Abstract
Background
Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) measures are essential in economic evaluation, but sometimes primary sources are unavailable, and information from secondary sources is required. Existing HRQoL UK/US catalogues are based on earlier diagnosis classification systems, amongst other issues. A recently published Danish catalogue merged EQ-5D-3L data from national health surveys with national registers containing patient information on ICD-10 diagnoses, healthcare activities and socio-demographics.
Aims
To provide (1) UK/US EQ-5D-3L-based HRQoL utility population catalogues for 199 chronic conditions on the basis of ICD-10 codes and health risks and (2) regression models controlling for age, sex, comorbidities and health risks to enable predictions in other populations.
Methods
UK and US EQ-5D-3L value sets were applied to the EQ-5D-3L responses of the Danish dataset and modelled using adjusted limited dependent variable mixture models (ALDVMMs).
Results
Unadjusted mean utilities, percentiles and adjusted disutilities based on two ALDVMMs with different control variables were provided for both countries. Diseases from groups M, G, and F consistently had the smallest utilities and the largest negative disutilities: fibromyalgia (M797), sclerosis (G35), rheumatism (M790), dorsalgia (M54), cerebral palsy (G80-G83), post-traumatic stress disorder (F431), dementia (F00-2), and depression (F32, etc.). Risk factors, including stress, loneliness, and BMI30+, were also associated with lower HRQoL.
Conclusions
This study provides comprehensive catalogues of UK/US EQ-5D-3L HRQoL utilities. Results are relevant in cost-effectiveness analysis, for NICE submissions, and for comparing and identifying facets of disease burden.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40273-023-01285-4.
Key Points for Decision-Makers
| Two main types of catalogues are supplied for both the UK and the USA: 1. unadjusted sample mean utilities for 199 chronic conditions and health risks and 2. corresponding regression models for the USA and UK that can be used to make utility predictions in other populations. |
| Results indicate that health-related quality of life (HRQoL) varies across disease groups but is lowest for renal disease, mental and behavioural disorders, some cancers, blood diseases, digestive system diseases, and nervous system diseases. |
| Health risks and lifestyle factors, including loneliness, perceived stress, and high BMIs, are associated significantly with low HRQoL after controlling for chronic diseases. |
Introduction
Economic evaluations are routinely used in appraisals of health technologies, such as those used by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in England or the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) in the USA [1, 2]. These economic evaluations often measure benefits through the quality-adjusted life-year (QALY). The QALY combines quality and length of life considerations in a single measure [3, 4], and is usually based on generic patient-reported outcome measures such as EQ-5D. The EQ-5D is considered the most widely used generic health utility measure in the world [4], and it is the preferred health benefit measure of NICE for its technology appraisals [1]. It is applied in numerous research and clinical practice settings, such as cost-utility analysis (CUA), clinical trials, patient surveillance or monitoring, and population health measurement [5–8].
The EQ-5D instrument describes health using five dimensions: mobility, self-care, usual activities, pain/discomfort and anxiety/depression. There are currently two instrument versions: the original EQ-5D version, now named EQ-5D-3L [9], and the newer EQ5D-5L version [10]. Both include the same five health dimensions but differ in the number of levels of severity. In EQ-5D-3L, each dimension has three possible levels (no problems, some problems, extreme problems), and it can describe 243 unique health states [9, 11–13]. EQ-5D-5L incorporates two additional levels in each dimension to improve the sensitivity of the original three-level version. Separate studies have estimated country-specific utility value sets for the health states described by both instruments on the basis of general population values [11–15]. Utility values are anchored at an upper value of one equivalent to perfect health and zero for states considered equivalent to being ‘dead’. Negative values representing health states considered worse than dead are also possible [16]. NICE currently recommends using the three-level (3L) version in the UK [17]. However, mapping algorithms (crosswalks) exist to convert EQ-5D-3L to EQ-5D-5L values [18–20] which will allow for the translation of the EQ-5D-3L values in this catalogue to EQ-5D-5L utilities once the new UK EQ-5D-5L value set is released and additional countries, such as the USA, are included.
The importance of ensuring comparability across economic evaluation studies of technologies and over time has been stressed by health economists and organisations such as the Panel on Cost-Effectiveness in Health and Medicine (PCEHM) and NICE [17, 21–24]. The PCEHM recommended ‘the collection of a national catalogue of preference weights that could be used by CEA researchers without the burden of primary data collection’ given the large variability in the literature of utility values associated with different medical conditions [24, 25]. In response, Sullivan et al. (2006, 2011) published two separate EQ-5D-3L catalogues for the USA and the UK [24, 26–28], both based on regression estimation using representative US samples of the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS). They included 157 mostly self-reported chronic conditions classified according to the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision (ICD-9). The US catalogue was based on pooled 2000–2002 MEPS data and used the US utility value set [12]. The UK catalogue included an additional year of the MEPS dataset (2000–2003) and used the UK EQ-5D-3L value set [11]. The statistical models included gender, age, income, ethnicity, education, the number of comorbidities and the primarily self-reported chronic conditions but did not incorporate health risks. A number of less comprehensive catalogues are also available. For example, Finland (2006) [29] and Korean (2009) catalogues cover fewer than 30 conditions [30]. In 2019, a systematic review of 207 studies collated EQ-5D-3L estimates among fifteen ICD-10 disease groups [31]. However, the included studies used value sets for different countries (some failed to report the specific value set used) and even different versions of EQ-5D. These issues, coupled with heterogeneity in the quality of the studies, limit the practical usefulness of the estimates found in the review. Recently, a Danish study published a catalogue of Danish EQ-5D-3L preference scores for 199 chronic conditions based on newer, improved methodology, including the use of ICD-10-based conditions and regression models appropriate for EQ-5D [32, 33].
The current study is based on and broadly replicates the most recent Danish study, but applies the UK and US EQ-5D-3L value sets to convert the responses to the EQ-5D-3L instrument into utility scores to enable the use of these data in the UK and the USA. The objectives are: (1) to create population-level off-the-shelf catalogues of UK and US EQ-5D-3L preference-based scores for 199 ICD-10 defined chronic conditions to improve on existing UK and US catalogues and (2) to provide two separate statistical models to allow researchers to predict utilities in their own population of interest for any combination of chronic disease. This first catalogue supplies unadjusted, national sample population estimates of UK and US norm-based mean utilities for the 199 chronic conditions, socioeconomic covariates, and health risks. A second catalogue is also provided as a reference, and it presents UK and US regression-based utility estimates and marginal effects for the same 199 chronic diseases, socioeconomic covariates and health risks, adjusting for the sample composition allowing for direct comparisons across chronic diseases for the same representative individual. To construct this second catalogue, two alternative EQ-5D-3L model specifications are estimated, one with a core set of covariates and the second one including additional health risks and socioeconomic controls. To supplement the second catalogue, we also provide a Stata do file and a user guide in the online supplementary materials to enable health professionals to estimate EQ-5D-3L in their specific settings and populations. In combination with previous publications and details on the prevalence [34], multimorbidity associations [35], socioeconomic differences [36], and health risks disparities [37] of the same 199 chronic conditions, these estimates can provide valuable information for future resource allocation in the UK and the USA.
In common with the recently published Danish catalogue [32], there are several important differences with earlier studies. First, most previous studies rely partly on self-reported health conditions, which raises questions about accuracy [38–41]. Second, we use the newer ICD-10 classification system and include 199 ICD-10-based chronic conditions. Third, behavioural risk factors such as smoking, body mass index (BMI), stress and social networks have been suggested as potentially necessary controls [42]. These are missing from existing catalogues but are found important in explaining EQ-5D-3L in the Danish catalogue. Fourth, acknowledging the biases caused by model misspecification and the now well-documented idiosyncrasies of the distribution of EQ-5D, we use the adjusted limited dependent variable mixture model (ALDVMM) to model EQ-5D [43–48]. Using traditional linear models, preceding catalogues have been mainly developed to provide population-based utility estimates of individual chronic conditions and cannot be directly transferred to the populations of interest in economic evaluations where decrements in utility from developing a new chronic condition in these less healthy populations would not be expected to mirror the decrements observed in a healthier population. This has led to research into possible ways of combining utilities for individual chronic diseases estimated on separate disease-specific samples (multiplicative, additive and minimum estimators are a few common choices) [49–52]. However, the ALDVMM, a nonlinear model reflecting the characteristics of EQ-5D utility data, allows utility decrements to be dependent on the combinations of comorbidities and other covariates in the model, enabling researchers to estimate realistic, real-world multimorbid health states of their specific interest.
Methods
Data
Following Sullivan et al. [28], we use the responses from a large representative sample from a single country (Denmark) and derive the associated utility values using each country’s value sets. This is in line with patient reporting from multinational clinical trials where the same value set is used across data from all countries and mapping studies of EQ-5D, which often apply utility value sets that differ from the country’s data collection when, for example, country-specific population data are not accessible for researchers. The dataset combines three national health survey samples with seven national registers containing patient-level information on diagnoses, healthcare activity and socio-demographics using a civil registration number that uniquely identifies Danish citizens [33].
A brief summary of the data is presented below. Full details of the methodology, samples, variables, weighting and data handling, and content of all registers can be found in these references [32, 33, 53–55]. Details on variable names can also be found in the online Supplementary Material 1 (Appendix 1). Responses to the five items of the EQ-5D-3L questionnaire were included in three of the Danish National Public Health Survey (NPHS) samples [53, 56–58], and 55,616 unique responses were obtained using the last two consecutive waves (2010 and 2013), which incorporated the EQ5D-3L questionnaire [53]. Details on dataset and respondent characteristics can be found in Table 1 of an earlier publication [32] and in the online Supplementary Material 1 (Appendix 2) in the current study. The survey data based on randomly assigned nationals comprised self-reported data on HRQoL, health behaviours (e.g. lifestyle factors), BMI, education, stress, loneliness, etc. Data from the surveys were combined with patient-level register data on diagnoses, healthcare activity, and socio-demographics from seven national registers based on the unique civil registration number [34, 54, 55, 57, 59, 60]. The registers contained information from somatic [61] and psychiatric hospital contacts [62], primary healthcare [63], prescribed medicines [64], gender, age, and ethnicity,1 and residence place [65]. The aim was to derive each respondent’s ICD-10-based doctor-reported diagnosis, medicine and other relevant variables from identifying chronic conditions. A medical review team identified and grouped the chronic conditions from ICD-10 codes, and definitions, algorithms and methodology identifying the chronic conditions were clinically validated separately [54, 55]. EQ-5D-3L responses were converted to utility values using Dolan’s (1997), and Shaw et al. (2005) value sets for EQ-5D-3L for the UK and USA, respectively [11, 12].
Statistical analysis
We first compute sample means, medians and interquartile ranges for each country and the corresponding standard errors of EQ-5D-3L for the 199 chronic conditions and other socio-economic and health risk variables. These statistics are thus not adjusted for the potentially different sample composition of the chronic conditions groups but provide estimates of the population values instead.
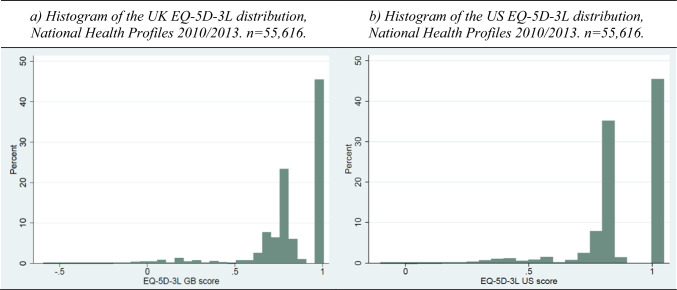
Subsequently, we conduct regression analyses controlling for several variables, as detailed below. Utilities originating from measures such as the EQ-5D have specific characteristics that challenge statistical regression modelling. The values are bounded between the minimum value, which differs by country, and the value of one (or full health). The data distribution is often multimodal and highly skewed, with a large group of observations around one, followed by a gap to the first possible utility value below full health [44, 45]. The minimum values in the UK and US EQ-5D-3L utility scores are –0.594 and –0.102, and the highest utility scores below one are 0.883 and 0.86, respectively. Figure 1 shows histograms of the distributions of EQ-5D-3L using the UK and US value sets. There are a large number of individuals in full health. In both cases, the distributions present two rough additional modes and skewness.
Fig. 1.
Histograms of EQ-5D-3L using the UK and US value sets
The ALDVMM was developed to model the UK EQ-5D-3L value set utility scores. It has been shown to offer several advantages and perform better than standard models, which do not take into account the characteristics of utility data when modelling not only EQ-5D-3L, but other generic preference-based measures such as EQ-5D-5L, SF-6D and HUI3 as well [43–48, 66]. The ALDVMM is a very flexible semi-parametric model which uses mixtures of Tobit-like components and can accommodate all the idiosyncrasies of the EQ-5D-3L distribution, such as the upper and lower boundaries, the mass of observations at full health, the gap between full health and the next feasible value in the value set, and can approximate the skewness and multimodality often present in this type of data.
Estimating mixture models is challenging, but even more so for extensive models such as the current study. They require a comprehensive search procedure to identify the global maximum because the likelihood is not globally concave. At the same time, the number of components in the mixture is unknown and requires selection as well. This involves estimating models with an increasingly higher number of components and using graphical methods and standard fit statistics to select the optimal model [66]. We used the community-contributed Stata ALDVMM command available for free download and published in the Stata Journal [44, 45].
Two separate ALDVMM regression models were estimated as follows for each of the UK and US EQ-5D-3L models:
Base model: EQ-5D-3L as a function of the 199 chronic conditions, sex, age, samples (to adjust for regional differences) and the number of comorbidities. This model is helpful for economic evaluations in which the extra controls included in the full model below are not available or required.
Full model: includes additional controls to adjust for common health risks and socioeconomic variables. The added variables are: family equalised income (£ and $), education (no education or training, students/training, short, middle bachelor equivalent, or higher education such as a master’s degree or higher, ethnicity origin (Danish, western or non-western), partnership status (partner or not), home living children (yes/no), social network (often feeling lonely or not), perceived stress (Cohen’s Perceived Stress Scale, 20% most stressed or not), BMI groups (< 18.5; 18.5–25; > 25 < 30; ≥ 30 < 35; ≥ 35), daily smoking (yes/no), alcohol intake grater national recommendations (yes/no), nationally recommended exercise and fruit intake (yes/no), SF-12 self-reported general health [67] (‘excellent’; ‘very good’; ‘good’; ‘fair’; ‘poor’; ‘missing’), and self-reported long-term illness or disability (‘none’; ‘yes’). See the online Supplementary Material 1 (Appendix 1) for model variable notations and details on model specifications.
Quadratic terms for family-equalised income and age were included in all estimated models where the levels of those variables were included.2 Non-response and population weights standardising by age, sex and education were used when calculating EQ-5D-3L sample statistics. The estimated ALDVMMs did not use weights but incorporated controls for variables comparable to those used in the weighting procedure.
After model estimation, marginal effects (ME) for the chronic conditions and other variables included in the model were also calculated. The structure of linear regression models implies that the expected decrease in EQ-5D-3L due to developing a chronic condition (the ME) is the same for every individual regardless of, for example, how many other chronic conditions the individual has. This ME is simply the coefficient of the chronic condition in the linear regression model. However, in nonlinear models, such as the ALDVMM, the ME is a function of that specific health condition and all the other covariates incorporated in the model, such as the presence of other chronic conditions, age, sex, etc. In this case, the decrease in EQ-5D due to a new chronic condition will be different for individuals with no previous chronic conditions and those with other chronic conditions already present. A user-written program was developed to handle the links between the 199 chronic conditions variables and the variable accounting for the number of comorbidities.
Preliminary data management of registers and surveys was conducted in SAS9.4 in a secure server at Statistics Denmark research server facilities following legal regulations. Data analysis was carried out in STATA15 using the same secure research servers. Online supplemental materials are provided, including documentation and Stata programs to facilitate the use of the estimated models by analysts to calculate predictions. The parameter estimates and the (co)variance matrices of the models are also made available to allow the use of probabilistic sensitivity analysis within economic evaluations [68].
Results
Sample-based estimates of the EQ-5D-3L
Table 1 provides a one-page overview of the UK and US EQ-5D-3L sample mean scores for the overall sample and sex and age intervals for 20 chronic disease groups, overweight and commonly prescribed medicines. The overall sample means of EQ-5D-3L utility scores are 0.829 and 0.869 for the UK and USA, respectively. These differences reflect the differences in the EQ-5D-3L countries’ value sets. Among the seven highest prevalent disease groups (E, G, H, I, J; M, F), chronic diseases within the respiratory system [J; scores 0.776 (UK); 0.831 (USA)], endocrine disorders [E; scores 0.742 (UK); 0.807 (USA)], diseases in the circulatory system [I; scores 0.741(UK); 0.807 (USA)] and diseases of the eye and adnexa [H; scores 0.736 (UK); 0.803 (USA)] had the highest HRQoL sample mean scores. Furthermore, highly prevalent diseases of the musculoskeletal system [M; scores 0.705 (UK); 0.782 (USA)], diseases of the nervous system [G; scores 0.697 (UK); 0.775 (USA)] and mental conditions [F; scores 0.651 (UK); 0.742 (USA)] had the lowest EQ-5D-3L sample mean scores. Finally, less prevalent disease groups such as genitourinary conditions [N; scores 0.625 (UK); 0.725 (USA)], benign neoplasm and diseases of the blood [group D; scores 0.687 (UK); 0.768 (USA)], and diseases in the digestive system [group K; scores 0.692 (UK); 0.773 (USA)] showed even lower HRQoL scores. In all cases, utilities based on the US value set were higher than those based on the UK value set. Although the differences in utilities between the UK and the USA were not constant, the ranking according to utilities was preserved across these broad disease groups. The sample of men appeared to have higher mean scores than the sample of women in most cases, and utilities tended to decrease with age in both the UK and US samples.
Table 1.
Overview of EQ-5D-3L UK and US sample utility scores, mean age and mean number of chronic conditions (NCC) across overall disease groups, prescribed medicine, gender and age
| Name | ICD-10 or medication code | Population frequencies and meansa | Sample EQ-5D-3L UK mean scores | Sample EQ-5D-3L US mean scores | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Age mean | NCC mean | All | Men | Women | Age 16–44 | Age 45–74 | Age 75+ | All | Men | Women | Age 16–44 | Age 45–74 | Age 75+ | ||
| B—viral hepatitis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease | B18, B20–B24 | 31 | 43.5 | 2.9 | 0.726 | 0.714 | 0.738 | 0.713 | 0.740 | n/a | 0.799 | 0.789 | 0.808 | 0.793 | 0.805 | n/a |
| C—malignant neoplasms | C00-C99; D32–D33; D35.2–D35.4; D42–D44 | 2947 | 64.7 | 5.3 | 0.736 | 0.752 | 0.724 | 0.814 | 0.754 | 0.659 | 0.803 | 0.814 | 0.794 | 0.856 | 0.816 | 0.749 |
| D—in situ, benign and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behaviour and diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs, etc. | D00-D09; D55–D59; D60–D67; D80–D89 | 1254 | 59.2 | 6.0 | 0.687 | 0.662 | 0.701 | 0.812 | 0.697 | 0.530 | 0.768 | 0.814 | 0.794 | 0.856 | 0.775 | 0.658 |
| E—endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases | E00–E14; E20–E29; E31–35; E70–E78; E84–E85; E88–E89 | 12,412 | 63.5 | 4.9 | 0.742 | 0.762 | 0.725 | 0.788 | 0.757 | 0.674 | 0.807 | 0.821 | 0.795 | 0.839 | 0.818 | 0.759 |
| G—Diseases of the nervous system | G00–G14; G20–G32; G35–G37; G40–47; G50–64; G70–73; G80–G83; G90–G99 | 6698 | 55.1 | 4.8 | 0.697 | 0.708 | 0.690 | 0.752 | 0.694 | 0.586 | 0.775 | 0.783 | 0.771 | 0.813 | 0.774 | 0.697 |
| H—diseases of the eye and adnexa and diseases of the ear and mastoid process | H02–H06; H17–H18; H25–H28; H31–H32; H34–H36; H40–55; H57; H80, H810; H93, H90–H93 | 6309 | 65.8 | 5.2 | 0.736 | 0.767 | 0.705 | 0.819 | 0.765 | 0.659 | 0.803 | 0.824 | 0.781 | 0.861 | 0.823 | 0.749 |
| I—diseases of the circulatory system | I05–I06; I10–28; I30–33; I36–141; I44–I52; I60–I88; I90–I94; I96–I99 | 16,990 | 62.9 | 4.6 | 0.741 | 0.760 | 0.726 | 0.798 | 0.756 | 0.668 | 0.807 | 0.820 | 0.796 | 0.847 | 0.817 | 0.755 |
| J—diseases of the respiratory system | J30.1; J40–J47; J60–J84; J95, J97–J99 | 14,087 | 51.5 | 4.0 | 0.776 | 0.803 | 0.757 | 0.845 | 0.753 | 0.641 | 0.831 | 0.851 | 0.818 | 0.880 | 0.815 | 0.736 |
| K—Diseases of the digestive system | K25–K27; K40, K43, K50–52; K58–K59; K71–K77; K86–K87 | 4462 | 56.8 | 5.2 | 0.692 | 0.721 | 0.669 | 0.780 | 0.692 | 0.558 | 0.773 | 0.792 | 0.756 | 0.833 | 0.772 | 0.678 |
| L—diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue | L40 | 722 | 56.0 | 4.3 | 0.749 | 0.769 | 0.730 | 0.832 | 0.733 | 0.647 | 0.813 | 0.827 | 0.799 | 0.869 | 0.804 | 0.738 |
| M—diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | M01–M25: M30–M36; M40–M54; M60.1–M99 | 13,163 | 57.0 | 4.4 | 0.705 | 0.732 | 0.683 | 0.754 | 0.704 | 0.630 | 0.782 | 0.801 | 0.767 | 0.817 | 0.782 | 0.729 |
| N—diseases of the genitourinary system | N18 | 224 | 66.3 | 8.1 | 0.625 | 0.656 | 0.579 | 0.616 | 0.653 | 0.592 | 0.725 | 0.746 | 0.695 | 0.727 | 0.744 | 0.700 |
| Q—congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities | Q00–Q56; Q60–Q99 | 1323 | 44.1 | 3.7 | 0.782 | 0.807 | 0.764 | 0.833 | 0.730 | 0.651 | 0.836 | 0.854 | 0.823 | 0.872 | 0.799 | 0.742 |
| F—mental and behavioural disorders | F00–99 | 6106 | 50.7 | 4.6 | 0.651 | 0.665 | 0.642 | 0.711 | 0.636 | 0.504 | 0.742 | 0.750 | 0.736 | 0.782 | 0.733 | 0.639 |
| Diagnosed overweight, admitted | E66 (doctor diagnosed) | 2761 | 46,2 | 3.6 | 0.726 | 0.683 | 0.737 | 0.780 | 0.671 | 0.601 | 0.797 | 0.769 | 0.805 | 0.835 | 0.760 | 0.707 |
| Having no chronic conditions | – | 18,136 | 37.7 | 0.0 | 0.908 | 0.914 | 0.900 | 0.913 | 0.900 | 0.828 | 0.926 | 0.931 | 0.920 | 0.930 | 0.920 | 0.868 |
| Having one or more chronic conditions | – | 37,480 | 53.2 | 3.2 | 0.783 | 0.803 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 0.777 | 0.687 | 0.836 | 0.850 | 0.824 | 0.867 | 0.832 | 0.768 |
| Depression medicineb | ATC: N06A | 5835 | 52.5 | 4.5 | 0.620 (0.0049) | 0.620 | 0.620 | 0.663 | 0.618 | 0.507 | 0.720 (0.0033) | 0.720 | 0.720 | 0.749 | 0.720 | 0.641 |
| Antipsychotic medicineb | ATC: N05A | 1127 | 53.2 | 5.5 | 0.559 (0.0123) | 0.576 | 0.546 | 0.576 | 0.575 | 0.445 | 0.678 (0.0081) | 0.688 | 0.671 | 0.690 | 0.689 | 0.598 |
| Indication prescribed anxiety medicineb | All prescriptions with indication codes 163 or 371 (for anxiety) | 1035 | 49.3 | 4.4 | 0.607 (0.0115) | 0.614 | 0.604 | 0.634 | 0.613 | 0.458 | 0.711 (0.0075) | 0.714 | 0.709 | 0.728 | 0.717 | 0.609 |
| Heart failure medicationb | ATC: C01AA05, C03, C07 or C09A w.indo code 430 | 58 | 69.6 | 8.0 | 0.607 (0.0396) | 0.631 | 0.571 | n/a | 0.603 | 0.593 | 0.707 (0.0276) | 0.724 | 0.679 | n/a | 0.699 | 0.699 |
| Ischemic heart medicationb | ATC: C01A, C01B, C01D, C01E | 2035 | 72.0 | 6.8 | 0.637 (0.0080) | 0.668 | 0.604 | 0.704 | 0.673 | 0.591 | 0.734 (0.0055) | 0.756 | 0.710 | 0.778 | 0.759 | 0.701 |
| All population | 55,616 | 47.6 | 2.1 | 0.829 | 0.849 | 0.809 | 0.873 | 0.807 | 0.694 | 0.869 | 0.883 | 0.854 | 0.901 | 0.854 | 0.773 | |
n/a not available, all means weighted, n is not weighted. All population estimates in bold
aEstimates adapted from Hvidberg et al. [69]
bTwo-year inclusion times. Standard error (SE) in brackets included only for medicine variables as they are not provided in any other tables
Table 2 presents a more disaggregated level of information and includes the sample mean EQ-5D-3L utility estimates and percentiles, mean age and number of chronic conditions (NCC) of all 199 chronic conditions and socio-economic and health risk variables for the UK and USA, respectively. The ten diseases with the lowest mean EQ-5D-3L scores are systemic sclerosis [M34; scores 0.362; 0.533 (USA)], fibromyalgia [M797; scores 0.369; 0.558 (USA)], unspecified rheumatism [M790; scores 0.390; 0.575 (USA)], dementia [F00, G30 etc.; scores 0.415 (UK); 0.572 (USA)], systemic atrophies [G10–G14, G30–G32; scores 0.475 (UK); 0.618 (USA)], post-traumatic stress disorder [F431; scores 0.482 (UK); 0.627 (USA)], cerebral palsy [G80–G83; scores 0.512 (UK); 0.646 (USA)], other inflammatory spondylopathies [M46; scores 0.522 (UK); 0.661 (USA)], dorsalgia [M54; scores 0.528 (UK); 0.662 (USA)], and spondylosis [M47; scores 0.538 (UK); 0.666 (USA)]. Furthermore, Table 2 presents that mean EQ-5D-3L scores are lower for groups with a higher number of comorbidities [0.908 versus 0.558 (UK); 0.926 versus 0.680 (USA) for 7+ conditions], lower in older age groups [from 0.891 to 0.694 (UK); 0.914 to 0.773 (USA)], lower for the lower educational groups excluding students [ranging from 0.75 to 0.898 (UK); 0.814 to 0.919 (USA)], average HRQoL is lower for women than men [0.809 versus 0.849 (UK); 0.854 versus 0.883 (USA)] and non-western immigrants [0.832 versus 0.758 (UK); 0.871 versus 0.819 (USA)]. Larger differences are found within health risk and lifestyle factors such as loneliness [0.630 versus 0.841 (UK); 0.728 versus 0.877 (USA)], high perceived stress [0.638 versus 0.881 (UK); 0.732 versus 0.906 (USA)], non-exercise [0.690 versus 0.858 (UK); 0.771 versus 0.889 (US)], BMI (normal weight 0.855 (UK); 0.887 (USA) versus BMI 35+ 0.707 (UK); 0.783 (USA)], daily smokers [0.774 versus 0.841 (UK); 0.830 versus 0.878 (USA)], but less so for those reporting excessive alcohol intake [0.813 versus 0.835 (UK); 0.857 versus 0.873 (USA)] and fruit intake below recommendations [0.829 versus 0.847 (UK); 0.869 versus 0.882 (USA)]. These averages do not consider potential differences in the composition of the groups; therefore, part of the differences between groups might be explained by the presence/absence of other comorbidities, health risks, etc. Below we present estimates that adjust for these potential differences.
