Abstract
The AAV9 gene therapy vector presented in this study is safe in mice and non-human primates and highly efficacious without causing overexpression toxicity, a major challenge for clinical translation of Rett syndrome gene therapy vectors to date. Our team designed a new truncated methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) promoter allowing widespread expression of MECP2 in mice and non-human primates after a single injection into the cerebrospinal fluid without causing overexpression symptoms up to 18 months after injection. Additionally, this new vector is highly efficacious at lower doses compared with previous constructs as demonstrated in extensive efficacy studies performed by two independent laboratories in two different Rett syndrome mouse models carrying either a knockout or one of the most frequent human mutations of Mecp2. Overall, data from this multicenter study highlight the efficacy and safety of this gene therapy construct, making it a promising candidate for first-in-human studies to treat Rett syndrome.
Keywords: Rett syndrome; gene therapy; adeno-associated virus serotype 9, scAAV9; methyl-CpG binding protein 2, MECP2; P546
Graphical abstract
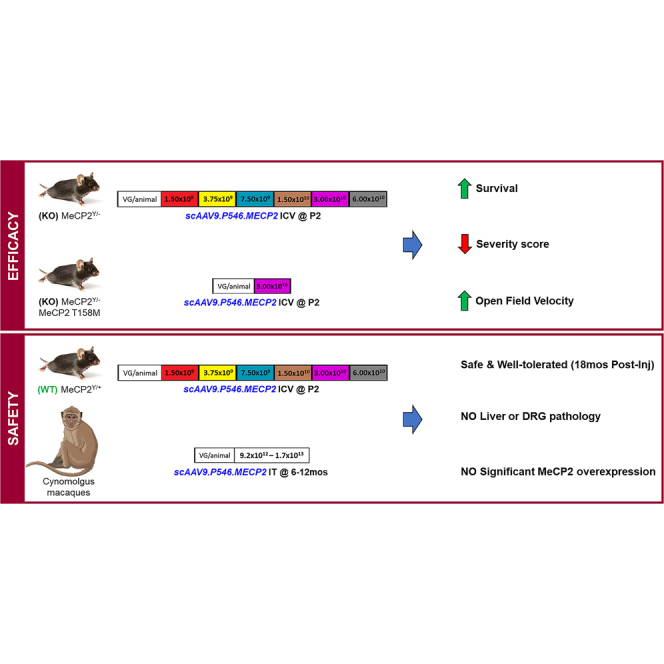

Meyer et al. performed multicentered efficacy and safety studies for a novel AAV9-based gene therapy for RTT. CSF delivery of scAAV9.P546.MeCP2 in two independent Rett mouse models significantly improved survival, severity score and open field performance. scAAV9.P546.MeCP2 treatment was safe and well-tolerated in mice and NHPs.
Introduction
Rett syndrome (RTT) is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting approximately 1 in 10,000 girls.1 The disease is caused by deficiency of the X-linked transcription factor methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2), a key regulator of gene expression in the CNS.2,3,4 X chromosome inactivation (XCI) plays an important role in RTT. XCI is a developmentally regulated process in females, wherein one X chromosome per cell is randomly inactivated per cell causing a mosaic expression of X-linked genes in females. Since males are hemizygous for X-linked genes, the MECP2 mutations leading to full loss of MECP2 function in males would typically result in approximately 50% expression in females. Thus, many MECP2 mutations are neonatally lethal in males or lead to a far more severe presentation of RTT syndrome.5,6
Approximately 6–18 months after birth, RTT patients experience loss of previously established developmental milestones, including motor function, speech, and purposeful hand movement, which is often replaced with stereotypic hand gestures.7 RTT does not seem to cause neurodegeneration.8 Only minor neuronal loss was reported in the brain and spinal cord from animal models and patient autopsy samples.9,10 Thus, it is generally thought that RTT neurons survive and, therefore, would be available for therapeutic targeting.11
An initial proof of concept for the therapeutic effect of restoring MECP2 function was shown in an animal model of RTT in 2007 by the Bird laboratory.11 In this experiment, endogenous MECP2 was re-introduced at physiological levels using a Cre-lox system in a post-symptomatic mouse model. The study showed that several RTT-like phenotypes, including behavioral abnormalities and reduced survival, were reversed when MECP2 expression was activated.11 Since the initial proof of concept study, several groups including ours, began developing adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene therapy approaches to express healthy MECP2 in the CNS12,13,14,15,16 AAV-based gene therapy constructs have a favorable clinical safety profile and lead to long-lasting transgene expression in non-dividing cells, including neurons.17 Several clinical trials have recently reported clinical efficacy of these vectors in other disorders.18,19,20,21,22
Proper regulation of MECP2 expression is pivotal because overexpression can be detrimental. Duplication of the gene causes MECP2 duplication syndrome (MDS) with variable psychiatric and autism spectrum disorder symptoms in females.23 Moreover, a handful of cases with MECP2 triplication syndrome have also been reported with the indication that MECP2 triplication is similar or more severe than MDS.24,25 Thus, it is crucial for any gene therapy-based approach introducing MECP2 to express it at physiological levels. With packaging restrictions for self-complementary AAV (scAAV), the endogenous Mecp2 promoter (approximately 1,080 bp)26,27 does not fit into the vector alongside the MECP2 cDNA sequence and hence cannot be used to achieve physiological levels of MECP2 expression. Previously, we showed that systemic delivery of an scAAV9 vector expressing MECP2 under the P738 Mecp2 promoter fragment results in physiological levels of MECP2 in brain and improves the disease phenotypes, including survival and phenotypic score in an RTT animal model.10 However, the size of the previous construct was still outside the optimal packaging range of scAAV. Here, we have further optimized the construct with use of a novel, even shorter, truncated Mecp2 promoter (P546) expressing human MECP2 coding sequence and a shorter synthetic poly A terminator to decrease the risks of partial or excessive empty particle production during AAV manufacturing.
Here we show that neonatal CSF delivery of the clinically optimized vector, scAAV9.P546.MECP2, is highly efficient in driving MECP2 expression in CNS and ameliorating RTT disease phenotype in two mouse RTT models at much lower vector doses than any previous studies reported.28,29,30 Additional rigor was added to the efficacy study by testing the vector in two independent laboratories in the United States and the UK. Moreover, long-term safety studies indicate a favorable safety profile in both wild-type (WT) mice and healthy non-human primates (NHPs) (cynomolgus macaques) for up to 18 months after injection. In conclusion, this vector seems to be both effective at ameliorating disease phenotypes in RTT mouse models and safe in both rodents and NHPs. Therefore, scAAV9.P546.MECP2 is a strong candidate for clinical translation as a gene therapy treatment for RTT patients.
Results
Intracerebroventricular delivery of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 prolongs survival and ameliorates behavioral abnormalities in KO mice
Early analysis of the mouse Mecp2 promoter revealed the presence of the core promoter at −309/–179, an enhancer region from −1071/–847, silencer regions from −681/–533 and −307/–309, and a positive regulatory element at −64/–46.26,27 Previously, we used P738, an MECP2 promoter fragment spanning −677/+56 of the 5′ untranslated region, while the Cobb and Gray laboratories generated a series of different MECP2 promoter truncations used in their collaboration and by the Roux and Bird laboratories.12,13,14,15,16,26,31,32 To further optimize our previous vector for clinical translation, we developed the P546 promoter, a further truncation from the P738 promoter omitting the silencer element at −681/–533 for potentially better expression. At the same time, we replaced the mouse Mecp2 coding sequence with human MECP2 sequence and added a short synthetic poly A terminator sequence, thus shortening the total vector genome size for better packaging in scAAV9 vector (Figure S1). Also, based on our previous studies in multiple mouse models of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, we chose to use an intra-CSF delivery route via intracerebroventricular (ICV) administration of the AAV9 vector in neonatal mice targeting majority of neurons as well as astrocytes in CNS as compared with adult systemic delivery.33,34,35,36
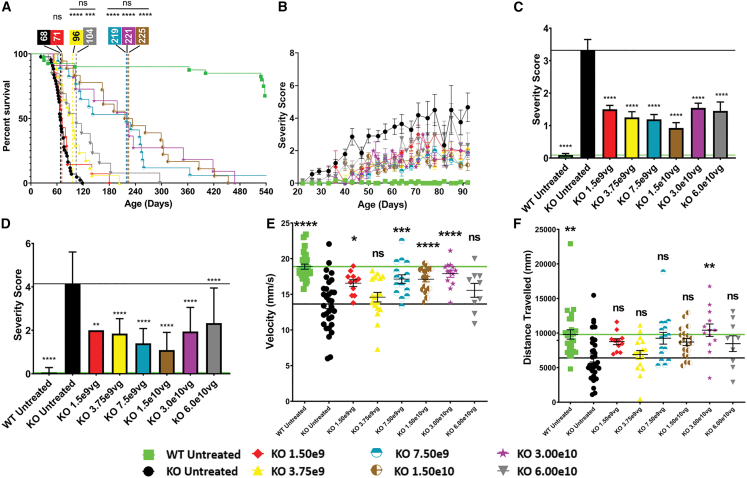
In studies performed by the Nationwide Children’s Hospital (NCH) team, Mecp2-/Y (knockout [KO]) male mice, the mouse model most frequently used in RTT research (female mice display only very mild disease phenotypes and are thus less suited) received a single ICV injection of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 into the CSF on postnatal day 2 (P2). Mice received one of the six doses of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 or no treatment (negative control). Dose escalation was performed starting at 1.50 × 109 viral genomes (vg)/animal increasing by 2-fold steps: 3.75 × 109 vg/animal, 7.50 × 109 vg/animal, 1.50 × 1010 vg/animal, 3.00 × 1010 vg/animal, and 6.00 × 1010 vg/animal. Each KO dosing group contained 11–18 mice. Untreated KO controls (n = 43) are represented at higher numbers as they were tracked over the multi-year course of the study, during testing of all individual vector dosing groups. This ensured that baseline phenotypes did not change over the period of the study. Note that the vector doses in the figures are based on the original silver staining titration performed by the virus manufacturer SAB Tech Inc, (Philadelphia, PA). Post-study initiation, vector batches were re-analyzed using digital droplet PCR (ddPCR). Both titers are summarized in Table S1. Importantly, all mouse studies used the same viral vector, NHPs received a different vector batch.
