ, Freeman JV, Preece MA. Body mass index reference curves for the UK, 1990. Arch Dis Child. 1995;73(1):25–29. doi: 10.1136/adc.73.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cole TJ, Pan H. LMS growth, a microsoft excel add-in to access growth references based on the LMS method. Version 2.77. 2012.
- 31.de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J. Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ. 2007;85(9):660–667. doi: 10.2471/BLT.07.043497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Flynn JT, Falkner BE. New clinical practice guideline for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Hypertension. 2017;70(4):683–686. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Léger LA, Lambert J. A maximal multistage 20-m shuttle run test to predict VO2 max. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1982;49(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00428958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Carolan E, Tobin LM, Mangan BA, Corrigan M, Gaoatswe G, Byrne G, et al. Altered distribution and increased IL-17 production by mucosal-associated invariant T cells in adult and childhood obesity. J Immun. 2015;194(12):5775–5780. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Balagopal PB, de Ferranti SD, Cook S, Daniels SR, Gidding SS, Hayman LL, et al. Nontraditional risk factors and biomarkers for cardiovascular disease: mechanistic, research, and clinical considerations for youth: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123(23):2749–2769. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e31821c7c64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972;18(6):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fang F, Zhang Q-Y, Zhang J, Lei X-P, Luo Z-C, Cheng H-D. Risk factors for recurrent macrosomia and child outcomes. World J Pediatr. 2019;15:289–296. doi: 10.1007/s12519-019-00249-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hardy R, Sovio U, King VJ, Skidmore PM, Helmsdal G, Olsen SF, et al. Birthweight and blood pressure in five European birth cohort studies: an investigation of confounding factors. Eur J Public Health. 2006;16(1):21–30. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/cki171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Patel N, Pasupathy D, Poston L. Determining the consequences of maternal obesity for offspring health. Exp Physiol. 2015;100(12):1421–1428. doi: 10.1113/EP085132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lee JW, Lee M, Lee J, Kim YJ, Ha E, Kim HS. The protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding on overweight/obesity in children with high birth weight. J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(10):e85. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.O'Brien EC, Alberdi G, Geraghty AA, McAuliffe FM. Lower education predicts poor response to dietary intervention in pregnancy, regardless of neighbourhood affluence: secondary analysis from the ROLO randomised control trial. Public Health Nutr. 2017;20(16):2959–2969. doi: 10.1017/S1368980017001951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yelverton CA, Geraghty AA, O'Brien EC, Killeen SL, Horan MK, Donnelly JM, et al. Breastfeeding and maternal eating behaviours are associated with child eating behaviours: findings from the ROLO Kids Study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2021;75(4):670–679. doi: 10.1038/s41430-020-00764-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH. Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity, and stages of puberty. Arch Dis Child. 1976;51(3):170–179. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.3.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kowalski KC, Crocker PR, Donen RM. The physical activity questionnaire for older children (PAQ-C) and adolescents (PAQ-A) manual. Coll Kinesiol Univ Sask. 2004;87(1):1–38. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bernhardsen GP, Stensrud T, Hansen BH, Steene-Johannesen J, Kolle E, Nystad W, et al. Birth weight, cardiometabolic risk factors and effect modification of physical activity in children and adolescents: pooled data from 12 international studies. Int J Obes (Lond) 2020;44(10):2052–2063. doi: 10.1038/s41366-020-0612-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Werneck AO, Silva DRP, Collings PJ, Fernandes RA, Ronque ERV, Coelho-e-Silva MJ, et al. Birth weight, biological maturation and obesity in adolescents: a mediation analysis. J Dev Orig Health Dis. 2017;8(4):502–507. doi: 10.1017/S2040174417000241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Althouse AD. Adjust for multiple comparisons? It's not that simple. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;101(5):1644–1645. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2015.11.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Growing Up in Ireland National Longitudinal Study of Children. Growing Up in Ireland. Key findings: cohort ’08 at 9 years old. Dublin, Ireland; 2018.
