Abstract
Globally, over 3.5 billion people are infected with intestinal parasites each year, resulting in over 200,000 deaths. Three of the most common protozoan pathogens that affect the gastrointestinal tract of humans are Cryptosporidium spp., Giardia intestinalis, and Entamoeba histolytica. Other protozoan agents that have been implicated in gastroenteritis in humans include Cyclospora cayetanensis, Dientamoeba fragilis, Blastocystis hominis, and the microsporidia Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Encephalitozoon intestinalis. Genetic Signatures previously developed a 3base™ multiplexed Real-Time PCR (mRT-PCR) enteric protozoan kit (EP001) for the detection of Giardia intestinalis/lamblia/duodenalis, Cryptosporidium spp., E. histolytica, D. fragilis, and B. hominis. We now describe improvements to this kit to produce a more comprehensive assay, including C. cayetanensis, E. bieneusi, and E. intestinalis, termed EP005. The clinical performance of EP005 was assessed using a set of 380 clinical samples against a commercially available PCR test and other in-house nucleic acid amplification tests where commercial tests were not available. All methods provided at least 90% agreement. EP005 had no cross-reactivity against 82 organisms commonly found in the gut. The EP005 method streamlines the detection of gastrointestinal parasites and addresses the many challenges of traditional microscopic detection, resulting in cost savings and significant improvements in patient care.
Keywords: gastrointestinal parasites, RT-PCR, genomic simplification
1. Introduction
The history of human parasitic infections dates to the Greek, Egyptian, and Roman Empires [1]. Infections with parasites, in particular protozoan agents, are a major health concern worldwide and cause over 200,000 deaths annually [2,3]. Intestinal protozoa are one of the most widespread infections in resource-limited countries and children, especially those under 5 years old [4], who are the most vulnerable population, as they tend to be more active in areas of high prevalence and not always adhere to strict hygienic practices [5]. Infections with Giardia intestinalis/lamblia/duodenalis (synonymous and referred to as G. intestinalis henceforth) and Cryptosporidium spp. are mainly transmitted to the population via water or food contaminated with cysts, and infection is typically characterized by acute diarrhea [6]. It has been estimated that Giardia infects more than 200 million individuals every year globally, and studies have suggested that chronic infection with Giardia in children can result in significant long-term growth retardation [7].
Entamoeba histolytica is the causative agent of amoebiasis and is responsible for dysentery and liver abscesses, with invasive disease developing in approximately 10% of infected individuals. The disease is endemic in many countries, including Central and South America, Africa, and Asia [8]. E. histolytica is transmitted to the population via contaminated water, foods, and through sexual contact [9].
Dientamoeba fragilis and Blastocystis hominis have also been implicated as intestinal protozoan capable of causing disease in humans. The prevalence of D. fragilis has been found to be between 0.4% and 71% depending on the population studied and the diagnostic methods used; in general, the prevalence is higher in developed countries [10]. Clinical symptoms range from asymptomatic to abdominal pain, weight loss, diarrhea, and altered bowel movements consistent with gastroenteritis [10]. It has been postulated that D. fragilis could be a heterogeneous species containing variants possessing different pathologies [11]. Blastocystis hominis is a controversial human pathogen, and the prevalence has been shown to be 0.5–24% in industrialized countries and 30–76% in resource-limited nations [12,13]. There have been many reports suggesting that B. hominis causes disease, and equally a number of reports that contradict this claim [14]. Nevertheless, B. hominis has been included in the Water Sanitation and Health programs of the World Health Organization, indicating its pathogenic potential [15]. Furthermore, recently, it was postulated that B. hominis subtypes ST1 and ST3 and Cryptosporidium spp. might be associated with colorectal cancer in a systematic review of the literature [16].
Cyclospora cayetanensis is distributed on a global scale and infects travelers, children, and immunocompromised patients in endemic countries; in industrialized countries, people of any age are susceptible. Transmission is generally food-borne and associated with contaminated fresh produce. Usually, infection is self-limiting with the major symptom of acute diarrhea; however, in a small number of immunocompromised patients, chronic diarrhea can occur with extra-intestinal organ colonization [17].
Microsporidia are a diverse group of pathogens that infect a wide range of animals and contain 14 species that can infect humans [18]. Microsporidia infections in humans occur globally, and prevalence rates of between 0–50% have been recorded depending on the diagnostic technique used, geographical region, and the population studied [19]. The most well-known are Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Encephalitozoon intestinalis, which infect a number of domestic, farm, and wild animals, leading to the theory that infection is a zoonotic disease. Microsporidia have been detected in fresh vegetables and fruit and thus may also be transferred to the human population as a food-borne disease [20]. Microsporidian infection predominately occurs in HIV-infected or immunocompromised individuals with the main symptoms of weight loss, persistent diarrhea, and abdominal pain. However, in some patients, dissemination to the hepatobiliary, pulmonary, and other organ systems occurs, resulting in life-threatening conditions [19]. Table 1 shows a summary of the symptoms and number of infections occurring annually as a result of infection with G. intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., E. histolytica, and C. cayetanensis.
Table 1.
Symptoms and number of infections annually worldwide for G. intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., E. histolytica, and C. cayetanensis.
| Organism | Symptoms | Infections |
|---|---|---|
| G. intestinalis | Acute, watery diarrhea. Chronic infections can result in weight loss and malabsorption and can cause long-term complications, including irritable bowel syndrome and chronic fatigue. | >200 million people annually. |
| Cryptosporidium spp. | Symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, vomiting, malabsorption, and self-limiting diarrhea. | >2.9 million cases of cryptosporidiosis in children aged <2 years old in sub-Saharan Africa alone annually. |
| E. histolytica | Asymptomatic to severe symptoms, including dysentery (bloody diarrhea) and extra-intestinal abscesses. | Amebiasis results in 100,000 deaths annually on a global basis. |
| C. cayetanensis | Watery diarrhea, weight loss, and cramping. | Outbreaks of cyclosporiasis occur regularly in the US, mostly linked to infected food or drink. |
Traditionally, the diagnosis of many gastrointestinal parasites has been based on the detection of trophozoites or cysts by microscopical examination of stool samples. However, the sensitivity of microscopy can be low (46%) because of the sporadic shedding of cysts into stool. To improve the sensitivity of microscopy, it is recommended that three consecutive samples be taken, which results in an improvement of sensitivity up to 94% [21]. However, microscopy is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and requires highly trained staff. In order to increase the sensitivity and make diagnosis simpler, immunological assays have been developed for the detection of enteric protozoa. Such tests are easier to perform and useful for the rapid investigation of a large number of stool specimens [22]. Combination tests for the detection of Giardia intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and E. histolytica in clinical samples, such as the Tri-Combo parasite screen test (TechLab, Blacksburg, VA, USA) and the Triage parasite panel (Biosite, San Diego, CA, USA), have been developed requiring minimal laboratory experience and reagents simplifying diagnosis further [23].