At NCH, animals were followed until humane endpoint or final endpoint of the study (540 days), when remaining animals were sacrificed. Untreated KO animals had a median survival of 68 days. Single ICV injection of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 in KO mice on P2 improved survival at every dose tested and only mice with the lowest dose (1.50 × 109 vg/animal) were not significantly different from untreated mice (Mantel Cox statistical analysis). Interestingly, the second lowest dose, 3.75 × 109 vg/animal, and the highest dose, 6.00 × 1010 vg/animal, led to a less pronounced improvement in survival than doses in the midrange. The optimal dose was 1.50 × 1010 vg/animal based on the strongest improvement in survival from 68 days (untreated) to 225 days (3.3-fold improvement). No statistically significant difference was observed between 1.50 × 1010 vg/animal and the next lower and higher doses (7.50 × 109 vg and 3.00 × 1010 vg; p = 0.8404), indicating a wide range of doses have approximately equivalent therapeutic potential (Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
ICV delivery of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 prolongs survival and ameliorates behavioral abnormalities in KO mice
(A) Survival was significantly improved in KO mice treated with most doses of vector vs. untreated KO mice (log rank/Mantel Cox test). p values vs. untreated KO: untreated WT, p < 0.0001; 1.50 × 109, p = 0.2511; 3.75 × 109, p < 0.0001; 7.50 × 109, p < 0.0001; 0, 1.50 × 1010, p < 0.0001; 3.00 × 1010, p < 0.0001; 6.00 × 1010 vg, p = 0.0005. There is no difference between survival curves for 3.75 × 109 and 6.00 × 1010 vg, p = 0.2650. There is no difference in survival curves for KO 7.5 × 109 to KO 3.00 × 1010 = ns, p = 0.8404. (B) Severity score is ameliorated in treated KO vs. untreated KO at all doses. (C) At 60 days, all doses significantly improved severity score in treated KO vs. untreated KO animals (p < 0.0001). (D) At 90 days, all doses significantly improved severity score in treated KO vs. untreated KO animals, KO 1.50 × 109, p = 0.0062; all other doses, p < 0.0001. (E) Vector treatment ameliorated open field velocity in KO mice treated with most doses. p values vs. untreated KO: untreated WT, p < 0.0001; 1.50 × 109, p = 0.0287; 3.75 × 109, p = 0.9832; 7.50 × 109, p = 0.0002 0; 1.50 × 1010, p < 0.0001; 3.00 × 1010, p < 0.0001; 6.00 × 1010 vg, p = 0.6557. (F) Vector treatment only corrected deficits in open field distance for KO animals treated with 3.00 × 1010 vg. p values vs. untreated KO: untreated WT, p = 0.0037; 1.50 × 109, p = 0.6534; 3.75 × 109, p < 0.9999; 7.50 × 109, p = 0.1464; 1.50 × 1010, p = 0.3728; 3.00 × 1010, p = 0.0081; 6.00 × 1010, vg p = 0.8895. Value representations are mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined via ANOVA with Tukey’s honest significance post hoc test (Tukey’s test). Significance is in relation to untreated KO animals. The 60 and 90-day average severity scores were taken ±2–4 days to account variability in biweekly scoring intervals. Open field assay was performed at 49–63 days. Vertical dashed lines indicate median survival for each dose: WT untreated WT n = 40; KO untreated, n = 43; KO-1.50 × 109, n = 14; KO- 3.75 × 109, n = 17; KO-7.50 × 109 n = 17; KO- 1.50 × 1010, n = 18; KO- 3.00 × 1010, n = 11; KO- 6.00 × 1010, n = 13. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.000. ns, not significant.
scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated and untreated control mice were scored weekly for RTT-like phenotypes (Figure 1B) using an established aggregate severity scoring method.11 Each phenotype is scored as 0 (unobserved/WT), 1 (symptom present), or 2 (symptom severe) for a maximum score of 12. Brief details of the scoring system are explained in the materials and methods section. Untreated KO males progressed from 0 to a mean peak score of approximately 5 by 92 days, at which point most untreated animals reached humane endpoint. In contrast, scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated animals stayed within the score range of 0–3 throughout the study. Although we analyzed the cumulative aggregate severity score, it was evident that scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated mice at all doses showed the most improvement in mobility, gait and breathing phenotypes, followed by clasping, tremors, and general body condition. For statistical analysis, we compared the severity scores for untreated KO animals vs. treated KO animals at two different timepoints—60 days and 90 days. Severity score for treated KO animals vs. untreated KO animals were significantly different at respective timepoints. This indicates that scAAV9.P546.MECP2 is able to ameliorate RTT-like phenotypes at a wide range of doses (Figures 1C and 1D). However, the severity scores treated KO at all doses were still different from the untreated WT animals, indicating that the scAAV9.P546.MECP2 treatment did not fully restore the normal phenotype.
We also performed open field testing of treated and untreated KO animals at 49–63 days of age to examine velocity and distance traveled.12 Overall, objective assessment in the open field analysis revealed relatively small differences between untreated KO and untreated WT animals. The lowest dose, 1.50 × 109 vg, and midrange doses, 7.50 × 109 vg – 3.00 × 1010 vg, were able to significantly improve velocity in treated KO mice as compared with untreated KO mice (Figure 1E) while only 3.00 × 1010 vg-treated KO animals showed improved distance traveled as compared with untreated KO mice (Figure 1F).
Weights were recorded for untreated WT, untreated KO, and vector-treated KO mice (Figure S2) until 92 days, when the majority of untreated KO have reached the endpoint. The overall difference in mean weight of untreated WT and KO animals was highest at early time points (6–8 weeks) when KO mice trail behind by 10 g. Later at 13 weeks, the difference between untreated WT and KO mice decreased to only 3.5 g. Importantly, treated KO mice showed a highly significant improvement in weight at these critical early time points of 6–8 weeks for most treatment groups (p < 0.0001) as compared with untreated KO mice.
ICV delivery of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 does not affect survival or behavioral phenotypes in WT mice
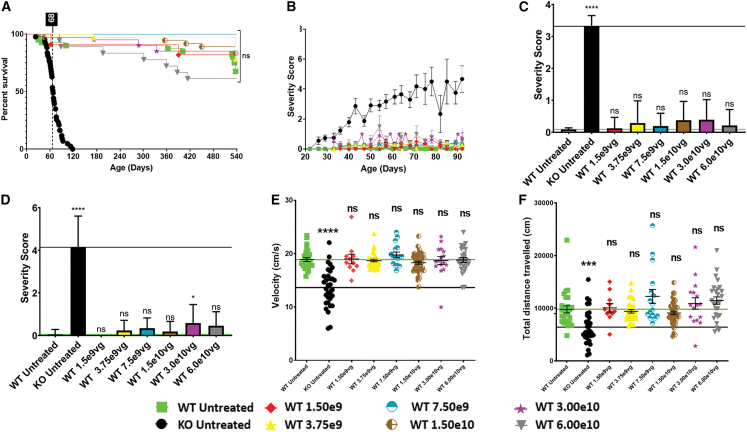
To assess safety, Mecp2+/Y (WT) mice received a single ICV injection of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 using the same protocol as for the KO mice. Each treated dosing group contained 11–36 animals. Untreated WT controls (n = 40) are represented at higher numbers since they were tracked over the entire multi-year course of the study during testing of individual dosing groups.
Mantel Cox analysis revealed no significant difference in survival between mice treated with any dose of vector and untreated WT animals through the study’s end at 18 months (Figure 2A).
Figure 2.
ICV Delivery of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 does not affect survival or behavioral phenotypes in WT mice
(A) Survival in WT mice treated with any vector dose is not significantly different from survival in untreated WT mice (p = 0.1525) (log-rank/Mantel Cox test). (B) Severity score of untreated WT- and vector-treated WT mice shows that treatment overwhelmingly does not affect score. (C) At 60 days, vector-treated WT mice do not have statistically different severity scores vs. untreated WT. p values: untreated KO, p < 0.0001; WT 1.50 × 109, p > 0.9999; WT 3.75 × 109, p = 0.9992; WT 7.50 × 109, p > 0.9999; WT 1.50 × 1010, p = 0.9512; WT 3.00 × 1010, p = 0.9876; WT 6.00 × 1010, p > 0.9999. (D) At 90 days, vector-treated WT mice do not have statistically different severity scores vs. WT, except 3.00 × 1010 vg. p values: untreated KO, p < 0.0001; 1.50 × 109, p > 0.9999; 3.75 × 109, p = 0.9911; 7.50 × 109, p > 0.8146; 1.50 × 1010, p = 0.9983; 3.00 × 1010, p = 0.0442; 6.00 × 1010, p > 0.4566. (E and F) Open field assay for distance and velocity was performed at 49–63 days. (E) Vector-treated WT mice do not have a significantly different open field velocity compared with untreated WT mice. p values vs. untreated WT: untreated KO, p < 0.0001; 1.50 × 109, p > 0.9999; 3.75 × 109, p > 0.9999; 7.50 × 109, p = 0.9959; 1.50 × 1010, p = 0.9991; 3.00 × 1010, p > 9999; 6.00 × 1010, p > 0.9999. (F) Vector-treated WT mice do not have a significantly different open field distance compared with untreated WT mice. p values vs. untreated WT: untreated KO, p = 0.0037; 1.5 × 109, p > 0.9999; 3.75 × 109, p > 0.9999; 7.5 × 109, p = 0.4199; 1.5 × 1010, p = 0.9998; 3.0 × 1010, p = 9976; 6.0 × 1010, p = 0.7980. 60 and 90-day average severity scores were taken ±2–4 days to account for slight time point variability in biweekly scoring intervals. WT untreated, n = 40; KO untreated, n = 43; WT- 1.50 × 109, n = 11; WT- 3.75 × 109, n = 32; WT-7.50 × 109, n = 16; WT- 1.50 × 1010, n = 36; WT- 3.00 × 1010, n = 20; WT- 6.00 × 1010, = 18. Statistical significance was determined via ANOVA with Tukey’s test. Significance is in relation to untreated WT mice. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.000. ns, not significant.
Mice were scored weekly for RTT-like phenotypes using the Bird aggregate severity scoring system.11 WT animals treated with all doses of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 maintained a WT behavioral profile. At 60 days, there were no differences between treated and untreated WT animals regardless of dose (Figure 2C). At 90 days, only WT mice treated with the 3.0 × 1010 vg dose showed a slightly different severity score. Since the higher dose of 6.0 × 1010 vg did not show any difference, this observation likely indicates random fluctuation. As the current scoring system is designed to score a number of symptoms arising from Mecp2 deficiency but not caused by Mecp2 duplication, it is not possible to determine the direct effect of MECP2 overexpression in WT mice.
