Abstract
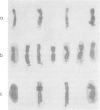
A clinical and cytogenetic study has been made of subjects from families who have possible X linked mental retardation. The families were distinguished as those with a clinical diagnosis of Renpenning syndrome and those with other behavioural or physical abnormalities obviating such a diagnosis. All subjects with REnpenning syndrome carried a fragile Xq27-28 chromosome in more than 4% of their blood lymphocytes. In addition, two other families who did not have Renpenning syndrome but had similar clinical features also carried the fragile site Xq27-28. A female age effect was observed and one possible carrier of Renpenning syndrome exhibited the fragile X in 10% of her lymphocytes but was also mentally retarded. Subjects within the same family did not always exhibit the fragile site on a comparable proportion of their cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Harvey J., Judge C., Wiener S. Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):46–50. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath C. W., Jr Cytogenetic observations in vitamin B12 and folate deficiency. Blood. 1966 Jun;27(6):800–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Peebles P. N., Stoddard G. R., Mims M. G. Familial X-linked mental retardation, verbal disability, and marker X chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):214–222. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Mayer M., Rudak E., Gerrard J., Ives E. J., Shokeir M. H., Hall J., Jennings M., Hoehn H. More on marker X chromosomes, mental retardation and macro-orchidism. N Engl J Med. 1979 Mar 29;300(13):737–738. doi: 10.1056/nejm197903293001320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrke R. G. X-linked mental retardation and verbal disability. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1974;10(1):1–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A. A marker X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 May;21(3):231–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin J. F., Kriegsmann E. Developmental dyspraxia in a family with X-linked mental retardation (Renpenning syndrome). Dev Med Child Neurol. 1980 Feb;22(1):84–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1980.tb04308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prader A. Testicular size: assessment and clinical importance. Triangle. 1966;7(6):240–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENPENNING H., GERRARD J. W., ZALESKI W. A., TABATA T. Familial sex-linked mental retardation. Can Med Assoc J. 1962 Nov 3;87:954–956. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Ashforth P. L. X-linked mental retardation with macro-orchidism and the fragile site at Xq 27 or 28. Hum Genet. 1979 Apr 17;48(1):117–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00273283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes I. Factors affecting expression in lymphocyte culture. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes II. Distribution, phenotypic effects, and cytogenetics. Am J Hum Genet. 1979 Mar;31(2):136–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes. III. Detection of fra(X)(q27) in males with X-linked mental retardation and in their female relatives. Hum Genet. 1979;53(1):23–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00289445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Eastman C., Casey J., McLeay A., Procopis P., Turner B. X-linked mental retardation associated with macro-orchidism. J Med Genet. 1975 Dec;12(4):367–371. doi: 10.1136/jmg.12.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Till R., Daniel A. Marker X chromosomes, mental retardation and macro-orchidism. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1472–1472. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Turner B., Collins E. X-linked mental retardation without physical abnormality: Renpenning's syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1971 Feb;13(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1971.tb03033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachmann M., Prader A., Kind H. P., Häfliger H., Budliger H. Testicular volume during adolescence. Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1974 Apr;29(1):61–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]