A wide range of PCR and RT-PCR-based techniques has been developed for the detection of intestinal parasites in clinical samples [24]. The advantage of these methods is that, in general, they tend to be more sensitive and specific compared to traditional microscopy and immunoassays [25]. Many commercially available RT-PCR tests exist that commonly detect the presence of Giardia intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and E. histolytica directly from stool samples [26]. Basmaciyan et al. compared four commercially available tests, finding the assays were an alternative method compared to traditional techniques for the detection of the three protozoan targets in stool samples [27]. However, the authors noted differences in the sensitivity and specificity of each assay for the detection of Giardia intestinalis and Cryptosporidium spp., indicating that care should be taken when choosing an assay [27].
Table 2 compares the test menu of ten commercially available molecular assays that detect intestinal protozoan in clinical samples. All tests detect the presence of G. intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and E. histolytica. Certest, SeeGene, Ausdiagnostic, and Genetic Signatures assays additionally detect D. fragilis and B. hominis with the Biofire, SeeGene, Ausdiagnostics, and Genetic Signatures assays detecting C. cayetanensis. The only assay capable of detecting all, including microsporidian targets, is the Genetic Signatures EP005 assay.
Table 2.
Commercially available enteric protozoan assays.
| Manufacturer | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Becton Dickinson (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) | Diagenode (Denville, NJ, USA) | R-Biopharm (Hessen, Germany) | Fast Track (Esch-sur-Alzette, Luxembourg) | Savyon (Ashdod, Israel) | Certest (Zaragoza, Spain) | Biofire (Salt Lake City, UT, USA) | SeeGene (Seoul, Republic of Korea) | AusDiagnostics (Mascot, NSW, Australia) | Genetic Signatures (Newtown, NSW, Australia) | |
| Target | BD MAX™ | Gastro panel | RIDAGENE | FTD Stool | NanoCHIP | VIASURE | Filmarray | ALLplex | Parasite 8 | EP005 |
| G. intestinalis | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cryptosporidium spp. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| E. histolytica * | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| D. fragilis | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| B. hominis | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| C. cayetanensis | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| E. bieneusi | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
| E. intestinalis | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
* All assays listed are specific for E. histolytica and do not detect E. dispar or E. moshkovski.
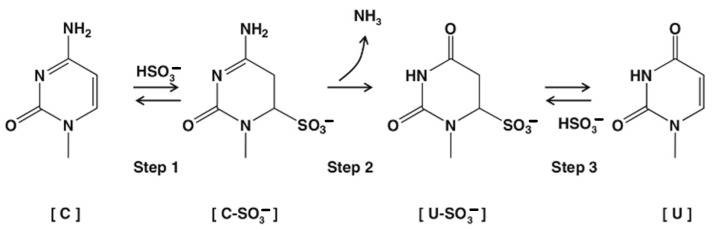
We previously developed a novel RT-PCR technology based on the bisulphite deamination of cytosine to thymine via a uracil intermediate, which simplifies conventional nucleic acid sequences containing adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine to a 3baseTM form consisting of just adenine, thymine, and guanine. The deamination reaction of cytosine to uracil was first described in 1970 by Hayatsu [28,29] and has been studied in detail since. The first step of the reaction involves the sulphonation of cytosine to cytosine sulphonate followed by deamination of cytosine to a uracil sulphonate intermediate and subsequently the removal of the sulphate adduct to uracil, traditionally by the use of strong alkali (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Bisulphite mediated conversion of cytosine to uracil.
After conversion, sequences become more similar at the nucleic acid level, allowing the detection of, for example, viruses from families containing large numbers of individual pathogens such as human papillomavirus [30], Norovirus GI and GII [31], and flavivirus [32]. In addition, the conversion of cytosine bases to thymine within target sequences contributes to improved PCR efficiency for organisms with high G-C content, such as G. intestinalis, where inefficiencies with amplification have been reported using conventional assays [33]. By way of demonstration, Table 3 shows the reduction in G-C content for Entamoeba spp., G. intestinalis, D. fragilis, Cryptosporidium, and B. hominis in an earlier version of our enteric protozoan detection kit, using a universal primer set and specific probes to differentiate the individual pathogens, except Entamoeba, where the Entamoeba complex was detected (E. histolytica, E. dispar, and E. moshkovski).
Table 3.
Examples of the reduction in melting temperature that can be achieved in mRT-PCR using 3base™ technology.
| 4Base Sequence | 3Base™ Sequence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Sequence | Tm °C | Sequence | Tm °C |
| Primer-1 | GTACACACCGCCCGTCGCTCCTACC | 66.6 | GTATATATTGTTTGTTGTTTTTATT | 51 |
| Primer-2 | GAGGAAGGTGAAGTCGTAACAAG | 55.2 | GAGGAAGGTGAAGTTGTAATAAG | 49.7 |
| Entamoeba spp. Probe | TGAATAAAGAGGTGAAATTCTAGG | 51.3 | TGAATAAGAGGTGAAATTTTAGG | 49 |
| G. intestinalis Probe | GCGCGAAGGGCCGCGAGCCCCCGCGC | 78.8 | GTGTGAAGGGTTGTGAGTTTTTGTGT | 57.9 |
| D. fragilis Probe | TTTAAATGAAAAGGTGATTAAATCACG | 51.2 | TTTAAATGAAAAGGTGATTAAATTATG | 47.7 |
| Cryptosporidium spp. Probe | GACCATACTTTGTAGCAATACATGTAAGGA | 56.6 | GATTATATTTTGTAGTAATATATGTAAGGA | 48.1 |
| B. hominis Probe | TATTGAAAGAAGTTGTGTAAATCTTACCATT | 53.9 | TATTGAAAGAAGTTGTGTAAATTTTATTATT | 50 |
Using this 3base method, we developed a new mRT-PCR assay (EasyScreen™ Gastrointestinal Parasite Detection Kit, EP005) capable of detecting the presence of eight of the most important protozoan parasites infecting the gastrointestinal tract of humans. All assays target the 18S/small subunit ribosomal RNA gene transcripts.
