Case Report
A 35-year-old right-handed man with late-onset Rasmussen encephalitis1 involving the right hemisphere reported focal aware seizures with motor onset, rare focal-to-bilateral tonic-clonic seizures, and epilepsia partialis continua to the left upper limb (eAppendix 1 and eFigures 1–3, links.lww.com/WNL/C831). Over time, a new seizure type mimicking dystonic posturing of the left arm became recurrent (Video 1), consistently triggered by voluntary movements of the limb.
Video-EEG With Polygraphic Recording. Left deltoid (EMG1), biceps (EMG2), triceps (EMG3), flexor (EMG4), and extensor carpi (EMG5) muscles. Reflex seizures (triggered by voluntary arm lifting) with dystonic features characterized by ulnar deviation and flexion of the wrist, flexion and internal rotation of the forearm. Red arrows indicate fast activity over the right central region.Download Supplementary Video 1 (37.6MB, mov) via http://dx.doi.org/10.1212/207412_Video_1
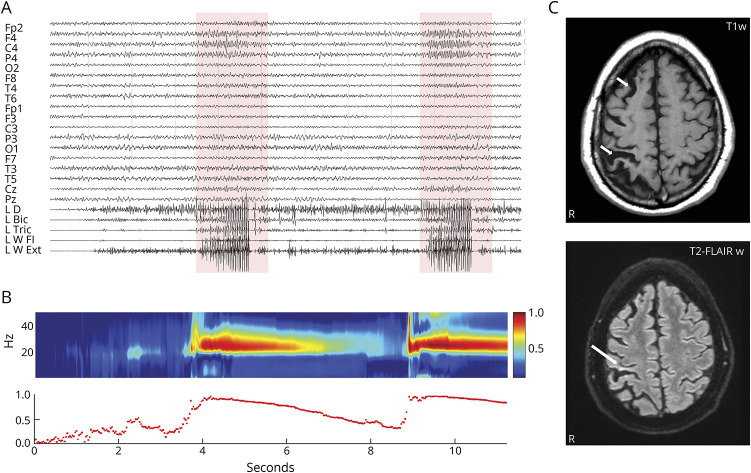
The EEG-polygraphic recording showed fast activity in the right central region associated with the clinical seizure. Time-varying corticomuscular coherence analysis, a method commonly applied to evaluate the functional connection between the cortex and muscles during muscle contraction, helped us identify the pattern of the paroxysmal dystonic episodes as reflex focal aware seizures (Figure 1), probably evoked by abnormal afferents to the right sensorimotor cortex during voluntary muscle activation.
Figure 1. EEG-Polygraphic Recording, CMC Analysis, and Brain MRI.
(A) Two reflex seizures over the right central leads associated with muscular bursts (boxes). (B) Sudden increase of C4/left wrist flexor muscles CMC2 during voluntary movement to seizure shift. (C) Brain MRI shows (top) right hemisphere atrophy and (bottom) signal hyperintensity in the right postcentral gyrus (arrows). CMC = corticomuscular coherence.
As expected in this immune-mediated brain disorder, reflex seizures poorly responded to various antiseizure medications while periodic IV immunoglobulin administration resulted in a transient beneficial effect.
Footnotes
Teaching slides links.lww.com/WNL/C830
Author Contributions
A. Stabile: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; study concept or design; analysis or interpretation of data. S. Franceschetti: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; study concept or design; analysis or interpretation of data. F. Deleo: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; study concept or design; analysis or interpretation of data. R. Di Giacomo: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; analysis or interpretation of data. G. Didato: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; analysis or interpretation of data. C. Pastori: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; analysis or interpretation of data. F. Panzica: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; analysis or interpretation of data. M. De Curtis: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; study concept or design; analysis or interpretation of data. F. Villani: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; study concept or design; analysis or interpretation of data. L. Canafoglia: drafting/revision of the manuscript for content, including medical writing for content; major role in the acquisition of data; study concept or design; analysis or interpretation of data.
Study Funding
This work was supported by the Italian Ministry of Health (RRC).
Disclosure
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to Neurology.org/N for full disclosures.
References
- 1.Doniselli FM, Deleo F, Criscuolo S, et al. MRI in late-onset Rasmussen encephalitis: a long-term follow-up study. Diagnostics. 2022;12(2):502. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12020502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Panzica F, Canafoglia L, Franceschetti S. EEG-EMG information flow in movement-activated myoclonus in patients with Unverricht-Lundborg disease. Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(9):1803-1808. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Video-EEG With Polygraphic Recording. Left deltoid (EMG1), biceps (EMG2), triceps (EMG3), flexor (EMG4), and extensor carpi (EMG5) muscles. Reflex seizures (triggered by voluntary arm lifting) with dystonic features characterized by ulnar deviation and flexion of the wrist, flexion and internal rotation of the forearm. Red arrows indicate fast activity over the right central region.Download Supplementary Video 1 (37.6MB, mov) via http://dx.doi.org/10.1212/207412_Video_1