We also performed open field testing at 49–63 days to examine velocity and distance covered.12 We observed a significant deficit in untreated KO mice compared with untreated WT animals. We did not observe any significant alterations in velocity (Figure 2E), or distance traveled (Figure 2F) in WT animals treated with any vector doses. In summary, treatment of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 was well tolerated in WT mice over a wide range of doses.
ICV delivery of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 in KO and WT mice does not cause significant overexpression of MECP2 protein in the brain
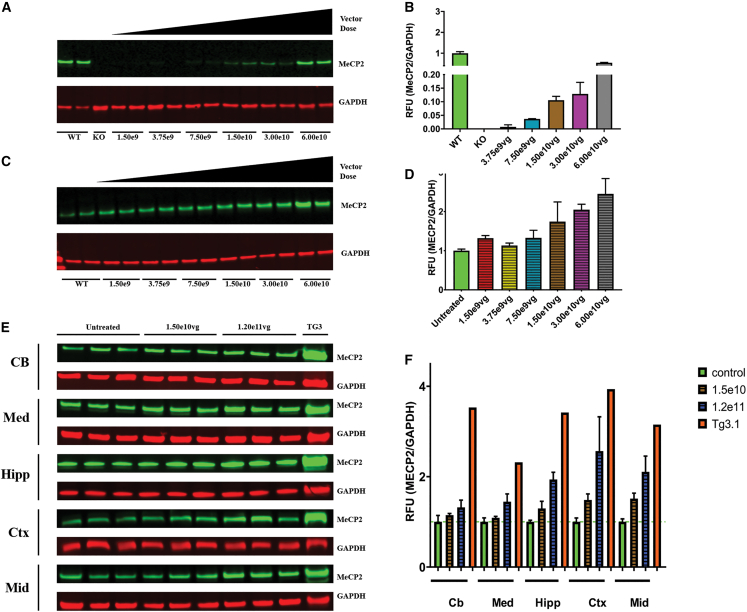
To assess MECP2 protein levels in the brain of treated animals, we homogenized brain hemispheres from KO mice and WT mice approximately 28 days after injection and performed western blot. Expression was normalized to MeCP2 levels in untreated WT brains. The two lowest doses (1.50 × 109 and 3.75 × 109 vg/animal) were below the detection threshold using this method. At our midrange doses, 7.50 × 109, 1.50 × 1010, and 3.00 × 1010 vg/animal, MECP2 protein expression ranged from 4%–13% of that of WT MECP2 protein levels. At 6.00 × 1010 vg/animal, expression of human MECP2 reached 54% of WT mouse Mecp2 levels (Figures 3A and 3B).
Figure 3.
ICV scAAV9.P546.MECP2 treatment of RTT mice and WT mice does not cause strong overexpression of MECP2 protein in the brain
(A) Western blot shows MECP2 protein expression in brain of untreated WT, untreated KO, and treated KO mice with ICV vector doses from 1.50 × 109 to 6.0 × 1010 vg. (B) No dose results in MeCP2 expression in excess of endogenous WT levels. (C) MECP2 expression in of brain of untreated WT and vector-treated WT mice with ICV vector doses from 1.50 × 109 to 6.0 × 1010 vg. (D) MECP2 expression exceeds 2-fold of endogenous levels at only the two highest doses. (E) Western blot for MeCP2 expression in untreated WT vs. WT treated with extended vector dosing and untreated TG3 in discrete brain regions. (F) All vector doses express MECP2 below corresponding regional levels in the Tg3 mouse. Blotting was performed on left brain hemispheres or discrete brain regions from the right hemisphere at 21 days after injection. For blots A/C, untreated WT n = 2, untreated KO n = 1, vector-treated KO n = 2 per dose, and vector-treated WT n = 2 per dose. For blot E, untreated WT n = 3, vector-treated WT n = 3 per dose, TG3 n = 1. Cb, cerebellum; Ctx, cerebral cortex; Hipp, hippocampus; Med, medulla oblongata; Mid, midbrain. Tg3 indicates samples taken from a severe mouse model of MDS.
We also evaluated expression of MECP2 in brains of treated WT mice. Values in scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated WT mice ranged from 1.13- to 2.45-fold of normal Mecp2 protein levels. Importantly, only the two highest doses exceeded a 2-fold increase in expression of total MECP2 protein (Figures 3C and 3D).
To test the upper limit of dosing range of our vector, we injected three additional WT mice with 1.20 × 1011 vg/animal (2-fold higher than the highest dose in our study). MECP2 protein levels of injected animals were compared with WT mice injected with our optimal dose (1.50 × 1010 vg/animal) and TG3 mice, modeling MDS.37 Furthermore, to determine whether region specific hot spots were masked by total hemisphere homogenization, we dissected brains into cerebral cortex, medulla oblongata, cerebellum, hippocampus, and midbrain for analysis. Treatment with 1.50 × 1010 vg/animal led to MECP2 protein levels between 1- and 1.5-fold of those measured in WT brain regions for all areas (Figures 3E and 3F). Although we did observe certain regional hot spots like the cortex and midbrain regions of 1.50 × 1010 vg-treated WT animals with a higher fold increase (approximately 1.5-fold) compared with other regions, it was clear that the region-specific hot spots were not masked by the total hemisphere homogenization; instead, it took into account the reginal differences. The highest dose (1.20 × 1011 vg/animal) yielded MECP2 expression ranging from 1.3- to 2.6-fold of WT levels. Importantly, MECP2 levels for all scAAV9.P546.MECP2 doses including 1.20 × 1011 vg remained below levels found in the corresponding brain regions of TG3 mice, thus suggesting the scAAV9.P546.MECP2 treatment did not surpass the MECP2 expression threshold indicative of MDS in mice.
Independent evaluation of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 in two RTT mouse models at the University of Edinburgh, UK, confirms the efficacy of the construct
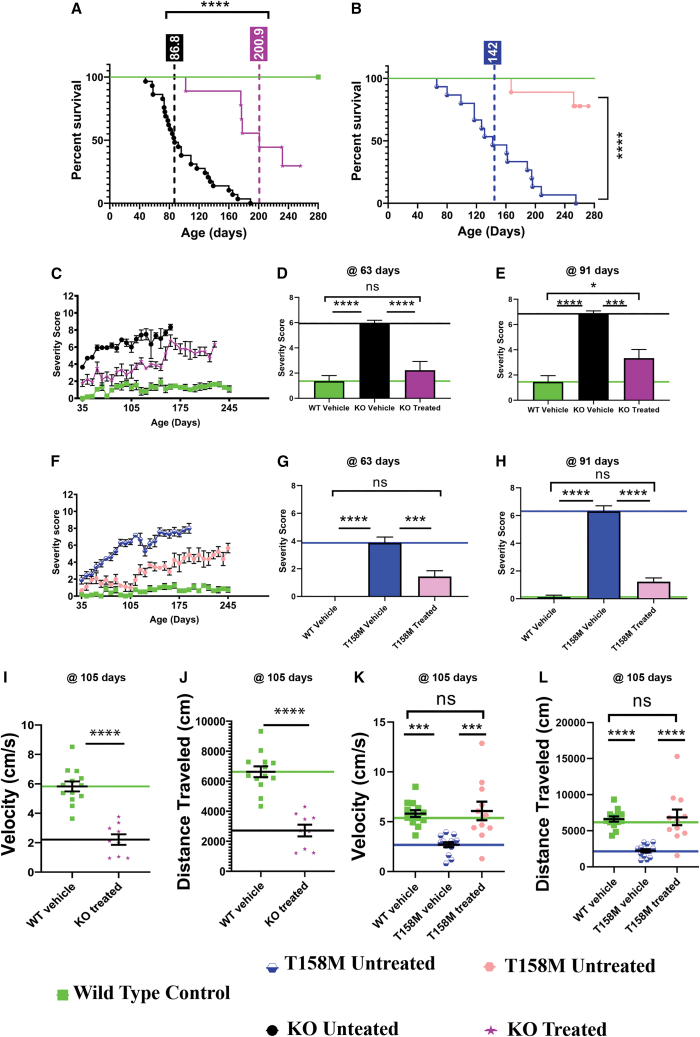
To independently confirm efficacy of scAAV9.P546.MECP2, the vector was tested in the Mecp2–/YKO model (same one as used at NCH) and in a second mouse model carrying a mutant Mecp2 gene (T158M) at a collaborating independent laboratory (Dr. S. Cobb, University of Edinburgh, UK). For this study, neonatal KO mice received a single scAAV9.P546.MECP2 dose of 3.00 × 1010 vg/animal at P1 via ICV injection or received vehicle (saline). All animals were followed until humane endpoint or until the final endpoint (280 days), when remaining animals were sacrificed. Notably, vehicle-treated KO mice in this colony displayed a higher median survival time (86.8 days) vs. the KO colony at NCH (68 days). This variability likely reflects slight differences in housing conditions and/or phenotypic drift of these geographically distant sub-strains. Nonetheless, the median survival in the vector-treated KO animals was 200.9 days, a 2.3-fold improvement in lifespan vs. vehicle-treated KO controls (Figure 4A). The average severity scores of scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated KO mice were less than 4 through 140 days after injection vs. scores approaching 7 in vehicle-treated control animals (Figure 4C). Baseline severity scores differed between the two laboratories because of the qualitative nature of the assay; nevertheless, improvements with the treatment were observed and were consistent within both laboratories. We performed statistical analyses of aggregate severity score at 60 and 90 days. At 60 and 90 days, vector-treated KO mice had a significantly improved severity score compared with vehicle-treated KO mice. Additionally, at 60 days, there was no significant difference in severity score between vector-treated KO mice and vehicle-treated WT mice, suggesting the restoration of normal phenotype (Figure 4D). However, unlike the 60-day time point, at 90 days, there was a significant difference between vector-treated KO mice and vehicle-treated WT mice (Figure 4E).
Figure 4.