2. Results
Table 3 shows that using the 3base™ approach greatly reduces the G-C content of the primers and probe sequences. Before 3base™ conversion, the melting temperature of the primers varied by 11.4 °C, whereas after, there was only a 1.2 °C difference. Similarly, the melting temperature of the probes ranged from as low as 51.3 °C to a high of 78.8 °C, with the temperature difference reduced to 49–57.9 °C after treatment. Such large variations in temperature would lead to inefficient amplification of the targets as well as suboptimal probe binding. Therefore, the use of 3base™ can be advantageous when performing mRT-PCR where target sequences have a wide range of G-C content, thus normalizing PCR cycling conditions.
2.1. Assay Sensitivity
Table 4 shows the strains used to assess the lower limit of detection (LLOD) of the assays. All targets were diluted in a negative stool background, and then serial dilutions were extracted and purified prior to PCR amplification.
Table 4.
Organisms used to assess the LLOD of each target.
| Target Organism; Strain (Accession Number) | Target Type (ATCC Cat. Number) |
|---|---|
| Blastocystis hominis NANDII | Culture (50177) |
| Blastocystis hominis NTY | Culture (50610) |
| Cryptosporidium parvum; (* CP082114.1) | Clinical stool |
| Cryptosporidium hominis; (* XM_661199.1) | Clinical stool |
| Cyclospora cayetanensis; (* AF111183.1) | Clinical stool |
| Dientamoeba fragilis; (* JQ677148.1) | Culture |
| Dientamoeba fragilis; (* JQ677148.1) | Clinical stool |
| Entamoeba histolytica HU-21:AMC | Culture (30457) |
| Enterocytozoon bieneusi; (* AF023245.1) | Clinical stool |
| Enterocytozoon bieneusi; MWC_m4 (MG976813.1) | Clinical stool |
| Encephalitozoon intestinalis | Culture (50506) |
| Giardia lamblia, Human isolate—H3 (AF023245.1) | Quantified non-viable oocysts |
| Giardia intestinalis; BE-1 | Culture PRA-42 |
* The accession number was the best match for sequencing of the PCR amplicons.
Table 5 shows that the LLOD of the assay components ranged from 4 organisms/mL for Enterocytozoon bieneusi to 5700 genome equivalents (GE)/mL for Giardia intestinalis.
Table 5.
LLOD of each target in the EP005 panels.
| LLOD | Positive Replicates | Ct Value Average | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Concentration | Isolate 1 | Isolate 2 | Isolate 1 | Isolate 2 |
| Dientamoeba fragilis | 125 org/mL | 20/20 | 20/20 | 32.45 | 30.66 |
| Cryptosporidium parvum | 1600 org/mL | 19/20 | 20/20 | 32.54 | 31.95 |
| Cryptosporidium hominis | 1600 org/mL | 20/20 | 20/20 | 31.81 | 30.34 |
| Cyclospora cayetanensis | 25 GE/mL | 20/20 | 20/20 | 33.11 | 31.76 |
| Blastocystis hominis | 100 org/mL | 20/20 | 19/20 | 31.96 | 33.56 |
| Giardia intestinalis | 5700 GE/mL | 20/20 | 19/20 | 32.23 | 32.63 |
| Entamoeba histolytica | 3000 org/mL | 20/20 | 20/20 | 33.76 | 32.81 |
| Enterocytozoon bieneusi | 4 org/mL | 20/20 | 20/20 | 34.53 | 32.79 |
| Encephalitozoon intestinalis | 1200–2500 org/mL | 20/20 * | 20/20 # | 33.04 | 29.84 |
* Isolate 1 was tested at 1200 organisms/mL, and # Isolate 2 was tested at 2500 organisms/mL.
To ensure the assay was capable of detecting a wide range of strains of each target organism, a number of cultures, clinical isolates, and DNA were obtained and tested at 3× the LLOD (See Table 6). All strains and cultured samples were successfully detected using the assay.
Table 6.
Assay inclusivity using clinical samples and cultured isolates.
| Organism; Strain (Accession Number) | Target Type * | Organism; Strain (Accession Number) | Target Type * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blastocystis hominis; BT1 | Culture (50608) | Dientamoeba fragilis | Clinical |
| Blastocystis hominis; NMH | Culture (50754) | Dientamoeba fragilis | Clinical |
| Blastocystis hominis; DL | Culture (50626) | Dientamoeba fragilis | Clinical |
| Cryptosporidium parvum | Clinical | Encephalitozoon intestinalis; CDC:V297 (50651) | Culture (50651) |
| Cryptosporidium parvum | Clinical | Encephalitozoon intestinalis; nasal isolate (50507) | Culture (50507) |
| Cryptosporidium parvum | Clinical | Encephalitozoon intestinalis; CDC:V307 (50603) | Culture (50603) |
| Cryptosporidium parvum | Clinical | Encephalitozoon intestinalis; CDC:V308 (50790) | Culture (50790) |
| Cryptosporidium parvum | Clinical | Enterocytozoon bieneusi | DNA |
| Cryptosporidium hominis | Clinical | Entamoeba histolytica; HB-301:NIH (30190) | Culture (30190) |
| Cryptosporidium hominis | Clinical | Entamoeba histolytica; HK-9 Clone 6 (50544) | Culture (50544) |
| Cryptosporidium hominis | Clinical | Entamoeba histolytica; HB-301:NIH CL-1-3 (50547) | Culture (50547) |
| Cryptosporidium hominis | Clinical | Giardia intestinalis; WB (30957) | Culture (30957) |
| Cryptosporidium hominis | Clinical | Giardia intestinalis; WB clone C6 (50803) | Culture (50803) |
| Dientamoeba fragilis | Clinical | Giardia intestinalis; GS clone H7 (50581) | Culture (50581) |
| Cyclospora cayetanensis (KX618190) | Clinical | Giardia intestinalis; Portland-1 (30888) | Culture (30888) |
| Cyclospora cayetanensis (MN316534) | Clinical | Giardia intestinalis; (Lambl) Alexeieff Strain PR-15 | Culture |
| Cyclospora cayetanensis (MN316534) | Clinical | Giardia lamblia; CM (PRA242) | Culture (PRA242) |
| Cyclospora cayetanensis (MN316535) | Clinical | ||
| Dientamoeba fragilis | Clinical |
* Where applicable, the ATCC catalogue numbers have been included in brackets. For clinical samples, the accession number for the best match on sequencing of the PCR amplicon is listed.
