Abstract
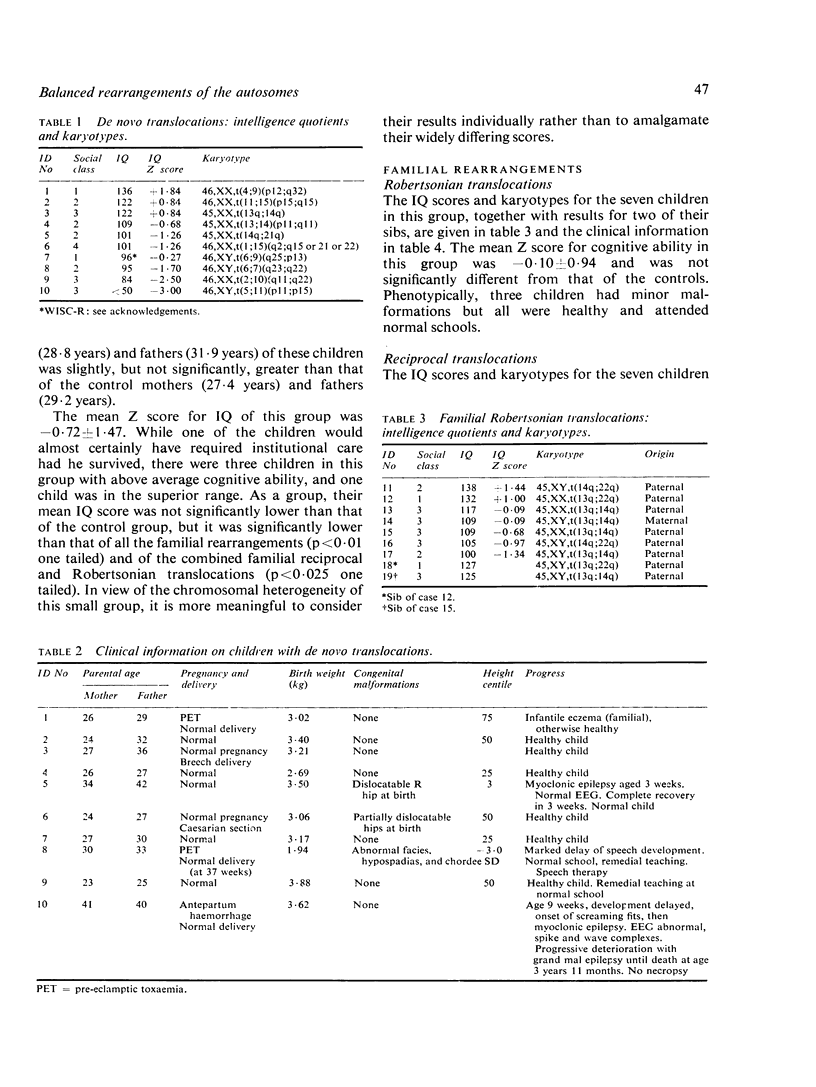
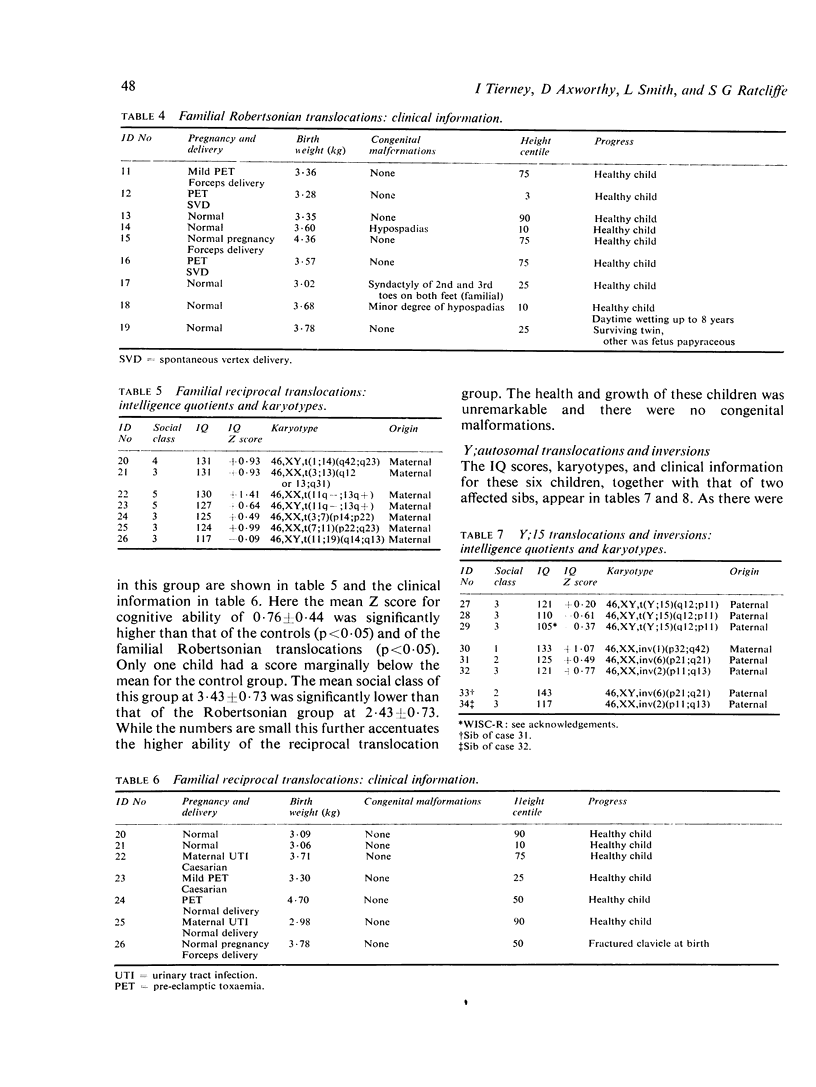
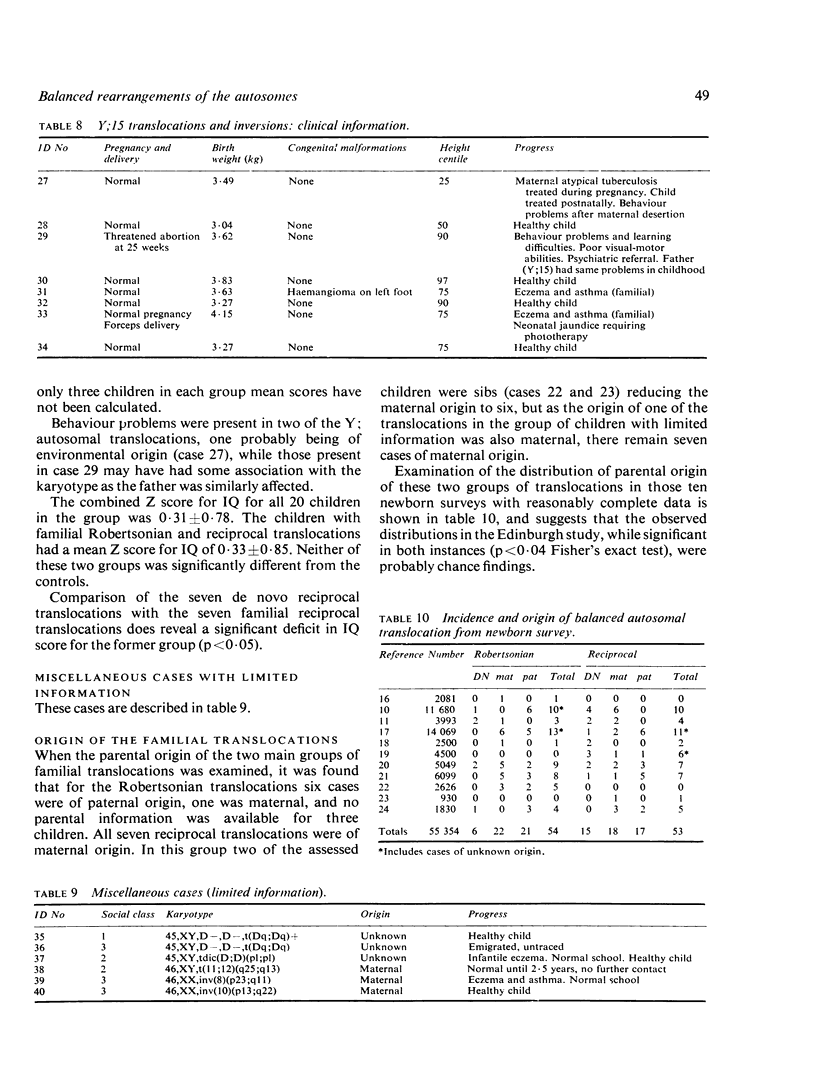
Thirty-six infants were identified by cytogenetic screening at birth as having balanced rearrangements of their autosomes, and 30 of them took part in a longitudinal study of their development, together with four of their affected sibs. With the exception of one child with a de novo reciprocal translocation who died, all children attended normal schools. Congenital malformations and short stature were present in only one child who had a de novo reciprocal translocation. The IQ scores of the 10 children with de novo translocations were significantly lower than those of the 20 children with familial translocations, but there were children in the de novo group of above average intelligence. Children with familial reciprocal translocations had significantly higher IQ scores than both the Robertsonian translocations and the controls, but the numbers in each category were small and a variety of different chromosomes were involved.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bochkov N. P., Kuleshov N. P., Chebotarev A. N., Alekhin V. I., Midian S. A. Population cytogenetic investigation of newborns in Moscow. Humangenetik. 1974 May 17;22(2):139–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00278453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breg W. R., Miller D. A., Allderdice P. W., Miller O. J. Identification of translocation chromosomes by quinacrine fluorescence. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Jun;123(6):561–564. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110120085007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckton K. E., O'Riordan M. L., Ratcliffe S., Slight J., Mitchell M., McBeath S., Keay A. J., Barr D., Short M. A G-band study of chromosomes in liveborn infants. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Jan;43(3):227–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans J. A., Canning N., Hunter A. G., Martsolf J. T., Ray M., Thompson D. R., Hamerton J. L. A cytogenetic survey of 14,069 newborn infants. III. an analysis of the significance and cytologic behavior of the Robertsonian and reciprocal translocations. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;20(1-6):96–123. doi: 10.1159/000130843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich U., Nielsen J. Chromosome studies in 5,049 consecutive newborn children. Clin Genet. 1973;4(4):333–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., van den Berghe H. Possible excess of mental handicap and congenital malformations in autosomal reciprocal translocations. Ann Genet. 1979;22(3):125–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funderburk S. J., Spence M. A., Sparkes R. S. Mental retardation associated with "balanced" chromosome rearrangements. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Mar;29(2):136–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamerton J. L., Canning N., Ray M., Smith S. A cytogenetic survey of 14,069 newborn infants. I. Incidence of chromosome abnormalities. Clin Genet. 1975 Oct;8(4):223–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1975.tb01498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansteen I. L., Varslot K., Steen-Johnsen J., Langård S. Cytogenetic screening of a new-born population. Clin Genet. 1982 May;21(5):309–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A. Correlation between euploid structural chromosome rearrangements and mental subnormality in humans. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):164–165. doi: 10.1038/249164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Matsuura J. S., Mayer M., Newlands I. M. A cytogenetic survey of an institution for the mentally retarded: I. Chromosome abnormalities. Clin Genet. 1978 Jan;13(1):37–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1978.tb04127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Melville M., Ratcliffe S., Keay A. J., Syme J. A cytogenetic survey of 11,680 newborn infants. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 May;37(4):359–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. C., Gedeon M. M., Griffith P., Smink W. K., Newton D. R., Wilkie L., Sewell L. M. Chromosome analysis on 930 consecutive newborn children using quinacrine fluorescent banding technique. Hum Genet. 1976 Mar 12;31(3):315–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00270861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Ohno M., Takada M., Kato Y., Nishida M., Jobo T., Adachi H., Taguchi A. A cytogenetic survey of consecutive liveborn infants-incidence and type of chromosome abnormalities. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1978 Sep;23(3):217–224. doi: 10.1007/BF01872471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Krag-Olsen B. Follow-up of 32 children with autosomal translocations found among 11,148 consecutively newborn children from 1969 to 1974. Clin Genet. 1981 Jul;20(1):48–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb01806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Sillesen I. Incidence of chromosome aberrations among 11148 newborn children. Humangenetik. 1975 Oct 20;30(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00273626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergovich F., Valentine G. H., Chen A. T., Kinch R. A., Smout M. S. Chromosome aberrations in 2159 consecutive newborn babies. N Engl J Med. 1969 Apr 17;280(16):851–855. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196904172801602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speed R. M., Johnston A. W., Evans H. J. Chromosome survey of total population of mentally subnormal in North-East of Scotland. J Med Genet. 1976 Aug;13(4):295–306. doi: 10.1136/jmg.13.4.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tharapel A. T., Summitt R. L., Wilroy R. S., Jr, Martens P. Apparently balanced de novo translocations in patients with abnormal phenotypes: report of 6 cases. Clin Genet. 1977 Apr;11(4):255–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. Superior intelligence of children blinded from retinoblastoma. Arch Dis Child. 1968 Apr;43(228):204–210. doi: 10.1136/adc.43.228.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