- 49.Derraik JG, Maessen SE, Gibbins JD, Cutfield WS, Lundgren M, Ahlsson F. Large-for-gestational-age phenotypes and obesity risk in adulthood: a study of 195,936 women. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58827-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Usta A, Usta CS, Yildiz A, Ozcaglayan R, Dalkiran ES, Savkli A, et al. Frequency of fetal macrosomia and the associated risk factors in pregnancies without gestational diabetes mellitus. Pan Afr Med J. 2017;26:62. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2017.26.62.11440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Singhal A, Wells J, Cole TJ, Fewtrell M, Lucas A. Programming of lean body mass: a link between birth weight, obesity, and cardiovascular disease? Am J Clin Nutr. 2003;77(3):726–730. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/77.3.726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Salonen MK, Kajantie E, Osmond C, Forsen T, Ylihärsilä H, Paile-Hyvärinen M, et al. Developmental origins of physical fitness: the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chiavaroli V, Derraik JG, Hofman PL, Cutfield WS. Born large for gestational age: bigger is not always better. J Pediatr. 2016;170:307–311. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2015.11.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.O'Keeffe LM, Yelverton CA, Bartels HC, O'Neill KN, McDonnell C, McAuliffe FM. Application of multilevel linear spline models for analysis of growth trajectories in a cohort with repeat antenatal and postnatal measures of growth: a prospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2023;13(3):e065701. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-065701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Peters JT, Woelfle J, Joergens S, Schreiner F, Bartmann P, Gohlke B. Effect of post-natal catch-down and feeding practices on auxology, body composition and muscle function in children born large-for-gestational-age. J Diabetes Metab. 2017;8(9):1–6. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rodríguez G, Moreno LA, Blay MG, Blay VA, Garagorri JM, Sarría A, et al. Body composition in adolescents: measurements and metabolic aspects. Int J Obes. 2004;28(3):S54–S58. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fonseca MJ, Severo M, Lawlor DA, Barros H, Santos AC. Direct and BMI-mediated effect of birthweight on childhood cardio-metabolic health—a birth cohort study. Int J Obes. 2019;43(10):1923–1931. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0413-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bartels HC, O'Keeffe LM, Yelverton CA, O'Neill KN, Geraghty AA, O'Brien EC, et al. Associations between maternal metabolic parameters during pregnancy and fetal and child growth trajectories from 20 weeks' gestation to 5 years of age: secondary analysis from the ROLO longitudinal birth cohort study. Pediatr Obes. 2023;18(1):e12976. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Callanan S, Yelverton CA, Geraghty AA, O'Brien EC, Donnelly JM, Larkin E, et al. The association of a low glycaemic index diet in pregnancy with child body composition at 5 years of age: a secondary analysis of the ROLO study. Pediatr Obes. 2021;16(12):e12820. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Geraghty AA, Sexton-Oates A, O'Brien EC, Saffery R, McAuliffe FM. Epigenetic patterns in five-year-old children exposed to a low glycemic index dietary intervention during pregnancy: results from the ROLO Kids Study. Nutrients. 2020;12(12):3602. doi: 10.3390/nu12123602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Geraghty AA, O'Brien EC, Alberdi G, Horan MK, Donnelly J, Larkin E, et al. Maternal protein intake during pregnancy is associated with child growth up to 5 years of age, but not through insulin-like growth factor-1: findings from the ROLO study. Br J Nutr. 2018;120(11):1252–1261. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518002611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Horan MK, Donnelly JM, McGowan CA, Gibney ER, McAuliffe FM. The association between maternal nutrition and lifestyle during pregnancy and 2-year-old offspring adiposity: analysis from the ROLO study. Z Gesundh Wiss. 2016;24(5):427–436. doi: 10.1007/s10389-016-0740-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Horan MK, McGowan CA, Gibney ER, Donnelly JM, McAuliffe FM. The association between maternal dietary micronutrient intake and neonatal anthropometry—secondary analysis from the ROLO study. Nutr J. 2015;14(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12937-015-0095-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hu J, Aris IM, Lin P-ID, Rifas-Shiman SL, Perng W, Woo Baidal JA, et al. Longitudinal associations of modifiable risk factors in the first 1000 days with weight status and metabolic risk in early adolescence. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;113(1):113–22. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Schellong K, Schulz S, Harder T, Plagemann A. Birth weight and long-term overweight risk: systematic review and a meta-analysis including 643,902 persons from 66 studies and 26 countries globally. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Meloni A, Cadeddu C, Cugusi L, Donataccio MP, Deidda M, Sciomer S, et al. Gender differences and cardiometabolic risk: the importance of the risk factors. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1588. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Differences in baseline characteristics between the original ROLO pregnancy cohort and the follow-up cohort at 9–11 years
Additional file 2. Comparison of cardiometabolic health in 9–11-year-old preteens born with a birthweight ≥90th and <90th centile
Additional file 3. Multiple linear regression models between birthweight centile and preteen anthropometry and body composition
Additional file 4. Multiple linear regression models between birthweight centile and preteen cardiometabolic outcomes
Additional file 5. Sensitivity analyses between macrosomia and preteen anthropometry and body composition
Additional file 6. Sensitivity analyses between macrosomia and preteen cardiometabolic outcomes
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.