2.2. Assay specificity
Either cultured organisms or purified nucleic acids from the organisms listed in Table 7 were diluted to approximately 106 CFU/mL or 109 copies/mL, respectively, using a negative stool matrix. All samples were tested in triplicate to determine potential cross-reactivity with no amplification detected from EP005 using any of the non-target organisms.
Table 7.
Species used to assess assay specificity.
| Cross-Reactivity Species Tested | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Atopobium vaginae * | Cedecea davisae * | Human adenovirus 5 | Proteus vulgaris |
| Abiotrophia defective * | Chlamydia trachomatis | Klebsiella oxytoca | Providencia stuartii |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | Chryseobacterium gleum * | Lactobacillus acidophilus | Rotavirus A |
| Adenovirus | Citrobacter freundii | Lactococcus lactis | Saccharomyces cerevisiae * |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | Clostridium perfringens | Leminorella grimontii * | Salmonella enterica |
| Akkermansia muciniphila | Corynebacterium glutamicum * | Listeria monocytogenes | Sapovirus |
| Alcaligenes faecalis | Cronobacter sakazakii | Mycobacterium abscessus | Serratia marcescens |
| Anaerococcus tetradius * | Desulfovibrio pigerl * | Mycobacterium avium | Shigella flexneri |
| Arcobacter butzleri * | Edwardsiella tarda * | Mycobacterium spp. | Shigella sonnei |
| Astrovirus | Eggerthella lenta | Mycoplasma fermentans | Staphylococcus aureus |
| Atopogium vaginae * | Enterococcus faecalis | Mycoplasma hominis | Staphylococcus hominis |
| Bacillus cereus | Enterococcus faecium | Mycoplasma salivarium | Stenotrophomonas maltophila |
| Bacteroides fragilis | Enterovirus | Neisseria flava | Streptococcus mitis |
| Bifidobacterium adolescentis | Escherichia coli | Norovirus GI | Streptococcus pyogenes |
| Bocavirus | Eubacterium rectale * | Norovirus GII | Streptococcus salivarius |
| Campylobacter coli | Faecalibacterium prausnitzii * | Peptoniphilus asaccharolyticus * | Streptococcus sanguinis |
| Campylobacter hominis | Fusobacterium varium * | Peptostreptococcus anaerobius | Streptococcus thermophilus |
| Campylobacter jejuni | Gardnerella vaginalis | Porphyromonas asaccharolytica * | Veillonella parvula |
| Campylobacter lari | Gemella morbillorum * | Porphyromonas levii * | Yersinia pseudotuberculosis |
| Candida albicans | Hafnia alvei | Prevotella melaninogenica | |
| Capnocytophaga gingivalis | Helicobacter pylori | Proteus mirabilis | |
* Cultured isolates.
2.3. Microbial Interference Studies
Each target organism was tested at 2× LLOD in a negative stool matrix containing either cultured organisms at 106 CFU/mL or purified nucleic acids at 109 copies/mL using the strains shown in Table 8. Each sample was then tested in triplicate to determine potential competitive inhibition with high concentrations of non-target organisms. All targets from EP005 were amplified at 2× LLOD.
Table 8.
Organisms used in the competitive interference study.
| Target Organism | Target Type (ATCC Cat. Number) |
|---|---|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ATCC 47085DQ |
| Candida albicans | ATCC MYA-2876D-5 |
| Clostridioides perfringens | ATCC 13124DQ |
| non-pathogenic Escherichia coli | ATCC 25922DQ |
| Enterococcus faecalis | ATCC 700802DQ |
| Bacteroides fragilis | ATCC 25285D-5 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | ATCC 13883DQ |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae * | ATCC MYA-796 |
* Cultured isolate.
2.4. Quality Assurance Panels
The assay was further validated with a quality assurance panel obtained from QCMD (Quality Controls for Molecular Diagnostics, Glasgow, Scotland) consisting of nine blinded samples. QCMD panels consist of whole inactivated organisms in a synthetic stool background. The panels were sent to participating laboratories to be coded, then samples were tested, and the results were returned before the panel content was released. As can be seen from Table 9, the results obtained were in agreement with the expected results.
Table 9.
Results generated with the QCMD quality assurance panel.
| Sample | QCMD Result | EP005 Result |
|---|---|---|
| EP19S-01 | D. fragilis/B. hominis | D. fragilis/B. hominis |
| EP19S-02 | E. histolytica | E. histolytica |
| EP19S-03 | Negative | Negative |
| EP19S-04 | E. histolytica | E. histolytica |
| EP19S-05 | G. intestinalis | G. intestinalis |
| EP19S-06 | Cryptosporidium spp. | Cryptosporidium spp. |
| EP19S-07 | G. intestinalis | G. intestinalis |
| EP19S-08 | Cryptosporidium spp. | Cryptosporidium spp. |
| EP19S-09 | G. intestinalis | G. intestinalis |
2.5. Clinical Studies
To assess clinical sensitivity, 380 samples were tested with both the BD MAX™ Enteric Parasite Panel and the EasyScreen™ Gastrointestinal Parasite Detection Kit, EP005 (Table 10). The BD MAX™ Enteric Parasite Panel detects G. intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and E. histolytica. In order to confirm the presence of pathogens not covered in the BD MAX™ panel, individual conventional 4base primers sets were designed for D. fragilis, C. cayetanensis, B. hominis, E. bieneusi, and E. intestinalis. Samples positive for these targets were re-amplified with these assays and sequenced to confirm the identity of the pathogen detected.