Table 2.
Sample EQ-5D-3L mean scores, percentiles, n, mean number chronic conditions and percentiles for the 199+ chronic conditions, socioeconomic variables, and health risks for the UK and US
| No | Name of chronic condition or variable | ICD-10 code | Population frequencies and meansA | UK EQ-5D-3L unadjusted sample utilities | US EQ-5D-3L unadjusted sample utilities | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | Mean age | Mean NCC | NCC SE | EQ-5D utility | EQ-5D SE | EQ-5D 25% | EQ-5D 50% | EQ-5D 75% | EQ-5D utility | EQ-5D SE | EQ-5D 25% | EQ-5D 50% | EQ-5D 75% | |||
| B—viral hepatitis and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease | B18, B20–B24 | 31 | 43.5 | 2.9 | 0.2938 | 0.726 | 0.0668 | 0.656 | 0.727 | 1 | 0.799 | 0.0448 | 0.748 | 0.810 | 1 | |
| 1 | Chronic viral hepatitis | B18 | 17 | 44.7 | 2.9 | 0.5118 | 0.755 | 0.0443 | 0.689 | 0.725 | 1 | 0.820 | 0.0324 | 0.767 | 0.800 | 1 |
| 2 | Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease | B20–24 | 14 | 42.4 | 2.8 | 0.3139 | 0.696 | 0.1274 | 0.620 | 0.883 | 1 | 0.778 | 0.0843 | 0.706 | 0.860 | 1 |
| C—malignant neoplasms | C00–C99; D32–D33; D35.2–D35.4; D42–D44 | 2947 | 64.7 | 5.3 | 0.0699 | 0.736 | 0.0058 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.803 | 0.0040 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| 3 | Malignant neoplasms of other and unspecified localisations | C00–C14; C30–C33; C37–C42; C45–C49; C69; C73–74; C754–C759 | 248 | 61.2 | 6.0 | 0.2729 | 0.727 | 0.0217 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.796 | 0.0148 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 4 | Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs | C15–C17; C22–C26 | 64 | 68.4 | 5.5 | 0.4174 | 0.607 | 0.0497 | 0.383 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0.711 | 0.0351 | 0.576 | 0.767 | 0.827 |
| 5 | Malignant neoplasm of colon | C18 | 262 | 71.3 | 5.8 | 0.2398 | 0.720 | 0.0175 | 0.623 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.790 | 0.0123 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 6 | Malignant neoplasms of rectosigmoid junction, rectum, anus and anal canal | C19–C21 | 174 | 70.6 | 5.8 | 0.2662 | 0.739 | 0.0247 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.806 | 0.0170 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 7 | Malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung | C34 | 159 | 67.9 | 7.1 | 0.3313 | 0.613 | 0.0313 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.719 | 0.0211 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 8 | Malignant melanoma of skin | C43 | 220 | 58.4 | 4.5 | 0.2171 | 0.812 | 0.0165 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.855 | 0.0116 | 0.810 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 9 | Other malignant neoplasms of skin | C44 | 122 | 71.5 | 6.4 | 0.3756 | 0.737 | 0.0280 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.805 | 0.0190 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 1 | Malignant neoplasm of breast | C50 | 681 | 64.5 | 4.9 | 0.1391 | 0.715 | 0.0118 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.786 | 0.0080 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 11 | Malignant neoplasms of female genital organs | C51–C52; C56–C58 | 113 | 63.1 | 5.2 | 0.3169 | 0.718 | 0.0311 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.795 | 0.0208 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 12 | Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri, corpus uteri and part unspecified | C53–C55 | 140 | 62.6 | 5.0 | 0.3140 | 0.742 | 0.0252 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.809 | 0.0171 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 13 | Malignant tumour of the male genitalia | C60, C62–C63 | 54 | 46.3 | 3.0 | 0.3342 | 0.831 | 0.0311 | 0.725 | 1 | 1 | 0.873 | 0.0223 | 0.800 | 1 | 1 |
| 14 | Malignant neoplasm of prostate | C61 | 440 | 72.4 | 5.6 | 0.1775 | 0.754 | 0.0142 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.815 | 0.0098 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 15 | Malignant neoplasms of urinary tract | C64-C68 | 166 | 71.5 | 5.9 | 0.2721 | 0.705 | 0.0282 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.783 | 0.0194 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 16 | Brain cancera | C71, C75.1–C75.3, D33.0–D33.2, D35.2–D35.4, D43.0–D43.2, D44.3–D44.5 (brain). C70, D32, D42 (brain membrane). C72, D33.3–D33.9, D43.3–D43.9 (cranial nerve, spinal cord) | 202 | 54.4 | 5.8 | 0.2964 | 0.758 | 0.0238 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.819 | 0.0166 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 17 | Malignant neoplasms of ill-defined, secondary and unspecified sites, and of independent (primary) multiple sites | C76–C80, C97 | 326 | 64.0 | 5.9 | 0.1953 | 0.709 | 0.0166 | 0.639 | 0.760 | 0.814 | 0.782 | 0.0115 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.843 |
| 18 | Malignant neoplasms, stated or presumed to be primary, of lymphoid, haematopoietic and related tissue | C81–C96 | 213 | 62.3 | 5.7 | 0.2828 | 0.719 | 0.0203 | 0.620 | 0.796 | 0.883 | 0.788 | 0.0137 | 0.706 | 0.827 | 0.860 |
| D—in situ, benign and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behaviour and diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | D00–D09; D55–D59; D60–D67; D80–D89 | 1254 | 59.2 | 6.0 | 0.1270 | 0.687 | 0.0102 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.768 | 0.0070 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 | |
| 19 | In situ neoplasms | D00–D09 | 289 | 55.3 | 4.3 | 0.2018 | 0.784 | 0.0154 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.835 | 0.0108 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 20 | Haemolytic anaemias | D55–D59 | 20 | 52.6 | 6.4 | 1.0464 | 0.770 | 0.0564 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 0.883 | 0.822 | 0.0381 | 0.816 | 0.827 | 0.860 |
| 21 | Aplastic and other anaemias | D60–D63 | 167 | 64.6 | 7.7 | 0.3523 | 0.581 | 0.0311 | 0.293 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.697 | 0.0213 | 0.527 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 22 | Other anaemias | D64 | 463 | 67.3 | 7.5 | 0.2227 | 0.593 | 0.0187 | 0.364 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.702 | 0.0129 | 0.576 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 23 | Coagulation defects, purpura and other haemorrhagic conditions | D65–D69 | 216 | 50.9 | 5.4 | 0.2931 | 0.737 | 0.0250 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.803 | 0.0172 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 24 | Other diseases of blood and blood-forming organs | D70–D77 | 81 | 56.0 | 5.9 | 0.4067 | 0.708 | 0.0276 | 0.620 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.782 | 0.0199 | 0.706 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 25 | Certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | D80–D89 | 102 | 50.2 | 5.4 | 0.3896 | 0.729 | 0.0339 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.800 | 0.0228 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| E—endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases | E00–E14; E20–E29; E31–35; E70–E78; E84–E85; E88-E89 | 12,412 | 63.5 | 4.9 | 0.0308 | 0.742 | 0.0029 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.807 | 0.0020 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| 26 | Diseases of the thyroida | E00–E04, E06, E07 | 1515 | 60.1 | 4.9 | 0.0936 | 0.739 | 0.0083 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.805 | 0.0057 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 27 | Thyrotoxicosisa | E05 | 714 | 61.0 | 4.6 | 0.1182 | 0.725 | 0.0135 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.795 | 0.0093 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 28 | Diabetes type 1a | E10 | 284 | 45.1 | 4.4 | 0.2139 | 0.769 | 0.0190 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.826 | 0.0130 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 29 | Diabetes type 2a | E11 | 3253 | 65.6 | 5.8 | 0.0626 | 0.701 | 0.0061 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.779 | 0.0042 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.860 |
| 30 | Diabetes othersa | E12–E14 | 18 | 59.5 | 5.4 | 0.8595 | 0.664 | 0.0699 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.883 | 0.755 | 0.0458 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.860 |
| 31 | Disorders of other endocrine glands | E20–E35, except E30 | 252 | 44.9 | 5.0 | 0.2608 | 0.690 | 0.0223 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.770 | 0.0151 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.860 |
| 32 | Metabolic disorders | E70–E77; E79–E83; E85, E88–E89; | 224 | 56.8 | 6.2 | 0.3054 | 0.681 | 0.0234 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.766 | 0.0158 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 33 | Disturbances in lipoprotein circulation and other lipidsa | E78 | 9685 | 65.8 | 5.2 | 0.0351 | 0.743 | 0.0032 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.808 | 0.0022 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 34 | Cystic fibrosisa | E84 | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| G—diseases of the nervous system | G00–G14; G20–G32; G35–G37; G40–47; G50–64; G70–73; G80–G83; G90–G99 | 6698 | 55.1 | 4.8 | 0.0473 | 0.697 | 0.0045 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.775 | 0.0031 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.860 | |
| 35 | Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system | G00–G09 | 66 | 52.0 | 5.0 | 0.5228 | 0.690 | 0.0451 | 0.516 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.766 | 0.0313 | 0.594 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 36 | Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system and other degenerative diseases | G10–G14, G30–G32 | 70 | 69.6 | 6.4 | 0.5117 | 0.475 | 0.0518 | 0.258 | 0.587 | 0.796 | 0.618 | 0.0352 | 0.498 | 0.687 | 0.827 |
| 37 | Parkinson’s diseasea | G20, G21, G22, F02.3 | 611 | 62.8 | 6.6 | 0.1637 | 0.584 | 0.0162 | 0.362 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.697 | 0.0110 | 0.550 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 38 | Extrapyramidal and movement disorders | G23–G26 | 107 | 60.1 | 7.0 | 0.4221 | 0.636 | 0.0328 | 0.585 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 0.733 | 0.0226 | 0.677 | 0.800 | 0.827 |
| 39 | Sclerosis | G35 | 155 | 49.1 | 4.4 | 0.2975 | 0.584 | 0.0310 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.689 | 0.0225 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 40 | Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system | G36–G37 | 62 | 49.0 | 4.5 | 0.3909 | 0.628 | 0.0470 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.721 | 0.0330 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 |
| 41 | Epilepsya | G40–G41 | 585 | 51.9 | 5.8 | 0.1776 | 0.647 | 0.0160 | 0.587 | 0.725 | 0.85 | 0.742 | 0.0110 | 0.687 | 0.800 | 0.854 |
| 42 | Migrainea | G43 | 2042 | 49.2 | 4.0 | 0.0743 | 0.736 | 0.0074 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.804 | 0.0050 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 43 | Other headache syndromes | G44 | 143 | 44.8 | 5.1 | 0.3383 | 0.640 | 0.0339 | 0.587 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 0.740 | 0.0227 | 0.687 | 0.800 | 0.844 |
| 44 | Transient cerebral ischaemic attacks and related syndromes and vascular syndromes of brain in cerebrovascular diseases | G45–G46 | 623 | 68.0 | 6.6 | 0.1690 | 0.689 | 0.0149 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.771 | 0.0101 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 45 | Sleep disorders | G47 | 453 | 53.7 | 5.2 | 0.1967 | 0.727 | 0.0155 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.795 | 0.0106 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 46 | Disorders of trigeminal nerve and facial nerve disorders | G50–G51 | 207 | 56.3 | 5.2 | 0.2405 | 0.706 | 0.0273 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.783 | 0.0185 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 47 | Disorders of other cranial nerves, cranial nerve disorders in diseases classified elsewhere, nerve root and plexus disorders and nerve root and plexus compressions in diseases classified elsewhere | G52–G55 | 109 | 59.1 | 5.6 | 0.4117 | 0.616 | 0.0420 | 0.433 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.724 | 0.0285 | 0.593 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 48 | Mononeuropathies of upper limb | G56 | 1460 | 57.4 | 5.0 | 0.1029 | 0.715 | 0.0088 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0.883 | 0.789 | 0.0060 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 0.860 |
| 49 | Mononeuropathies of lower limb, other mononeuropathies and mononeuropathy in diseases classified elsewhere | G57–G59 | 193 | 56.9 | 4.9 | 0.2683 | 0.685 | 0.0257 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.85 | 0.768 | 0.0178 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.854 |
| 50 | Polyneuropathies and other disorders of the peripheral nervous system | G60–G64 | 296 | 61.5 | 6.4 | 0.2665 | 0.596 | 0.0235 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.706 | 0.0161 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 51 | Diseases of myoneural junction and muscle | G70–G73 | 56 | 50.9 | 4.8 | 0.3841 | 0.600 | 0.0490 | 0.383 | 0.692 | 0.796 | 0.711 | 0.0329 | 0.574 | 0.781 | 0.827 |
| 52 | Cerebral palsy and other paralytic syndromes | G80–G83 | 113 | 47.9 | 5.0 | 0.2800 | 0.512 | 0.0404 | 0.159 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.646 | 0.0282 | 0.446 | 0.775 | 0.827 |
| 53 | Other disorders of the nervous system | G90–G99 | 257 | 53.8 | 5.7 | 0.2311 | 0.652 | 0.0230 | 0.585 | 0.727 | 0.814 | 0.745 | 0.0158 | 0.677 | 0.810 | 0.843 |
| H—diseases of the eye and adnexa and diseases of the ear and mastoid process | H02–H06; H17–H18; H25–H28; H31–H32; H34–H36; H40–55; H57; H80,H810; H93, H90-H93 | 6309 | 65.8 | 5.2 | 0.0468 | 0.736 | 0.0043 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.803 | 0.0030 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| 54 | Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit | H02–H06 | 257 | 62.3 | 5.5 | 0.2078 | 0.745 | 0.0191 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.808 | 0.0133 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 55 | Corneal scars and opacities | H17 | 34 | 60.6 | 5.8 | 0.7866 | 0.751 | 0.0608 | 0.691 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.819 | 0.0414 | 0.777 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 56 | Other disorders of cornea | H18 | 132 | 60.1 | 5.1 | 0.3893 | 0.760 | 0.0311 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.820 | 0.0218 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 57 | Diseases of the eye lens (cataracts) | H25–H28 | 928 | 73.5 | 6.1 | 0.1210 | 0.713 | 0.0110 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.786 | 0.0076 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 58 | Disorders of the choroid and retina | H31–H32 | 36 | 59.1 | 6.5 | 1.1796 | 0.666 | 0.1063 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.751 | 0.0752 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 59 | Retinal vascular occlusions | H34 | 115 | 73.2 | 6.4 | 0.3273 | 0.719 | 0.0350 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.788 | 0.0248 | 0.775 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 60 | Other retinal disorders | H35 | 749 | 72.0 | 6.2 | 0.1601 | 0.691 | 0.0144 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.773 | 0.0100 | 0.706 | 0.814 | 1 |
| 61 | Retinal disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | H36 | 175 | 58.5 | 7.1 | 0.3437 | 0.695 | 0.0317 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.772 | 0.0221 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 62 | Glaucomac | H40–H42 | 858 | 70.8 | 5.4 | 0.1259 | 0.732 | 0.0106 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.801 | 0.0074 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 63 | Disorders of the vitreous body and globe | H43–H45 | 136 | 56.7 | 5.4 | 0.4032 | 0.676 | 0.0357 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.812 | 0.760 | 0.0251 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.833 |
| 64 | Disorders of optic nerve and visual pathways | H46–H48 | 74 | 53.1 | 5.7 | 0.3592 | 0.657 | 0.0499 | 0.556 | 0.727 | 0.883 | 0.746 | 0.0340 | 0.626 | 0.810 | 0.860 |
| 65 | Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction | H49–H52 | 294 | 43.9 | 3.4 | 0.1717 | 0.837 | 0.0139 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.873 | 0.0099 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 |
| 66 | Visual disturbances | H53 | 360 | 55.8 | 5.9 | 0.2253 | 0.716 | 0.0188 | 0.656 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.789 | 0.0129 | 0.761 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 67 | Blindness and partial sight | H54 | 58 | 60.9 | 5.8 | 0.4786 | 0.676 | 0.0533 | 0.364 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.764 | 0.0369 | 0.576 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 68 | Nystagmus and other irregular eye movements and other disorders of eye and adnexa | H55, H57 | 80 | 54.9 | 4.8 | 0.3937 | 0.755 | 0.0354 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.819 | 0.0251 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 69 | Otosclerosis | H80 | 161 | 61.5 | 4.9 | 0.2926 | 0.803 | 0.0211 | 0.725 | 0.814 | 1 | 0.848 | 0.0148 | 0.800 | 0.843 | 1 |
| 70 | Ménière’s diseasea | H810 | 143 | 66.4 | 6.2 | 0.3259 | 0.718 | 0.0257 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0.85 | 0.787 | 0.0178 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 0.854 |
| 71 | Other diseases of the inner ear | H83 | 882 | 68.3 | 6.0 | 0.1175 | 0.747 | 0.0110 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.811 | 0.0075 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 72 | Conductive and sensorineural hearing loss | H90 | 566 | 64.5 | 6.0 | 0.1722 | 0.742 | 0.0142 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.807 | 0.0097 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 73 | Other hearing loss and other disorders of ear, not elsewhere classified | H910, H912, H913, H918, H930, H932, H933 | 114 | 61.5 | 6.1 | 0.3573 | 0.714 | 0.0301 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.788 | 0.0206 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 74 | Presbycusis (age-related hearing loss) | H911 | 1477 | 79.3 | 6.4 | 0.0956 | 0.697 | 0.0089 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.775 | 0.0061 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.860 |
| 75 | Hearing loss, unspecified | H919 | 1149 | 66.7 | 6.0 | 0.1060 | 0.731 | 0.0105 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.800 | 0.0071 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 76 | Tinnitus | H931 | 769 | 63.6 | 5.8 | 0.1303 | 0.734 | 0.0121 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.801 | 0.0082 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 77 | Other specified disorders of ear | H938 | 350 | 66.6 | 5.9 | 0.2202 | 0.734 | 0.0178 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.801 | 0.0123 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| I—diseases of the circulatory system | I05–I06; I10–28; I30–33;I36–141; I44–I52; I60–I88; I90–I94; I96–I99 | 16,990 | 62.9 | 4.6 | 0.0260 | 0.741 | 0.0025 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.807 | 0.0017 | 0.775 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| 78 | Aortic and mitral valve diseasea | I05, I06, I34, I35 | 426 | 72.3 | 7.5 | 0.1964 | 0.684 | 0.0149 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.848 | 0.764 | 0.0102 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.844 |
| 79 | Hypertensive diseasesa | I10–I15 | 14,504 | 64.8 | 4.8 | 0.0285 | 0.732 | 0.0027 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.801 | 0.0019 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 80 | Heart failurea | I11.0, I13.0, I13.2, I42.0, I42.6, I42.7, I42.9, I50.0, I50.1, I50.9 | 369 | 72.4 | 8.4 | 0.2128 | 0.603 | 0.0193 | 0.433 | 0.691 | 0.814 | 0.709 | 0.0133 | 0.593 | 0.777 | 0.843 |
| 80A | Ischaemic heart diseases | I20–I25 | 2017 | 67.9 | 7.5 | 0.0906 | 0.660 | 0.0083 | 0.620 | 0.725 | 0.814 | 0.750 | 0.0057 | 0.706 | 0.800 | 0.843 |
| 81 | Angina pectoris | I20 | 1253 | 66.3 | 7.3 | 0.1144 | 0.667 | 0.0100 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.755 | 0.0068 | 0.706 | 0.800 | 0.827 |
| 82 | Acute myocardial infarction and subsequent myocardial infarction | I21–I22 | 494 | 68.0 | 7.9 | 0.1866 | 0.682 | 0.0165 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.766 | 0.0113 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 83 | AMI complex/other | I23–I24 | 28 | 67.8 | 8.6 | 0.6266 | 0.603 | 0.0717 | 0.364 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.714 | 0.0465 | 0.576 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 84 | Chronic ischaemic heart disease | I25 | 1234 | 69.7 | 8.3 | 0.1145 | 0.648 | 0.0106 | 0.587 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.742 | 0.0072 | 0.687 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 85 | Pulmonary heart disease and diseases of pulmonary circulation | I26–I28 | 154 | 67.9 | 7.3 | 0.3405 | 0.604 | 0.0305 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.709 | 0.0206 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 86 | Acute pericarditis | I30 | 53 | 53.8 | 4.9 | 0.4336 | 0.836 | 0.0338 | 0.725 | 0.814 | 1 | 0.876 | 0.0237 | 0.800 | 0.843 | 1 |
| 87 | Other forms of heart disease | I31–I43, except I34–I35 and I42 | 85 | 58.8 | 7.2 | 0.4830 | 0.714 | 0.0294 | 0.623 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.786 | 0.0196 | 0.742 | 0.816 | 0.860 |
| 88 | Atrioventricular and left bundle-branch block | I44 | 178 | 71.0 | 7.0 | 0.3626 | 0.721 | 0.0310 | 0.639 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.791 | 0.0212 | 0.706 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 89 | Other conduction disorders | I45–46 | 129 | 62.7 | 6.4 | 0.3714 | 0.756 | 0.0223 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.814 | 0.0159 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 90 | Paroxysmal tachycardia | I47 | 593 | 63.4 | 6.4 | 0.1655 | 0.720 | 0.0128 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.793 | 0.0087 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 91 | Atrial fibrillation and flutter | I48 | 1480 | 71.9 | 6.9 | 0.1032 | 0.689 | 0.0091 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.727 | 0.770 | 0.0063 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.860 |
| 92 | Other cardiac arrhythmias | I49 | 423 | 67.3 | 6.9 | 0.2076 | 0.709 | 0.0173 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.783 | 0.0117 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 93 | Complications and ill-defined descriptions of heart disease and other heart disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | I51–52 | 50 | 71.1 | 8.9 | 0.5591 | 0.586 | 0.0449 | 0.516 | 0.689 | 0.76 | 0.697 | 0.0304 | 0.594 | 0.767 | 0.816 |
| 94 | Stroke | I60, I61, I63–I64, Z501 (rehabilitation) | 812 | 68.6 | 7.0 | 0.1344 | 0.641 | 0.0124 | 0.516 | 0.710 | 0.848 | 0.733 | 0.0086 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.844 |
| 95 | Cerebrovascular diseases | I62, I65–I68 | 180 | 63.8 | 7.4 | 0.2833 | 0.604 | 0.0283 | 0.433 | 0.710 | 0.796 | 0.708 | 0.0188 | 0.593 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 96 | Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease | I69 | 513 | 70.0 | 8.3 | 0.1842 | 0.555 | 0.0168 | 0.260 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0.675 | 0.0116 | 0.508 | 0.767 | 0.827 |
| 97 | Atherosclerosis | I70 | 397 | 71.2 | 8.6 | 0.2239 | 0.563 | 0.0203 | 0.260 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.682 | 0.0140 | 0.508 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 98 | Aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection | I71 | 121 | 70.7 | 7.5 | 0.3367 | 0.699 | 0.0236 | 0.620 | 0.710 | 0.796 | 0.777 | 0.0161 | 0.706 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 99 | Diseases of arteries, arterioles and capillaries | I72, I74, I77–I79 | 142 | 61.2 | 6.6 | 0.3864 | 0.731 | 0.0254 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.801 | 0.0175 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 100 | Other peripheral vascular diseases | I73 | 391 | 68.3 | 7.7 | 0.2142 | 0.615 | 0.0188 | 0.585 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.721 | 0.0126 | 0.677 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 101 | Phlebitis, thrombosis of the portal vein and others | I80–I82 | 439 | 60.9 | 5.8 | 0.1940 | 0.706 | 0.0164 | 0.656 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.782 | 0.0111 | 0.748 | 0.816 | 0.860 |
| 102 | Varicose veins of lower extremities | I83 | 494 | 55.2 | 3.7 | 0.1448 | 0.811 | 0.0136 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.855 | 0.0096 | 0.810 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 103 | Haemorrhoidsa | I84 | 1048 | 50.7 | 4.0 | 0.1059 | 0.760 | 0.0099 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.819 | 0.0069 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 104 | Oesophageal varices (chronic), varicose veins of other sites, other disorders of veins, nonspecific lymphadenitis, other noninfective disorders of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes and other and unspecified disorders of the circulatory system | I85–I99, except I89 and I95 | 145 | 50.0 | 4.8 | 0.3354 | 0.746 | 0.0236 | 0.656 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.808 | 0.0165 | 0.748 | 0.827 | 1 |
| J—diseases of the respiratory system | J30.1; J40–J47; J60–J84; J95, J97–J99 | 14,087 | 51.5 | 4.0 | 0.0288 | 0.776 | 0.0026 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.831 | 0.0018 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| 105 | Respiratory allergya | J30, except J30.0 | 9792 | 50.2 | 3.8 | 0.0337 | 0.788 | 0.0030 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.840 | 0.0021 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 105A | Chronic lower respiratory diseasesa | J40–J43, J47 | 5046 | 55.0 | 5.2 | 0.0522 | 0.740 | 0.0046 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.807 | 0.0032 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 106 |
Bronchitis, not specified as acute or chronic, simple and mucopurulent chronic bronchitis and unspecified chronic bronchitis |
J40-J42 | 182 | 67.3 | 8.9 | 0.3503 | 0.569 | 0.0343 | 0.364 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.686 | 0.0236 | 0.576 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 107 | Emphysema | J43 | 76 | 62.9 | 7.6 | 0.4699 | 0.622 | 0.0405 | 0.312 | 0.691 | 0.812 | 0.728 | 0.0267 | 0.525 | 0.777 | 0.833 |
| 108 | Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD)a | J44, J96, J13–J18 | 2435 | 61.3 | 6.4 | 0.0851 | 0.680 | 0.0076 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.763 | 0.0052 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 109 | Asthma, status asthmaticusa | J45–J46 | 4107 | 52.3 | 5.3 | 0.0583 | 0.736 | 0.0053 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.803 | 0.0037 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 110 | Bronchiectasis | J47 | 52 | 58.6 | 6.8 | 0.6295 | 0.694 | 0.0602 | 0.362 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.780 | 0.0405 | 0.566 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 111 | Other diseases of the respiratory system | J60–J84; J95, J97–J99 | 217 | 62.2 | 7.1 | 0.2852 | 0.617 | 0.0271 | 0.364 | 0.725 | 0.812 | 0.720 | 0.0185 | 0.576 | 0.794 | 0.833 |
| K—diseases of the digestive system | K25–K27; K40, K43, K50–52; K58–K59; K71–K77; K86–K87 | 4462 | 56.8 | 5.2 | 0.0602 | 0.692 | 0.0053 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.773 | 0.0036 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.860 | |
| 112 | Ulcersa | K25–K27 | 2245 | 59.6 | 5.8 | 0.0893 | 0.644 | 0.0078 | 0.587 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 0.739 | 0.0053 | 0.687 | 0.800 | 0.827 |
| 113 | Inguinal hernia | K40 | 480 | 58.1 | 4.0 | 0.1605 | 0.812 | 0.0124 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.857 | 0.0086 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 114 | Ventral hernia | K43 | 134 | 60.4 | 5.7 | 0.3646 | 0.690 | 0.0280 | 0.587 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.774 | 0.0191 | 0.687 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 115 | Crohn's disease | K50 | 212 | 47.2 | 4.6 | 0.2653 | 0.715 | 0.0252 | 0.620 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.787 | 0.0177 | 0.706 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 116 | Ulcerative colitis | K51 | 371 | 50.9 | 4.7 | 0.2182 | 0.731 | 0.0194 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.800 | 0.0133 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 117 | Other noninfective gastroenteritis and colitis | K52 | 209 | 61.8 | 6.9 | 0.3066 | 0.627 | 0.0270 | 0.552 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.726 | 0.0180 | 0.671 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 118 | Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) | K58 | 566 | 49.3 | 5.1 | 0.1826 | 0.722 | 0.0136 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.793 | 0.0093 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 119 | Other functional intestinal disorders | K59 | 542 | 58.8 | 6.3 | 0.1840 | 0.635 | 0.0175 | 0.587 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 0.731 | 0.0120 | 0.687 | 0.800 | 0.827 |
| 120 | Diseases of liver, biliary tract and pancreas | K71–K77; K86–K87 | 274 | 57.3 | 6.0 | 0.2602 | 0.671 | 0.0193 | 0.620 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 0.758 | 0.0131 | 0.706 | 0.800 | 0.827 |
