Abstract
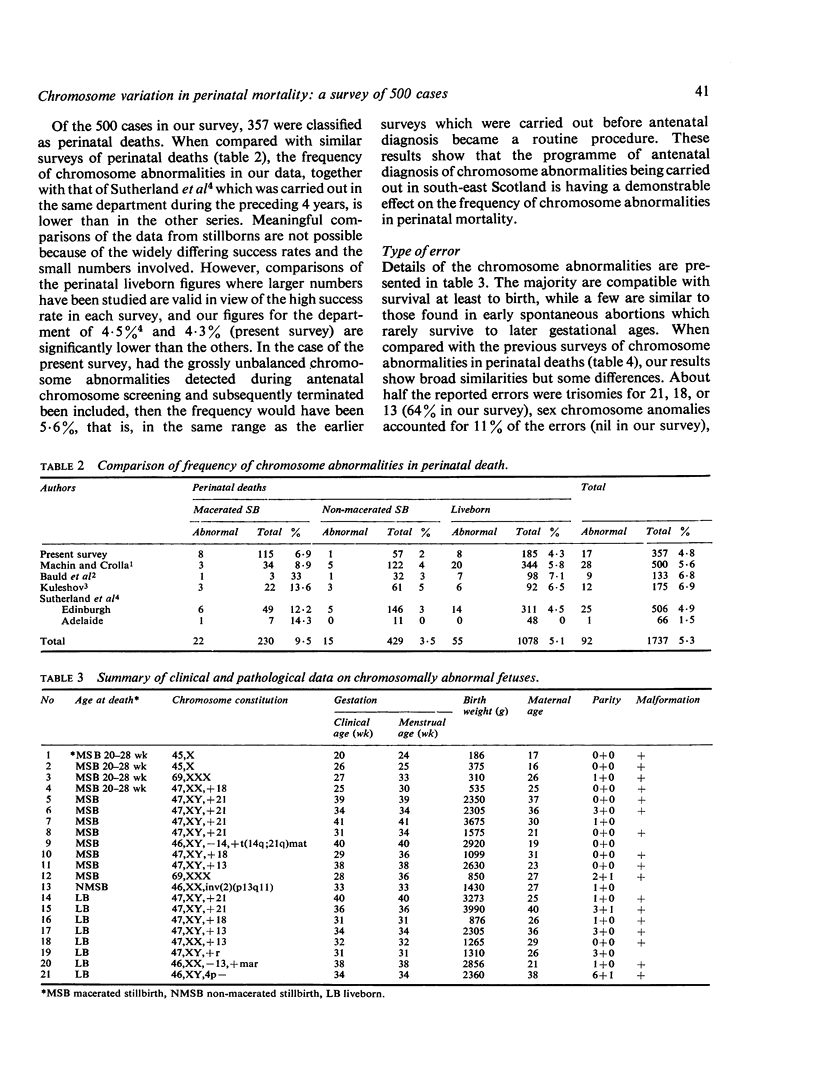
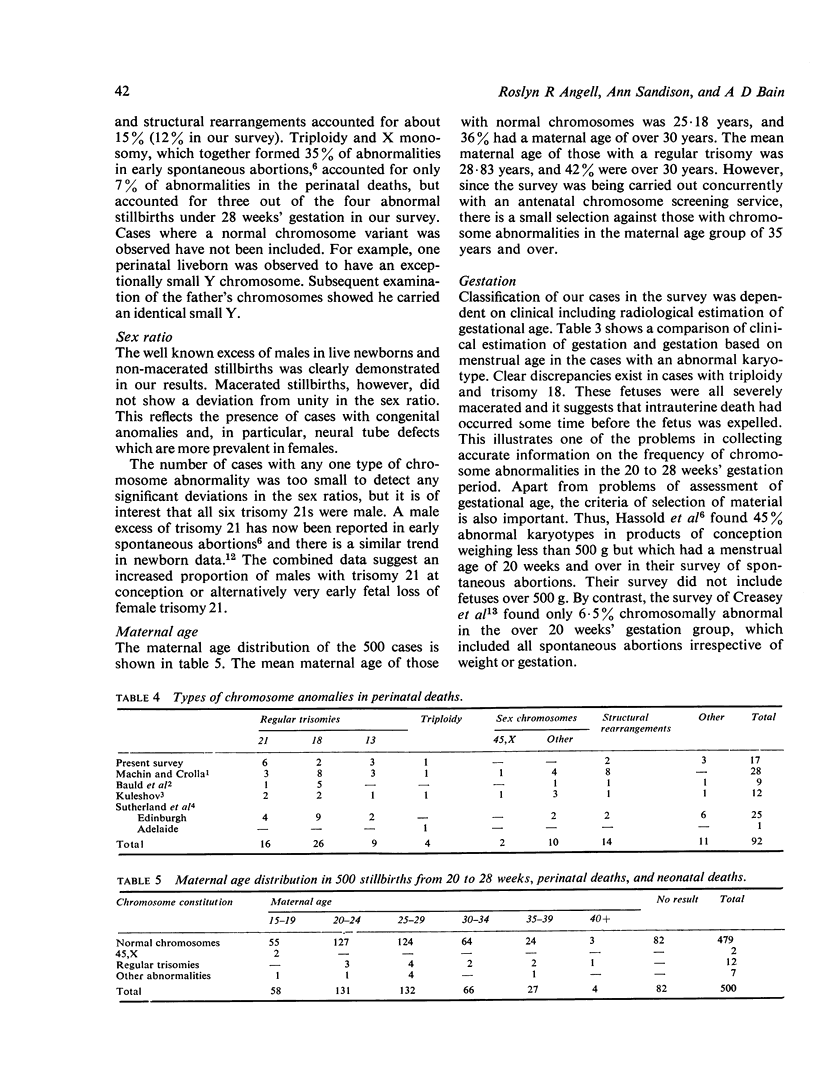
The results of chromosome analyses on 500 cases of perinatal deaths are reported. It was found that 4.8% were chromosomally abnormal, but 90% of the chromosomally abnormal were either clinically malformed or macerated fetuses. Of the macerated fetuses, 9% were chromosomally abnormal and of these 33% had trisomy 21. The data suggest that the high loss of trisomy 21 fetuses in later stages of pregnancy is of an order sufficient to explain the discrepancy between the higher numbers of trisomy 21 detected during amniotic fluid sampling than found at birth in women of 35 years and over.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauld R., Sutherland G. R., Bain A. D. Chromosome studies in investigation of stillbirths and neonatal deaths. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Oct;49(10):782–788. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.10.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boué J. G., Boué A. Chromosomal anomalies in early spontaneous abortion. (Their consequences on early embryogenesis and in vitro growth of embryonic cells). Curr Top Pathol. 1976;62:193–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasy M. R., Crolla J. A., Alberman E. D. A cytogenetic study of human spontaneous abortions using banding techniques. Hum Genet. 1976 Feb 29;31(2):177–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00296145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans H. J. Chromosome anomalies among livebirths. J Med Genet. 1977 Oct;14(5):309–312. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.5.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith M. A. Letter: Prospective data on risk of Down syndrome in relation to maternal age. Lancet. 1976 Jul 31;2(7979):252–252. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARNDEN D. G. A human skin culture technique used for cytological examinations. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Feb;41:31–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T., Chen N., Funkhouser J., Jooss T., Manuel B., Matsuura J., Matsuyama A., Wilson C., Yamane J. A., Jacobs P. A. A cytogenetic study of 1000 spontaneous abortions. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Oct;44(Pt 2):151–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb00955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B. Rates of Down's syndrome in live births and at midtrimester amniocentesis. Lancet. 1978 May 13;1(8072):1053–1054. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90787-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. B. Spontaneous deaths of fetuses with chromosomal abnormalities diagnosed prenatally. N Engl J Med. 1978 Nov 9;299(19):1036–1038. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197811092991903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuleshov N. P. Chromosome anomalies of infants dying during the perinatal period and premature newborn. Hum Genet. 1976 Feb 29;31(2):151–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00296143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machin G. A., Crolla J. A. Chromosome constitution of 500 infants dying during the perinatal period. With an appendix concerning other genetic disorders among these infants. Humangenetik. 1974;23(3):183–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00285104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R., Carter R. F., Bauld R., Smith I. I., Bain A. D. Chromosome studies at the paediatric necropsy. Ann Hum Genet. 1978 Oct;42(2):173–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1978.tb00647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