ICV delivery of SCAAV9.P546.MECP2 prolongs survival and ameliorates behavioral abnormalities in KO mice and T158M mice
Independent testing of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 treatment at University of Edinburgh shows significant amelioration of RTT-like phenotypes for KO and T158M mice treated with a 3.00 × 1010 vg/animal. (A and B) Treatment significantly improves lifespan for both mouse models (p < 0.0001) (log-rank/Mantel Cox test). (C) Severity score of vehicle-treated WT, vehicle-treated KO, and vector-treated KO mice shows that treatment ameliorates score. (D) At 63 days, vector-treated KO mice were not significantly different from WT mice (p = 0.4172). Each had a significantly lower score than vehicle-treated KO (p < 0.0001). (E) At 91 days, vector-treated KO mice were similar in score to vehicle-treated WT mice. Each had a significantly lower score than vehicle-treated KO mice (vehicle-treated WT, p < 0.0001; vector-treated KO, p = 0.0001). There was a small statistical difference between vehicle-treated WT and vector-treated KO mice (p = 0.0323). (F) Severity score of vehicle-treated WT, vehicle-treated T158M, and scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated T158M mice shows that vector treatment ameliorates score. (G) At 63 days, vector-treated T158M mice were not significantly different from vehicle-treated WT mice (p = 0.771). Each had a significantly lower score than vehicle-treated T158M mice (vehicle-treated WT, p < 0.0001; vector-treated T158M p = 0.0004). (H) At 91 days, vector-treated T158M mice were not significantly different from WT mice (p = 0.1086). Each had a significantly lower score than vehicle-treated T158M mice (p < 0.0001). (I and J) Open field assay was performed at 105 days and vehicle-treated KO mice were not tested due to high mortality. (I) Vector-treated KO mice have significantly different velocity in the open field than vehicle-treated WT mice (p < 0.0001). (J) Vector-treated KO mice have significantly different distance in the open field than vehicle-treated WT mice (p < 0.0001). (K and L) Vector treatment significantly improves open field performance velocity in T158M mice. (K) Vehicle-treated WT mice and vector-treated T158M mice each had a significantly higher velocity than vehicle-treated T158M mice (vehicle-treated WT, p = 0.0004; vector-treated T158M, p = 0.0003) and were not significantly different from each other (p = 0.9387). (L) Vehicle-treated WT mice and vector-treated T158M mice each had a significantly higher velocity than vehicle-treated T158M mice (p < 0.0001) and were not significantly different from each other (p = 0.9625). For testing of KO mice, vehicle-treated WT, n = 11, vehicle-treated KO n = 29, vector-treated KO n = 9. For testing of T158M mice, vehicle-treated WT, n = 8, vehicle-treated T158M, n = 15, vector-treated T158M, n = 9. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.000. ns, not significant.
In addition to KO mice, the University of Edinburgh assessed the therapeutic potential of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 in a mouse model harboring the most common MECP2 missense mutation (T158M) seen in RTT patients. This model shows a milder disease phenotype and longer survival than the KO model. Treatment of T158M mice with 3.00 × 1010 vg significantly improved survival and ameliorated the neurological phenotype similarly to the KO model. The median survival of the vehicle-treated T158M group was 140 days. Approximately 80% of T158M mice treated with scAAV9.P546.MECP2 survived to 280 days, when surviving animals were euthanized to terminate the study, indicating that the lifespan was greatly improved by treatment (Figure 4B).
At 175 days, vehicle-treated T158M mice reached a score of approximately 7. while scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated animals had a score of only approximately 4 (Figure 4F). We performed statistical analysis of aggregate severity score at 60 and 90 days. At both time points, vector-treated T158M mice showed a significant improvement in severity score vs. vehicle-treated T158M mice (p = 0.0004 at 60 days, p < 0.0001 at 90 days). The improvement was so pronounced that vector-treated T158M mice were not statistically different from vehicle-treated WT mice at either timepoints (p = 0.0771 at 60 days, p = 0.1086 at 90 days) (Figures 4G and 4H).
The University of Edinburgh performed open field analysis at 56 days (Figures S3A–S3D) and 105 days (Figures 4I and 4J), analyzing velocity and distance traveled in both mouse models.12 With respect to the KO model, no improvement was seen in vector-treated KO animals vs. vehicle-treated KO animals at 56 days (Figures S3A and S3B). By 105 days, most vehicle-treated KO animals reached the endpoint and hence were not available to compare with the treated KO animals to systematically assess the difference in mobility. The remaining vehicle-treated KO mice were not included in the statistical analysis because of the low number of surviving animals. However, comparing the vector-treated KO mice with vehicle-treated WT mice at 56 days (Figures S3A and S3B) and at 105 days (Figures 4I and 4J), unlike our study at NCH, we did not observe any improvement in velocity and distance traveled at either timepoint.
The same open field testing regimens were used for the T158M mouse model as the KO. At 56 days of age, no improvement was observed in velocity for scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated T158M animals vs. vehicle-treated T158M animals, but there was a decrease in the distance moved in treated T158M animals vs. vehicle-treated T158M animals (Figures S3C and S3D). Also, both vehicle- and scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated T158M animals performed worse in velocity and distance traveled than vehicle-treated WT animals at 56 days of age (Figures S3C and S3D). However, open field testing performed at the later disease progression time of 105 days, revealed a significant improvement in both the measures in scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated T158M mouse group vs. vehicle-treated T158M animals. Moreover, no significant difference was found between scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated T158M mice and vehicle-treated WT mice at 105 days, underlining the positive effect of the treatment (Figures 4K and 4L). Overall, objective data acquired in two independent laboratories from large cohorts of two RTT mouse models strongly support the efficacy of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 for restoring MECP2 levels in the CNS and for improving neurological function.
Intrathecal delivery of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 in NHPs results in widespread vector RNA expression throughout the CNS and is safe and well tolerated
To further advance this program toward the clinic, we performed safety studies in NHPs, cynomolgus macaques (Macaca fascicularis), following the intrathecal (IT) delivery of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 via lumbar infusion and Trendelenburg tilting. We chose this route of delivery for its potential for being the likely route of injection in a first-in-human clinical trial for RTT. However, unlike in-human studies, none of the animals received any steroid treatment prior, at the time of infusion, or throughout the study.
Five juvenile NHPs (cynomolgus macaques) were treated with scAAV9.P546.MECP2. Two 12-month-old male NHPs were treated with scAAV9.P546.MECP2 at 1.3 × 1013 vg/animal and 1.8 × 1013 vg/animal and followed for short-term analysis (35 days). For long-term analysis, three male NHPs (6–12 months old) received scAAV9.P546.MECP2 at 1.6 × 1013 vg/animal (two 12-month-old animals) or 9.2 × 1012 vg/animal (one 6-month-old animal) and followed up to 18 months after injection. Vector doses were based on previous dosing studies in NHPs and are sufficient to target the brain and spinal cord.33,38 The injections and in-life portion of the study were performed at Mannheimer Foundation, Homestead, Florida.
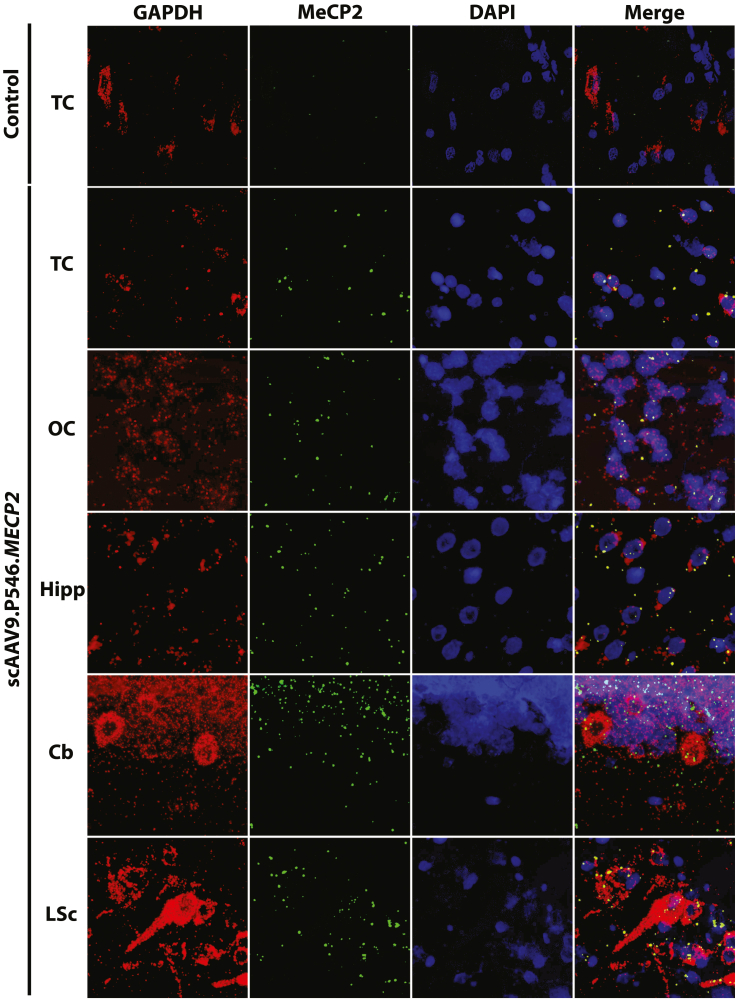
In situ hybridization was performed to confirm that vector derived human MECP2 transcript was present and actively expressed in the CNS of treated NHPs. All CNS regions examined showed expression of vector-derived MECP2 mRNA transcript that was absent in historical (saline injected) control tissues of animals from the same colony (Figures 5 and S4). Furthermore, vector-derived mRNA was widely distributed in the tissues analyzed, indicating effective targeting of many CNS regions located at a considerable distance from the IT injection site.
Figure 5.
ISH in CNS from control and SCAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated NHPs at 18 months after injection
ISH shows vector-derived RNA transcripts in multiple key regions from brains of SCAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated NHPs but not untreated controls. Probes against glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (red), vector-derived human MECP2 mRNA (green), and nuclear labeling (Dapi, blue). Cb, cerebellum; Hipp, hippocampus; Lumb, lumbar spinal cord; OC, occipital cortex; TC, temporal cortex.