| L—diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue | L40 | 722 | 56.0 | 4.3 | 0.1248 | 0.749 | 0.0119 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.813 | 0.0082 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| 121 | Psoriasisa | L40 | 722 | 56.0 | 4.3 | 0.1248 | 0.749 | 0.0119 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.813 | 0.0082 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| M—diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | M01–M25: M30–M36; M40–M54; M60.1–M99 | 13,163 | 57.0 | 4.4 | 0.0311 | 0.705 | 0.0029 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 0.85 | 0.782 | 0.0020 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 0.854 | |
| 122 | Infectious arthropathies | M01-M03 | 101 | 47.6 | 4.7 | 0.4562 | 0.737 | 0.0350 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0 | 0.804 | 0.0244 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 122A | Inflammatory polyarthropathies and ankylosing spondylitisa | M05–M14, M45 | 2008 | 60.3 | 5.7 | 0.0909 | 0.666 | 0.0075 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.755 | 0.0051 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 |
| 123 | Rheumatoid arthritisa | M05, M06, M07.1, M07.2, M07.3, M08, M09 | 919 | 56.8 | 5.7 | 0.1351 | 0.646 | 0.0115 | 0.587 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 0.741 | 0.0079 | 0.687 | 0.800 | 0.827 |
| 124 | Inflammatory polyarthropathies—except rheumatoid arthritisa | M074–M079, M10–M14, M45 | 1478 | 61.3 | 5.9 | 0.1062 | 0.662 | 0.0090 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.752 | 0.0061 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 |
| 125 | Polyarthrosis (arthrosis) | M15 | 169 | 67.5 | 7.4 | 0.3209 | 0.543 | 0.0301 | 0.228 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.672 | 0.0200 | 0.463 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 126 | Coxarthrosis (arthrosis of hip) | M16 | 1458 | 70.7 | 5.8 | 0.0968 | 0.663 | 0.0083 | 0.620 | 0.692 | 0.796 | 0.752 | 0.0056 | 0.706 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 127 | Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of knee) | M17 | 2590 | 63.3 | 5.2 | 0.0730 | 0.688 | 0.0065 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.771 | 0.0044 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 |
| 128 | Arthrosis of first carpometacarpal joint and other arthrosis | M18–M19 | 1036 | 61.2 | 5.7 | 0.1309 | 0.673 | 0.0101 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.727 | 0.760 | 0.0069 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 |
| 129 | Acquired deformities of fingers and toes | M20 | 616 | 56.1 | 5.0 | 0.1511 | 0.735 | 0.0126 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.803 | 0.0086 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 130 | Other acquired deformities of limbs | M21 | 275 | 52.5 | 5.5 | 0.2333 | 0.702 | 0.0227 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.782 | 0.0151 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 0.860 |
| 131 | Disorders of patella (kneecap) | M22 | 496 | 36.0 | 3.3 | 0.1242 | 0.749 | 0.0154 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.813 | 0.0104 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 132 | Internal derangement of knee | M230, M231, M233, M235, M236, M238 | 128 | 44.5 | 4.0 | 0.2667 | 0.715 | 0.0244 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.796 | 0.790 | 0.0163 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 0.827 |
| 133 | Derangement of meniscus due to old tear or injury | M232 | 497 | 48.3 | 3.8 | 0.1510 | 0.775 | 0.0131 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.832 | 0.0090 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 134 | Internal derangement of knee, unspecified | M239 | 382 | 44.3 | 3.3 | 0.1495 | 0.790 | 0.0126 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.842 | 0.0087 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 135 | Other specific joint derangements | M24, except M240–M241 | 58 | 40.3 | 3.7 | 0.4177 | 0.720 | 0.0411 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.795 | 0.0285 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 136 | Other joint disorders, not elsewhere classified | M25 | 193 | 48.6 | 4.6 | 0.2656 | 0.673 | 0.0253 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 0.759 | 0.0169 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.827 |
| 137 | Systemic connective tissue disorders | M30–M36, except M32, M34 | 463 | 61.5 | 6.4 | 0.1995 | 0.633 | 0.0181 | 0.516 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.734 | 0.0122 | 0.594 | 0.810 | 0.827 |
| 138 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | M32 | 45 | 51.5 | 7.2 | 0.5933 | 0.603 | 0.0595 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.710 | 0.0411 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 139 | Dermatopolymyositis | M33 | 15 | 60.0 | 7.1 | 0.9106 | 0.667 | 0.0917 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.85 | 0.753 | 0.0617 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.854 |
| 140 | Systemic sclerosis | M34 | 13 | 62.4 | 8.9 | 2.9138 | 0.362 | 0.2482 | -0.319 | 0.620 | 0.796 | 0.533 | 0.1746 | 0.053 | 0.706 | 0.827 |
| 141 | Kyphosis, lordosis | M40 | 54 | 53.2 | 5.3 | 0.6530 | 0.632 | 0.0504 | 0.620 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.736 | 0.0341 | 0.706 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 142 | Scoliosis | M41 | 164 | 40.8 | 4.3 | 0.3292 | 0.671 | 0.0307 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.759 | 0.0214 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 143 | Spinal osteochondrosis | M42 | 69 | 47.7 | 4.7 | 0.4656 | 0.593 | 0.0550 | 0.364 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.711 | 0.0368 | 0.576 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 144 | Other deforming dorsopathies | M43 | 275 | 56.8 | 5.8 | 0.2341 | 0.577 | 0.0228 | 0.260 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.697 | 0.0151 | 0.463 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 145 | Other inflammatory spondylopathies | M46 | 62 | 53.5 | 6.7 | 0.5913 | 0.522 | 0.0540 | 0.159 | 0.620 | 0.796 | 0.661 | 0.0352 | 0.446 | 0.706 | 0.827 |
| 146 | Spondylosis | M47 | 924 | 63.3 | 6.5 | 0.1451 | 0.538 | 0.0123 | 0.189 | 0.689 | 0.76 | 0.669 | 0.0082 | 0.446 | 0.767 | 0.816 |
| 147 | Other spondylopathies and spondylopathies in diseases classified elsewhere | M48, M49 | 483 | 67.7 | 7.5 | 0.2112 | 0.539 | 0.0167 | 0.208 | 0.689 | 0.76 | 0.668 | 0.0111 | 0.457 | 0.767 | 0.816 |
| 148 | Cervical disc disorders | M50 | 131 | 50.8 | 4.7 | 0.2913 | 0.613 | 0.0291 | 0.362 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.723 | 0.0193 | 0.566 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 149 | Other intervertebral disc disorders | M51 | 501 | 51.3 | 5.0 | 0.1734 | 0.557 | 0.0165 | 0.228 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.683 | 0.0109 | 0.463 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 150 | Other dorsopathies, not elsewhere classified | M53 | 92 | 49.4 | 4.9 | 0.3938 | 0.575 | 0.0394 | 0.264 | 0.691 | 0.76 | 0.693 | 0.0268 | 0.467 | 0.777 | 0.816 |
| 151 | Dorsalgia | M54 | 621 | 50.6 | 5.3 | 0.1649 | 0.528 | 0.0159 | 0.197 | 0.689 | 0.76 | 0.662 | 0.0105 | 0.446 | 0.767 | 0.816 |
| 152 | Soft tissue disorders | M60–M63, except M60.0 | 133 | 48.2 | 5.2 | 0.3852 | 0.663 | 0.0333 | 0.656 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 0.753 | 0.0224 | 0.748 | 0.816 | 0.827 |
| 153 | Synovitis and tenosynovitis | M65 | 270 | 50.8 | 4.4 | 0.2146 | 0.738 | 0.0200 | 0.691 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.803 | 0.0141 | 0.777 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 154 | Disorders of synovium and tendon | M66–68 | 238 | 43.6 | 3.8 | 0.2025 | 0.742 | 0.0215 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.811 | 0.0145 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 155 | Soft tissue disorders related to use, overuse and pressure | M70 | 175 | 53.2 | 5.2 | 0.3170 | 0.665 | 0.0272 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.758 | 0.0184 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 |
| 156 | Fibroblastic disorders | M72 | 521 | 62.1 | 4.6 | 0.1432 | 0.761 | 0.0140 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.822 | 0.0097 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 157 | Shoulder lesions | M75 | 899 | 52.3 | 4.3 | 0.1174 | 0.696 | 0.0116 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 0.776 | 0.0078 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 0.827 |
| 158 | Enthesopathies of lower limb, excluding foot | M76 | 111 | 43.9 | 3.4 | 0.2444 | 0.718 | 0.0297 | 0.656 | 0.760 | 0.85 | 0.794 | 0.0196 | 0.761 | 0.816 | 0.854 |
| 159 | Other enthesopathies | M77 | 156 | 47.7 | 4.1 | 0.2912 | 0.669 | 0.0276 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.760 | 0.0184 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 |
| 160 | Rheumatism, unspecified | M790 | 113 | 53.3 | 6.4 | 0.3457 | 0.390 | 0.0382 | 0.088 | 0.362 | 0.691 | 0.575 | 0.0250 | 0.397 | 0.566 | 0.777 |
| 161 | Myalgia | M791 | 107 | 53.6 | 5.6 | 0.4644 | 0.632 | 0.0326 | 0.516 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 0.731 | 0.0217 | 0.594 | 0.816 | 0.827 |
| 162 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified | M792–M794; M798–M799 | 81 | 53.0 | 5.4 | 0.4018 | 0.571 | 0.0439 | 0.255 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.691 | 0.0292 | 0.506 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 163 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified: pain in limb | M796 | 250 | 50.8 | 5.1 | 0.2466 | 0.653 | 0.0237 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 0.747 | 0.0157 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.827 |
| 164 | Fibromyalgia | M797 | 36 | 48.4 | 7.8 | 0.6511 | 0.369 | 0.0620 | 0.055 | 0.364 | 0.691 | 0.558 | 0.0397 | 0.360 | 0.576 | 0.777 |
| 165 | Osteoporosisa | M80–M81 | 1817 | 71.8 | 6.1 | 0.0907 | 0.648 | 0.0085 | 0.620 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 0.742 | 0.0058 | 0.704 | 0.800 | 0.827 |
| 166 | Osteoporosis in diseases classified elsewhere | M82 | 16 | 61.4 | 9.9 | 1.1443 | 0.541 | 0.1106 | 0.053 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.666 | 0.0786 | 0.368 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 167 | Adult osteomalacia and other disorders of bone density and structure | M83, M85, except M833 | 582 | 62.6 | 5.4 | 0.1485 | 0.709 | 0.0132 | 0.656 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.784 | 0.0091 | 0.748 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 168 | Disorders of continuity of bone | M84 | 29 | 44.5 | 5.0 | 0.8657 | 0.633 | 0.0748 | 0.195 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.736 | 0.0497 | 0.457 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 169 | Other osteopathies | M86–M90 | 160 | 56.7 | 5.6 | 0.3518 | 0.647 | 0.0314 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 0.744 | 0.0212 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.827 |
| 170 | Other disorders of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | M95–M99 | 253 | 52.2 | 5.3 | 0.2724 | 0.679 | 0.0212 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.764 | 0.0142 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| N—diseases of the genitourinary system | N18 | 224 | 66.3 | 8.1 | 0.2867 | 0.625 | 0.0237 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.814 | 0.725 | 0.0161 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.843 | |
| 171 | Chronic renal failure (CRF)a | N18 | 224 | 66.3 | 8.1 | 0.2867 | 0.625 | 0.0237 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.814 | 0.725 | 0.0161 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.843 |
| Q—congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities | Q00–Q56; Q60–Q99 | 1323 | 44.1 | 3.7 | 0.0881 | 0.782 | 0.0087 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.836 | 0.0060 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| 172 | Congenital malformations: of the nervous, circulatory, respiratory system; cleft palate and cleft lip, urinary tract, bones and muscles, other and chromosomal abnormalities not elsewhere classified | Q00–Q07; Q20–Q37; Q60–Q99 | 863 | 43.6 | 3.9 | 0.1138 | 0.757 | 0.0118 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.819 | 0.0081 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 173 | Congenital malformations of eye, ear, face and neck | Q10–Q18 | 205 | 37.9 | 2.8 | 0.1329 | 0.847 | 0.0144 | 0.796 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.879 | 0.0103 | 0.825 | 0.844 | 1 |
| 174 | Other congenital malformations of the digestive system | Q38–Q45 | 80 | 57.3 | 4.8 | 0.4178 | 0.779 | 0.0312 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.833 | 0.0223 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 175 | Congenital malformations of the sexual organs | Q50–Q56 | 198 | 47.2 | 3.3 | 0.2240 | 0.816 | 0.0176 | 0.725 | 0.812 | 1 | 0.858 | 0.0126 | 0.800 | 0.833 | 1 |
| F—mental and behavioural disorders | F00–99 | 6106 | 50.7 | 4.6 | 0.0453 | 0.651 | 0.0047 | 0.620 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 0.742 | 0.0031 | 0.706 | 0.800 | 0.844 | |
| 176 | Dementiaa | F00, G30, F01, F02.0, F03.9, G31.8B, G31.8E, G31.9, G31.0B | 179 | 80.9 | 6.9 | 0.2702 | 0.415 | 0.0305 | 0.159 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.572 | 0.0210 | 0.399 | 0.594 | 0.777 |
| 177 | Organic, including symptomatic, mental disorders | F04–F09 | 160 | 60.1 | 6.8 | 0.3135 | 0.604 | 0.0316 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.707 | 0.0214 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.827 |
| 178 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to use of alcohol | F10 | 382 | 47.5 | 5.4 | 0.2005 | 0.638 | 0.0182 | 0.516 | 0.691 | 0.812 | 0.735 | 0.0123 | 0.594 | 0.777 | 0.833 |
| 179 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to psychoactive substance use | F11–F19 | 368 | 48.0 | 5.1 | 0.1795 | 0.664 | 0.0190 | 0.620 | 0.743 | 0.848 | 0.753 | 0.0129 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.844 |
| 180 | Schizophreniaa | F20 | 143 | 44.7 | 5.6 | 0.2907 | 0.608 | 0.0330 | 0.331 | 0.725 | 0.812 | 0.714 | 0.0216 | 0.512 | 0.794 | 0.833 |
| 181 | Schizotypal and delusional disorders | F21–F29 | 193 | 48.2 | 6.7 | 0.2960 | 0.637 | 0.0265 | 0.378 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 0.733 | 0.0174 | 0.550 | 0.800 | 0.844 |
| 182 | Bipolar affective disordera | F30–F31 | 132 | 52.8 | 6.5 | 0.3870 | 0.597 | 0.0341 | 0.378 | 0.689 | 0.812 | 0.700 | 0.0222 | 0.550 | 0.767 | 0.833 |
| 183 | Depressiona | F32, F33, F34.1, F06.32 | 4619 | 52.5 | 4.9 | 0.0535 | 0.631 | 0.0055 | 0.516 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 0.727 | 0.0037 | 0.610 | 0.800 | 0.844 |
| 184 | Mood (affective) disorders | F340, F348–F349, F38–F39 | 44 | 48.5 | 7.4 | 0.6371 | 0.596 | 0.0614 | 0.378 | 0.621 | 0.812 | 0.698 | 0.0426 | 0.550 | 0.732 | 0.833 |
| 185 | Phobic anxiety disorders | F40 | 78 | 36.8 | 4.7 | 0.3321 | 0.550 | 0.0391 | 0.255 | 0.689 | 0.76 | 0.677 | 0.0250 | 0.506 | 0.767 | 0.816 |
| 186 | Other anxiety disorders | F41 | 226 | 43.5 | 5.9 | 0.2747 | 0.568 | 0.0247 | 0.258 | 0.689 | 0.812 | 0.686 | 0.0162 | 0.506 | 0.767 | 0.833 |
| 187 | Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)a | F42 | 70 | 34.2 | 5.1 | 0.4303 | 0.685 | 0.0342 | 0.620 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 0.763 | 0.0230 | 0.706 | 0.800 | 0.844 |
| 188 | Post-traumatic stress disorder | F431 | 73 | 45.4 | 5.1 | 0.3710 | 0.482 | 0.0468 | 0.197 | 0.620 | 0.725 | 0.627 | 0.0313 | 0.467 | 0.706 | 0.800 |
| 189 | Reactions to severe stress and adjustment disorders | F432–F439 | 386 | 39.7 | 5.1 | 0.1663 | 0.640 | 0.0184 | 0.516 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 0.735 | 0.0121 | 0.594 | 0.800 | 0.844 |
| 190 | Dissociative (conversion) disorders, somatoform disorders and other neurotic disorders | F44, F45, F48 | 170 | 49.2 | 6.4 | 0.3434 | 0.576 | 0.0309 | 0.293 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0.692 | 0.0207 | 0.527 | 0.767 | 0.827 |
| 191 | Eating disorders | F50 | 54 | 27.5 | 4.5 | 0.4739 | 0.683 | 0.0436 | 0.656 | 0.812 | 0.848 | 0.761 | 0.0291 | 0.761 | 0.833 | 0.844 |
| 192 | Behavioural syndromes associated with physiological disturbances and physical factors | F51–F59 | 58 | 41.9 | 4.6 | 0.4904 | 0.698 | 0.0519 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.780 | 0.0355 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 1 |
| 193 | Emotionally unstable personality disorder | F603 | 112 | 39.3 | 6.1 | 0.3266 | 0.596 | 0.0309 | 0.320 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0.705 | 0.0204 | 0.506 | 0.767 | 0.827 |
| 194 | Specific personality disorders | F602, F604–F609 | 363 | 43.1 | 5.6 | 0.1860 | 0.586 | 0.0201 | 0.291 | 0.689 | 0.812 | 0.698 | 0.0132 | 0.512 | 0.767 | 0.833 |
| 195 | Disorders of adult personality and behaviour | F61–F69 | 119 | 43.9 | 6.1 | 0.3491 | 0.592 | 0.0333 | 0.293 | 0.689 | 0.812 | 0.702 | 0.0214 | 0.527 | 0.767 | 0.833 |
| 196 | Mental retardation | F70–F79 | 44 | 38.8 | 5.4 | 0.7177 | 0.694 | 0.0507 | 0.585 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.768 | 0.0355 | 0.677 | 0.827 | 1 |
| 197 | Disorders of psychological development | F80–F89 | 44 | 24.1 | 3.7 | 0.3364 | 0.685 | 0.0581 | 0.689 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.766 | 0.0389 | 0.767 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 198 | Hyperkinetic disorders (ADHD)a | F90 | 193 | 31.7 | 4.0 | 0.2147 | 0.694 | 0.0214 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.770 | 0.0142 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.844 |
| 199 | Behavioural and emotional disorders with onset usually occurring in childhood and adolescence | F91–F99 | 244 | 38.4 | 5.7 | 0.2425 | 0.622 | 0.0255 | 0.309 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 0.724 | 0.0170 | 0.517 | 0.794 | 0.844 |
| Extra conditions | ||||||||||||||||
| Ischaemic heart diseases broad | I05–I06; I11–I13; I20–I28; I30–I52 | 4221 | 67.5 | 6.5 | 0.0600 | 0.693 | 0.0054 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.773 | 0.0037 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.860 | |
| Arthritis | M01–M03; M5–M9; M7–M14; M15–M20; M45 | 612 | 61.9 | 5.1 | 0.0460 | 0.695 | 0.0040 | 0.623 | 0.760 | 0.814 | 0.775 | 0.0027 | 0.742 | 0.816 | 0.833 | |
| Arthrosis | M15–M19 | 4589 | 64.2 | 5.2 | 0.0555 | 0.684 | 0.0048 | 0.62 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.767 | 0.0033 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 | |
| Back conditions | M32–34; M41–M43; M46–49; M50–51; M53–M54 | 2620 | 55.4 | 5.3 | 0.0819 | 0.589 | 0.0074 | 0.364 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0.704 | 0.0049 | 0.576 | 0.777 | 0.827 | |
| Overweight, clinical diagnosed (BMI > 35) | E66 | 2761 | 46.2 | 3.6 | 0.0712 | 0.726 | 0.0067 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.797 | 0.0046 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| Endometriosis | N80 | 428 | 44.7 | 2.7 | 0.1504 | 0.726 | 0.0164 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.798 | 0.0110 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 | |
| NCCs | ||||||||||||||||
| Having no chronic conditions | 18,136 | 37.7 | 0.0 | n/a | 0.908 | 0.0014 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.926 | 0.0010 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Having 1 chronic condition | 11,303 | 44.4 | 1.0 | n/a | 0.868 | 0.0020 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.895 | 0.0014 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Comorbidity: 2 conditions | 7657 | 50.1 | 2.0 | n/a | 0.826 | 0.0029 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.866 | 0.0021 | 0.816 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Comorbidity: 3 conditions | 5698 | 54.6 | 3.0 | n/a | 0.792 | 0.0037 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.842 | 0.0026 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Comorbidity: 4 conditions | 3959 | 58.7 | 4.0 | n/a | 0.752 | 0.0045 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.813 | 0.0031 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Comorbidity: 5 conditions | 2805 | 61.8 | 5.0 | n/a | 0.708 | 0.0061 | 0.656 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.783 | 0.0042 | 0.761 | 0.816 | 0.844 | ||
| Comorbidity: 6 conditions | 1915 | 63.8 | 6.0 | n/a | 0.679 | 0.0079 | 0.620 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 0.762 | 0.0054 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 | ||
| Comorbidity: 7 or more conditions | 4143 | 67.1 | 9.0 | 0.0406 | 0.558 | 0.0061 | 0.293 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0.680 | 0.0041 | 0.517 | 0.767 | 0.827 | ||
| One or more chronic conditions | 37,480 | 53.2 | 3.2 | 0.0150 | 0.783 | 0.0015 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.836 | 0.0011 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Gender | ||||||||||||||||
| Women | 29,268 | 48.2 | 2.3 | 0.0152 | 0.809 | 0.0017 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.854 | 0.0012 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Men | 26,348 | 47.0 | 1.8 | 0.0167 | 0.849 | 0.0016 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.883 | 0.0011 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age | ||||||||||||||||
| Age 16–24 years | 5993 | 19.9 | 0.6 | 0.0169 | 0.891 | 0.0028 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.914 | 0.0020 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age 25–34 years | 5388 | 29.7 | 1.0 | 0.0220 | 0.882 | 0.0028 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.906 | 0.0020 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age 35–44 years | 8516 | 39.8 | 1.3 | 0.0220 | 0.852 | 0.0027 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.886 | 0.0019 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Age 45–54 years | 1657 | 49.6 | 1.9 | 0.0248 | 0.813 | 0.0028 | 0.725 | 0.725 | 1 | 0.857 | 0.0019 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Age 55–64 years | 11,198 | 59.8 | 2.6 | 0.0282 | 0.805 | 0.0027 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.852 | 0.0019 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Age 65–74 years | 8840 | 69.1 | 3.6 | 0.0360 | 0.803 | 0.0028 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.850 | 0.0020 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Age 75+ years | 5024 | 81.3 | 4.9 | 0.0518 | 0.694 | 0.0048 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.773 | 0.0033 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 0.860 | ||
| Education | ||||||||||||||||
| No education/training | 14,603 | 58.2 | 3.1 | 0.0287 | 0.750 | 0.0027 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.814 | 0.0019 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Students or in training | 4968 | 21.8 | 0.7 | 0.0212 | 0.892 | 0.0028 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.914 | 0.0021 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Short education | 24,455 | 48.7 | 2.0 | 0.0172 | 0.834 | 0.0017 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.873 | 0.0012 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Middle education (e.g. bachelor’s degree) | 8315 | 47.5 | 1.8 | 0.0273 | 0.866 | 0.0024 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.895 | 0.0017 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| High education (master’s degree or higher) | 3028 | 45.0 | 1.4 | 0.0382 | 0.898 | 0.0035 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.919 | 0.0026 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Missing | 247 | 56.8 | 2.5 | 0.2225 | 0.670 | 0.0244 | 0.587 | 0.727 | 0.85 | 0.752 | 0.0172 | 0.687 | 0.810 | 0.854 | ||
| Ethnicity | ||||||||||||||||
| Danish | 53,268 | 48.1 | 2.1 | 0.0124 | 0.832 | 0.0011 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.871 | 0.0008 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Other Western | 1144 | 44.0 | 1.4 | 0.0728 | 0.815 | 0.0084 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.857 | 0.0059 | 0.800 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Non-Western | 1204 | 38.4 | 1.5 | 0.0699 | 0.758 | 0.0100 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.819 | 0.0070 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Family equalised income | ||||||||||||||||
| < £20,000 | 5066 | 41.0 | 1.8 | 0.0392 | 0.798 | 0.0045 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.872 | 0.0038 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| £20,000–39,999 | 26,123 | 50.5 | 2.5 | 0.0197 | 0.799 | 0.0018 | 0.725 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.830 | 0.0015 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| £40,000–59,999 | 17,368 | 45.1 | 1.6 | 0.0171 | 0.868 | 0.0015 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.889 | 0.0011 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| £60,000–79,999 | 4961 | 48.4 | 1.6 | 0.0301 | 0.884 | 0.0026 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.902 | 0.0015 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| £80,000+ | 2098 | 51.0 | 1.6 | 0.0472 | 0.887 | 0.0040 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.910 | 0.0021 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Family equalised income quartiles | ||||||||||||||||
| 1st quartile | 14.248 | 50.5 | 2.7 | 0.0294 | 0.770 | 0.0028 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.827 | 0.0020 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| 2nd quartile | 14.244 | 47.4 | 2.1 | 0.0240 | 0.818 | 0.0023 | 0.727 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.861 | 0.0016 | 0.810 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| 3rd quartile | 14.247 | 44.3 | 1.6 | 0.0196 | 0.860 | 0.0018 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.891 | 0.0013 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 4th quartile | 14.247 | 47.6 | 1.6 | 0.0183 | 0.879 | 0.0016 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.905 | 0.0012 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Socio-economic position | ||||||||||||||||
| Retired, age | 12,408 | 74.9 | 4.3 | 0.0325 | 0.750 | 0.0028 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 0 | 0.812 | 0.0020 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Retirement, free | 2414 | 63.1 | 2.7 | 0.0545 | 0.839 | 0.0042 | 0.760 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.874 | 0.0030 | 0.816 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Early retirement, health reasons | 2227 | 52.1 | 4.7 | 0.0778 | 0.547 | 0.0079 | 0.255 | 0.689 | 0.76 | 0.674 | 0.0053 | 0.506 | 0.767 | 0.816 | ||
| Seek leave and other leave | 507 | 39.1 | 2.6 | 0.1343 | 0.654 | 0.0167 | 0.516 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 0.747 | 0.0112 | 0.594 | 0.816 | 0.844 | ||
| Unemployed, social benefits longer term | 555 | 37.3 | 2.8 | 0.1199 | 0.547 | 0.0168 | 0.195 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 0.676 | 0.0111 | 0.467 | 0.767 | 0.827 | ||
| Unemployed minimum 6 months, ordinary | 673 | 43.3 | 1.6 | 0.0872 | 0.838 | 0.0091 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.874 | 0.0065 | 0.800 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| In training or education | 3472 | 19.8 | 0.5 | 0.0198 | 0.899 | 0.0036 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.919 | 0.0026 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Employed | 32,262 | 42.2 | 1.3 | 0.0100 | 0.878 | 0.0011 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.904 | 0.0008 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Others not in workforce | 1098 | 36.1 | 1.4 | 0.0661 | 0.795 | 0.0090 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.845 | 0.0063 | 0.800 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Partnership | ||||||||||||||||
| Having a partner | 28,055 | 50.1 | 2.1 | 0.0172 | 0.829 | 0.0016 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.869 | 0.0011 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Not married/not in a relationship | 27,561 | 45.3 | 2.0 | 0.0171 | 0.828 | 0.0016 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.868 | 0.0012 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Children home | ||||||||||||||||
| No children home | 41,004 | 51.7 | 2.4 | 0.0155 | 0.815 | 0.0014 | 0.725 | 0.812 | 1 | 0.859 | 0.0010 | 0.800 | 0.833 | 1 | ||
| Having children living home under 15 years | 13,959 | 37.1 | 1.2 | 0.0156 | 0.867 | 0.0020 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.896 | 0.0014 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Missing | 653 | 41.3 | 2.0 | 0.1136 | 0.762 | 0.0157 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.820 | 0.0108 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Social network – loneliness | ||||||||||||||||
| Not lonely or seldom lonely | 52,523 | 47.3 | 2.0 | 0.0119 | 0.841 | 0.0011 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.877 | 0.0008 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Often lonely, self-reported | 2407 | 49.0 | 3.2 | 0.0778 | 0.630 | 0.0081 | 0.516 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 0.728 | 0.0055 | 0.594 | 0.800 | 0.844 | ||
| Missing | 686 | 59.3 | 3.5 | 0.1301 | 0.769 | 0.0121 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.828 | 0.0085 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Stress – Cohen’s Perceived Stress Scale | ||||||||||||||||