Table 10.
Results generated comparing the assay to an alternative commercially available test and PCR and sequencing with other nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAAT).
| Target | Specimen Type | Samples Tested | EP005 Positive | Confirmatory Method | Positive with Confirmatory Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptosporidium spp. | Prospective | 380 | 10 | BD MAX™ | 9 |
| G. intestinalis | Prospective | 380 | 20 | BD MAX™ | 21 |
| E. histolytica | Prospective | 380 | 8 | BD MAX™ | 8 |
| B. hominis | Prospective | 380 | 24 | NAAT | 11/16 * |
| D. fragilis | Prospective | 380 | 37 | NAAT | 15/16 * |
| C. cayetanensis | Retrospective | 11 | 11 | NAAT | 11 |
| E. bieneusi | Retrospective | 21 | 21 | NAAT | 19 ** |
| E. intestinalis | Contrived/Retrospective | 5 | 5 | NAAT | 5 |
* 16 samples of each were selected for sequencing with five B. hominis and one D. fragilis samples negative by NAAT due to the improved sensitivity of the 3base™ assay. ** 2 samples were negative by NAAT due to the improved sensitivity of the 3base™ assay.
Table 11 shows the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of the EP005 assay compared to the gold standard BDMax™ assay. As can be seen from the data, the EP005 assay showed a high level of sensitivity and specificity compared to the comparator assay.
Table 11.
Specificity, sensitivity, PPV, and NPV of the EP005 assay compared to the BDMax™ assay.
| Target | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | PPV (95% CI) | NPV (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptosporidium spp. | 100% (66.37–100) | 99.7% (98.51–99.99) | 90% (55.97–98.46) | 100% |
| G. intestinalis | 95.45% (77.16–99.88) | 100% (98.98–100) | 100% | 99.74% (98.14–99.96) |
| E. histolytica | 100% (63.06–100) | 100% (99.01–100) | 100% | 100% |
Cryptosporidium was detected in 10 samples using the EP005 assay (2.6%), and 9 of these were also positive using the BD MAX™ assay. Twenty samples tested positive for G. intestinalis using EP005 (5.3%), with an extra positive sample found when using the BD MAX™ assay. Eight samples tested positive for E. histolytica using both methods (2.1%).
Thirty-seven samples (9.7%) were positive for D. fragilis, and sixteen of these samples were selected for re-amplification and sequencing, with fifteen samples tested confirmed as D. fragilis. B. hominis was detected in a total of 24/380 (6.3%) samples, and again, sixteen of the positive samples were analyzed by sequencing, confirming eleven as B. hominis. The increase in positive samples using the EP005 assay was due to the improved sensitivity of EP005 compared to the NAAT assays.
C. cayetanensis was detected in eleven retrospective samples, and again, all samples were confirmed to contain C. cayetanensis on sequencing. In a retrospective study, twenty-one samples that had previously tested positive for E. bieneusi using an alternative assay were tested, and all samples produced positive amplification curves for E. bieneusi. Nineteen of twenty-one of these samples tested positive on sequencing; however, two samples were negative as a result of the reduced sensitivity of the NAAT primers sets. Five samples were positive for E. intestinalis using both the 3base™ assay and PCR followed by sequencing. Finally, 3% of samples contained mixed infection with two or more parasites detected. The Ct values of all positive samples detected in the study are shown in Supplementary Table S2.
3. Discussion
The three most commonly occurring protozoan parasites that infect humans are G. intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and E. histolytica. A number of other species, including C. cayetanensis, E. bieneusi, and E. intestinalis, are well-established disease-causing protozoa that infect the gut. Both D. fragilis and B. hominis have been implicated in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal disease for many years and are commonly found in the intestinal tract.
Traditional methods used for the detection of these parasites have been microscopy and immunoassays. However, microscopy is time-consuming, and the results require highly trained technicians. Immunoassays suffer from reduced sensitivity and specificity and can have trouble differentiating pathogenic E. histolytica from the non-pathogenic E. dispar and E. moshkovskii compared to PCR-based methodologies. Both conventional and real-time PCR have become well-established techniques for the detection of protozoan parasites. In general, PCR methods are easy to perform, more sensitive, and have the added advantage that they can be used to detect multiple pathogens in the same sample.
Most commercially available PCR assays target G. intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and E. histolytica, with some additionally targeting D. fragilis, B. hominis, or C. cayetanensis. Protozoan infections can be successfully treated using a number of drugs, including metronidazole, tinidazole, and nitazoxanide; thus, it is vital to have rapid and sensitive assays that can detect the parasite responsible for disease and to administer appropriate anti-protozoan drugs if required. To date, no commercial assay is available that detects all these parasites and the microsporidian targets. We developed a novel assay that targets all eight human protozoan parasites. The method has the advantage that the primers and probes used in the assays have a more similar melting temperature, which improves the efficiency of mRT-PCR.
The analytical sensitivity of the method was shown to be: 4 organisms/mL for E. bieneusi, 25 GE/mL for Cyclospora cayetanensis, 100 organisms/mL B. hominis, 125 org/mL for D. fragilis, 1600 org/mL for Cryptosporidium, and 1200–2500, 3000, and 5700 organisms or GE/mL for E. intestinalis, E. histolytica, and Giardia intestinalis, respectively. Given that the assays target the 18S/small subunit ribosomal RNA gene transcripts, the differing sensitivities may partially reflect the different copy numbers and expression levels of the 18S rRNA genes in different species, cultures, and clinical isolates. Testing a range of different isolates and cultures confirmed that the assay was able to detect all strains that were analyzed. No cross-reactivity was seen using a wide range of organisms that would be commonly found in stool samples.