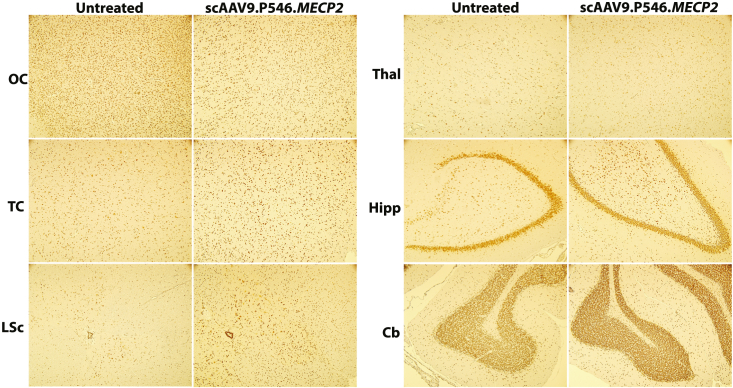
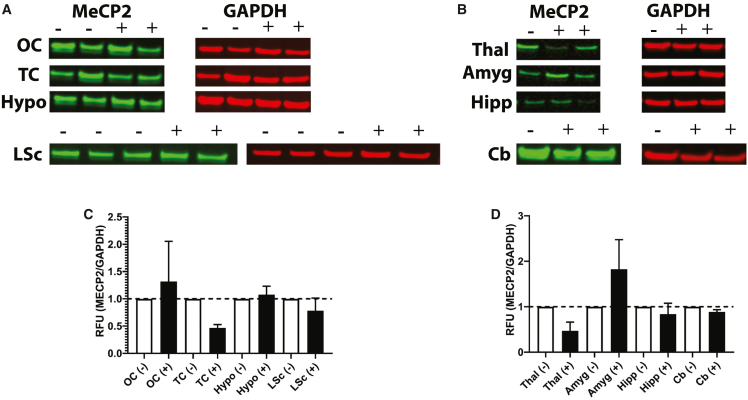
CNS regions were also examined for MECP2 protein distribution by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Importantly, no antibody distinguishes NHP endogenous MECP2 protein from human protein. The goal of protein analysis was to ensure that no overexpression was observed. All examined regions of scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated NHPs showed similar levels of MECP2 expression as compared with the historical control tissue (Figure 6). Furthermore, western blots performed on homogenized tissue from scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated NHPs confirmed that no brain or spinal cord region showed a more than 2-fold increase in MECP2 expression as compared with the historical controls (Figure 7).
Figure 6.
Immunohistochemical assessment of MECP2 expression in NHPs at 5 weeks after injection
Similar levels of MECP2 is expressed throughout scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated and control NHP CNS. Anti-MECP2 IHC revealed no gross structural abnormalities or obvious differences in MeCP2 expression. Cb, cerebellum; Hipp, hippocampus; LSc, lumbar spinal cord; OC, occipital Cortex; Thal, thalamus, TC, temporal cortex.
Figure 7.
Western blot expression of CNS from scAAV9.P546.MECP2 injected NHPs at 5 weeks after injection
Similar MECP2 protein levels are expressed in scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated and control primate tissue. (A) OC, occipital cortex; TC, temporal cortex; Hypo, hypothalamus; LSc, lumbar spinal cord. (B) Thal, thalamus; Amyg, amygdala; Hipp, hippocampus; Cb, cerebellum. (C) Quantification of blot A. (D) Quantification of blot B. Relative fluorescent units (RFU) are normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), treated NHP tissue is normalized to control tissue. scAAV9.P546.MECP2-treated (+/black) n = 2, and control (-/white), n = 1–3 NHPs.
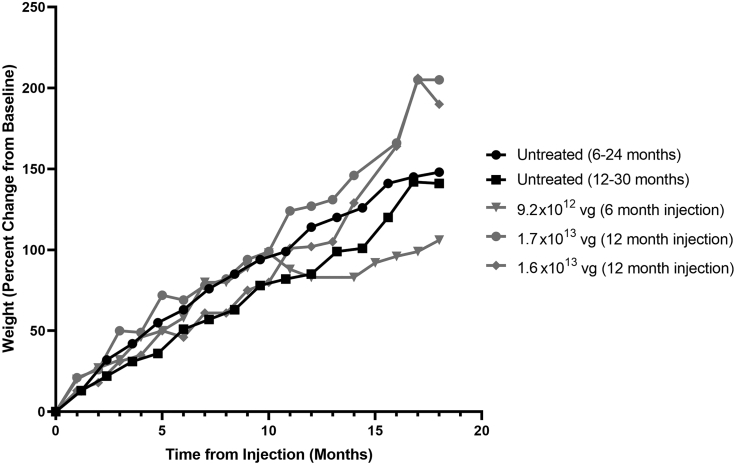
We also performed a long-term safety analysis on the animals that were followed up to 18 months after infusion. Body weight, hematology, and serum chemistry data were collected monthly for the first 6 months after injection and every 2 months thereafter. No abnormal clinical signs were noted during daily cage-side observations throughout the study duration. Overall, weight (Figure 8), serum chemistry (Figures S5 and S6), and hematology (Figure S7) from vector-treated animals were normal. Neither serum chemistry nor hematology values for any vector-treated animal substantially deviated from controls for more than two consecutive observations, except serum amylase activity in two animals, which was already higher at baseline (i.e., before treatment). Notably, platelet values and liver function tests (alanine and aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, albumin, globulin, and bilirubin) always remained within the normal ranges.
Figure 8.
Effect of IT dosing with scAAV9.P546.MECP2 on Weight of NHPs
Weight expressed as percent change from baseline. Weight gains from vector-treated animals were consistent with untreated controls through 18 months after treatment.
Tissue specimens from treated NHPs of both short- and long-term groups were sent for pathology examination via independent ACVP board-certified veterinary pathologist. In the short-term treated animals, analysis revealed no substantial microscopic lesions in protocol-specified major tissues: adrenal gland, heart, kidney, liver, lung, inguinal lymph node, 19 brain and spinal cord regions, dorsal root ganglia, eye, pancreas, skeletal muscles, small intestine, testis, spleen, thymus, and urinary bladder. In long-term treated animals, only two pathological findings were described: one animal showed minimally diffuse hypertrophy in the liver and another animal displayed perivascular lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates, both of which were interpreted as non-adverse. This shows that scAAV9.P546.MECP2 treatment via IT injection was safe and well tolerated in large NHPs commonly used for evaluating potential risk to patients.
Discussion
RTT is a devastating condition affecting the quality of life of many patients and their families. There is an urgent need for treatment options that ameliorate or even reverse the disease phenotype. Groundbreaking work from the Bird laboratory showed that restoration of MECP2 expression is capable of reversing RTT-like phenotypes in mice, indicating that MECP2 gene therapy holds great potential for RTT patients.11 RTT gene therapy must maintain a narrow MECP2 expression window to achieve therapeutic efficacy and avoid toxic overexpression.23,24,25,37,39,40,41,42,43,44,45 Within the past 15 years, several gene therapy approaches have been published.12,13,14,15,16,22,30,32
It is important to note that most of these RTT studies use male Mecp2-/Y (KO) mice to determine the therapeutic effects of the treatment, despite the fact that majority of RTT patients are female. This is because male mice are the superior model for RTT research. Both male and female mice feature phenotypes that overlap with RTT patient symptoms, including locomotive features such as decreased mobility, ataxic gate, dystonia, rigidity, tremors, and neurological symptoms, such as decreased brain volume, learning delays, and aberrant social behavior, among others. Yet in addition to these RTT-like phenotypes, females have a unique, severe obesity phenotype, that is not recapitulated in the majority of RTT patients.43 Generally, obesity in mice is itself linked to a host of problems including neurological phenotypes44 and locomotor abnormalities.45 Thus, it is difficult to separate obesity-linked phenotypes in RTT female mice from those linked to Mecp2 deficiency. Additionally, symptom onset in male mice begins at approximately 4 weeks of age, while it does not begin for females until approximately 6 months of age. Furthermore, female X chromosome mosaicism results in a population with continuous range of phenotypes vs. the comparably discrete phenotypes of hemizygous males.46 Overall, obesity, later disease onset, and variability of Mecp2 expression make efficacy studies in female RTT mice much more challenging, time consuming, and expensive, making the male KO mouse an attractive and commonly used alternative.
Previous work by our laboratory in collaboration with the Mandel laboratory demonstrated phenotypic improvement in Mecp2–/Y KO mice with a 2.5-fold increase in median lifespan by intravenous delivery of a vector using a longer MeCP2 promoter fragment (P738).12 This study offered proof of concept, but the modest survival improvement and high vector dose required via IV delivery were insufficient for clinical translation. Thus, our new approach focused on three areas important for translation: the (1) new vector design, (2) direct CSF delivery route allowing for reduction of vector dose, and (3) extensive dose ranging studies.
We previously showed that IT delivery efficiently allows for widespread CNS delivery with significantly lower vector doses than IV delivery and reduced overexpression risk in peripheral organs.33 Of note, vector CNS biodistribution in NHPs after IT delivery has been published by several groups with varying results.47,48,49,50 Many variables complicate a direct comparison between individual studies including differences in injection volume and speed, vector formulation, tilting of the animal, anesthetics, and vector titration methods. IT injections are standard procedures in hospitals and display a preferred safety profile over cisterna magna or ICV injection in human patients.46,51, 52, 53, 54
Here, we developed a novel, optimized, clinical ready vector, scAAV9.P546.MECP2, for the treatment of RTT. We completed scAAV9.P546.MECP2 mouse efficacy studies featuring large sample sizes of two different mouse models of RTT (KO and T158M), performed independently by two separate laboratories at NCH in the United States and at the University of Edinburgh in the UK. We unequivocally show that scAAV9.P546.MECP2 is highly effective at ameliorating RTT-like phenotypes in both mouse models.10,55
For each model, we saw an improvement in open field performance, severity scores, and survival. Differences in disease course between different laboratories were likely the reason for slight variability in effects observed (open field testing). Importantly, such differences are not uncommon and likely arise from variations in the genetic background and housing conditions for the two colonies. The fact that University of Edinburgh saw differences in open field testing in both mouse models at later stages of the disease supports this hypothesis.
The aggregate severity scoring system, assessing several neurological phenotypes arising from Mecp2 deficiency, is a key assessment in RTT models. Notably, NCH found that every dose of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 led to an improvement in severity score as compared with untreated KO mice. This improvement was also seen in in the University of Edinburgh for KO and T158M mice, indicating high therapeutic potential for amelioration of RTT-like phenotypes.