| 80% least stressed | 43,466 | 47.1 | 1.8 | 0.0119 | 0.881 | 0.0009 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.906 | 0.0007 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 20% most stressed (cut point 18) | 9851 | 47.0 | 3.0 | 0.0357 | 0.638 | 0.0036 | 0.587 | 0.725 | 0.814 | 0.732 | 0.0024 | 0.687 | 0.800 | 0.843 | ||
| Missing | 2299 | 57.8 | 3.0 | 0.0686 | 0.763 | 0.0073 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.823 | 0.0051 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Body mass index (kg/m2), self-reported | ||||||||||||||||
| BMI < 18.5 | 1193 | 39.9 | 1.9 | 0.0827 | 0.783 | 0.0098 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.836 | 0.0069 | 0.800 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| BMI > 18.5 < 25 | 25,087 | 44.4 | 1.7 | 0.0159 | 0.855 | 0.0016 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.887 | 0.0011 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| BMI > 25 < 30 | 19,387 | 50.6 | 2.2 | 0.0206 | 0.831 | 0.0019 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.870 | 0.0013 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| BMI ≥ 30 < 35 | 6317 | 50.3 | 2.7 | 0.0410 | 0.780 | 0.0038 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.834 | 0.0026 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| BMI ≥ 35 | 2015 | 47.9 | 3.2 | 0.0816 | 0.707 | 0.0078 | 0.656 | 0.760 | 0.883 | 0.783 | 0.0053 | 0.761 | 0.816 | 0.860 | ||
| Missing | 1617 | 58.5 | 3.2 | 0.0859 | 0.747 | 0.0087 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.811 | 0.0060 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Daily smoker | ||||||||||||||||
| Do not smoke daily | 45,779 | 47.3 | 2.0 | 0.0131 | 0.841 | 0.0012 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.878 | 0.0009 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Smoking daily | 8968 | 47.6 | 2.2 | 0.0314 | 0.774 | 0.0033 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.830 | 0.0023 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Missing | 869 | 59.7 | 3.4 | 0.1119 | 0.749 | 0.0110 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.813 | 0.0077 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Alcohol intake | ||||||||||||||||
| Do not exceed National Board of Health’s recommendations | 46,937 | 47.4 | 2.0 | 0.0129 | 0.835 | 0.0012 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.873 | 0.0009 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Exceed recommendations with more than 7 drinks a week/woman or 14 drinks a week/man | 4274 | 43.9 | 1.9 | 0.0418 | 0.813 | 0.0045 | 0.725 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.857 | 0.0031 | 0.800 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| Missing | 4405 | 52.7 | 2.9 | 0.0508 | 0.781 | 0.0048 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.835 | 0.0033 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Exercise | ||||||||||||||||
| Exercise at least 4 h a week | 45,913 | 46.2 | 1.8 | 0.0117 | 0.858 | 0.0010 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.889 | 0.0008 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Do not exercise during the week | 8457 | 52.4 | 3.1 | 0.0404 | 0.690 | 0.0041 | 0.620 | 0.760 | 1 | 0.771 | 0.0028 | 0.706 | 0.816 | 1 | ||
| Missing | 1246 | 62.3 | 3.6 | 0.1009 | 0.735 | 0.0104 | 0.689 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.802 | 0.0073 | 0.767 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Fruit intake | ||||||||||||||||
| Do not meet National Board of Health’s recommendations | 50,958 | 47.3 | 2.0 | 0.0126 | 0.829 | 0.0012 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.869 | 0.0008 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| 5 or more portions of fruit a day as recommended | 3486 | 47.0 | 2.0 | 0.0449 | 0.847 | 0.0043 | 0.760 | 1 | 1 | 0.882 | 0.0030 | 0.816 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Missing | 1172 | 58.8 | 3.3 | 0.0947 | 0.770 | 0.0092 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.827 | 0.0064 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| SF-12 General Health (self-reported) | ||||||||||||||||
| Excellent | 6231 | 37.9 | 0.7 | 0.0174 | 0.972 | 0.0013 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.976 | 0.0010 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Very good | 20,840 | 42.7 | 1.2 | 0.0121 | 0.924 | 0.0010 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.936 | 0.0008 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Good | 21,183 | 51.8 | 2.3 | 0.0188 | 0.817 | 0.0014 | 0.727 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.856 | 0.0010 | 0.800 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Fair | 6846 | 56.7 | 4.4 | 0.0468 | 0.554 | 0.0039 | 0.364 | 0.689 | 0.725 | 0.676 | 0.0025 | 0.574 | 0.767 | 0.800 | ||
| Poor | 1341 | 56.8 | 5.8 | 0.1182 | 0.210 | 0.0101 | -0.016 | 0.157 | 0.516 | 0.448 | 0.0068 | 0.307 | 0.420 | 0.594 | ||
| Missing | 547 | 60.7 | 3.3 | 0.1644 | 0.749 | 0.0217 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.812 | 0.0147 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Long-term illness or disability (self-reported) | ||||||||||||||||
| No long-term illness | 36,747 | 44.4 | 1.2 | 0.0098 | 0.905 | 0.0009 | 0.796 | 1 | 1 | 0.923 | 0.0007 | 0.827 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Long term illness | 18,488 | 52.6 | 3.6 | 0.0262 | 0.676 | 0.0025 | 0.620 | 0.743 | 0.796 | 0.760 | 0.0017 | 0.706 | 0.810 | 0.827 | ||
| Missing | 1753 | 63.5 | 3.6 | 0.0890 | 0.754 | 0.0087 | 0.691 | 0.796 | 1 | 0.816 | 0.0060 | 0.777 | 0.827 | 1 | ||
| Samples | ||||||||||||||||
| NDR sample | 40,816 | 47.6 | 2.1 | 0.0144 | 0.826 | 0.0014 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.867 | 0.0010 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| DK sample | 14,800 | 47.6 | 2.0 | 0.0225 | 0.835 | 0.0020 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.873 | 0.0014 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | ||
| All population | – | 55,616 | 47.6 | 2.1 | 0.0121 | 0.829 | 0.0012 | 0.760 | 0.848 | 1 | 0.869 | 0.0008 | 0.816 | 0.844 | 1 | |
Note: n = 55,616 in all models. All NCC means and unadjusted EQ-5D estimates are weighted. Frequencies (n) are not weighted. Conditions no. marked with ‘A’ are overlapping other conditions, usually due to complex register definition [54]. Bold text signifies aggregated disease groups, health variables and total population estimates
ICD-10 International Classification of Diseases version 10, n/a not availableAEstimates adapted from Hvidberg et al. [69]
aComplex defined conditions
Model-based adjusted estimates of the base and full model
Even though the underlying EQ-5D-3L response data are the same for both models and the distributions of the UK and USA, EQ-5D-3L (Fig. 1) show some similarities in terms of skewness and the number of modes, and the use of different value sets translates into some differences in the overall distribution, making it important to carry out the estimation procedure separately for the UK and the USA. Extensive searches were carried out for both countries’ ALDVMMs. A three-component model was chosen for the UK on the basis of sample fit measures, information criteria (AIC and BIC) and graphical methods. A two-component model was selected using the same methodological procedure for the USA. Searches for a third component did not yield any model that improved fit over the two-component models. Table 3 presents measures of fit and information criteria for the selected models for the UK and USA, respectively. Including the additional covariates in the model substantially improves the measures of fit. However, even the basic model, including all 199 chronic conditions and controlling for age and sex, shows a relatively good fit to the data (see Figs. 2 and 3 for plots of the cumulative distribution of EQ-5D-3L implied by the models versus the data). The online Supplementary Materials 2 and 3 provides the full set of parameter estimates of the selected models as Stata and Excel file downloads.
Table 3.
Summary measures of fit for the UK and US base and full ALDVMMs
| AIC | BIC | Mean absolute error | Root mean squared error | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK base model | ||||
| 1 component | 31,698.45 | 33,590.81 | 0.1394863 | 0.18995961 |
| 2 components | 17,218.26 | 21,092.24 | 0.1399875 | 0.19214219 |
| 3 components | 10,982.12 | 16,855.58 | 0.13895 | 0.18989694 |
| UK full model | ||||
| 1 component | 30,691.11 | 32,663.8 | 0.1379652 | 0.18803380 |
| 2 components | 3018.952 | 7544.548 | 0.114237 | 0.1504211 |
| 3 components | – 12,349.21 | – 5458.163 | 0.1063071 | 0.14735358 |
| US base model | ||||
| 1 component | – 815.7213 | 1076.639 | 0.1045412 | 0.13479988 |
| 2 components | – 26,770.45 | – 22,887.54 | 0.1043856 | 0.13512545 |
| US full model | ||||
| 1 component | – 9718.437 | – 7567.216 | 0.0954433 | 0.12264923 |
| 2 components | – 42,413.68 | – 37,888.08 | 0.0872551 | 0.10835724 |
Fig. 2.
Cumulative percentage plots of UK models
Fig. 3.
Cumulative percentage plots of US models
The parameters of nonlinear models cannot be interpreted directly in the same way as the parameters of linear models. In nonlinear models, the effect of the conditioning variable depends on the value of the other variables in the model. For example, in our case, the disutility of a chronic condition will generally be different for a person who has no other chronic conditions and a person who already has some other chronic conditions. To interpret and compare the models and conditions meaningfully, we calculate the MEs for two representative 50-year-old individuals, male and female, with no chronic conditions. We set the rest of the variables to the mean sample values for continuous variables and the mode for discrete variables. The MEs for age are calculated by varying the age of the same individuals while maintaining the rest of the characteristics. Tables 4 and 5 present the predictions and marginal effects for the base and the full UK models. Tables 6 and 7 present the same information for the US models.
Table 4.
ALDVMM predictions and marginal effects of representative 50-year-olds by sex: UK base model—chronic conditions and age
| No. | Condition or covariable | Representative 50-year-old male with no chronic conditions | Representative 50-year-old female with no chronic conditions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model prediction | Marginal effect | Model prediction | Marginal effect | ||||||||||
| β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | ||
| No conditions | 0.8958 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | 0.9098 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 1 | Chronic viral hepatitis | 0.8228 | 0.0218 | 0.000 | − 0.0730 | 0.0218 | 0.001 | 0.8412 | 0.0185 | 0.000 | − 0.0686 | 0.0185 | 0.000 |
| 2 | Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease | 0.8125 | 0.0316 | 0.000 | − 0.0833 | 0.0316 | 0.009 | 0.8326 | 0.0287 | 0.000 | − 0.0772 | 0.0287 | 0.007 |
| 3 | Malignant neoplasms of other and unspecified localizations | 0.8734 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0224 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.8879 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0055 | 0.000 |
| 4 | Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs | 0.8190 | 0.0117 | 0.000 | − 0.0768 | 0.0117 | 0.000 | 0.8409 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | − 0.0689 | 0.0104 | 0.000 |
| 5 | Malignant neoplasm of colon | 0.8729 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0229 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | 0.8875 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0223 | 0.0058 | 0.000 |
| 6 | Malignant neoplasms of rectosigmoid junction, rectum, anus and anal canal | 0.8807 | 0.0076 | 0.000 | − 0.0151 | 0.0076 | 0.046 | 0.8943 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0154 | 0.0070 | 0.027 |
| 7 | Malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung | 0.8622 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0335 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | 0.8785 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | − 0.0313 | 0.0072 | 0.000 |
| 8 | Malignant melanoma of skin | 0.8796 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0162 | 0.0052 | 0.002 | 0.8934 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0163 | 0.0046 | 0.000 |
| 9 | Other malignant neoplasms of skin | 0.8832 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0126 | 0.0048 | 0.009 | 0.8964 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0133 | 0.0044 | 0.003 |
| 10 | Malignant neoplasm of breast | 0.8639 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0319 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | 0.8796 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0302 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 11 | Malignant neoplasms of female genital organs | 0.8638 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0320 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.8785 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0312 | 0.0058 | 0.000 |
| 12 | Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri, corpus uteri and part unspecified | 0.8684 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0274 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | 0.8840 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0258 | 0.0062 | 0.000 |
| 13 | Malignant tumour of the male genitalia | 0.8649 | 0.0089 | 0.000 | − 0.0309 | 0.0090 | 0.001 | 0.8790 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0308 | 0.0079 | 0.000 |
| 14 | Malignant neoplasm of prostate | 0.8714 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0244 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | 0.8865 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0232 | 0.0043 | 0.000 |
| 15 | Malignant neoplasms of urinary tract | 0.8672 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0286 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | 0.8826 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0272 | 0.0058 | 0.000 |
| 16 | Brain cancera | 0.8771 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0187 | 0.0067 | 0.006 | 0.8915 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0183 | 0.0061 | 0.003 |
| 17 | Malignant neoplasms of ill-defined, secondary and unspecified sites, and of independent (primary) multiple sites | 0.8560 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0398 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | 0.8732 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0365 | 0.0061 | 0.000 |
| 18 | Malignant neoplasms, stated or presumed to be primary, of lymphoid, haematopoietic and related tissue | 0.8727 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0231 | 0.0074 | 0.002 | 0.8880 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0066 | 0.001 |
| 19 | In situ neoplasms | 0.8763 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0195 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | 0.8905 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0193 | 0.0039 | 0.000 |
| 20 | Haemolytic anaemias | 0.9133 | 0.0198 | 0.000 | 0.0175 | 0.0198 | 0.376 | 0.9245 | 0.0183 | 0.000 | 0.0148 | 0.0183 | 0.420 |
| 21 | Aplastic and other anaemias | 0.8649 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | − 0.0309 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | 0.8810 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0288 | 0.0064 | 0.000 |
| 22 | Other anaemias | 0.8552 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0406 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | 0.8721 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0376 | 0.0045 | 0.000 |
| 23 | Coagulation defects, purpura and other haemorrhagic conditions | 0.8782 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0176 | 0.0063 | 0.006 | 0.8927 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0170 | 0.0059 | 0.004 |
| 24 | Other diseases of blood and blood-forming organs | 0.8549 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0409 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | 0.8707 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0390 | 0.0072 | 0.000 |
| 25 | Certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | 0.8670 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0288 | 0.0086 | 0.001 | 0.8830 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0267 | 0.0078 | 0.001 |
| 26 | Diseases of the thyroida | 0.8662 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0296 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.8816 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0281 | 0.0027 | 0.000 |
| 27 | Thyrotoxicosisa | 0.8685 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0273 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.8836 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0261 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 28 | Diabetes type 1a | 0.8630 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0328 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | 0.8785 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0313 | 0.0049 | 0.000 |
| 29 | Diabetes type 2a | 0.8582 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0376 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | 0.8747 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0351 | 0.0025 | 0.000 |
| 30 | Diabetes othersa | 0.8474 | 0.0199 | 0.000 | − 0.0484 | 0.0200 | 0.015 | 0.8632 | 0.0180 | 0.000 | − 0.0465 | 0.0181 | 0.010 |
| 31 | Disorders of other endocrine glands | 0.8573 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0385 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.8741 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0357 | 0.0053 | 0.000 |
| 32 | Metabolic disorders | 0.8602 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0356 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | 0.8765 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0332 | 0.0057 | 0.000 |
| 33 | Disturbances in lipoprotein circulation and other lipidsa | 0.8739 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0219 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.8882 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0215 | 0.0023 | 0.000 |
| 34 | Cystic fibrosisa | 0.8682 | 0.0132 | 0.000 | − 0.0275 | 0.0132 | 0.037 | 0.8830 | 0.0124 | 0.000 | − 0.0268 | 0.0123 | 0.030 |
| 35 | Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system | 0.8768 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0190 | 0.0082 | 0.020 | 0.8903 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0195 | 0.0074 | 0.009 |
| 36 | Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system and other degenerative diseases | 0.8479 | 0.0184 | 0.000 | − 0.0479 | 0.0184 | 0.009 | 0.8661 | 0.0166 | 0.000 | − 0.0436 | 0.0166 | 0.009 |
| 37 | Parkinson’s diseasea | 0.8424 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0534 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | 0.8610 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0488 | 0.0051 | 0.000 |
| 38 | Extrapyramidal and movement disorders | 0.8604 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0353 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | 0.8763 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0334 | 0.0085 | 0.000 |
| 39 | Sclerosis | 0.7579 | 0.0271 | 0.000 | − 0.1379 | 0.0271 | 0.000 | 0.7824 | 0.0261 | 0.000 | − 0.1273 | 0.0261 | 0.000 |
| 40 | Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system | 0.8576 | 0.0177 | 0.000 | − 0.0381 | 0.0176 | 0.031 | 0.8748 | 0.0153 | 0.000 | − 0.0349 | 0.0153 | 0.022 |
| 41 | Epilepsya | 0.8556 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0402 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | 0.8726 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0372 | 0.0045 | 0.000 |
| 42 | Migrainea | 0.8622 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0336 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.8783 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0314 | 0.0027 | 0.000 |
| 43 | Other headache syndromes | 0.8559 | 0.0113 | 0.000 | − 0.0399 | 0.0114 | 0.000 | 0.8730 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | − 0.0368 | 0.0099 | 0.000 |
| 44 | Transient cerebral ischaemic attacks and related syndromes and vascular syndromes of brain in cerebrovascular diseases | 0.8731 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0227 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | 0.8879 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0034 | 0.000 |
| 45 | Sleep disorders | 0.8605 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0353 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | 0.8766 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0332 | 0.0040 | 0.000 |
| 46 | Disorders of trigeminal nerve and facial nerve disorders | 0.8626 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0332 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.8782 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0315 | 0.0052 | 0.000 |
| 47 | Disorders of other cranial nerves, cranial nerve disorders in diseases classified elsewhere, nerve root and plexus disorders and Nerve root and plexus compressions in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8471 | 0.0134 | 0.000 | − 0.0487 | 0.0134 | 0.000 | 0.8652 | 0.0119 | 0.000 | − 0.0446 | 0.0119 | 0.000 |
| 48 | Mononeuropathies of upper limb | 0.8654 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0304 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.8809 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0288 | 0.0027 | 0.000 |
| 49 | Mononeuropathies of lower limb, other mononeuropathies and mononeuropathy in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8522 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0436 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | 0.8698 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0399 | 0.0074 | 0.000 |
| 50 | Polyneuropathies and other disorders of the peripheral nervous system | 0.8478 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0480 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | 0.8656 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0441 | 0.0061 | 0.000 |
| 51 | Diseases of myoneural junction and muscle | 0.8148 | 0.0246 | 0.000 | − 0.0810 | 0.0246 | 0.001 | 0.8355 | 0.0229 | 0.000 | − 0.0742 | 0.0229 | 0.001 |
| 52 | Cerebral palsy and other paralytic syndromes | 0.7924 | 0.0293 | 0.000 | − 0.1034 | 0.0293 | 0.000 | 0.8153 | 0.0275 | 0.000 | − 0.0945 | 0.0276 | 0.001 |
| 53 | Other disorders of the nervous system | 0.8536 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0422 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.8709 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0389 | 0.0056 | 0.000 |
| 54 | Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit | 0.8733 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0225 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.8889 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0209 | 0.0053 | 0.000 |
| 55 | Corneal scars and opacities | 0.8745 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | − 0.0213 | 0.0090 | 0.018 | 0.8874 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0224 | 0.0079 | 0.004 |
| 56 | Other disorders of cornea | 0.8743 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0215 | 0.0084 | 0.011 | 0.8884 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0214 | 0.0078 | 0.006 |
| 57 | Diseases of the eye lens (cataracts) | 0.8665 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0293 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.8818 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0280 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 58 | Disorders of the choroid and retina | 0.8526 | 0.0135 | 0.000 | − 0.0432 | 0.0135 | 0.001 | 0.8691 | 0.0125 | 0.000 | − 0.0406 | 0.0124 | 0.001 |
| 59 | Retinal vascular occlusions | 0.8829 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0129 | 0.0095 | 0.173 | 0.8971 | 0.0089 | 0.000 | − 0.0127 | 0.0088 | 0.151 |
| 60 | Other retinal disorders | 0.8655 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0303 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | 0.8808 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0290 | 0.0032 | 0.000 |
| 61 | Retinal disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8704 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0254 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | 0.8852 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0053 | 0.000 |
| 62 | Glaucomac | 0.8665 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0293 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | 0.8817 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0280 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 63 | Disorders of the vitreous body and globe | 0.8564 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | − 0.0394 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | 0.8735 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0362 | 0.0080 | 0.000 |
| 64 | Disorders of optic nerve and visual pathways | 0.8659 | 0.0159 | 0.000 | − 0.0298 | 0.0159 | 0.060 | 0.8810 | 0.0160 | 0.000 | − 0.0288 | 0.0159 | 0.071 |
| 65 | Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction | 0.8820 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0138 | 0.0052 | 0.008 | 0.8958 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0139 | 0.0046 | 0.003 |
| 66 | Visual disturbances | 0.8725 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0233 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | 0.8876 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0221 | 0.0055 | 0.000 |
| 67 | Blindness and partial sight | 0.8722 | 0.0116 | 0.000 | − 0.0236 | 0.0115 | 0.040 | 0.8873 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | − 0.0225 | 0.0103 | 0.029 |
| 68 | Nystagmus and other irregular eye movements and other disorders of eye and adnexa | 0.8674 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0284 | 0.0084 | 0.001 | 0.8821 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0277 | 0.0074 | 0.000 |
| 69 | Otosclerosis | 0.8866 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | − 0.0092 | 0.0099 | 0.351 | 0.8998 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0100 | 0.0087 | 0.250 |
| 70 | Ménière’s diseasea | 0.8679 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0279 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | 0.8832 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0265 | 0.0059 | 0.000 |
| 71 | Other diseases of the inner ear | 0.8708 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0250 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | 0.8858 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0240 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 72 | Conductive and sensorineural hearing loss | 0.8694 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0264 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | 0.8844 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0254 | 0.0035 | 0.000 |
| 73 | Other hearing loss and other disorders of ear, not elsewhere classified | 0.8584 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | − 0.0374 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | 0.8754 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0343 | 0.0079 | 0.000 |
| 74 | Presbycusis (age-related hearing loss) | 0.8735 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0223 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | 0.8882 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0216 | 0.0029 | 0.000 |
| 75 | Hearing loss, unspecified | 0.8699 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0259 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | 0.8847 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0251 | 0.0029 | 0.000 |
| 76 | Tinnitus | 0.8676 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0282 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | 0.8829 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0269 | 0.0034 | 0.000 |
| 77 | Other specified disorders of ear | 0.8648 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0310 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | 0.8803 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0294 | 0.0044 | 0.000 |
| 78 | Aortic and mitral valve diseasea | 0.8713 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | 0.8862 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0235 | 0.0044 | 0.000 |
| 79 | Hypertensive diseasesa | 0.8647 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0311 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | 0.8803 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0294 | 0.0022 | 0.000 |
| 80 | Heart failurea | 0.8514 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0444 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | 0.8688 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0410 | 0.0064 | 0.000 |
| 81 | Angina pectoris | 0.8595 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0363 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | 0.8762 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0336 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 82 | Acute myocardial infarction and subsequent myocardial infarction | 0.8705 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0253 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | 0.8854 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0244 | 0.0047 | 0.000 |
| 83 | AMI complex/other | 0.8256 | 0.0319 | 0.000 | − 0.0702 | 0.0320 | 0.028 | 0.8456 | 0.0300 | 0.000 | − 0.0641 | 0.0300 | 0.033 |
