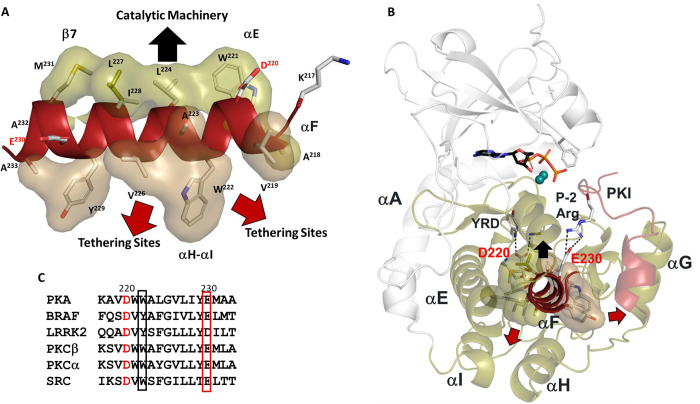
Figure 1. Hydrophobic αF-helix serves as a central scaffold.
(A). αF-helix is very hydrophobic and creates an interface with multiple motifs including the Catalytic machinery (colored in tan) and tethering sites (in sand) of PKA C-subunit. Two key charged residues, D220 and E230, sit at the two ends of αF-helix. (B). αF-helix is a central scaffold for assembly of the entire molecule. D220 forms two H-bonds to Y164 and R165 of YRD motif, and E230 salt-bridges to P-2 Arg of PKI. (C). Sequence alignment of αF-helix segment of PKA with other kinases. All share a very hydrophobic helix, the highly conserved residues, D220 are colored in red and E230 in red box.