Importantly, we achieved unprecedented levels of increase in survival in both RTT mouse models. The improvement of median survival of 3.3-fold in KO mice treated with 1.5 × 1010 vg scAAV9.P546.MECP2 at NCH is the largest improvement in survival ever achieved through gene therapy in this model. Variation in survival improvement between the two laboratories arise primarily due to variation between mouse colonies (median survival of 68 days at NCH vs. 86.8 days at University of Edinburgh). Among previously published studies, the closest survival increase compared with our data is a study by the Cobb and Gray laboratories that yielded a promising 3.1-fold extension of survival in KO mice after ICV injection.15,32 However, the effective doses of scAAV9.P546.MECP2 are 3- to 13-fold lower (7.5 × 109 to 3.00 × 1010), than the effective dose (1 × 1011 vg/animal) of the Cobb/Gray second-generation vector.32 Additionally, while the Cobb/Gray second-generation vector leads to only a marginal improvement in the weight of treated animals, scAAV9.P546.MECP2 significantly improves weight during critical time points in the early disease course, when weight difference between KO and WT animals are highly pronounced. scAAV9.P546.MECP2 did not lead to overexpression toxicity at any therapeutic dose tested and achieved more robust phenotypic amelioration than other recently published vectors at doses more than two orders of magnitude lower, which might be a significant safety advantage from an immunological perspective.
To verify the safety of the vector, we performed extensive dose-ranging studies in mice and NHPs. We verified that overexpression phenotypes were predominantly absent in WT mice with a maximum MECP2 protein expression of approximately 2-fold relative to untreated WT levels, which was considerably lower than levels expressed by the TG3 MDS mouse model. Thus, suggesting that, with the current vector and the dosing regimen, we were able to achieve the therapeutic benefit without crossing the MECP2 expression threshold for duplication/triplication syndrome.
In NHPs, no clinical symptoms were observed at any time point. In situ hybridization of vector-derived RNA shows strong vector targeting and expression throughout the entire CNS, indicating effective distribution along the neuraxis. The lack of overt MECP2 overexpression shown via western blot and IHC suggest that healthy neurons maintain physiological levels of MECP2 expression in the context of a relatively broad dose range of scAAV9.P546.MECP2. Pathological examination of major organs and large samples of tissue from treated NHPs did not show evidence of toxicity. In contrast with reports by Wilson et al.,56 we did not observe pathology in the DRGs. Possible explanations for this discrepancy are differences in manufacturing/purification process of the viral vector, dose, formulation, injection procedures, time points of analysis. among others. Our data are in line with the recent meta-analysis by the Wilson laboratory comparing 33 studies with more than 250 NHPs in which no AAV vectors expressing therapeutic transgenes lead to more than minimal or mild findings in DRGs with no clinical symptoms observed throughout all studies.57
Overall, our data establish scAAV9.P546.MECP2 as a strong candidate for clinical trials. The vector backbone and serotype (AAV9) has already been successfully and safely translated to clinic for several other neurological and neuromuscular disorders.18,58,59,60 While our data are compelling and clearly indicate the potential of this therapeutic vector for treatment of RTT, safety in human patients must be established. It is possible that species-specific differences might lead to a narrower window for dosing in human patients or that additional side effects might be observed in humans that were absent in animal models. Additionally, while minimal neurodegeneration was observed in human patient postmortem samples,9,10 it remains to be proven that symptoms are reversible in humans after the patient has suffered from MECP2 depletion during key developmental windows. Likely, the most significant impact on disease symptoms will be achieved by treating RTT patients as early as possible, similar to other gene replacement therapies.18,58,59,60
Materials and methods
scAAV9.P546.MECP2 preparation
AAV9 was produced using three plasmids: a double-stranded AAV2-ITR-based CAG-Cre or Mecp2 minimal promoter-Mecp2 (E1) vector, and a plasmid encoding Rep2Cap9 sequence described previously, with the adenoviral helper plasmid pHelper (Stratagene) in 293 cells61,62,63 with double cesium chloride density gradient ultracentrifugation purification. Virus was titered by silver staining and ddPCR.
University of Edinburgh mouse handling, care, and observations
Experiments were performed in accordance with the European Communities Council Directive (86/609/EEC) and within terms of a project license under the UK Scientific Procedures Act (1986). The KO and T158M (B6.129P2[Cg]-Mecp2tm4.1Bird/J) mice were maintained on a C57BL/6J background; Het female T158M females were crossed with WT C57BL/6J males. Animals were housed in a room with temperature: 20°C–24°C, 45%–65% humidity, and 12-h:12-h light/dark cycles, with free access to pelleted rodent chow and water. Mice were genotyped as described.11,64 Vector (2 μL per site; dose = 3 × 1010 vg per mouse) was injected bilaterally into unanesthetized P1males as described.13 Control groups were injected with the same volume of PBS (vehicle). Injected pups were returned to the home cage and assessed weekly for development and progression of the RTT-like phenotypes as described before with the observer masked to animal genotype and treatment.10 Motor function was assessed at 56 and 105 days after injection in the open field. Briefly, mice were allowed to ambulate freely in a 40-cm-diameter arena for 40 min. Digital tracks were analyzed for various motor parameters using Ethovision XT 11.5 tracking software (Noldus, Leesburg, VA).
NCH mouse handling, care, and observations
Procedures performed were in accordance with US National Institutes of Health guidelines and approved by the Research Institute at NCH (Columbus, OH), Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) Protocol (#AR14-00019). Female Mecp2 heterozygous (B6.129P2(C)-Mecp2tm1.1Bird/J, The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME) were bred with C57BL/6J (The Jackson Laboratory) males. Housing temperatures: 20.6°C–23.9°C and humidity at 30–70%. Genotyping was performed as described.12 ICV injections of mice (P2) was performed with a Hamilton syringe (Catalog No. 80330 700RN 10 μL SYR [26s/2”/2] REV M Lot #324603 11/08/2005 Hamilton, Reno, NV) and needles (Catalog No. 7803-05 NDL. NDL 6pk 33 GA RN 75″20 DEG PT S/0# 83521 02/17/2005 Hamilton). Vectors were diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) for lower doses up to 4 μL. Mouse RTT behavior phenotype was assessed via Bird scoring system as described in Guy et al.11 Scoring was performed by a blinded observer. Aggregate severity score is a cumulative score of 6 different symptoms observed in Mecp2 mice arising from Mecp2 deficiency in comparison with wildtype mice (Table 1). Briefly, each of six symptoms were scored as 0 (absent or as WT), 1 (symptom present), or 2 (symptom severe). Mice were also weighed at each scoring session. Locomotor behavior was evaluated using open field assessment.12 Open field was performed on a photobeam activity system (PAS) at approximately 49–63 days after birth as described.12 Data were analyzed via PAS access software. TG3 tissue (FVB-Tg[MECP2]3Hzo/J) was donated by Kevin Foust.
Table 1.
Aggregate behavioral scoring system
| Symptom | Severity score |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | |
| Mobility | as WT | reduced movement (extended freezing) | no spontaneous movement |
| Gait | as WT | waddling gate | more severe abnormalities (bunny hops, more severe waddling/diagonal gait, etc.) |
| Hindlimb clasping | legs splayed outwards | one or both hindlimbs drawn toward each other or body | both legs pulled in tightly touching each other or body |
| Tremor | No tremor | intermittent or mild tremor | continuous or intermittent violent tremor |
| Breathing | normal breathing | short periods of rapid breathing or pauses in breathing | very irregular breathing (gasping or panting) |
| General condition | clean shiny coat, clear eyes, normal stance | dull eyes, dull coat/ungroomed, somewhat hunched stance | crusted or narrowed eyes, piloerection, hunched posture |
NHP handling, care, and delivery of vector to the CNS at the Mannheimer Foundation
All procedures performed were in accordance with the US National Institutes of Health guidelines and approved in advance by the Mannheimer Foundation (Homestead, FL) IACUC. Monitoring of overall health and weight was performed before and at least monthly after injections to assess welfare. IT injections in NHPs were performed as described.33
MECP2 IHC
MECP2 IHC was outsourced to the Morphology Core at NCH. Tissue was fixed in 4% methanol-free formaldehyde (pH 7.4) for approximately 72 h at 4°C then processed into paraffin blocks. We mounted and treated 40-μm-thick coronal sections (1) deparaffinized with citrate (pH 6) washes, (2) water washes (3) DAKO washes (Carpenteria, CA), Background Sniper and SuperBlock reagents (ThermoFisher, Waltham, MA), (4) 4°C incubation for 72 h with rabbit monoclonal anti-MECP2 D4F3 (1:500) (Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA) in DAKO solution, (5) DAKO, MACH2 detection reagent washes, (6) water washes, (7) DAKO DAB incubation, (8) Shandon hematoxylin, tap water, ammonia, and xylene washes, and (9) coverslip using Permount.
In situ hybridization
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (ISH) was performed by Reveal Biosciences using a probe designed by Affymetrix (Santa Clara, CA)/ThermoFisher (Waltham, MA) specific for human MECP2 mRNA. ISH was performed according to the RNA ISH Assay using Affymetrix ViewRNA ISH Tissue 2-Plex Assay Protocol. The following conditions were used: heat treatment for 10 min and protease digestion for 20 min. Probe sets used were M. fascicularis GapD (# VF6-19786; Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA) as a housekeeping gene, type 6 detected using Fast Blue; human MEPC2 (#VA1-300656; Affymetrix) as the gene of interest, type 1 detected using Fast Red; Bacillus subtilis DapB (#VF6-10407; Affymetrix) as the negative control gene, type 6 detected using Fast Blue, B. subtilis DapB (#VF1-11712, Affymetrix) used as a negative control, and type 1, detected using Fast Red. Whole-slide imaging was performed with 3DHistech Panoramic SCAN 150 using fluorescence to image DAPI, TRITC, and Cy5 fluorophores.