| 84 | Chronic ischaemic heart disease | 0.8635 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0323 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.8788 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0309 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 85 | Pulmonary heart disease and diseases of pulmonary circulation | 0.8611 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0347 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | 0.8778 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0319 | 0.0078 | 0.000 |
| 86 | Acute pericarditis | 0.8682 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0276 | 0.0081 | 0.001 | 0.8826 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0272 | 0.0075 | 0.000 |
| 87 | Other forms of heart disease | 0.8689 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0269 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | 0.8830 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0267 | 0.0066 | 0.000 |
| 88 | Atrioventricular and left bundle-branch block | 0.8728 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0230 | 0.0070 | 0.001 | 0.8876 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0221 | 0.0064 | 0.001 |
| 89 | Other conduction disorders | 0.8734 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0224 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.8870 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0228 | 0.0056 | 0.000 |
| 90 | Paroxysmal tachycardia | 0.8685 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0273 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | 0.8836 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0261 | 0.0037 | 0.000 |
| 91 | Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 0.8631 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0327 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | 0.8786 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0311 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 92 | Other cardiac arrhythmias | 0.8733 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0225 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | 0.8885 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0212 | 0.0038 | 0.000 |
| 93 | Complications and ill-defined descriptions of heart disease and other heart disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8580 | 0.0133 | 0.000 | − 0.0378 | 0.0133 | 0.005 | 0.8741 | 0.0120 | 0.000 | − 0.0356 | 0.0119 | 0.003 |
| 94 | Stroke | 0.8562 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0396 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | 0.8731 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0366 | 0.0042 | 0.000 |
| 95 | Cerebrovascular diseases | 0.8593 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0365 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | 0.8764 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0334 | 0.0078 | 0.000 |
| 96 | Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease | 0.8526 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0432 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | 0.8698 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0400 | 0.0053 | 0.000 |
| 97 | Atherosclerosis | 0.8563 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0395 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.8736 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0362 | 0.0054 | 0.000 |
| 98 | Aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection | 0.8495 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0463 | 0.0076 | 0.000 | 0.8663 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0435 | 0.0068 | 0.000 |
| 99 | Diseases of arteries, arterioles and capillaries | 0.8743 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0214 | 0.0066 | 0.001 | 0.8892 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0206 | 0.0058 | 0.000 |
| 100 | Other peripheral vascular diseases | 0.8492 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0465 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.8667 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0431 | 0.0053 | 0.000 |
| 101 | Phlebitis, thrombosis of the portal vein and others | 0.8617 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0340 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | 0.8777 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0321 | 0.0044 | 0.000 |
| 102 | Varicose veins of lower extremities | 0.8786 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0172 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.8922 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0176 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 103 | Haemorrhoidsa | 0.8661 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0297 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | 0.8820 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0277 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 104 | Oesophageal varices (chronic), varicose veins of other sites, other disorders of veins, nonspecific lymphadenitis, other non-infective disorders of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes and other and unspecified disorders of the circulatory system | 0.8648 | 0.0076 | 0.000 | − 0.0310 | 0.0076 | 0.000 | 0.8802 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0296 | 0.0071 | 0.000 |
| 105 | Respiratory allergya | 0.8711 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0247 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | 0.8859 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0239 | 0.0021 | 0.000 |
| 105A | Chronic lower respiratory diseasesa | 0.8665 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0293 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | 0.8819 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0279 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 106 | Bronchitis, not specified as acute or chronic, simple and mucopurulent chronic bronchitis and unspecified chronic bronchitis | 0.8645 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0313 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | 0.8803 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0295 | 0.0058 | 0.000 |
| 107 | Emphysema | 0.8610 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | − 0.0348 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | 0.8765 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0333 | 0.0081 | 0.000 |
| 108 | Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD)a | 0.8591 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0367 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.8756 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0341 | 0.0027 | 0.000 |
| 109 | Asthma, status asthmaticusa | 0.8676 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0282 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | 0.8830 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0268 | 0.0025 | 0.000 |
| 110 | Bronchiectasis | 0.9037 | 0.0145 | 0.000 | 0.0079 | 0.0145 | 0.583 | 0.9159 | 0.0138 | 0.000 | 0.0061 | 0.0138 | 0.657 |
| 111 | Other diseases of the respiratory system | 0.8674 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0284 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | 0.8828 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0270 | 0.0056 | 0.000 |
| 112 | Ulcersa | 0.8540 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0418 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.8713 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0384 | 0.0027 | 0.000 |
| 113 | Inguinal hernia | 0.8707 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0251 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | 0.8853 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0035 | 0.000 |
| 114 | Ventral hernia | 0.8603 | 0.0097 | 0.000 | − 0.0355 | 0.0097 | 0.000 | 0.8770 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0328 | 0.0085 | 0.000 |
| 115 | Crohn’s disease | 0.8582 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0376 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | 0.8747 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0350 | 0.0056 | 0.000 |
| 116 | Ulcerative colitis | 0.8624 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0334 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | 0.8783 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0315 | 0.0043 | 0.000 |
| 117 | Other non-infective gastroenteritis and colitis | 0.8656 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0302 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | 0.8812 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0286 | 0.0051 | 0.000 |
| 118 | Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) | 0.8652 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0306 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | 0.8807 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0290 | 0.0034 | 0.000 |
| 119 | Other functional intestinal disorders | 0.8563 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0395 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | 0.8734 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0364 | 0.0044 | 0.000 |
| 120 | Diseases of liver, biliary tract and pancreas | 0.8482 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0476 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | 0.8660 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0437 | 0.0058 | 0.000 |
| 121 | Psoriasisa | 0.8688 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0270 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.8841 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0256 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 122 | Infectious arthropathies | 0.8567 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0391 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | 0.8729 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0368 | 0.0073 | 0.000 |
| 123 | Rheumatoid arthritisa | 0.8447 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0511 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | 0.8628 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0470 | 0.0039 | 0.000 |
| 124 | Inflammatory polyarthropathies, except rheumatoid arthritisa | 0.8566 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0392 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | 0.8732 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0366 | 0.0029 | 0.000 |
| 125 | Polyarthrosis (arthrosis) | 0.8525 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0433 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | 0.8698 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0400 | 0.0069 | 0.000 |
| 126 | Coxarthrosis (arthrosis of hip) | 0.8549 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0409 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | 0.8716 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0381 | 0.0029 | 0.000 |
| 127 | Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of knee) | 0.8537 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0421 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | 0.8707 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0391 | 0.0026 | 0.000 |
| 128 | Arthrosis of first carpometacarpal joint and other arthrosis | 0.8564 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0394 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | 0.8733 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0365 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 129 | Acquired deformities of fingers and toes | 0.8694 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0264 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | 0.8841 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0257 | 0.0031 | 0.000 |
| 130 | Other acquired deformities of limbs | 0.8613 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0345 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | 0.8770 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0328 | 0.0041 | 0.000 |
| 131 | Disorders of patella (kneecap) | 0.8568 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0390 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | 0.8740 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0358 | 0.0045 | 0.000 |
| 132 | Internal derangement of knee | 0.8370 | 0.0124 | 0.000 | − 0.0588 | 0.0124 | 0.000 | 0.8564 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | − 0.0534 | 0.0111 | 0.000 |
| 133 | Derangement of meniscus due to old tear or injury | 0.8651 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0307 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | 0.8804 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0294 | 0.0035 | 0.000 |
| 134 | Internal derangement of knee, unspecified | 0.8602 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0356 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | 0.8762 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0335 | 0.0044 | 0.000 |
| 135 | Other specific joint derangements | 0.8306 | 0.0174 | 0.000 | − 0.0652 | 0.0174 | 0.000 | 0.8498 | 0.0155 | 0.000 | − 0.0599 | 0.0155 | 0.000 |
| 136 | Other joint disorders, not elsewhere classified | 0.8491 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0467 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | 0.8667 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0431 | 0.0059 | 0.000 |
| 137 | Systemic connective tissue disorders | 0.8672 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0286 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | 0.8826 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0272 | 0.0037 | 0.000 |
| 138 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | 0.8753 | 0.0144 | 0.000 | − 0.0205 | 0.0144 | 0.153 | 0.8910 | 0.0125 | 0.000 | − 0.0187 | 0.0125 | 0.133 |
| 139 | Dermatopolymyositis | 0.8791 | 0.0258 | 0.000 | − 0.0167 | 0.0258 | 0.518 | 0.8933 | 0.0238 | 0.000 | − 0.0164 | 0.0238 | 0.491 |
| 140 | Systemic sclerosis | 0.8716 | 0.0169 | 0.000 | − 0.0242 | 0.0169 | 0.151 | 0.8853 | 0.0157 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0157 | 0.118 |
| 141 | Kyphosis, lordosis | 0.8609 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0349 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | 0.8753 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0344 | 0.0065 | 0.000 |
| 142 | Scoliosis | 0.8475 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0483 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | 0.8651 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0446 | 0.0069 | 0.000 |
| 143 | Spinal osteochondrosis | 0.8154 | 0.0186 | 0.000 | − 0.0804 | 0.0186 | 0.000 | 0.8365 | 0.0170 | 0.000 | − 0.0733 | 0.0170 | 0.000 |
| 144 | Other deforming dorsopathies | 0.8336 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0622 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | 0.8529 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | − 0.0568 | 0.0083 | 0.000 |
| 145 | Other inflammatory spondylopathies | 0.8287 | 0.0230 | 0.000 | − 0.0671 | 0.0230 | 0.004 | 0.8488 | 0.0214 | 0.000 | − 0.0610 | 0.0214 | 0.004 |
| 146 | Spondylosis | 0.8298 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0660 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | 0.8497 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0601 | 0.0060 | 0.000 |
| 147 | Other spondylopathies and spondylopathies in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8579 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0379 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | 0.8740 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0357 | 0.0040 | 0.000 |
| 148 | Cervical disc disorders | 0.8434 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | − 0.0524 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | 0.8616 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0482 | 0.0097 | 0.000 |
| 149 | Other intervertebral disc disorders | 0.8129 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | − 0.0829 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | 0.8343 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0754 | 0.0094 | 0.000 |
| 150 | Other dorsopathies, not elsewhere classified | 0.8244 | 0.0153 | 0.000 | − 0.0714 | 0.0153 | 0.000 | 0.8448 | 0.0139 | 0.000 | − 0.0650 | 0.0139 | 0.000 |
| 151 | Dorsalgia | 0.7917 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | − 0.1041 | 0.0100 | 0.000 | 0.8144 | 0.0093 | 0.000 | − 0.0954 | 0.0094 | 0.000 |
| 152 | Soft tissue disorders | 0.8508 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | − 0.0450 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | 0.8689 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | − 0.0408 | 0.0090 | 0.000 |
| 153 | Synovitis and tenosynovitis | 0.8619 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0339 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | 0.8784 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0314 | 0.0049 | 0.000 |
| 154 | Disorders of synovium and tendon | 0.8591 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0367 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.8753 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0344 | 0.0055 | 0.000 |
| 155 | Soft tissue disorders related to use, overuse and pressure | 0.8441 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | − 0.0517 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | 0.8624 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0474 | 0.0073 | 0.000 |
| 156 | Fibroblastic disorders | 0.8670 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0288 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | 0.8823 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0275 | 0.0035 | 0.000 |
| 157 | Shoulder lesions | 0.8458 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0499 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | 0.8642 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0455 | 0.0045 | 0.000 |
| 158 | Enthesopathies of lower limb, excluding foot | 0.8480 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | − 0.0478 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | 0.8660 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | − 0.0437 | 0.0099 | 0.000 |
| 159 | Other enthesopathies | 0.8302 | 0.0138 | 0.000 | − 0.0656 | 0.0138 | 0.000 | 0.8500 | 0.0124 | 0.000 | − 0.0598 | 0.0124 | 0.000 |
| 160 | Rheumatism, unspecified | 0.7622 | 0.0268 | 0.000 | − 0.1336 | 0.0268 | 0.000 | 0.7861 | 0.0262 | 0.000 | − 0.1236 | 0.0262 | 0.000 |
| 161 | Myalgia | 0.8579 | 0.0145 | 0.000 | − 0.0379 | 0.0145 | 0.009 | 0.8753 | 0.0127 | 0.000 | − 0.0345 | 0.0128 | 0.007 |
| 162 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified | 0.8379 | 0.0198 | 0.000 | − 0.0579 | 0.0197 | 0.003 | 0.8575 | 0.0181 | 0.000 | − 0.0522 | 0.0181 | 0.004 |
| 163 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified: pain in limb | 0.8489 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0469 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | 0.8667 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0430 | 0.0059 | 0.000 |
| 164 | Fibromyalgia | 0.6959 | 0.0481 | 0.000 | − 0.1999 | 0.0481 | 0.000 | 0.7198 | 0.0489 | 0.000 | − 0.1900 | 0.0489 | 0.000 |
| 165 | Osteoporosisa | 0.8599 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0359 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | 0.8763 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0335 | 0.0027 | 0.000 |
| 166 | Osteoporosis in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8733 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | − 0.0225 | 0.0103 | 0.029 | 0.8875 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | − 0.0222 | 0.0094 | 0.018 |
| 167 | Adult osteomalacia and other disorders of bone density and structure | 0.8650 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0308 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | 0.8805 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0293 | 0.0034 | 0.000 |
| 168 | Disorders of continuity of bone | 0.8564 | 0.0180 | 0.000 | − 0.0394 | 0.0180 | 0.029 | 0.8741 | 0.0161 | 0.000 | − 0.0357 | 0.0161 | 0.026 |
| 169 | Other osteopathies | 0.8600 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0358 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | 0.8765 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0333 | 0.0059 | 0.000 |
| 170 | Other disorders of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | 0.8594 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0364 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | 0.8759 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0339 | 0.0059 | 0.000 |
| 171 | Chronic renal failure (CRF)a | 0.8665 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0293 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | 0.8825 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0273 | 0.0072 | 0.000 |
| 172 | Congenital malformations: of the nervous, circulatory, respiratory system; cleft palate and cleft lip, urinary tract, bones and muscles, other and chromosomal abnormalities not elsewhere classified | 0.8634 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0324 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | 0.8792 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0306 | 0.0032 | 0.000 |
| 173 | Congenital malformations of eye, ear, face and neck | 0.8716 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0242 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | 0.8869 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0228 | 0.0048 | 0.000 |
| 174 | Other congenital malformations of the digestive system | 0.8715 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0243 | 0.0082 | 0.003 | 0.8860 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0238 | 0.0074 | 0.001 |
| 175 | Congenital malformations of the sexual organs | 0.8713 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | 0.8861 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0236 | 0.0051 | 0.000 |
| 176 | Dementiaa | 0.8152 | 0.0151 | 0.000 | − 0.0806 | 0.0151 | 0.000 | 0.8354 | 0.0139 | 0.000 | − 0.0744 | 0.0138 | 0.000 |
| 177 | Organic, including symptomatic, mental disorders | 0.8675 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | − 0.0283 | 0.0096 | 0.003 | 0.8830 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0268 | 0.0087 | 0.002 |
| 178 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to use of alcohol | 0.8509 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0449 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.8682 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0416 | 0.0053 | 0.000 |
| 179 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to psychoactive substance use | 0.8605 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0353 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | 0.8770 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0328 | 0.0052 | 0.000 |
| 180 | Schizophreniaa | 0.8451 | 0.0133 | 0.000 | − 0.0507 | 0.0133 | 0.000 | 0.8633 | 0.0118 | 0.000 | − 0.0464 | 0.0118 | 0.000 |
| 181 | Schizotypal and delusional disorders | 0.8840 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0118 | 0.0075 | 0.115 | 0.8977 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0120 | 0.0070 | 0.085 |
| 182 | Bipolar affective disordera | 0.8703 | 0.0097 | 0.000 | − 0.0255 | 0.0097 | 0.009 | 0.8850 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | − 0.0247 | 0.0090 | 0.006 |
| 183 | Depressiona | 0.8171 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0787 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.8381 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0716 | 0.0035 | 0.000 |
| 184 | Mood (affective) disorders | 0.8657 | 0.0146 | 0.000 | − 0.0300 | 0.0146 | 0.040 | 0.8798 | 0.0137 | 0.000 | − 0.0299 | 0.0136 | 0.028 |
| 185 | Phobic anxiety disorders | 0.8378 | 0.0154 | 0.000 | − 0.0580 | 0.0154 | 0.000 | 0.8570 | 0.0140 | 0.000 | − 0.0528 | 0.0140 | 0.000 |
| 186 | Other anxiety disorders | 0.8523 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0435 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | 0.8702 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0395 | 0.0078 | 0.000 |
| 187 | Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)a | 0.8616 | 0.0150 | 0.000 | − 0.0342 | 0.0150 | 0.023 | 0.8786 | 0.0137 | 0.000 | − 0.0312 | 0.0137 | 0.023 |
| 188 | Post-traumatic stress disorder | 0.8039 | 0.0197 | 0.000 | − 0.0919 | 0.0196 | 0.000 | 0.8260 | 0.0179 | 0.000 | − 0.0837 | 0.0179 | 0.000 |
| 189 | Reactions to severe stress and adjustment disorders | 0.8609 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0348 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | 0.8782 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0316 | 0.0065 | 0.000 |
| 190 | Dissociative (conversion) disorders, somatoform disorders and other neurotic disorders | 0.8360 | 0.0148 | 0.000 | − 0.0598 | 0.0148 | 0.000 | 0.8552 | 0.0134 | 0.000 | − 0.0546 | 0.0134 | 0.000 |
| 191 | Eating disorders | 0.8557 | 0.0218 | 0.000 | − 0.0401 | 0.0217 | 0.065 | 0.8738 | 0.0202 | 0.000 | − 0.0360 | 0.0202 | 0.074 |
| 192 | Behavioural syndromes associated with physiological disturbances and physical factors | 0.8672 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0286 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | 0.8817 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0280 | 0.0064 | 0.000 |
| 193 | Emotionally unstable personality disorder | 0.8450 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0508 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | 0.8615 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0483 | 0.0071 | 0.000 |
| 194 | Specific personality disorders | 0.8376 | 0.0100 | 0.000 | − 0.0582 | 0.0100 | 0.000 | 0.8570 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | − 0.0527 | 0.0092 | 0.000 |
| 195 | Disorders of adult personality and behaviour | 0.8559 | 0.0155 | 0.000 | − 0.0399 | 0.0155 | 0.010 | 0.8736 | 0.0141 | 0.000 | − 0.0362 | 0.0141 | 0.011 |
| 196 | Mental retardation | 0.9142 | 0.0236 | 0.000 | 0.0184 | 0.0237 | 0.436 | 0.9277 | 0.0215 | 0.000 | 0.0179 | 0.0215 | 0.404 |
| 197 | Disorders of psychological development | 0.8468 | 0.0169 | 0.000 | − 0.0490 | 0.0169 | 0.004 | 0.8651 | 0.0152 | 0.000 | − 0.0447 | 0.0151 | 0.003 |
| 198 | Hyperkinetic disorders (ADHD)a | 0.8456 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0502 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | 0.8634 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0463 | 0.0075 | 0.000 |
| 199 | Behavioural and emotional disorders with onset usually occurring in childhood and adolescence | 0.8704 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0254 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | 0.8846 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0251 | 0.0057 | 0.000 |
| Denmark sample (base) | 0.8993 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | 0.9127 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | |||||||
| North Denmark Region (sample 2-3) | 0.8958 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0036 | 0.0008 | 0.000 | 0.9098 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0029 | 0.0006 | 0.000 | |
| Specific ages (dydx) | |||||||||||||
| Age 16 | 0.9121 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.215 | 0.9270 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.594 | |
| Age 20 | 0.9121 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0002 | 0.114 | 0.9264 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.009 | |
| Age 25 | 0.9097 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9236 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 30 | 0.9061 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | − 0.0008 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9198 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | − 0.0008 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 35 | 0.9024 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9161 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 40 | 0.8992 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9130 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 45 | 0.8970 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9109 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 50 | 0.8958 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.015 | 0.9098 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.036 | |
| Age 55 | 0.8954 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.742 | 0.9095 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.800 | |
| Age 60 | 0.8953 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.780 | 0.9098 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.583 | |
| Age 65 | 0.8947 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.051 | 0.9098 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.403 | |
| Age 70 | 0.8922 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0008 | 0.0002 | 0.000 | 0.9083 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0002 | 0.000 | |
| Age 75 | 0.8857 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0019 | 0.0003 | 0.000 | 0.9033 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0003 | 0.000 | |
| Age 80 | 0.8719 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0037 | 0.0006 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0032 | 0.0005 | 0.000 | |
| Age 85 | 0.8468 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0065 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | 0.8702 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0057 | 0.0009 | 0.000 | |
Note: n = 55,616 in all models
aComplex defined condition
Table 5.
