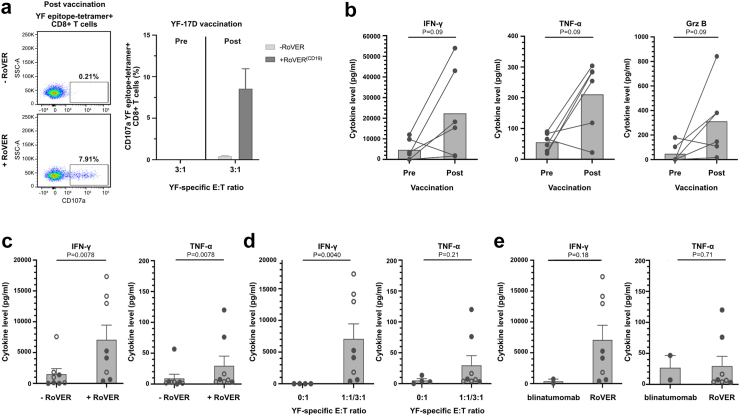
Fig. 4.
Degranulation and cytokine release from in vitro target killing assays using blinatumomab or RoVER. Detetction of CD107α degranulation and Mesoscale multiplex analyses of supernatants from in vitro cell killing assays. a) Representative flow cytometry plots of CD107α surface expression following in vitro cell killing assay showing RoVER-induced degranulating YF epitope-specific CD8+ T cells (left). Percentage of degranulating YF epitope-specific CD8+ T cells (n = 4) (right). b) Analysis of IFN-γ, TNF-α or Grz B in supernatant from RoVER-mediated killing of target cells using PBMCs obtained pre and post vaccination (21 ± 3 days) (n = 6, 100,000 PBMCs/well) (). IFN-γ or TNF-α cytokine release from RoVER-mediated target cell killing assays c) with or without exposure to RoVER (n = 8) or d) at YF-E:T 0:1 or 1:1 (n = 4, solid circles) and 3:1 (n = 4, open circles) using YF epitope-specific CD8+ T cell obtained from study participants post YF-17D vaccination (21 ± 3 days) (n = 8). e) Comparison of IFN-y and TNF-a release from in vitro target cell killing using blinatumomab (n = 2) or RoVER (n = 8). Data are mean ± SEM. p-values were calculated using Wilcoxon test when comparing paired data and Mann–Whitney statistical test when comparing unpaired data.