Tissue homogenization and western blot
Snap frozen tissue was resuspended in 0.2 mL elution buffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7.2, 450 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM DTT, 10% glycerol), containing complete protease inhibitor cocktail (Cat. # 11697498001; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO)/0.04 g. Samples were mechanically homogenized and sonicated. We loaded 10 μg protein onto NuPAGE 4%–12% Bis Tris 1.0 mm Gels (Cat. # NP0302BOX, ThermoFisher) and separated at 180 V for 35 min. Gels were transferred to PVDF membrane (Immobilon FL, Cat. # IPFL00010; Millipore, Burlington, MA) in NuPAGE transfer buffer (Cat. # NP0006-T; ThermoFisher) at 60V for 95 min. Membranes were blocked with Odyssey Blocking Buffer PBS (Cat. # 927–40000; Li-Cor, Lincoln, NE) and incubated overnight at 4°C with rabbit monoclonal anti-MeCP2 antibody (1:500, Cat. # 3456S, Cell Signaling) and mouse anti glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (1:15,000, Cat. # MAB374; Millipore). Membrane was incubated with IRDye secondary antibodies: 680LT goat anti-mouse LT (Cat. #926-68020, Li-Cor, Lincoln, NE) and 800 CW donkey anti-rabbit (Cat. # 925–32213, Li-Cor) (1:25,000) for 60 min at room temperature. Fluorescence was quantified with Image Studio Lite.
Statistical analyses
The mean aggregate severity scores were plotted over time with the SEM. Survival was monitored and plotted in a Kaplan-Meier survival curve from weaning at 21–540 days (18 months) of age. Median survival, if reached before 18 months, was calculated for each group. Significance was determined via log-rank test.
The mean open field scores for distance traveled and average velocity were plotted on a bar graph with SEM. ANOVA was performed with all doses compared with untreated KO scores except WT, which was calculated via unpaired T test. Significance was calculated with Dunnett’s post hoc multiple comparisons test. For all statistical tests, values represent means ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Morphology Core at NCH for performing IHC staining and Reveal Biosciences for performing in situ hybridization. This work was funded by a generous consortium grant from the Rett Syndrome Research Trust to B.K.K. and K.M. at NCH and to S.C. at the University of Edinburgh.
Author contributions
S.Powers: Project management, mouse colony husbandry, injections, genotyping, and behavioral and survival analysis, NHP and mouse tissue processing and Western blot, protein quantification, statistical analysis and figure preparation; S.L.: vector design, NHP tissue processing, manuscript editing, figure preparation, and revisions; K.G.: management of University of Edinburgh study; C.M.: project management, mouse colony husbandry, injections, behavioral and survival analysis, and statistical analysis; A.H.: mouse colony husbandry and maintenance, injections and behavioral and survival analysis, genotyping, and mouse and NHP tissue processing; C.D.: mouse and NHP tissue processing and western blotting; K.F.: vector design; P.M.: veterinary care, NHP injections, maintenance, and pathology and health measurement; C.P.: NHP tissue processing and neuroanatomical dissection and identification; F.R.: NHP tissue processing and immunohistochemistry; S.Perry: tissue processing and western blotting, and genotyping; B.B.: histopathology analysis and manuscript editing; N.W.: project management advisor; S.C.: independent analysis and primary investigator; B.K.: primary investigator; K.M.: primary investigator.
Declaration of interests
B.K.K. and NCH hold patent filings on this work and received royalties. B.B. received compensation for histopathological analysis.
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.07.013.
Contributor Information
Samantha Powers, Email: Samantha.powers@nationwidechildrens.org.
Kathrin C. Meyer, Email: Kathrin.meyer@nationwidechildrens.org.
Supplemental information
Data and code availability
All available materials described in this study may be obtained through material transfer agreement.
References
- 1.Hagberg B. Rett’s syndrome: prevalence and impact on progressive severe mental retardation in girls. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 1985;74:405–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Renieri A., Meloni I., Longo I., Ariani F., Mari F., Pescucci C., Cambi F. Rett syndrome: the complex nature of a monogenic disease. J. Mol. Med. 2003;81:346–354. doi: 10.1007/s00109-003-0444-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ehrhart F., Sangani N.B., Curfs L.M.G. Current developments in the genetics of Rett and Rett-like syndrome. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry. 2018;31:103–108. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Amir R.E., Van den Veyver I.B., Wan M., Tran C.Q., Francke U., Zoghbi H.Y., Veyver I.B.V.D., Wan M., Tran C.Q., Francke U., et al. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat. Genet. 1999;23:185–188. doi: 10.1038/13810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schanen N.C., Kurczynski T.W., Brunelle D., Woodcock M.M., Dure L.S., 4th, Percy A.K. Neonatal encephalopathy in two boys in families with recurrent Rett syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 1998;13:229–231. doi: 10.1177/088307389801300507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Villard L., Kpebe A., Cardoso C., Chelly P.J., Tardieu P.M., Fontes M. Two affected boys in a Rett syndrome family: Clinical and molecular findings. Neurology. 2000;55:1188–1193. doi: 10.1212/WNL.55.8.1188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nomura Y., Segawa M. Natural history of Rett syndrome. J. Child Neurol. 2005;20:764–768. doi: 10.1177/08830738050200091201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Akbarian S. The neurobiology of Rett syndrome. Neuroscientist. 2003;9:57–63. doi: 10.1177/1073858402239591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bauman M.L., Kemper T.L., Arin D.M. Pervasive neuroanatomic abnormalities of the brain in three cases of Rett’s syndrome. Neurology. 1995;45:1581–1586. doi: 10.1212/WNL.45.8.1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Guy J., Hendrich B., Holmes M., Martin J.E., Bird a ( A mouse Mecp2-null mutation causes neurological symptoms that mimic Rett syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2001;27:322–326. doi: 10.1038/85899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Guy J., Gan J., Selfridge J., Cobb S., Bird A. Reversal of Neurological Defects in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome. Science. 2007;315:1143–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.1138389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Garg S.K., Lioy D.T., Cheval H., McGann J.C., Bissonnette J.M., Murtha M.J., Foust K.D., Kaspar B.K., Bird A., Mandel G. Systemic Delivery of MeCP2 Rescues Behavioral and Cellular Deficits in Female Mouse Models of Rett Syndrome. J. Neurosci. 2013;33:13612–13620. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1854-13.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gadalla K.K.E., Bailey M.E.S., Spike R.C., Ross P.D., Woodard K.T., Kalburgi S.N., Bachaboina L., Deng J.V., West A.E., Samulski R.J., et al. Improved Survival and Reduced Phenotypic Severity Following AAV9/MECP2 Gene Transfer to Neonatal and Juvenile Male Mecp2 Knockout Mice. Mol. Ther. 2013;21:18–30. doi: 10.1038/mt.2012.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Matagne V., Ehinger Y., Saidi L., Borges-Correia A., Barkats M., Bartoli M., Villard L., Roux J.-C. A codon-optimized Mecp2 transgene corrects breathing deficits and improves survival in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017;99:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sinnett S.E., Hector R.D., Gadalla K.K.E., Heindel C., Chen D., Zaric V., Bailey M.E.S., Cobb S.R., Gray S.J. Improved MECP2 Gene Therapy Extends the Survival of MeCP2-Null Mice without Apparent Toxicity after Intracisternal Delivery. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2017;5:106–115. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2017.04.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tillotson R., Selfridge J., Koerner M.V., Gadalla K.K.E., Guy J., De Sousa D., Hector R.D., Cobb S.R., Bird A. Radically truncated MeCP2 rescues Rett syndrome-like neurological defects. Nature. 2017;550:398–401. doi: 10.1038/nature24058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Leone P., Shera D., McPhee S.W.J., Francis J.S., Kolodny E.H., Bilaniuk L.T., Wang D.-J., Assadi M., Goldfarb O., Goldman H.W., et al. Long-term follow-up after gene therapy for canavan disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012;4:165ra163. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mendell J.R., Al-Zaidy S., Shell R., Arnold W.D., Rodino-Klapac L.R., Prior T.W., Lowes L., Alfano L., Berry K., Church K., et al. Single-Dose Gene-Replacement Therapy for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017;377:1713–1722. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1706198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vance M., Llanga T., Bennett W., Woodard K., Murlidharan G., Chungfat N., Asokan A., Gilger B., Kurtzberg J., Samulski R.J., Hirsch M.L. AAV Gene Therapy for MPS1-associated Corneal Blindness. Sci. Rep. 2016;6 doi: 10.1038/srep22131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nathwani A.C., Rosales C., McIntosh J., Rastegarlari G., Nathwani D., Raj D., Nawathe S., Waddington S.N., Bronson R., Jackson S., et al. Long-term Safety and Efficacy Following Systemic Administration of a Self-complementary AAV Vector Encoding Human FIX Pseudotyped With Serotype 5 and 8 Capsid Proteins. Mol. Ther. 2011;19:876–885. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hwu W.-L., Muramatsu S. -i., Tseng S.-H., Tzen K.-Y., Lee N.-C., Chien Y.-H., Snyder R.O., Byrne B.J., Tai C.-H., Wu R.-M. Gene Therapy for Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase Deficiency. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012;4:134ra61. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Luoni M., Giannelli S., Indrigo M.T., Niro A., Massimino L., Iannielli A., Passeri L., Russo F., Morabito G., Calamita P., et al. Whole brain delivery of an instability-prone Mecp2 transgene improves behavioral and molecular pathological defects in mouse models of Rett syndrome. Elife. 2020;9 doi: 10.7554/eLife.52629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ramocki M.B., Peters S.U., Tavyev Y.J., Zhang F., Carvalho C.M.B., Schaaf C.P., Richman R., Fang P., Glaze D.G., Lupski J.R., Zoghbi H.Y. Autism and other neuropsychiatric symptoms are prevalent in individuals with MECP2 duplication syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 2009;66:771–782. doi: 10.1002/ana.21715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wax J.R., Pinette M.G., Smith R., Chard R., Cartin A. Second-trimester prenasal and prefrontal skin thickening—Association with MECP2 triplication syndrome. J. Clin. Ultrasound. 2013;41:434–437. doi: 10.1002/JCU.22065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tang S.S., Fernandez D., Lazarou L.P., Singh R., Fallon P. MECP2 triplication in 3 brothers - A rarely described cause of familial neurological regression in boys. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012;16:209–212. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2011.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Adachi, M., Keefer, E.W., and Jones, F.S. A segment of the Mecp2 promoter is sufficient to drive expression in neurons. 