ALDVMM predictions and marginal effects of representative 50-year-olds by sex: UK full model – chronic conditions, socio-economic, lifestyle and risk variables
| No. | Condition or covariable | Representative 50-year-old male with no chronic conditions | Representative 50-year-old female with no chronic conditions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model prediction | Marginal effect | Model prediction | Marginal effect | ||||||||||
| β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | ||
| No conditions | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 1 | Chronic viral hepatitis | 0.8409 | 0.0119 | 0.000 | − 0.0394 | 0.0118 | 0.001 | 0.8540 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | − 0.0380 | 0.0110 | 0.001 |
| 2 | Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease | 0.8294 | 0.0209 | 0.000 | − 0.0509 | 0.0208 | 0.015 | 0.8433 | 0.0196 | 0.000 | − 0.0486 | 0.0195 | 0.013 |
| 3 | Malignant neoplasms of other and unspecified localizations | 0.8775 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0027 | 0.0049 | 0.574 | 0.8888 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0032 | 0.0046 | 0.486 |
| 4 | Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs | 0.8486 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0316 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | 0.8625 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0295 | 0.0060 | 0.000 |
| 5 | Malignant neoplasm of colon | 0.8676 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0127 | 0.0067 | 0.061 | 0.8800 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0120 | 0.0063 | 0.058 |
| 6 | Malignant neoplasms of rectosigmoid junction, rectum, anus and anal canal | 0.8827 | 0.0102 | 0.000 | 0.0024 | 0.0101 | 0.812 | 0.8938 | 0.0097 | 0.000 | 0.0018 | 0.0096 | 0.849 |
| 7 | Malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung | 0.8737 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0066 | 0.0076 | 0.385 | 0.8853 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0067 | 0.0067 | 0.319 |
| 8 | Malignant melanoma of skin | 0.8769 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0034 | 0.0047 | 0.467 | 0.8886 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0034 | 0.0044 | 0.439 |
| 9 | Other malignant neoplasms of skin | 0.8843 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | 0.0040 | 0.0054 | 0.455 | 0.8953 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | 0.0034 | 0.0050 | 0.501 |
| 10 | Malignant neoplasm of breast | 0.8715 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0088 | 0.0033 | 0.008 | 0.8835 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0085 | 0.0031 | 0.007 |
| 11 | Malignant neoplasms of female genital organs | 0.8675 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0128 | 0.0059 | 0.030 | 0.8793 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0127 | 0.0055 | 0.021 |
| 12 | Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri, corpus uteri and part unspecified | 0.8728 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0075 | 0.0052 | 0.154 | 0.8848 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0072 | 0.0048 | 0.136 |
| 13 | Malignant tumour of the male genitalia | 0.8756 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0047 | 0.0079 | 0.549 | 0.8868 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0052 | 0.0074 | 0.481 |
| 14 | Malignant neoplasm of prostate | 0.8797 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0041 | 0.896 | 0.8909 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0011 | 0.0039 | 0.787 |
| 15 | Malignant neoplasms of urinary tract | 0.8783 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0020 | 0.0068 | 0.767 | 0.8896 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0023 | 0.0064 | 0.714 |
| 16 | Brain cancera | 0.8860 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | 0.0057 | 0.0057 | 0.317 | 0.8966 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | 0.0046 | 0.0054 | 0.398 |
| 17 | Malignant neoplasms of ill-defined, secondary and unspecified sites, and of independent (primary) multiple sites | 0.8756 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0047 | 0.0044 | 0.282 | 0.8868 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0042 | 0.218 |
| 18 | Malignant neoplasms, stated or presumed to be primary, of lymphoid, haematopoietic and related tissue | 0.8745 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0058 | 0.0060 | 0.338 | 0.8866 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0053 | 0.0056 | 0.341 |
| 19 | In situ neoplasms | 0.8755 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0047 | 0.0043 | 0.272 | 0.8873 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0047 | 0.0039 | 0.231 |
| 20 | Haemolytic anaemias | 0.8862 | 0.0102 | 0.000 | 0.0059 | 0.0102 | 0.564 | 0.8972 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | 0.0053 | 0.0096 | 0.581 |
| 21 | Aplastic and other anaemias | 0.8698 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0105 | 0.0066 | 0.112 | 0.8819 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0101 | 0.0062 | 0.102 |
| 22 | Other anaemias | 0.8695 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0107 | 0.0051 | 0.033 | 0.8823 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0097 | 0.0046 | 0.037 |
| 23 | Coagulation defects, purpura and other haemorrhagic conditions | 0.8818 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | 0.0015 | 0.0061 | 0.806 | 0.8929 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | 0.0009 | 0.0057 | 0.871 |
| 24 | Other diseases of blood and blood-forming organs | 0.8570 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0233 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.8697 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0223 | 0.0058 | 0.000 |
| 25 | Certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | 0.8696 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0107 | 0.0081 | 0.184 | 0.8816 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0104 | 0.0074 | 0.162 |
| 26 | Diseases of the thyroida | 0.8718 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0085 | 0.0025 | 0.001 | 0.8836 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0084 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 27 | Thyrotoxicosisa | 0.8723 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0033 | 0.015 | 0.8842 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0078 | 0.0031 | 0.013 |
| 28 | Diabetes type 1a | 0.8756 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0047 | 0.0051 | 0.358 | 0.8869 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0048 | 0.290 |
| 29 | Diabetes type 2a | 0.8701 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | 0.8822 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0098 | 0.0023 | 0.000 |
| 30 | Diabetes othersa | 0.8726 | 0.0119 | 0.000 | − 0.0077 | 0.0118 | 0.515 | 0.8841 | 0.0113 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0112 | 0.481 |
| 31 | Disorders of other endocrine glands | 0.8723 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0048 | 0.098 | 0.8844 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0075 | 0.0045 | 0.091 |
| 32 | Metabolic disorders | 0.8600 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | 0.0203 | 0.0065 | 0.002 | 0.8734 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0186 | 0.0058 | 0.001 |
| 33 | Disturbances in lipoprotein circulation and other lipidsa | 0.8775 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0028 | 0.0020 | 0.167 | 0.8888 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0032 | 0.0020 | 0.114 |
| 34 | Cystic fibrosisa | 0.8811 | 0.0115 | 0.000 | 0.0008 | 0.0115 | 0.941 | 0.8923 | 0.0110 | 0.000 | 0.0004 | 0.0110 | 0.974 |
| 35 | Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system | 0.8816 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | 0.0014 | 0.0096 | 0.886 | 0.8926 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | 0.0006 | 0.0090 | 0.943 |
| 36 | Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system and other degenerative diseases | 0.8686 | 0.0131 | 0.000 | − 0.0117 | 0.0132 | 0.374 | 0.8824 | 0.0121 | 0.000 | − 0.0096 | 0.0121 | 0.429 |
| 37 | Parkinson’s diseasea | 0.8664 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0139 | 0.0041 | 0.001 | 0.8788 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0132 | 0.0038 | 0.001 |
| 38 | Extrapyramidal and movement disorders | 0.8642 | 0.0102 | 0.000 | − 0.0161 | 0.0101 | 0.113 | 0.8769 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0150 | 0.0093 | 0.104 |
| 39 | Sclerosis | 0.8501 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0302 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | 0.8638 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0282 | 0.0069 | 0.000 |
| 40 | Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system | 0.8690 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0113 | 0.0086 | 0.192 | 0.8811 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0109 | 0.0080 | 0.172 |
| 41 | Epilepsya | 0.8708 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0095 | 0.0037 | 0.010 | 0.8827 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0093 | 0.0035 | 0.008 |
| 42 | Migrainea | 0.8686 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0117 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | 0.8810 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0110 | 0.0022 | 0.000 |
| 43 | Other headache syndromes | 0.8740 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0063 | 0.0065 | 0.333 | 0.8859 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0061 | 0.0059 | 0.302 |
| 44 | Transient cerebral ischaemic attacks and related syndromes and vascular syndromes of brain in cerebrovascular diseases | 0.8714 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0088 | 0.0036 | 0.015 | 0.8836 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0084 | 0.0034 | 0.014 |
| 45 | Sleep disorders | 0.8721 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0082 | 0.0036 | 0.023 | 0.8840 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0034 | 0.018 |
| 46 | Disorders of trigeminal nerve and facial nerve disorders | 0.8717 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0086 | 0.0049 | 0.077 | 0.8833 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0087 | 0.0044 | 0.049 |
| 47 | Disorders of other cranial nerves, cranial nerve disorders in diseases classified elsewhere, nerve root and plexus disorders and nerve root and plexus compressions in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8685 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0118 | 0.0065 | 0.069 | 0.8804 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0116 | 0.0059 | 0.051 |
| 48 | Mononeuropathies of upper limb | 0.8721 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0082 | 0.0025 | 0.001 | 0.8838 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0024 | 0.001 |
| 49 | Mononeuropathies of lower limb, other mononeuropathies and mononeuropathy in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8685 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0118 | 0.0051 | 0.022 | 0.8808 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0112 | 0.0047 | 0.018 |
| 50 | Polyneuropathies and other disorders of the peripheral nervous system | 0.8644 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0159 | 0.0048 | 0.001 | 0.8767 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0153 | 0.0045 | 0.001 |
| 51 | Diseases of myoneural junction and muscle | 0.8654 | 0.0156 | 0.000 | − 0.0149 | 0.0156 | 0.338 | 0.8788 | 0.0138 | 0.000 | − 0.0132 | 0.0137 | 0.335 |
| 52 | Cerebral palsy and other paralytic syndromes | 0.8403 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0400 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | 0.8548 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0372 | 0.0087 | 0.000 |
| 53 | Other disorders of the nervous system | 0.8664 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0138 | 0.0046 | 0.003 | 0.8787 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0133 | 0.0043 | 0.002 |
| 54 | Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit | 0.8798 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0051 | 0.931 | 0.8916 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0048 | 0.932 |
| 55 | Corneal scars and opacities | 0.8666 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0137 | 0.0080 | 0.086 | 0.8788 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0132 | 0.0073 | 0.069 |
| 56 | Other disorders of cornea | 0.8647 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0156 | 0.0097 | 0.109 | 0.8766 | 0.0093 | 0.000 | − 0.0153 | 0.0091 | 0.093 |
| 57 | Diseases of the eye lens (cataracts) | 0.8720 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0083 | 0.0033 | 0.013 | 0.8837 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0083 | 0.0032 | 0.009 |
| 58 | Disorders of the choroid and retina | 0.8512 | 0.0137 | 0.000 | − 0.0291 | 0.0137 | 0.034 | 0.8647 | 0.0125 | 0.000 | − 0.0273 | 0.0125 | 0.029 |
| 59 | Retinal vascular occlusions | 0.8940 | 0.0128 | 0.000 | 0.0137 | 0.0128 | 0.283 | 0.9046 | 0.0123 | 0.000 | 0.0127 | 0.0123 | 0.302 |
| 60 | Other retinal disorders | 0.8718 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0084 | 0.0032 | 0.009 | 0.8837 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0083 | 0.0031 | 0.007 |
| 61 | Retinal disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8732 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0071 | 0.0052 | 0.172 | 0.8846 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0074 | 0.0049 | 0.136 |
| 62 | Glaucomac | 0.8696 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0106 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | 0.8816 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0104 | 0.0028 | 0.000 |
| 63 | Disorders of the vitreous body and globe | 0.8679 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | − 0.0124 | 0.0089 | 0.163 | 0.8804 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0116 | 0.0079 | 0.146 |
| 64 | Disorders of optic nerve and visual pathways | 0.8686 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | − 0.0117 | 0.0090 | 0.196 | 0.8805 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0115 | 0.0085 | 0.173 |
| 65 | Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction | 0.8820 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | 0.0017 | 0.0051 | 0.740 | 0.8934 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | 0.0014 | 0.0048 | 0.766 |
| 66 | Visual disturbances | 0.8745 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0058 | 0.0052 | 0.263 | 0.8860 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0060 | 0.0049 | 0.220 |
| 67 | Blindness and partial sight | 0.8818 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | 0.0016 | 0.0082 | 0.850 | 0.8928 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | 0.0009 | 0.0078 | 0.913 |
| 68 | Nystagmus and other irregular eye movements and other disorders of eye and adnexa | 0.8752 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0050 | 0.0058 | 0.383 | 0.8866 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0053 | 0.0054 | 0.326 |
| 69 | Otosclerosis | 0.8844 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | 0.0041 | 0.0058 | 0.482 | 0.8951 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | 0.0031 | 0.0055 | 0.572 |
| 70 | Ménière’s diseasea | 0.8773 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0029 | 0.0057 | 0.608 | 0.8887 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0033 | 0.0054 | 0.536 |
| 71 | Other diseases of the inner ear | 0.8761 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0041 | 0.0032 | 0.200 | 0.8876 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0044 | 0.0031 | 0.152 |
| 72 | Conductive and sensorineural hearing loss | 0.8730 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0072 | 0.0037 | 0.052 | 0.8847 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0072 | 0.0035 | 0.040 |
| 73 | Other hearing loss and other disorders of ear, not elsewhere classified | 0.8752 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0058 | 0.381 | 0.8866 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0054 | 0.0055 | 0.329 |
| 74 | Presbycusis (age-related hearing loss) | 0.8721 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0031 | 0.009 | 0.8842 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0078 | 0.0029 | 0.008 |
| 75 | Hearing loss, unspecified | 0.8750 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0053 | 0.0031 | 0.084 | 0.8864 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0029 | 0.058 |
| 76 | Tinnitus | 0.8716 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0087 | 0.0035 | 0.012 | 0.8836 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0084 | 0.0032 | 0.009 |
| 77 | Other specified disorders of ear | 0.8700 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0103 | 0.0048 | 0.031 | 0.8818 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0045 | 0.024 |
| 78 | Aortic and mitral valve diseasea | 0.8748 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0055 | 0.0041 | 0.181 | 0.8866 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0054 | 0.0039 | 0.168 |
| 79 | Hypertensive diseasesa | 0.8722 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | 0.8840 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0019 | 0.000 |
| 80 | Heart failurea | 0.8648 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | − 0.0155 | 0.0069 | 0.026 | 0.8771 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0149 | 0.0065 | 0.022 |
| 81 | Angina pectoris | 0.8685 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0118 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | 0.8809 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0111 | 0.0029 | 0.000 |
| 82 | Acute myocardial infarction and subsequent myocardial infarction | 0.8771 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0032 | 0.0049 | 0.509 | 0.8884 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0035 | 0.0046 | 0.444 |
| 83 | AMI complex/other | 0.8764 | 0.0201 | 0.000 | − 0.0039 | 0.0200 | 0.846 | 0.8889 | 0.0174 | 0.000 | − 0.0030 | 0.0173 | 0.860 |
| 84 | Chronic ischaemic heart disease | 0.8678 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0125 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | 0.8798 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0121 | 0.0031 | 0.000 |
| 85 | Pulmonary heart disease and diseases of pulmonary circulation | 0.8782 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0021 | 0.0085 | 0.805 | 0.8896 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0024 | 0.0081 | 0.765 |
| 86 | Acute pericarditis | 0.8709 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | − 0.0094 | 0.0103 | 0.362 | 0.8826 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | − 0.0093 | 0.0096 | 0.329 |
| 87 | Other forms of heart disease | 0.8629 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0174 | 0.0073 | 0.018 | 0.8756 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0164 | 0.0067 | 0.015 |
| 88 | Atrioventricular and left bundle-branch block | 0.8235 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | − 0.0568 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | 0.8402 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | − 0.0518 | 0.0105 | 0.000 |
| 89 | Other conduction disorders | 0.8668 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0135 | 0.0057 | 0.018 | 0.8786 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0134 | 0.0054 | 0.013 |
| 90 | Paroxysmal tachycardia | 0.8708 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0095 | 0.0035 | 0.008 | 0.8830 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0090 | 0.0033 | 0.007 |
| 91 | Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 0.8713 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0090 | 0.0030 | 0.003 | 0.8830 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0089 | 0.0029 | 0.002 |
| 92 | Other cardiac arrhythmias | 0.8769 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0034 | 0.0039 | 0.381 | 0.8886 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0033 | 0.0036 | 0.352 |
| 93 | Complications and ill-defined descriptions of heart disease and other heart disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8596 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | − 0.0207 | 0.0104 | 0.047 | 0.8720 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0199 | 0.0098 | 0.041 |
| 94 | Stroke | 0.8701 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0044 | 0.020 | 0.8820 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0100 | 0.0041 | 0.016 |
| 95 | Cerebrovascular diseases | 0.8762 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0041 | 0.0076 | 0.592 | 0.8881 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | − 0.0039 | 0.0069 | 0.578 |
| 96 | Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease | 0.8668 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0134 | 0.0062 | 0.030 | 0.8789 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0130 | 0.0058 | 0.026 |
| 97 | Atherosclerosis | 0.8636 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0167 | 0.0058 | 0.004 | 0.8766 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0154 | 0.0054 | 0.005 |
| 98 | Aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection | 0.8620 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0183 | 0.0059 | 0.002 | 0.8743 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0177 | 0.0055 | 0.001 |
| 99 | Diseases of arteries, arterioles and capillaries | 0.8811 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | 0.0008 | 0.0060 | 0.895 | 0.8928 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | 0.0008 | 0.0057 | 0.882 |
| 100 | Other peripheral vascular diseases | 0.8619 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0184 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | 0.8745 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0175 | 0.0043 | 0.000 |
| 101 | Phlebitis, thrombosis of the portal vein and others | 0.8708 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0094 | 0.0042 | 0.025 | 0.8828 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0092 | 0.0039 | 0.020 |
| 102 | Varicose veins of lower extremities | 0.8751 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0052 | 0.0034 | 0.128 | 0.8866 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0054 | 0.0032 | 0.094 |
| 103 | Haemorrhoidsa | 0.8722 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0028 | 0.004 | 0.8841 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0027 | 0.003 |
| 104 | Oesophageal varices (chronic), varicose veins of other sites, other disorders of veins, nonspecific lymphadenitis, other non-infective disorders of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes and other and unspecified disorders of the circulatory system | 0.8750 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0052 | 0.0064 | 0.411 | 0.8865 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0055 | 0.0060 | 0.358 |
| 105 | Respiratory allergya | 0.8738 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0065 | 0.0019 | 0.001 | 0.8855 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0065 | 0.0019 | 0.001 |
| 105A | Chronic lower respiratory diseasesa | 0.8724 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | 0.8841 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0022 | 0.000 |
| 106 | Bronchitis, not specified as acute or chronic, simple and mucopurulent chronic bronchitis and unspecified chronic bronchitis | 0.8718 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0085 | 0.0064 | 0.183 | 0.8839 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0058 | 0.168 |
| 107 | Emphysema | 0.8751 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | − 0.0052 | 0.0104 | 0.616 | 0.8863 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | − 0.0057 | 0.0098 | 0.562 |
| 108 | Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD)a | 0.8727 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0076 | 0.0025 | 0.003 | 0.8845 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0075 | 0.0024 | 0.002 |
| 109 | Asthma, status asthmaticusa | 0.8739 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0064 | 0.0023 | 0.006 | 0.8856 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0063 | 0.0022 | 0.005 |
| 110 | Bronchiectasis | 0.8854 | 0.0122 | 0.000 | 0.0051 | 0.0122 | 0.676 | 0.8960 | 0.0116 | 0.000 | 0.0040 | 0.0116 | 0.728 |
| 111 | Other diseases of the respiratory system | 0.8751 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0058 | 0.374 | 0.8869 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0053 | 0.339 |
| 112 | Ulcersa | 0.8677 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0125 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.8803 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0116 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 113 | Inguinal hernia | 0.8721 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0082 | 0.0036 | 0.021 | 0.8840 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0033 | 0.016 |
| 114 | Ventral hernia | 0.8743 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0060 | 0.0066 | 0.366 | 0.8859 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0060 | 0.0063 | 0.337 |
| 115 | Crohn’s disease | 0.8690 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0113 | 0.0048 | 0.018 | 0.8809 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0111 | 0.0045 | 0.014 |
| 116 | Ulcerative colitis | 0.8726 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0077 | 0.0037 | 0.040 | 0.8841 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0036 | 0.027 |
| 117 | Other non-infective gastroenteritis and colitis | 0.8787 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0016 | 0.0048 | 0.734 | 0.8899 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0020 | 0.0045 | 0.650 |
| 118 | Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) | 0.8727 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0076 | 0.0033 | 0.022 | 0.8845 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0075 | 0.0031 | 0.016 |
| 119 | Other functional intestinal disorders | 0.8708 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0094 | 0.0035 | 0.007 | 0.8829 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0091 | 0.0032 | 0.005 |
| 120 | Diseases of liver, biliary tract and pancreas | 0.8602 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0201 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | 0.8738 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0181 | 0.0050 | 0.000 |
| 121 | Psoriasisa | 0.8723 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0031 | 0.011 | 0.8841 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0078 | 0.0030 | 0.008 |
| 122 | Infectious arthropathies | 0.8641 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0162 | 0.0078 | 0.039 | 0.8764 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0156 | 0.0071 | 0.029 |
| 123 | Rheumatoid arthritisa | 0.8636 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0167 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | 0.8760 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0160 | 0.0029 | 0.000 |
| 124 | Inflammatory polyarthropathies, except rheumatoid arthritisa | 0.8649 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0153 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | 0.8774 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0146 | 0.0026 | 0.000 |
| 125 | Polyarthrosis (arthrosis) | 0.8606 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0197 | 0.0078 | 0.012 | 0.8740 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0180 | 0.0069 | 0.009 |
| 126 | Coxarthrosis (arthrosis of hip) | 0.8563 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0240 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | 0.8696 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0224 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 127 | Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of knee) | 0.8597 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0206 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.8728 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0191 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 128 | Arthrosis of first carpometacarpal joint and other arthrosis | 0.8654 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0149 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.8781 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0139 | 0.0027 | 0.000 |
| 129 | Acquired deformities of fingers and toes | 0.8694 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0109 | 0.0032 | 0.001 | 0.8814 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0106 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 130 | Other acquired deformities of limbs | 0.8685 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0117 | 0.0038 | 0.002 | 0.8804 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0116 | 0.0036 | 0.001 |
| 131 | Disorders of patella (kneecap) | 0.8681 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0122 | 0.0036 | 0.001 | 0.8805 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0115 | 0.0033 | 0.001 |
| 132 | Internal derangement of knee | 0.8541 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | − 0.0262 | 0.0092 | 0.004 | 0.8685 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0235 | 0.0080 | 0.003 |
| 133 | Derangement of meniscus due to old tear or injury | 0.8647 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0156 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | 0.8769 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0151 | 0.0035 | 0.000 |
| 134 | Internal derangement of knee, unspecified | 0.8622 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0181 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | 0.8752 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0168 | 0.0039 | 0.000 |
| 135 | Other specific joint derangements | 0.8626 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0177 | 0.0064 | 0.006 | 0.8745 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0175 | 0.0061 | 0.004 |
| 136 | Other joint disorders, not elsewhere classified | 0.8586 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | − 0.0217 | 0.0105 | 0.039 | 0.8722 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0198 | 0.0088 | 0.024 |
| 137 | Systemic connective tissue disorders | 0.8766 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0037 | 0.0036 | 0.314 | 0.8884 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0035 | 0.0034 | 0.292 |
| 138 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | 0.8941 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | 0.0138 | 0.0104 | 0.186 | 0.9047 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | 0.0127 | 0.0098 | 0.196 |
| 139 | Dermatopolymyositis | 0.8747 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0081 | 0.489 | 0.8857 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0063 | 0.0077 | 0.415 |
| 140 | Systemic sclerosis | 0.8731 | 0.0175 | 0.000 | − 0.0072 | 0.0174 | 0.679 | 0.8850 | 0.0157 | 0.000 | − 0.0070 | 0.0157 | 0.658 |
| 141 | Kyphosis, lordosis | 0.8545 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | − 0.0258 | 0.0095 | 0.007 | 0.8680 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | − 0.0240 | 0.0083 | 0.004 |
| 142 | Scoliosis | 0.8633 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0170 | 0.0070 | 0.016 | 0.8762 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0158 | 0.0061 | 0.010 |
| 143 | Spinal osteochondrosis | 0.8384 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | − 0.0419 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | 0.8535 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0385 | 0.0097 | 0.000 |
| 144 | Other deforming dorsopathies | 0.8561 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0241 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | 0.8698 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0221 | 0.0050 | 0.000 |
| 145 | Other inflammatory spondylopathies | 0.8522 | 0.0135 | 0.000 | − 0.0281 | 0.0135 | 0.037 | 0.8668 | 0.0122 | 0.000 | − 0.0252 | 0.0122 | 0.039 |
| 146 | Spondylosis | 0.8583 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | 0.0220 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | 0.8717 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0203 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 147 | Other spondylopathies and spondylopathies in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8624 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0179 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | 0.8751 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0169 | 0.0037 | 0.000 |
| 148 | Cervical disc disorders | 0.8665 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0138 | 0.0043 | 0.001 | 0.8782 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0138 | 0.0041 | 0.001 |
| 149 | Other intervertebral disc disorders | 0.8558 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | 0.8691 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0229 | 0.0040 | 0.000 |
| 150 | Other dorsopathies, not elsewhere classified | 0.8532 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0271 | 0.0088 | 0.002 | 0.8675 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0080 | 0.002 |
| 151 | Dorsalgia | 0.8478 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0325 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.8625 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0295 | 0.0055 | 0.000 |
| 152 | Soft tissue disorders | 0.8722 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0053 | 0.127 | 0.8838 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0050 | 0.101 |
| 153 | Synovitis and tenosynovitis | 0.8680 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0123 | 0.0043 | 0.004 | 0.8804 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0116 | 0.0039 | 0.003 |