Previously, a number of studies have compared our EasyScreenTM Enteric Detection Kit EP001 to traditional ova and parasite (O&P) examinations [31,34,35]. In a study analyzing 358 samples, the EP001 kit yielded 92–100% sensitivity (compared to 55–77% for traditional O&P) and 100% specificity (compared to 95–100% for traditional O&P) for the detection of Cryptosporidium spp., G. intestinalis, Entamoeba spp., D. fragilis, and B. hominis [35].
A clinical trial was conducted to assess the performance of the new EP005 assay consisting of 380 stool samples, and the results were compared to another commercially available assay, the BD MAX™ Enteric Parasite Panel, which detects the presence of G. intestinalis, Cryptosporidium spp., and E. histolytica. To confirm the presence of pathogens not included in the BD MAX™ system, alternative PCR assays were designed, and positive samples were re-amplified with these primers and then sequenced to determine the identity of the suspected pathogen. Overall, there was a high level of agreement of the assay with the BD MAX™ with 10 samples positive for Cryptosporidium spp. using the EP005 assay compared to the 9 for the BD MAX™; 20 samples were positive using the EP005 assay for G. intestinalis compared to the 21 for the BD MAX™, and 8 samples were positive for E. histolytica using both. The use of alternative PCR assays and sequencing for the detection of pathogens not targeted by the BD MAX™ system showed a high degree of concordance with the expected results. Interestingly, 3% of samples contained mixed infections, demonstrating the utility of the multiplex assay to detect co-infections.
mRT-PCR technologies will most likely never be a substitute for microscopy as they do not detect the presence of all enteric protozoa or parasites that can cause infection. The EP005 assay uses automated sample extraction technologies, simplifying the process of nucleic acid purification from stool samples and decreasing the involvement of highly trained employees, thus reducing hospital costs and streamlining laboratory workflows. The EP005 assay is a sensitive and specific assay for the detection of enteric protozoan in clinical samples and has the most comprehensive assay menu available. Results are generated within 4 h; thus, drugs can be prescribed in a timely manner if required, ultimately improving patient care.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. EP005 PCR Assays
Real-time PCR assays were designed against 18S/small subunit ribosomal RNA consensus sequences obtained from public databases (Genbank, NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA). Sequences were first 3base converted by changing all C bases to T in the sense strand. Some targets (D. fragilis, Cryptosporidium spp., B. hominis, and G. intestinalis) use common forward and reverse primers but specific fluorescent probes for each target. The other four targets use unique primers and probes. Sequences are commercial in confidence. To formulate EP005, targets were divided into three multiplex panels per Table 12 below. Each panel also includes a control; Panels A and C contain an extraction control (EC) pan-bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA target to ascertain sample quality (i.e., bacterial load), and panel B contains an internal positive control (IPC) to indicate any PCR inhibition, whereby amplification should occur within a defined cycle threshold (Ct) range in the absence of inhibition. Each probe fluoresces at a given wavelength, and the signals are measured and distinguished from each other by the real-time PCR platform. The real-time PCR software provided with each instrument interprets all data collection and provides the information for automated or manual result analysis.
Table 12.
Panel and target composition of the EP005 kit.
| Channel/Representative Fluorophore | Panel A | Panel B | Panel C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fam | D. fragilis | B. hominis | E. bieneusi |
| Hex/Vic | EC | IPC | EC |
| Texas Red/Rox | C. cayetanensis | E. histolytica | E. intestinalis |
| Cy5 | Cryptosporidium. spp. | G. intestinalis | Not used |
4.2. Preparation of Negative Stool
Stool specimens known to be free of the eight EP005 targets, either by microscopy or using EP001, were processed using the SP008B sample-processing kit according to the instructions (Genetic Signatures, Sydney, Australia) on the GS1 automated sample-processing platform and amplified with the EasyScreen™ Gastrointestinal Parasite Detection kit (EP005) to confirm the absence of EP005 targets. Negative samples were then pooled, and 10 volumes of PBS were added per gram of stool and re-tested using EP005. The confirmed negative stool matrix was then stored at −80 °C until required.
4.3. LLOD and Inclusivity Studies
Target organisms were quantified using synthetic double-stranded DNA (gBlocks, IDT, Sydney, Australia), listed in Supplementary Table S1. gBlocks were serially diluted and compared to DNA extracted from the target organisms. A standard curve was generated using the Bio-Rad CFX Manager 3.1 Software, and this was used to calculate the copy number of each target. The quantified targets were then diluted into a negative stool background and extracted on the GS1 automated platform. The eluates were PCR-amplified using the EP005 assay (Genetic Signatures, Sydney, Australia). The acceptance criteria for LLOD were the concentration at which 95% or greater detection of the specified target was achieved.
The inclusivity of the EasyScreen™ Gastrointestinal Parasite Detection Kit (EP005) was also evaluated using a collection of 37 isolates (ATCC culture and quantified sequenced clinical specimens) representing the eight EP005 targets. Targets were tested at no higher than 3 times the LLOD in a negative stool matrix. Samples were extracted and tested in triplicate, with 100% detection for the specified target as the acceptance criteria.
4.4. Cross-Reactivity Studies
Cultured organisms or DNA samples were obtained from ATCC and diluted to 106 CFU/mL or 109 copies/mL, respectively, in a negative stool background. Samples were then tested in triplicate, according to Section 4.2.
4.5. Clinical Samples
In total, 380 clinical samples were obtained from local Sydney hospitals and universities, and these were processed according to Section 4.2. In addition, the samples were also processed using the BD MAX™ Enteric Parasite Panel according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.6. Confirmatory Nucleic Acid Amplification Techniques
Table 13 lists the sequences of the primers used to confirm the results generated using the EP005 system that was not covered by the BD MAX™ Enteric Parasite Panel. Primers were synthesized by IDT technologies (Sydney, Australia). PCR conditions were as follows: 42 °C 15 min, 95 °C 3 min; 95 °C 15 s 62–65 °C for 60 s repeated 50 cycles. The SsoAdvanced Universal SYBR Green Supermix (BioRad, Sydney, Australia) was used as a PCR mastermix. All positive samples were sent for sequencing using the same forward and reverse primers used in the RT-PCR reaction. The PCR product (~17 μL) and 100 μL of 3.2 μM of each primer were sent to AGRF Molecular Genetics (Sydney, Australia) for PCR cleanup and Sanger sequencing.