10.1093/hmg/ddi402. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Liu, J., and Francke, U. Identification of cis-regulatory elements for MECP2 expression. 10.1093/hmg/ddl099. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Panayotis N., Ehinger Y., Felix M.S., Roux J.C. State-of-the-art therapies for Rett syndrome. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2023;65:162–170. doi: 10.1111/DMCN.15383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sinnett S.E., Gray S.J. Recent Endeavors in MECP2 Gene Transfer for Gene Therapy of Rett Syndrome. Discov. Med. 2017;24:153–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sinnett S.E., Boyle E., Lyons C., Gray S.J., Gray S.J. Engineered microRNA-based regulatory element permits safe high-dose miniMECP2 gene therapy in Rett mice. Brain. 2021;144:3005–3019. doi: 10.1093/BRAIN/AWAB182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rastegar M., Hotta A., Pasceri P., Makarem M., Cheung A.Y.L., Elliott S., Park K.J., Adachi M., Jones F.S., Clarke I.D., et al. MECP2 Isoform-Specific Vectors with Regulated Expression for Rett Syndrome Gene Therapy. PLoS One. 2009;4 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gadalla K.K.E., Vudhironarit T., Hector R.D., Sinnett S., Bahey N.G., Bailey M.E.S., Gray S.J., Cobb S.R. Development of a Novel AAV Gene Therapy Cassette with Improved Safety Features and Efficacy in a Mouse Model of Rett Syndrome. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2017;5:180–190. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2017.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Meyer K., Ferraiuolo L., Schmelzer L., Braun L., Mcgovern V., Likhite S., Michels O., Govoni A., Fitzgerald J., Morales P., et al. Improving Single Injection CSF Delivery of AAV9-mediated Gene Therapy for SMA : A Dose – response Study in Mice and Nonhuman Primates. Mol. Ther. 2015;23:477–487. doi: 10.1038/mt.2014.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Johnson T.B., White K.A., Brudvig J.J., Cain J.T., Langin L., Pratt M.A., Booth C.D., Timm D.J., Davis S.S., B M., et al. AAV9 Gene Therapy Increases Lifespan and Treats Pathological and Behavioral Abnormalities in a Mouse Model of CLN8-Batten Disease. Mol. Ther. 2021;29:162–175. doi: 10.1016/J.YMTHE.2020.09.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cain J.T., Likhite S., White K.A., Timm D.J., Davis S.S., Johnson T.B., Dennys-Rivers C.N., Rinaldi F., Motti D., Corcoran S., et al. Gene Therapy Corrects Brain and Behavioral Pathologies in CLN6-Batten Disease. Mol. Ther. 2019;27:1836–1847. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.06.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gene Therapy for Children with CLN3 Batten Disease - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03770572?cond=Batten&draw=2&rank=2
- 37.Collins A.L., Levenson J.M., Vilaythong A.P., Richman R., Armstrong D.L., Noebels J.L., David Sweatt J., Zoghbi H.Y. Mild overexpression of MeCP2 causes a progressive neurological disorder in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004;13:2679–2689. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddh282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Foust K.D., Salazar D.L., Likhite S., Ferraiuolo L., Ditsworth D., Ilieva H., Meyer K., Schmelzer L., Braun L., Cleveland D.W., Kaspar B.K. Therapeutic AAV9-mediated suppression of mutant SOD1 slows disease progression and extends survival in models of inherited ALS. Mol. Ther. 2013;21:2148–2159. doi: 10.1038/MT.2013.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Van Esch H., Bauters M., Ignatius J., Jansen M., Raynaud M., Hollanders K., Lugtenberg D., Bienvenu T., Jensen L.R., Gécz J., et al. Duplication of the MECP2 Region Is a Frequent Cause of Severe Mental Retardation and Progressive Neurological Symptoms in Males. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005;77:442–453. doi: 10.1086/444549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Miguet M., Faivre L., Amiel J., Nizon M., Touraine R., Prieur F., Pasquier L., Lefebvre M., Thevenon J., Dubourg C., et al. Further delineation of the MECP2 duplication syndrome phenotype in 59 French male patients, with a particular focus on morphological and neurological features. J. Med. Genet. 2018;55:359–371. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-104956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Heckman L.D., Chahrour M.H., Zoghbi H.Y. Rett-causing mutations reveal two domains critical for MeCP2 function and for toxicity in MECP2 duplication syndrome mice. Elife. 2014;3 doi: 10.7554/eLife.02676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.del Gaudio D., Fang P., Scaglia F., Ward P.A., Craigen W.J., Glaze D.G., Neul J.L., Patel A., Lee J.A., Irons M., et al. Increased MECP2 gene copy number as the result of genomic duplication in neurodevelopmentally delayed males. Genet. Med. 2006;8:784–792. doi: 10.1097/01.gim.0000250502.28516.3c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Signorini C., De Felice C., Leoncini S., Møller R.S., Zollo G., Buoni S., Cortelazzo A., Guerranti R., Durand T., Ciccoli L., et al. MECP2 Duplication Syndrome: Evidence of Enhanced Oxidative Stress. A Comparison with Rett Syndrome. PLoS One. 2016;11 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Van Esch H. MECP2 duplication syndrome. Mol. Syndromol. 2012;2:128–136. doi: 10.1159/000329580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.San Antonio-Arce V., Fenollar-Cortés M., Oancea Ionescu R., DeSantos-Moreno T., Gallego-Merlo J., Illana Cámara F.J., Cotarelo Pérez M.C. MECP2 Duplications in Symptomatic Females. Child Neurol. Open. 2016;3 doi: 10.1177/2329048x16630673. 2329048X1663067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gong D., Yu H., Yuan X. A new method of subarachnoid puncture for clinical diagnosis and treatment: Lateral atlanto-occipital space puncture. J. Neurosurg. 2018;129:146–152. doi: 10.3171/2017.1.JNS161089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Meseck E.K., Guibinga G., Wang S., Mcelroy C., Hudry E., Mansfield K. Intrathecal sc-AAV9-CB-GFP: Systemic Distribution Predominates Following Single-Dose Administration in Cynomolgus Macaques. bioRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1177/01926233221101309. Preprint at. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bey K., Deniaud J., Dubreil L., Joussemet B., Cristini J., Ciron C., Hordeaux J., Le Boulc’h M., Marche K., Maquigneau M., et al. Intra-CSF AAV9 and AAVrh10 Administration in Nonhuman Primates: Promising Routes and Vectors for Which Neurological Diseases? Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020;17:771–784. doi: 10.1016/J.OMTM.2020.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ohno K., Samaranch L., Hadaczek P., Bringas J.R., Allen P.C., Sudhakar V., Stockinger D.E., Snieckus C., Campagna M.V., San Sebastian W., et al. Kinetics and MR-Based Monitoring of AAV9 Vector Delivery into Cerebrospinal Fluid of Nonhuman Primates. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2019;13:47–54. doi: 10.1016/J.OMTM.2018.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Passini M.A., Bu J., Richards A.M., Treleaven C.M., Sullivan J.A., O’Riordan C.R., Scaria A., Kells A.P., Samaranch L., San Sebastian W., et al. Translational fidelity of intrathecal delivery of self-complementary AAV9-survival motor neuron 1 for spinal muscular atrophy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2014;25:619–630. doi: 10.1089/HUM.2014.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wilson T.J., Stetler W.R., Al-Holou W.N., Sullivan S.E. Comparison of the accuracy of ventricular catheter placement using freehand placement, ultrasonic guidance, and stereotactic neuronavigation. J. Neurosurg. 2013;119:66–70. doi: 10.3171/2012.11.JNS111384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Keane, J.R., and Angeles, L. Cisternal Puncture Complications Treatment of Coccidioidal Meningitis with Amphotericin B.Calif. Med.,119(3), p.10 [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 53.Luján Feliu-Pascual A., Garosi L., Dennis R., Platt S. Iatrogenic brainstem injury during cerebellomedullary cistern puncture. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2008;49:467–471. doi: 10.1111/J.1740-8261.2008.00410.X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Brocal J., Guevar J., Stalin C., Durand A., Gutierrez-Quintana R. Intra-parenchymal brainstem haemorrhage secondary to iatrogenic needle injury after a parenteral injection in a cat. JFMS Open Rep. 2016;2 doi: 10.1177/2055116916631562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Brown K., Selfridge J., Lagger S., Connelly J., De Sousa D., Kerr A., Webb S., Guy J., Merusi C., Koerner M.V., Bird A. The molecular basis of variable phenotypic severity among common missense mutations causing Rett syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016;25:558–570. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hinderer C., Katz N., Buza E.L., Dyer C., Goode T., Bell P., Richman L.K., Wilson J.M. Severe Toxicity in Nonhuman Primates and Piglets Following High-Dose Intravenous Administration of an Adeno-Associated Virus Vector Expressing Human SMN. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018;29:285–298. doi: 10.1089/hum.2018.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hordeaux J., Buza E.L., Dyer C., Goode T., Mitchell T.W., Richman L., Denton N., Hinderer C., Katz N., Schmid R., et al. Adeno-Associated Virus-Induced Dorsal Root Ganglion Pathology. Human Gene Therapy. 2020;31:808–818. doi: 10.1089/HUM.2020.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.AAV9 U7snRNA Gene Therapy to Treat Boys With DMD Exon 2 Duplications. - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04240314?term=AAV9&draw=2&rank=4
- 59.Gene Therapy for Children With Variant Late Infantile Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis 6 (vLINCL6) Disease - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02725580?term=AAV9&draw=2&rank=5
- 60.Single-Dose Gene Replacement Therapy Clinical Trial for Patients With Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1 - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03461289?term=AAV9&draw=2&rank=7
- 61.Fu H., Muenzer J., Samulski R.J., Breese G., Sifford J., Zeng X., McCarty D.M. Self-complementary adeno-associated virus serotype 2 vector: global distribution and broad dispersion of AAV-mediated transgene expression in mouse brain. Mol. Ther. 2003;8:911–917. doi: 10.1016/J.YMTHE.2003.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Gao G., Luk †, Alvira M.R., Lu Y., Calcedo R., Zhou X., Wilson J.M., Wilson J.M., Program G.T. Clades of Adeno-Associated Viruses Are Widely Disseminated in Human Tissues. J. Virol. 2004;78:6381–6388. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.12.6381-6388.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ayuso E., Mingozzi F., Bosch F. Production, Purification and Characterization of Adeno-Associated Vectors. Curr. Gene Ther. 2010;10:423–436. doi: 10.2174/156652310793797685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Buchovecky C.M., Turley S.D., Russell D.W., Kyle S.M., McDonald J.G., Liu B., Pieper A.A., Huang W., Katz D.M., Brown H.M., et al. A suppressor screen in Mecp2 mutant mice implicates cholesterol metabolism in Rett syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2013;45:1013–1020. doi: 10.1038/ng.2714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All available materials described in this study may be obtained through material transfer agreement.