| 154 | Disorders of synovium and tendon | 0.8660 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0142 | 0.0047 | 0.002 | 0.8785 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0135 | 0.0042 | 0.001 |
| 155 | Soft tissue disorders related to use, overuse and pressure | 0.8595 | 0.0076 | 0.000 | − 0.0208 | 0.0074 | 0.005 | 0.8728 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0192 | 0.0065 | 0.003 |
| 156 | Fibroblastic disorders | 0.8698 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0105 | 0.0036 | 0.004 | 0.8817 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0103 | 0.0034 | 0.002 |
| 157 | Shoulder lesions | 0.8637 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0166 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.8769 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0150 | 0.0032 | 0.000 |
| 158 | Enthesopathies of lower limb, excluding foot | 0.8582 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | − 0.0220 | 0.0104 | 0.034 | 0.8714 | 0.0093 | 0.000 | − 0.0206 | 0.0091 | 0.023 |
| 159 | Other enthesopathies | 0.8603 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0200 | 0.0066 | 0.003 | 0.8734 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0186 | 0.0058 | 0.001 |
| 160 | Rheumatism, unspecified | 0.8539 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | − 0.0264 | 0.0094 | 0.005 | 0.8663 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0257 | 0.0085 | 0.003 |
| 161 | Myalgia | 0.8771 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0032 | 0.0056 | 0.567 | 0.8883 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0037 | 0.0052 | 0.475 |
| 162 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified | 0.8649 | 0.0097 | 0.000 | − 0.0154 | 0.0097 | 0.111 | 0.8784 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0136 | 0.0085 | 0.108 |
| 163 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified: pain in limb | 0.8639 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0164 | 0.0052 | 0.002 | 0.8768 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0152 | 0.0046 | 0.001 |
| 164 | Fibromyalgia | 0.5191 | 0.0343 | 0.000 | − 0.3612 | 0.0345 | 0.000 | 0.5091 | 0.0365 | 0.000 | − 0.3829 | 0.0368 | 0.000 |
| 165 | Osteoporosisa | 0.8690 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0113 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.8811 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0109 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 166 | Osteoporosis in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8658 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | − 0.0145 | 0.0111 | 0.190 | 0.8775 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | − 0.0145 | 0.0105 | 0.166 |
| 167 | Adult osteomalacia and other disorders of bone density and structure | 0.8709 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0094 | 0.0034 | 0.006 | 0.8828 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0091 | 0.0032 | 0.005 |
| 168 | Disorders of continuity of bone | 0.8748 | 0.0155 | 0.000 | − 0.0055 | 0.0154 | 0.720 | 0.8871 | 0.0141 | 0.000 | − 0.0049 | 0.0141 | 0.729 |
| 169 | Other osteopathies | 0.8709 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0094 | 0.0059 | 0.110 | 0.8832 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0088 | 0.0053 | 0.097 |
| 170 | Other disorders of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | 0.8685 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0117 | 0.0047 | 0.013 | 0.8806 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0114 | 0.0043 | 0.009 |
| 171 | Chronic renal failure (CRF)a | 0.8808 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | 0.0006 | 0.0092 | 0.951 | 0.8922 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | 0.0002 | 0.0087 | 0.979 |
| 172 | Congenital malformations: of the nervous, circulatory, respiratory system; cleft palate and cleft lip, urinary tract, bones and muscles, other and chromosomal abnormalities not elsewhere classified | 0.8663 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0140 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | 0.8785 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0135 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 173 | Congenital malformations of eye, ear, face and neck | 0.8812 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | 0.0009 | 0.0047 | 0.848 | 0.8925 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.0045 | 0.915 |
| 174 | Other congenital malformations of the digestive system | 0.8762 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0041 | 0.0071 | 0.561 | 0.8874 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0046 | 0.0067 | 0.492 |
| 175 | Congenital malformations of the sexual organs | 0.8751 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0046 | 0.263 | 0.8867 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0053 | 0.0044 | 0.223 |
| 176 | Dementiaa | 0.8423 | 0.0138 | 0.000 | − 0.0380 | 0.0136 | 0.005 | 0.8559 | 0.0128 | 0.000 | − 0.0361 | 0.0127 | 0.005 |
| 177 | Organic, including symptomatic, mental disorders | 0.8672 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0131 | 0.0067 | 0.050 | 0.8794 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0126 | 0.0062 | 0.043 |
| 178 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to use of alcohol | 0.8676 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0127 | 0.0051 | 0.012 | 0.8796 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0123 | 0.0048 | 0.009 |
| 179 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to psychoactive substance use | 0.8757 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0046 | 0.0043 | 0.285 | 0.8873 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0046 | 0.0041 | 0.254 |
| 180 | Schizophreniaa | 0.8599 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0203 | 0.0085 | 0.017 | 0.8734 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0186 | 0.0078 | 0.016 |
| 181 | Schizotypal and delusional disorders | 0.8925 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | 0.0122 | 0.0098 | 0.216 | 0.9028 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | 0.0109 | 0.0094 | 0.249 |
| 182 | Bipolar affective disordera | 0.8723 | 0.0114 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0114 | 0.481 | 0.8841 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0107 | 0.459 |
| 183 | Depressiona | 0.8513 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0290 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.8655 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0265 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 184 | Mood (affective) disorders | 0.8599 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | − 0.0203 | 0.0108 | 0.061 | 0.8722 | 0.0102 | 0.000 | − 0.0198 | 0.0102 | 0.051 |
| 185 | Phobic anxiety disorders | 0.8635 | 0.0107 | 0.000 | − 0.0168 | 0.0107 | 0.116 | 0.8768 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0152 | 0.0097 | 0.119 |
| 186 | Other anxiety disorders | 0.8785 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0018 | 0.0071 | 0.801 | 0.8899 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0021 | 0.0067 | 0.757 |
| 187 | Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)a | 0.8647 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0156 | 0.0087 | 0.073 | 0.8777 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0143 | 0.0081 | 0.079 |
| 188 | Post-traumatic stress disorder | 0.8613 | 0.0107 | 0.000 | − 0.0190 | 0.0106 | 0.074 | 0.8733 | 0.0101 | 0.000 | − 0.0186 | 0.0100 | 0.062 |
| 189 | Reactions to severe stress and adjustment disorders | 0.8820 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | 0.0017 | 0.0066 | 0.795 | 0.8933 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.0013 | 0.0063 | 0.834 |
| 190 | Dissociative (conversion) disorders, somatoform disorders and other neurotic disorders | 0.8651 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0152 | 0.0084 | 0.073 | 0.8780 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0139 | 0.0072 | 0.053 |
| 191 | Eating disorders | 0.9110 | 0.0290 | 0.000 | 0.0307 | 0.0291 | 0.291 | 0.9215 | 0.0288 | 0.000 | 0.0295 | 0.0287 | 0.304 |
| 192 | Behavioural syndromes associated with physiological disturbances and physical factors | 0.8768 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0035 | 0.0061 | 0.564 | 0.8879 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0041 | 0.0058 | 0.480 |
| 193 | Emotionally unstable personality disorder | 0.8634 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0169 | 0.0065 | 0.009 | 0.8752 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0167 | 0.0061 | 0.006 |
| 194 | Specific personality disorders | 0.8740 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0063 | 0.0057 | 0.273 | 0.8860 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0060 | 0.0053 | 0.259 |
| 195 | Disorders of adult personality and behaviour | 0.8785 | 0.0113 | 0.000 | − 0.0017 | 0.0113 | 0.877 | 0.8898 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | − 0.0022 | 0.0107 | 0.838 |
| 196 | Mental retardation | 0.9524 | 0.0229 | 0.000 | 0.0722 | 0.0231 | 0.002 | 0.9599 | 0.0211 | 0.000 | 0.0679 | 0.0212 | 0.001 |
| 197 | Disorders of psychological development | 0.8882 | 0.0122 | 0.000 | 0.0079 | 0.0122 | 0.514 | 0.9003 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | 0.0083 | 0.0111 | 0.452 |
| 198 | Hyperkinetic disorders (ADHD)a | 0.8732 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0071 | 0.0059 | 0.230 | 0.8850 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0070 | 0.0055 | 0.203 |
| 199 | Behavioural and emotional disorders with onset usually occurring in childhood and adolescence | 0.8747 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0060 | 0.354 | 0.8862 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0058 | 0.0057 | 0.312 |
| Denmark sample (base) | 0.8818 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8934 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| North Denmark Region (sample 2–3) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0016 | 0.0007 | 0.019 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0014 | 0.0006 | 0.024 | |
| Specific ages (dydx) | |||||||||||||
| Age 16 | 0.8990 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.226 | 0.9122 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0002 | 0.045 | |
| Age 20 | 0.8973 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0002 | 0.016 | 0.9100 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0002 | 0.002 | |
| Age 25 | 0.8943 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 0.9065 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0002 | 0.000 | |
| Age 30 | 0.8909 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0002 | 0.000 | 0.9029 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0002 | 0.000 | |
| Age 35 | 0.8877 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.8994 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 40 | 0.8847 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.8964 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 45 | 0.8822 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.8939 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 50 | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 55 | 0.8789 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.004 | 0.8907 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.015 | |
| Age 60 | 0.8781 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.320 | 0.8901 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.586 | |
| Age 65 | 0.8779 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.978 | 0.8901 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.648 | |
| Age 70 | 0.8780 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.705 | 0.8907 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.347 | |
| Age 75 | 0.8784 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.757 | 0.8916 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.301 | |
| Age 80 | 0.8784 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.705 | 0.8924 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.553 | |
| Age 85 | 0.8773 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.148 | 0.8924 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.541 | |
| Education | |||||||||||||
| No education (base) | 0.8778 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.8895 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Student | 0.8788 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | 0.0011 | 0.0038 | 0.778 | 0.8901 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | 0.0006 | 0.0038 | 0.885 | |
| Short | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.0025 | 0.0020 | 0.197 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | 0.0024 | 0.0020 | 0.219 | |
| Middle (BSc eq) | 0.8899 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | 0.0121 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | 0.9012 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | 0.0117 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | |
| Higher (MSc+) | 0.9029 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | 0.0252 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | 0.9139 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | 0.0244 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | |
| Ethnicity | |||||||||||||
| Danish (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Western | 0.8704 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0099 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.8833 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0087 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | |
| Non-Western | 0.8703 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0100 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | 0.8828 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0092 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | |
| Income | |||||||||||||
| 0.19 (25%) | 0.8806 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0044 | 0.0046 | 0.339 | 0.8924 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0048 | 0.292 | |
| 0.26 (50%) | 0.8804 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0043 | 0.0046 | 0.346 | 0.8921 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0050 | 0.0048 | 0.299 | |
| 0.33 (75%) | 0.8800 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0042 | 0.0045 | 0.355 | 0.8917 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0048 | 0.0047 | 0.307 | |
| Marriage/partner | |||||||||||||
| Partner/married (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| No partner | 0.8806 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | 0.0003 | 0.0006 | 0.574 | 0.8923 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | 0.564 | |
| Children | |||||||||||||
| No children < 15 (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Children < 15 | 0.8804 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0008 | 0.863 | 0.8921 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0007 | 0.874 | |
| Loneliness | |||||||||||||
| Not/seldom lonely (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Often lonely | 0.8651 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0152 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | 0.8784 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0136 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | |
| Stress | |||||||||||||
| 80% least stressed (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 20% most stressed | 0.8208 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0595 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | 0.8385 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0535 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | |
| BMI | |||||||||||||
| BMI < 18.5 | 0.8788 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0021 | 0.463 | 0.8905 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0019 | 0.435 | |
| BMI 18.5–25 (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| BMI > 25 < 30 | 0.8772 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0030 | 0.0007 | 0.000 | 0.8891 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0029 | 0.0006 | 0.000 | |
| BMI ≥ 30 < 35 | 0.8742 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0061 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | 0.8863 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0009 | 0.000 | |
| BMI ≥ 35 | 0.8674 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0129 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | 0.8807 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0113 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | |
| Smoking | |||||||||||||
| Do not smoke daily (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Smoke daily | 0.8762 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0040 | 0.0008 | 0.000 | 0.8883 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | − 0.0037 | 0.0007 | 0.000 | |
| Drinking | |||||||||||||
| Do not exceed recommendations (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Exceed recommendations | 0.8779 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0024 | 0.0012 | 0.047 | 0.8900 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0020 | 0.0011 | 0.065 | |
| Exercise | |||||||||||||
| Exercise at least 4 h/day (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Do not exercise | 0.8690 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0112 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | 0.8818 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0009 | 0.000 | |
| Fruit intake | |||||||||||||
| Do not meet recommendations (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 5 or more portions | 0.8801 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0012 | 0.887 | 0.8918 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0011 | 0.877 | |
| SF-12 General Health (self-reported) | |||||||||||||
| Excellent | 0.9791 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | 0.0988 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.9832 | 0.0009 | 0.000 | 0.0912 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |
| Very good | 0.9399 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | 0.0596 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | 0.9484 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0564 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | |
| Good (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Fair | 0.7625 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.1178 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | 0.7731 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.1188 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | |
| Poor | 0.6434 | 0.0171 | 0.000 | − 0.2369 | 0.0169 | 0.000 | 0.6659 | 0.0173 | 0.000 | − 0.2260 | 0.0171 | 0.000 | |
| Missing | 0.8812 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | 0.0009 | 0.0080 | 0.905 | 0.8942 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | 0.0022 | 0.0077 | 0.778 | |
| Long-term illness or disability (self-reported) | |||||||||||||
| No long-term illness (base) | 0.8803 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.8920 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Long-term illness | 0.8075 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0728 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | 0.8186 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0733 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | |
Note: n = 55,616 in all models
aComplex defined condition
Table 6.
ALDVMM predictions and marginal effects of representative 50-year-olds by sex: US base model—chronic conditions and age
| No. | Condition or covariable | Representative 50-year-old male with no chronic conditions | Representative 50-year-old female with no chronic conditions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model prediction | Marginal effect | Model prediction | Marginal effect | ||||||||||
| β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | ||
| No conditions | 0.9149 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | 0.9249 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 1 | Chronic viral hepatitis | 0.8125 | 0.0384 | 0.000 | − 0.1024 | 0.0383 | 0.008 | 0.8209 | 0.0409 | 0.000 | − 0.1040 | 0.0408 | 0.011 |
| 2 | Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease | 0.8984 | 0.0553 | 0.000 | − 0.0165 | 0.0553 | 0.766 | 0.9099 | 0.0524 | 0.000 | − 0.0150 | 0.0524 | 0.775 |
| 3 | Malignant neoplasms of other and unspecified localizations | 0.9058 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0091 | 0.0067 | 0.175 | 0.9168 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0064 | 0.207 |
| 4 | Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs | 0.8584 | 0.0142 | 0.000 | − 0.0565 | 0.0142 | 0.000 | 0.8706 | 0.0143 | 0.000 | − 0.0543 | 0.0143 | 0.000 |
| 5 | Malignant neoplasm of colon | 0.9005 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0144 | 0.0074 | 0.053 | 0.9117 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0132 | 0.0072 | 0.065 |
| 6 | Malignant neoplasms of rectosigmoid junction, rectum, anus and anal canal | 0.9135 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0014 | 0.0082 | 0.867 | 0.9242 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0008 | 0.0078 | 0.922 |
| 7 | Malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung | 0.8878 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0271 | 0.0094 | 0.004 | 0.8995 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | − 0.0254 | 0.0092 | 0.006 |
| 8 | Malignant melanoma of skin | 0.9126 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0023 | 0.0061 | 0.710 | 0.9233 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0016 | 0.0058 | 0.778 |
| 9 | Other malignant neoplasms of skin | 0.9149 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | 0.0001 | 0.0077 | 0.995 | 0.9255 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.0073 | 0.941 |
| 10 | Malignant neoplasm of breast | 0.8936 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0213 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | 0.9051 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0199 | 0.0040 | 0.000 |
| 11 | Malignant neoplasms of female genital organs | 0.9053 | 0.0107 | 0.000 | − 0.0096 | 0.0107 | 0.370 | 0.9164 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | − 0.0085 | 0.0102 | 0.404 |
| 12 | Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri, corpus uteri and part unspecified | 0.9023 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0126 | 0.0078 | 0.106 | 0.9136 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0114 | 0.0075 | 0.127 |
| 13 | Malignant tumour of the male genitalia | 0.9129 | 0.0179 | 0.000 | − 0.0020 | 0.0178 | 0.910 | 0.9235 | 0.0171 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0170 | 0.931 |
| 14 | Malignant neoplasm of prostate | 0.9064 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0084 | 0.0052 | 0.103 | 0.9175 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0075 | 0.0049 | 0.130 |
| 15 | Malignant neoplasms of urinary tract | 0.8979 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0170 | 0.0078 | 0.029 | 0.9092 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0157 | 0.0075 | 0.037 |
| 16 | Brain cancera | 0.9176 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | 0.0027 | 0.0075 | 0.719 | 0.9280 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | 0.0031 | 0.0070 | 0.660 |
| 17 | Malignant neoplasms of ill-defined, secondary and unspecified sites, and of independent (primary) multiple sites | 0.8915 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0234 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.9032 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0061 | 0.000 |
| 18 | Malignant neoplasms, stated or presumed to be primary, of lymphoid, haematopoietic and related tissue | 0.9070 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0075 | 0.295 | 0.9181 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0069 | 0.0072 | 0.337 |
| 19 | In situ neoplasms | 0.9013 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0136 | 0.0055 | 0.013 | 0.9124 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0126 | 0.0053 | 0.017 |
| 20 | Haemolytic anaemias | 0.9392 | 0.0167 | 0.000 | 0.0243 | 0.0167 | 0.145 | 0.9481 | 0.0152 | 0.000 | 0.0232 | 0.0152 | 0.128 |
| 21 | Aplastic and other anaemias | 0.9021 | 0.0089 | 0.000 | − 0.0127 | 0.0089 | 0.153 | 0.9135 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0115 | 0.0085 | 0.178 |
| 22 | Other anaemias | 0.8965 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0184 | 0.0062 | 0.003 | 0.9080 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0169 | 0.0060 | 0.005 |
| 23 | Coagulation defects, purpura and other haemorrhagic conditions | 0.9140 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0009 | 0.0066 | 0.890 | 0.9246 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0062 | 0.956 |
| 24 | Other diseases of blood and blood-forming organs | 0.8736 | 0.0143 | 0.000 | − 0.0413 | 0.0143 | 0.004 | 0.8851 | 0.0144 | 0.000 | − 0.0399 | 0.0143 | 0.005 |
| 25 | Certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | 0.8939 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | − 0.0209 | 0.0106 | 0.049 | 0.9055 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | − 0.0194 | 0.0103 | 0.059 |
| 26 | Diseases of the thyroida | 0.8994 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0155 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.9107 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0143 | 0.0029 | 0.000 |
| 27 | Thyrotoxicosisa | 0.9031 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0117 | 0.0041 | 0.004 | 0.9143 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0106 | 0.0039 | 0.006 |
| 28 | Diabetes type 1a | 0.8945 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0204 | 0.0070 | 0.004 | 0.9058 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0191 | 0.0068 | 0.005 |
| 29 | Diabetes type 2a | 0.8934 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0215 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.9050 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0199 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 30 | Diabetes othersa | 0.8758 | 0.0351 | 0.000 | − 0.0391 | 0.0351 | 0.265 | 0.8875 | 0.0349 | 0.000 | − 0.0374 | 0.0349 | 0.283 |
| 31 | Disorders of other endocrine glands | 0.8817 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0331 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | 0.8936 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0313 | 0.0066 | 0.000 |
| 32 | Metabolic disorders | 0.8845 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0304 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | 0.8962 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0287 | 0.0068 | 0.000 |
| 33 | Disturbances in lipoprotein circulation and other lipidsa | 0.9085 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0064 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | 0.9193 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0017 | 0.001 |
| 34 | Cystic fibrosisa | 0.8542 | 0.0535 | 0.000 | − 0.0607 | 0.0535 | 0.257 | 0.8670 | 0.0532 | 0.000 | − 0.0579 | 0.0532 | 0.276 |
| 35 | Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system | 0.9052 | 0.0152 | 0.000 | − 0.0097 | 0.0152 | 0.521 | 0.9162 | 0.0146 | 0.000 | − 0.0088 | 0.0146 | 0.547 |
| 36 | Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system and other degenerative diseases | 0.8748 | 0.0157 | 0.000 | − 0.0401 | 0.0156 | 0.010 | 0.8869 | 0.0155 | 0.000 | − 0.0381 | 0.0154 | 0.014 |
| 37 | Parkinson’s diseasea | 0.8802 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0347 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | 0.8922 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0328 | 0.0053 | 0.000 |
| 38 | Extrapyramidal and movement disorders | 0.8975 | 0.0119 | 0.000 | − 0.0174 | 0.0118 | 0.143 | 0.9090 | 0.0115 | 0.000 | − 0.0160 | 0.0114 | 0.162 |
| 39 | Sclerosis | 0.8308 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | − 0.0841 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | 0.8433 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | − 0.0816 | 0.0104 | 0.000 |
| 40 | Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system | 0.8874 | 0.0126 | 0.000 | − 0.0275 | 0.0126 | 0.029 | 0.8992 | 0.0122 | 0.000 | − 0.0257 | 0.0122 | 0.035 |
| 41 | Epilepsya | 0.8873 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0275 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | 0.8992 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0258 | 0.0052 | 0.000 |
| 42 | Migrainea | 0.8895 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0254 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | 0.9012 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0237 | 0.0025 | 0.000 |
| 43 | Other headache syndromes | 0.8881 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0268 | 0.0088 | 0.002 | 0.9000 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0250 | 0.0085 | 0.003 |
| 44 | Transient cerebral ischaemic attacks and related syndromes and vascular syndromes of brain in cerebrovascular diseases | 0.9063 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0086 | 0.0044 | 0.053 | 0.9174 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0076 | 0.0042 | 0.073 |
| 45 | Sleep disorders | 0.8866 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0282 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | 0.8983 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0266 | 0.0050 | 0.000 |
| 46 | Disorders of trigeminal nerve and facial nerve disorders | 0.8988 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0161 | 0.0071 | 0.024 | 0.9101 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0149 | 0.0069 | 0.031 |
| 47 | Disorders of other cranial nerves, cranial nerve disorders in diseases classified elsewhere, nerve root and plexus disorders and nerve root and plexus compressions in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8878 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | − 0.0271 | 0.0104 | 0.009 | 0.8997 | 0.0101 | 0.000 | − 0.0253 | 0.0101 | 0.012 |
| 48 | Mononeuropathies of upper limb | 0.8931 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.9047 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0203 | 0.0029 | 0.000 |
| 49 | Mononeuropathies of lower limb, other mononeuropathies and mononeuropathy in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8900 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0249 | 0.0077 | 0.001 | 0.9018 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0232 | 0.0075 | 0.002 |
| 50 | Polyneuropathies and other disorders of the peripheral nervous system | 0.8807 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0341 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | 0.8927 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0322 | 0.0072 | 0.000 |
| 51 | Diseases of myoneural junction and muscle | 0.8750 | 0.0153 | 0.000 | − 0.0399 | 0.0153 | 0.009 | 0.8871 | 0.0152 | 0.000 | − 0.0378 | 0.0151 | 0.012 |
| 52 | Cerebral palsy and other paralytic syndromes | 0.8581 | 0.0142 | 0.000 | − 0.0568 | 0.0142 | 0.000 | 0.8706 | 0.0141 | 0.000 | − 0.0543 | 0.0142 | 0.000 |
| 53 | Other disorders of the nervous system | 0.8830 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | − 0.0319 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | 0.8949 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0301 | 0.0069 | 0.000 |
| 54 | Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit | 0.9076 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0073 | 0.0060 | 0.224 | 0.9186 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0064 | 0.0057 | 0.266 |
| 55 | Corneal scars and opacities | 0.8967 | 0.0173 | 0.000 | − 0.0182 | 0.0173 | 0.291 | 0.9080 | 0.0168 | 0.000 | − 0.0170 | 0.0167 | 0.310 |
| 56 | Other disorders of cornea | 0.9232 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | 0.0083 | 0.0096 | 0.388 | 0.9333 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | 0.0083 | 0.0090 | 0.356 |
| 57 | Diseases of the eye lens (cataracts) | 0.9059 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0089 | 0.0041 | 0.030 | 0.9170 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0039 | 0.043 |
| 58 | Disorders of the choroid and retina | 0.8924 | 0.0190 | 0.000 | − 0.0225 | 0.0190 | 0.236 | 0.9040 | 0.0185 | 0.000 | − 0.0210 | 0.0185 | 0.256 |
| 59 | Retinal vascular occlusions | 0.9185 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | 0.0037 | 0.0094 | 0.696 | 0.9290 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | 0.0040 | 0.0088 | 0.645 |
| 60 | Other retinal disorders | 0.9031 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0118 | 0.0043 | 0.006 | 0.9143 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0107 | 0.0041 | 0.009 |
| 61 | Retinal disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8949 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0200 | 0.0085 | 0.018 | 0.9063 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | − 0.0186 | 0.0082 | 0.024 |
| 62 | Glaucomac | 0.9007 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0142 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | 0.9120 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0130 | 0.0036 | 0.000 |
| 63 | Disorders of the vitreous body and globe | 0.8814 | 0.0101 | 0.000 | − 0.0335 | 0.0101 | 0.001 | 0.8934 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | − 0.0316 | 0.0099 | 0.001 |
| 64 | Disorders of optic nerve and visual pathways | 0.9138 | 0.0135 | 0.000 | − 0.0011 | 0.0136 | 0.936 | 0.9245 | 0.0128 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0129 | 0.971 |
| 65 | Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction | 0.9110 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0038 | 0.0057 | 0.499 | 0.9215 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0034 | 0.0054 | 0.530 |
| 66 | Visual disturbances | 0.9140 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0008 | 0.0060 | 0.890 | 0.9247 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0057 | 0.973 |