Table 13.
Shows the sequences of the alternative NAAT assays used as confirmatory assays in the clinical study.
| Target | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Gene | Anneal Temp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D. fragilis Region 1 | AATACCTTTTAATAGGTAATCCAATCGA | GCCCTCTGCTAGGTTACAATATAC | 18S rRNA | 64 °C |
| D. fragilis Region 2 | TTTAATGACTGATCAGGCTATAGG | CATCACGGACCTGTTATTGCTACCA | 18S rRNA | 64 °C |
| C. cayetanensis Region 1 | CGCATTTGGCTTTAGCCGGCGATA | TTACTCTGGAAGGATTTTAAATTCCT | 18S rRNA | 62 °C |
| C. cayetanensis Region 2 | CACGCTCTACCAATATTCGTTATCA | GGATCGTGTTGGCTAGGTGTACTAA | Mitochondria | 65 °C |
| B. hominis Region 1 | AGTAGTCATACGCTCGTCTCAAA | TCTTCGTTACCCGTTACTGC | SSU RNA | 65 °C |
| B. hominis Region 2 | CAATTGGAGGGCAAGTCTGGTGC | CACCTCTAACTATTGAATATGAATACC | SSU RNA | 64 °C |
| E. bieneusi Region 1 | TAGCGGAACGGATAGGGAGTGTAGT | CTTGCGAGCGTACTATCCCCAGAG | SSU RNA | 64 °C |
| E. bieneusi Region 2 | CATTCGTTGATCGAATACGTGAGAAT | GTTACTAGGAATTCCTTATTCACTACG | SSU RNA | 64 °C |
| E. intestinalis Region 1 | TCACGGCATCCATTTCAAACGG | GATGAAGGACGAAGGCTAGAGGA | 16S rRNA | 64 °C |
| E. intestinalis Region 2 | GTCCAAGAGCACAGCCTTCGCTTC | GGGATCGGGGTTTGATTCCGGA | 16S rRNA | 64 °C |
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Gauri More for technical support and help with NAAT and sequencing of clinical samples.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms241713387/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.C., R.B., J.M. and D.M.; methodology, N.C., R.B. and D.M.; validation, M.A., M.J., S.P., J.N., L.T. and N.C.; formal analysis, N.C. and R.B.; resources, J.M.; data curation, N.C.; writing—original draft preparation, D.M.; writing—review and editing, M.A., M.J., S.P., J.N., B.C., A.C., N.C., R.B., J.E., T.O., D.S., J.J., J.M. and D.M.; supervision, N.C. and R.B.; project administration, N.C. and R.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to commercial in confidence.
Conflicts of Interest
M.A., M.J., S.P., J.N., B.C., A.C., N.C., R.B., J.J., J.M. and D.M. are (or were; L.T.) employees of Genetic Signatures, a company that commercializes enteric protozoan kits. J.E., T.O., and D.S. declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This research received no external funding.
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
References
- 1.Cox F.E. History of human parasitic diseases. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2004;18:171–188. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2004.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hajare S.T., Gobena R.K., Chauhan N.M., Erniso F. Prevalence of Intestinal Parasite Infections and Their Associated Factors among Food Handlers Working in Selected Catering Establishments from Bule Hora, Ethiopia. BioMed Res. Int. 2021;2021:6669742. doi: 10.1155/2021/6669742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Osman M., El Safadi D., Cian A., Benamrouz S., Nourrisson C., Poirier P., Pereira B., Razakandrainibe R., Pinon A., Lambert C., et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Intestinal Protozoan Infections with Cryptosporidium, Giardia, Blastocystis and Dientamoeba among Schoolchildren in Tripoli, Lebanon. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016;10:e0004496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Harhay M.O., Horton J., Olliaro P.L. Epidemiology and control of human gastrointestinal parasites in children. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2010;8:219–234. doi: 10.1586/eri.09.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kotloff K.L., Nataro J.P., Blackwelder W.C., Nasrin D., Farag T.H., Panchalingam S., Wu Y., Sow S.O., Sur D., Breiman R.F., et al. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): A prospective, case-control study. Lancet. 2013;382:209–222. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60844-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mbae C., Mulinge E., Guleid F., Wainaina J., Waruru A., Njiru Z.K., Kariuki S. Molecular Characterization of Giardia duodenalis in Children in Kenya. BMC Infect. Dis. 2016;16:135. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1436-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Maikai B.V., Umoh J.U., Lawal I.A., Kudi A.C., Ejembi C.L., Xiao L. Molecular characterizations of Cryptosporidium, Giardia, and Enterocytozoon in humans in Kaduna State, Nigeria. Exp. Parasitol. 2012;131:452–456. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2012.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Guillén N. Pathogenicity and virulence of Entamoeba histolytica, the agent of amoebiasis. Virulence. 2023;14:2158656. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2158656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lo Y.C., Ji D.D., Hung C.C. Prevalent and incident HIV diagnoses among Entamoeba histolytica-infected adult males: A changing epidemiology associated with sexual transmission--Taiwan, 2006–2013. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2014;8:e3222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stark D., Barratt J., Chan D., Ellis J.T. Dientamoeba fragilis, the Neglected Trichomonad of the Human Bowel. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016;29:553–580. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00076-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Vandenberg O., Peek R., Souayah H., Dediste A., Buset M., Scheen R., Retore P., Zissis G., van Gool T. Clinical and microbiological features of dientamoebiasis in patients suspected of suffering from a parasitic gastrointestinal illness: A comparison of Dientamoeba fragilis and Giardia lamblia infections. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2006;10:255–261. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2005.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Basak S., Rajurkar M.N., Mallick S.K. Detection of Blastocystis hominis: A controversial human pathogen. Parasitol. Res. 2013;113:261–265. doi: 10.1007/s00436-013-3652-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wawrzyniak I., Poirier P., Viscogliosi E., Dionigia M., Texier C., Delbac F., Alaoui H.E. Blastocystis, an unrecognized parasite: An overview of pathogenesis and diagnosis. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2013;1:167–178. doi: 10.1177/2049936113504754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stenzel D.J., Boreham P.F. Blastocystis hominis revisited. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1996;9:563–584. doi: 10.1128/CMR.9.4.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.WHO . Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality (3rd Edition, Incorporating First and Second Addenda) World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Taghipour A., Rayatdoost E., Bairami A., Bahadory S., Abdoli A. Are Blastocystis hominis and Cryptosporidium spp. playing a positive role in colorectal cancer risk? