Abstract
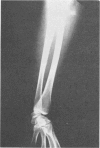
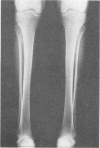
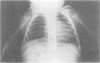
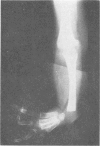
A syndrome characterised by asymmetrical radial dysplasia, dysmorphic facies, conductive deafness, and external ear deformity is described in a mother and her daughter. This combination of anomalies has previously been reported in members of a single family. The disorder appears to be clinically and genetically distinct from others associated with radial dysplasia, such as Nager's acrofacial dysostosis and the lachrimoauriculoradiodental syndrome. Inheritance is autosomal dominant, with marked variation in expression of the mutant gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carroll R. E., Louis D. S. Anomalies associated with radial dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1974 Mar;84(3):409–411. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80727-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORLIN R. J., JUE K. L., JACOBSEN U., GOLDSCHMIDT E. OCULOAURICULOVERTEBRAL DYSPLASIA. J Pediatr. 1963 Nov;63:991–999. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollister D. W., Klein S. H., De Jager H. J., Lachman R. S., Rimoin D. L. The lacrimo-auriculo-dento-digital syndrome. J Pediatr. 1973 Sep;83(3):438–444. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juberg R. C., Hayward J. R. A new familial syndrome of oral, cranial, and digital anomalies. J Pediatr. 1969 May;74(5):755–762. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause U. The syndrome of goldenhar affecting two siblings. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1970;48(3):494–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1970.tb03749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy W. J. Mesoectodermal dysplasia. A new combination of anomalies. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967 May;63(5):978–982. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(67)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelcorn M. S., Merin S., Cardarelli J. Goldenhar's syndrome and phocomelia. Case report and etiologic considerations. Am J Ophthalmol. 1971 Sep;72(3):618–621. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(71)90862-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nager G. T. Congenital aural atresia: anatomy and surgical management. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1971 Mar;07(4):33–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proto F., Scullica L. Contributo allo studio della ereditarietà dei dermoidi epibulbari. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma) 1966 Oct;15(4):351–363. doi: 10.1017/s1120962300014943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoll C., Levy J. M., Francfort J. J., Roos R., Rohmer A. L'association phocomelie-ectrodactylie Malformations des oreilles avec surdite, Arythmie sinusale, Constitue-t-ele un nouveau syndrome hereditaire. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1974 Aug-Sep;31(7):669–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. A. Apparent autosomal recessive inheritance of the Treacher Collins syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1974;10(8):135–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]