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Agents Cancer. 2022;17:32. doi: 10.1186/s13027-022-00447-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Almeria S., Cinar H.N., Dubey J.P. Cyclospora cayetanensis and Cyclosporiasis: An Update. Microorganisms. 2019;7:317. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7090317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li W., Xiao L. Ecological and public health significance of Enterocytozoon bieneusi. One Health. 2020;12:100209. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2020.100209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Didier E.S., Weiss L.M. Microsporidiosis: Current status. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2006;19:485–492. doi: 10.1097/01.qco.0000244055.46382.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li J., Wang Z., Karim M.R., Zhang L. Detection of human intestinal protozoan parasites in vegetables and fruits: A review. Parasites Vectors. 2020;13:380. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04255-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hanson K.L., Cartwright C.P. Use of an enzyme immunoassay does not eliminate the need to analyze multiple stool specimens for sensitive detection of Giardia lamblia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001;39:474–477. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.2.474-477.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jahan N., Khatoon R., Ahmad S. A Comparison of Microscopy and Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Diagnosis of Giardia lamblia in Human Faecal Specimens. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014;8:DC04-6. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/9484.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Christy N.C.V., Hencke J.D., Cadiz A.E.-D., Nazib F., von Thien H., Yagita K., Ligaba S., Haque R., Nozaki T., Tannich E., et al. Multisite performance evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Giardia, Cryptosporidium, and Entamoeba histolytica antigens in human stool. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012;50:1762–1763. doi: 10.1128/JCM.06483-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ryan U., Paparini A., Oskam C. New Technologies for Detection of Enteric Parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2017;33:532–546. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2017.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Friesen J., Fuhrmann J., Kietzmann H., Tannich E., Müller M., Ignatius R. Evaluation of the Roche LightMix Gastro parasites multiplex PCR assay detecting Giardia duodenalis, Entamoeba histolytica, cryptosporidia, Dientamoeba fragilis, and Blastocystis hominis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018;24:1333–1337. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Laude A., Valot S., Desoubeaux G., Argy N., Nourrisson C., Pomares C., Machouart M., Le Govic Y., Dalle F., Botterel F., et al. Is real-time PCR-based diagnosis similar in performance to routine parasitological examination for the identification of Giardia intestinalis, Cryptosporidium parvum/Cryptosporidium hominis and Entamoeba histolytica from stool samples? Evaluation of a new commercial multiplex PCR assay and literature review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016;22:190.e1–190.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Basmaciyan L., François A., Vincent A., Valot S., Bonnin A., Costa D., Razakandrainibe R., Morio F., Favennec L., Dalle F. Commercial Simplex and Multiplex PCR Assays for the Detection of Intestinal Parasites Giardia intestinalis, Entamoeba spp., and Cryptosporidium spp.: Comparative Evaluation of Seven Commercial PCR Kits with Routine In-House Simplex PCR Assays. Microorganisms. 2021;9:2325. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9112325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hayatsu H., Wataya Y., Kai K., Iida S. Reaction of sodium bisulfite with uracil, cytosine, and their derivatives. Biochemistry. 1970;9:2858–2865. doi: 10.1021/bi00816a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shapiro R., Weisgras J.M. Bisulfite-catalyzed transamination of cytosine and cytidine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1970;40:839–843. doi: 10.1016/0006-291X(70)90979-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Baleriola C., Millar D., Melki J., Coulston N., Altman P., Rismanto N., Rawlinson W. Comparison of a novel HPV test with the Hybrid Capture II (hcII) and a reference PCR method shows high specificity and positive predictive value for 13 high-risk human papillomavirus infections. J. Clin. Virol. 2008;42:22–26. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2007.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Siah S.P., Merif J., Kaur K., Nair J., Huntington P.G., Karagiannis T., Stark D., Rawlinson W., Olma T., Thomas L., et al. Improved detection of gastrointestinal pathogens using generalised sample processing and amplification panels. Pathology. 2014;46:53–59. doi: 10.1097/PAT.0000000000000022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garae C., Kalo K., Pakoa G.J., Baker R., Isaacs P., Millar D.S. Validation of the easyscreen flavivirus dengue alphavirus detection kit based on 3base amplification technology and its application to the 2016/17 Vanuatu dengue outbreak. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0227550. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rochelle P.A., De Leon R., Stewart M.H., Wolfe R.L. Comparison of primers and optimization of PCR conditions for detection of Cryptosporidium parvum and Giardia lamblia in water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997;63:106–114. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.1.106-114.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dirani G., Zannoli S., Paesini E., Farabegoli P., Dalmo B., Vocale C., Liguori G., Varani S., Sambri V. Easyscreen™ Enteric Protozoa Assay For the Detection of Intestinal Parasites: A Retrospective Bi-Center Study. J. Parasitol. 2019;105:58–63. doi: 10.1645/18-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Stark D., Roberts T., Ellis J.T., Marriott D., Harkness J. Evaluation of the EasyScreen™ enteric parasite detection kit for the detection of Blastocystis spp., Cryptosporidium spp., Dientamoeba fragilis, Entamoeba complex, and Giardia intestinalis from clinical stool samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014;78:149–152. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2013.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to commercial in confidence.