| 67 | Blindness and partial sight | 0.9116 | 0.0135 | 0.000 | − 0.0033 | 0.0135 | 0.809 | 0.9225 | 0.0127 | 0.000 | − 0.0025 | 0.0127 | 0.845 |
| 68 | Nystagmus and other irregular eye movements and other disorders of eye and adnexa | 0.9141 | 0.0112 | 0.000 | − 0.0008 | 0.0112 | 0.945 | 0.9248 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0105 | 0.991 |
| 69 | Otosclerosis | 0.9191 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | 0.0042 | 0.0073 | 0.564 | 0.9294 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | 0.0045 | 0.0068 | 0.512 |
| 70 | Ménière’s diseasea | 0.8836 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0313 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | 0.8952 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | − 0.0297 | 0.0082 | 0.000 |
| 71 | Other diseases of the inner ear | 0.9037 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0112 | 0.0040 | 0.006 | 0.9148 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0039 | 0.009 |
| 72 | Conductive and sensorineural hearing loss | 0.9051 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0098 | 0.0045 | 0.032 | 0.9162 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0088 | 0.0043 | 0.044 |
| 73 | Other hearing loss and other disorders of ear, not elsewhere classified | 0.8921 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | − 0.0227 | 0.0090 | 0.012 | 0.9038 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0212 | 0.0087 | 0.015 |
| 74 | Presbycusis (age-related hearing loss) | 0.9083 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0066 | 0.0032 | 0.039 | 0.9193 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0057 | 0.0030 | 0.060 |
| 75 | Hearing loss, unspecified | 0.9061 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0087 | 0.0036 | 0.014 | 0.9172 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0078 | 0.0034 | 0.022 |
| 76 | Tinnitus | 0.8975 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0174 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | 0.9088 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0161 | 0.0039 | 0.000 |
| 77 | Other specified disorders of ear | 0.9045 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0104 | 0.0056 | 0.066 | 0.9156 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0093 | 0.0054 | 0.085 |
| 78 | Aortic and mitral valve diseasea | 0.9035 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0113 | 0.0056 | 0.042 | 0.9147 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0103 | 0.0054 | 0.055 |
| 79 | Hypertensive diseasesa | 0.8968 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | − 0.0181 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | 0.9082 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | − 0.0167 | 0.0016 | 0.000 |
| 80 | Heart failurea | 0.8989 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0160 | 0.0072 | 0.027 | 0.9104 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0146 | 0.0069 | 0.035 |
| 81 | Angina pectoris | 0.8958 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0190 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | 0.9073 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0176 | 0.0037 | 0.000 |
| 82 | Acute myocardial infarction and subsequent myocardial infarction | 0.9125 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0024 | 0.0059 | 0.688 | 0.9233 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0017 | 0.0056 | 0.764 |
| 83 | AMI complex/other | 0.8696 | 0.0196 | 0.000 | − 0.0453 | 0.0196 | 0.021 | 0.8818 | 0.0194 | 0.000 | − 0.0431 | 0.0194 | 0.026 |
| 84 | Chronic ischaemic heart disease | 0.8986 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0163 | 0.0047 | 0.001 | 0.9100 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0150 | 0.0045 | 0.001 |
| 85 | Pulmonary heart disease and diseases of pulmonary circulation | 0.8993 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | − 0.0156 | 0.0103 | 0.131 | 0.9107 | 0.0100 | 0.000 | − 0.0142 | 0.0099 | 0.152 |
| 86 | Acute pericarditis | 0.9097 | 0.0149 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0149 | 0.729 | 0.9203 | 0.0143 | 0.000 | − 0.0046 | 0.0143 | 0.746 |
| 87 | Other forms of heart disease | 0.8869 | 0.0135 | 0.000 | − 0.0279 | 0.0135 | 0.039 | 0.8983 | 0.0134 | 0.000 | − 0.0266 | 0.0133 | 0.046 |
| 88 | Atrioventricular and left bundle-branch block | 0.9095 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0054 | 0.0077 | 0.483 | 0.9204 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0046 | 0.0073 | 0.532 |
| 89 | Other conduction disorders | 0.9002 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | − 0.0147 | 0.0103 | 0.153 | 0.9113 | 0.0100 | 0.000 | − 0.0136 | 0.0100 | 0.171 |
| 90 | Paroxysmal tachycardia | 0.9013 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0136 | 0.0046 | 0.003 | 0.9125 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0124 | 0.0044 | 0.005 |
| 91 | Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 0.8990 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0159 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.9103 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0147 | 0.0035 | 0.000 |
| 92 | Other cardiac arrhythmias | 0.9048 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0100 | 0.0050 | 0.043 | 0.9159 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0090 | 0.0047 | 0.057 |
| 93 | Complications and ill-defined descriptions of heart disease and other heart disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.9000 | 0.0218 | 0.000 | − 0.0149 | 0.0218 | 0.495 | 0.9114 | 0.0209 | 0.000 | − 0.0135 | 0.0209 | 0.518 |
| 94 | Stroke | 0.8943 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0206 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | 0.9059 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0191 | 0.0049 | 0.000 |
| 95 | Cerebrovascular diseases | 0.8803 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0346 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | 0.8923 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0327 | 0.0084 | 0.000 |
| 96 | Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease | 0.8864 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0285 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | 0.8983 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0267 | 0.0073 | 0.000 |
| 97 | Atherosclerosis | 0.8960 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0189 | 0.0070 | 0.007 | 0.9076 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0174 | 0.0067 | 0.010 |
| 98 | Aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection | 0.8768 | 0.0125 | 0.000 | − 0.0381 | 0.0124 | 0.002 | 0.8883 | 0.0124 | 0.000 | − 0.0366 | 0.0123 | 0.003 |
| 99 | Diseases of arteries, arterioles and capillaries | 0.9060 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0089 | 0.0078 | 0.256 | 0.9171 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0075 | 0.293 |
| 100 | Other peripheral vascular diseases | 0.8798 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0350 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | 0.8918 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0331 | 0.0068 | 0.000 |
| 101 | Phlebitis, thrombosis of the portal vein and others | 0.9006 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0143 | 0.0055 | 0.009 | 0.9119 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0131 | 0.0052 | 0.013 |
| 102 | Varicose veins of lower extremities | 0.9155 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | 0.0006 | 0.0043 | 0.881 | 0.9260 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | 0.0011 | 0.0041 | 0.796 |
| 103 | Haemorrhoidsa | 0.9007 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0142 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | 0.9120 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0130 | 0.0032 | 0.000 |
| 104 | Oesophageal varices (chronic), varicose veins of other sites, other disorders of veins, nonspecific lymphadenitis, other non-infective disorders of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes and other and unspecified disorders of the circulatory system | 0.9039 | 0.0102 | 0.000 | − 0.0110 | 0.0102 | 0.279 | 0.9150 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0100 | 0.0098 | 0.308 |
| 105 | Respiratory allergya | 0.9047 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | 0.9158 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0092 | 0.0014 | 0.000 |
| 105A | Chronic lower respiratory diseasesa | 0.9027 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0122 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | 0.9139 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0110 | 0.0021 | 0.000 |
| 106 | Bronchitis, not specified as acute or chronic, simple and mucopurulent chronic bronchitis and unspecified chronic bronchitis | 0.8948 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0201 | 0.0098 | 0.041 | 0.9063 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | − 0.0186 | 0.0095 | 0.050 |
| 107 | Emphysema | 0.9022 | 0.0132 | 0.000 | − 0.0127 | 0.0132 | 0.336 | 0.9135 | 0.0127 | 0.000 | − 0.0115 | 0.0126 | 0.365 |
| 108 | Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD)a | 0.8917 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0232 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | 0.9033 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0216 | 0.0028 | 0.000 |
| 109 | Asthma, status asthmaticusa | 0.8993 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0156 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.9107 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0143 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 110 | Bronchiectasis | 0.9386 | 0.0135 | 0.000 | 0.0237 | 0.0135 | 0.079 | 0.9475 | 0.0122 | 0.000 | 0.0226 | 0.0123 | 0.066 |
| 111 | Other diseases of the respiratory system | 0.8973 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | − 0.0176 | 0.0083 | 0.034 | 0.9088 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0161 | 0.0080 | 0.043 |
| 112 | Ulcersa | 0.8832 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0317 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | 0.8951 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0299 | 0.0026 | 0.000 |
| 113 | Inguinal hernia | 0.9073 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0076 | 0.0045 | 0.093 | 0.9182 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0067 | 0.0043 | 0.118 |
| 114 | Ventral hernia | 0.8989 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0160 | 0.0093 | 0.085 | 0.9104 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | − 0.0146 | 0.0089 | 0.102 |
| 115 | Crohn’s disease | 0.8855 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0294 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | 0.8971 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0278 | 0.0078 | 0.000 |
| 116 | Ulcerative colitis | 0.8928 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0221 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | 0.9043 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0206 | 0.0056 | 0.000 |
| 117 | Other non-infective gastroenteritis and colitis | 0.8963 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0186 | 0.0077 | 0.016 | 0.9078 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0172 | 0.0074 | 0.021 |
| 118 | Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) | 0.8913 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0236 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | 0.9028 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0221 | 0.0043 | 0.000 |
| 119 | Other functional intestinal disorders | 0.8908 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0241 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | 0.9025 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0224 | 0.0047 | 0.000 |
| 120 | Diseases of liver, biliary tract and pancreas | 0.8802 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0346 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | 0.8922 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0327 | 0.0068 | 0.000 |
| 121 | Psoriasisa | 0.9002 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0147 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | 0.9116 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0133 | 0.0037 | 0.000 |
| 122 | Infectious arthropathies | 0.8931 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0107 | 0.043 | 0.9047 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | − 0.0202 | 0.0104 | 0.052 |
| 123 | Rheumatoid arthritisa | 0.8745 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0404 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | 0.8865 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0385 | 0.0040 | 0.000 |
| 124 | Inflammatory polyarthropathies, except rheumatoid arthritisa | 0.8858 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0291 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | 0.8975 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0274 | 0.0033 | 0.000 |
| 125 | Polyarthrosis (arthrosis) | 0.8785 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | − 0.0364 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | 0.8905 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0344 | 0.0094 | 0.000 |
| 126 | Coxarthrosis (arthrosis of hip) | 0.8831 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0318 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | 0.8949 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0300 | 0.0034 | 0.000 |
| 127 | Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of knee) | 0.8771 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0377 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.8891 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0359 | 0.0024 | 0.000 |
| 128 | Arthrosis of first carpometacarpal joint and other arthrosis | 0.8848 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0300 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | 0.8966 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0283 | 0.0034 | 0.000 |
| 129 | Acquired deformities of fingers and toes | 0.9041 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0108 | 0.0042 | 0.011 | 0.9151 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0098 | 0.0041 | 0.016 |
| 130 | Other acquired deformities of limbs | 0.8874 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0275 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | 0.8991 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0259 | 0.0066 | 0.000 |
| 131 | Disorders of patella (kneecap) | 0.8859 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0290 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | 0.8978 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0272 | 0.0045 | 0.000 |
| 132 | Internal derangement of knee | 0.8747 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0402 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | 0.8868 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0381 | 0.0086 | 0.000 |
| 133 | Derangement of meniscus due to old tear or injury | 0.9005 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0144 | 0.0046 | 0.002 | 0.9117 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0133 | 0.0045 | 0.003 |
| 134 | Internal derangement of knee, unspecified | 0.8865 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0284 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | 0.8980 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0269 | 0.0050 | 0.000 |
| 135 | Other specific joint derangements | 0.8782 | 0.0155 | 0.000 | − 0.0367 | 0.0154 | 0.018 | 0.8903 | 0.0152 | 0.000 | − 0.0347 | 0.0152 | 0.022 |
| 136 | Other joint disorders, not elsewhere classified | 0.8625 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0523 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | 0.8747 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0503 | 0.0071 | 0.000 |
| 137 | Systemic connective tissue disorders | 0.8912 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0237 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | 0.9028 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0222 | 0.0051 | 0.000 |
| 138 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | 0.9175 | 0.0119 | 0.000 | 0.0026 | 0.0118 | 0.826 | 0.9279 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | 0.0030 | 0.0110 | 0.787 |
| 139 | Dermatopolymyositis | 0.9390 | 0.0249 | 0.000 | 0.0241 | 0.0249 | 0.334 | 0.9479 | 0.0228 | 0.000 | 0.0229 | 0.0227 | 0.313 |
| 140 | Systemic sclerosis | 0.8610 | 0.0308 | 0.000 | − 0.0538 | 0.0308 | 0.081 | 0.8738 | 0.0304 | 0.000 | − 0.0511 | 0.0304 | 0.093 |
| 141 | Kyphosis, lordosis | 0.8660 | 0.0145 | 0.000 | − 0.0489 | 0.0145 | 0.001 | 0.8781 | 0.0144 | 0.000 | − 0.0468 | 0.0144 | 0.001 |
| 142 | Scoliosis | 0.8701 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | − 0.0448 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | 0.8820 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | − 0.0429 | 0.0091 | 0.000 |
| 143 | Spinal osteochondrosis | 0.8636 | 0.0156 | 0.000 | − 0.0513 | 0.0156 | 0.001 | 0.8758 | 0.0155 | 0.000 | − 0.0491 | 0.0156 | 0.002 |
| 144 | Other deforming dorsopathies | 0.8629 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0520 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | 0.8750 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0500 | 0.0071 | 0.000 |
| 145 | Other inflammatory spondylopathies | 0.8893 | 0.0134 | 0.000 | − 0.0256 | 0.0133 | 0.055 | 0.9011 | 0.0130 | 0.000 | − 0.0238 | 0.0129 | 0.065 |
| 146 | Spondylosis | 0.8606 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0542 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | 0.8729 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0521 | 0.0042 | 0.000 |
| 147 | Other spondylopathies and spondylopathies in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.8813 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0336 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | 0.8931 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0319 | 0.0058 | 0.000 |
| 148 | Cervical disc disorders | 0.8783 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | − 0.0365 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | 0.8902 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | − 0.0347 | 0.0094 | 0.000 |
| 149 | Other intervertebral disc disorders | 0.8574 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0574 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.8698 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0552 | 0.0059 | 0.000 |
| 150 | Other dorsopathies, not elsewhere classified | 0.8590 | 0.0119 | 0.000 | − 0.0559 | 0.0118 | 0.000 | 0.8711 | 0.0119 | 0.000 | − 0.0538 | 0.0119 | 0.000 |
| 151 | Dorsalgia | 0.8433 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0716 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | 0.8554 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0695 | 0.0051 | 0.000 |
| 152 | Soft tissue disorders | 0.8810 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0339 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | 0.8931 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0319 | 0.0085 | 0.000 |
| 153 | Synovitis and tenosynovitis | 0.8950 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0199 | 0.0058 | 0.001 | 0.9066 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0184 | 0.0055 | 0.001 |
| 154 | Disorders of synovium and tendon | 0.8876 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0273 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | 0.8992 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0257 | 0.0063 | 0.000 |
| 155 | Soft tissue disorders related to use, overuse and pressure | 0.8773 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0375 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | 0.8893 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0357 | 0.0084 | 0.000 |
| 156 | Fibroblastic disorders | 0.9058 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0091 | 0.0046 | 0.048 | 0.9168 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0044 | 0.065 |
| 157 | Shoulder lesions | 0.8716 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0433 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | 0.8837 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0412 | 0.0035 | 0.000 |
| 158 | Enthesopathies of lower limb, excluding foot | 0.8782 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | − 0.0367 | 0.0105 | 0.001 | 0.8900 | 0.0103 | 0.000 | − 0.0349 | 0.0103 | 0.001 |
| 159 | Other enthesopathies | 0.8612 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0537 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | 0.8735 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0514 | 0.0088 | 0.000 |
| 160 | Rheumatism, unspecified | 0.8478 | 0.0154 | 0.000 | − 0.0671 | 0.0154 | 0.000 | 0.8599 | 0.0156 | 0.000 | − 0.0650 | 0.0156 | 0.000 |
| 161 | Myalgia | 0.8820 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | − 0.0329 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | 0.8940 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | − 0.0309 | 0.0090 | 0.001 |
| 162 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified | 0.8809 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | − 0.0340 | 0.0109 | 0.002 | 0.8928 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | − 0.0321 | 0.0106 | 0.003 |
| 163 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified: pain in limb | 0.8781 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0368 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | 0.8900 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0349 | 0.0069 | 0.000 |
| 164 | Fibromyalgia | 0.8592 | 0.0250 | 0.000 | − 0.0557 | 0.0250 | 0.026 | 0.8716 | 0.0250 | 0.000 | − 0.0534 | 0.0250 | 0.032 |
| 165 | Osteoporosisa | 0.8905 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0244 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | 0.9022 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0228 | 0.0028 | 0.000 |
| 166 | Osteoporosis in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.9225 | 0.0260 | 0.000 | 0.0076 | 0.0260 | 0.769 | 0.9327 | 0.0244 | 0.000 | 0.0077 | 0.0243 | 0.751 |
| 167 | Adult osteomalacia and other disorders of bone density and structure | 0.8956 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0193 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | 0.9070 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0179 | 0.0046 | 0.000 |
| 168 | Disorders of continuity of bone | 0.8925 | 0.0191 | 0.000 | − 0.0224 | 0.0191 | 0.242 | 0.9042 | 0.0185 | 0.000 | − 0.0207 | 0.0185 | 0.262 |
| 169 | Other osteopathies | 0.8867 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0282 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | 0.8985 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0264 | 0.0075 | 0.000 |
| 170 | Other disorders of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | 0.8884 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0265 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | 0.9001 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0248 | 0.0065 | 0.000 |
| 171 | Chronic renal failure (CRF)a | 0.9071 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0078 | 0.0085 | 0.357 | 0.9182 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0068 | 0.0081 | 0.400 |
| 172 | Congenital malformations: of the nervous, circulatory, respiratory system; cleft palate and cleft lip, urinary tract, bones and muscles, other and chromosomal abnormalities not elsewhere classified | 0.9003 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0146 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | 0.9116 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0133 | 0.0038 | 0.000 |
| 173 | Congenital malformations of eye, ear, face and neck | 0.9010 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0139 | 0.0065 | 0.033 | 0.9122 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0127 | 0.0062 | 0.041 |
| 174 | Other congenital malformations of the digestive system | 0.9050 | 0.0117 | 0.000 | − 0.0099 | 0.0117 | 0.397 | 0.9160 | 0.0113 | 0.000 | − 0.0090 | 0.0113 | 0.426 |
| 175 | Congenital malformations of the sexual organs | 0.9031 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0118 | 0.0072 | 0.103 | 0.9142 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0108 | 0.0069 | 0.120 |
| 176 | Dementiaa | 0.8886 | 0.0158 | 0.000 | − 0.0263 | 0.0158 | 0.096 | 0.9005 | 0.0153 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0153 | 0.109 |
| 177 | Organic, including symptomatic, mental disorders | 0.8974 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | − 0.0175 | 0.0111 | 0.114 | 0.9088 | 0.0107 | 0.000 | − 0.0161 | 0.0107 | 0.132 |
| 178 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to use of alcohol | 0.8846 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0303 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | 0.8964 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0285 | 0.0063 | 0.000 |
| 179 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to psychoactive substance use | 0.8979 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0170 | 0.0059 | 0.004 | 0.9094 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0156 | 0.0057 | 0.006 |
| 180 | Schizophreniaa | 0.8719 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | − 0.0430 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | 0.8840 | 0.0107 | 0.000 | − 0.0409 | 0.0106 | 0.000 |
| 181 | Schizotypal and delusional disorders | 0.9237 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | 0.0088 | 0.0088 | 0.317 | 0.9338 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | 0.0088 | 0.0082 | 0.281 |
| 182 | Bipolar affective disordera | 0.8959 | 0.0136 | 0.000 | − 0.0190 | 0.0136 | 0.164 | 0.9073 | 0.0132 | 0.000 | − 0.0177 | 0.0132 | 0.182 |
| 183 | Depressiona | 0.8533 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0616 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | 0.8655 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0594 | 0.0023 | 0.000 |
| 184 | Mood (affective) disorders | 0.8849 | 0.0250 | 0.000 | − 0.0300 | 0.0249 | 0.229 | 0.8962 | 0.0248 | 0.000 | − 0.0288 | 0.0247 | 0.245 |
| 185 | Phobic anxiety disorders | 0.8726 | 0.0131 | 0.000 | − 0.0422 | 0.0130 | 0.001 | 0.8847 | 0.0129 | 0.000 | − 0.0403 | 0.0129 | 0.002 |
| 186 | Other anxiety disorders | 0.8889 | 0.0076 | 0.000 | − 0.0260 | 0.0076 | 0.001 | 0.9007 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0242 | 0.0074 | 0.001 |
| 187 | Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)a | 0.8954 | 0.0132 | 0.000 | − 0.0195 | 0.0131 | 0.137 | 0.9067 | 0.0128 | 0.000 | 0.0182 | 0.0128 | 0.153 |
| 188 | Post-traumatic stress disorder | 0.8410 | 0.0235 | 0.000 | − 0.0739 | 0.0235 | 0.002 | 0.8533 | 0.0238 | 0.000 | − 0.0717 | 0.0238 | 0.003 |
| 189 | Reactions to severe stress and adjustment disorders | 0.8929 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0220 | 0.0064 | 0.001 | 0.9045 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0204 | 0.0062 | 0.001 |
| 190 | Dissociative (conversion) disorders, somatoform disorders and other neurotic disorders | 0.8903 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0087 | 0.005 | 0.9020 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0229 | 0.0085 | 0.007 |
| 191 | Eating disorders | 0.9111 | 0.0121 | 0.000 | − 0.0038 | 0.0121 | 0.754 | 0.9220 | 0.0115 | 0.000 | − 0.0030 | 0.0114 | 0.795 |
| 192 | Behavioural syndromes associated with physiological disturbances and physical factors | 0.8962 | 0.0133 | 0.000 | − 0.0187 | 0.0133 | 0.159 | 0.9074 | 0.0129 | 0.000 | − 0.0175 | 0.0129 | 0.174 |
| 193 | Emotionally unstable personality disorder | 0.8661 | 0.0146 | 0.000 | − 0.0488 | 0.0146 | 0.001 | 0.8780 | 0.0147 | 0.000 | − 0.0469 | 0.0146 | 0.001 |
| 194 | Specific personality disorders | 0.8834 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0315 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | 0.8953 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0297 | 0.0064 | 0.000 |
| 195 | Disorders of adult personality and behaviour | 0.9012 | 0.0136 | 0.000 | − 0.0137 | 0.0136 | 0.316 | 0.9126 | 0.0130 | 0.000 | − 0.0124 | 0.0130 | 0.343 |
| 196 | Mental retardation | 0.9154 | 0.0257 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.0257 | 0.985 | 0.9260 | 0.0241 | 0.000 | 0.0010 | 0.0241 | 0.965 |
| 197 | Disorders of psychological development | 0.8843 | 0.0158 | 0.000 | − 0.0305 | 0.0157 | 0.052 | 0.8961 | 0.0155 | 0.000 | − 0.0288 | 0.0154 | 0.062 |
| 198 | Hyperkinetic disorders (ADHD)a | 0.8694 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0455 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | 0.8815 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0435 | 0.0080 | 0.000 |
| 199 | Behavioural and emotional disorders with onset usually occurring in childhood and adolescence | 0.9041 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0108 | 0.0086 | 0.208 | 0.9153 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0097 | 0.0082 | 0.237 |
| Denmark sample (base) | 0.9179 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | 0.9278 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | |||||||
| North Denmark Region (sample 2–3) | 0.9149 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0030 | 0.0009 | 0.001 | 0.9249 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0028 | 0.0009 | 0.001 | |
| Specific ages (dydx) | |||||||||||||
| Age 16 | 0.9236 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.902 | 0.9334 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.954 | |
| Age 20 | 0.9234 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.349 | 0.9332 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.233 | |
| Age 25 | 0.9227 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.013 | 0.9325 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.005 | |
| Age 30 | 0.9216 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9314 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | − 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 35 | 0.9202 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9301 | 0.0009 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 40 | 0.9186 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9285 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 45 | 0.9168 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9268 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 50 | 0.9149 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9249 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 55 | 0.9128 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9230 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 60 | 0.9106 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9209 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 65 | 0.9081 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9186 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 70 | 0.9054 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9161 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 75 | 0.9024 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9133 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 80 | 0.8988 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0008 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9101 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 85 | 0.8945 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0009 | 0.0002 | 0.000 | 0.9062 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0009 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
Note: n = 55,616 in all models
aComplex defined condition
Table 7.
ALDVMM predictions and marginal effects of representative 50-year-olds by sex: US full model—chronic conditions, socio-economic, lifestyle and risk variables
| No. | Condition or covariable | Representative 50-year-old male with no chronic conditions | Representative 50-year-old female with no chronic conditions | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model prediction | Marginal effect | Model prediction | Marginal effect | ||||||||||
| β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | β | SE | p value | ||
| No conditions | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 1 | Chronic viral hepatitis | 0.8892 | 0.0360 | 0.000 | − 0.0446 | 0.0359 | 0.215 | 0.8982 | 0.0357 | 0.000 | − 0.0432 | 0.0356 | 0.226 |
| 2 | Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease | 0.9753 | 0.0374 | 0.000 | 0.0416 | 0.0374 | 0.266 | 0.9791 | 0.0323 | 0.000 | 0.0377 | 0.0324 | 0.244 |
| 3 | Malignant neoplasms of other and unspecified localizations | 0.9350 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | 0.0012 | 0.0061 | 0.848 | 0.9425 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | 0.0011 | 0.0057 | 0.847 |
| 4 | Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs | 0.8947 | 0.0142 | 0.000 | − 0.0391 | 0.0141 | 0.006 | 0.9037 | 0.0139 | 0.000 | − 0.0377 | 0.0139 | 0.007 |
| 5 | Malignant neoplasm of colon | 0.9314 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0024 | 0.0065 | 0.713 | 0.9392 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0022 | 0.0061 | 0.716 |
| 6 | Malignant neoplasms of rectosigmoid junction, rectum, anus and anal canal | 0.9394 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | 0.0056 | 0.0074 | 0.446 | 0.9467 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | 0.0053 | 0.0069 | 0.443 |
| 7 | Malignant neoplasm of bronchus and lung | 0.9206 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0132 | 0.0084 | 0.118 | 0.9289 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0125 | 0.0081 | 0.121 |
| 8 | Malignant melanoma of skin | 0.9310 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0028 | 0.0055 | 0.610 | 0.9387 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0026 | 0.0052 | 0.609 |
| 9 | Other malignant neoplasms of skin | 0.9431 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | 0.0094 | 0.0069 | 0.172 | 0.9501 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | 0.0088 | 0.0064 | 0.169 |
| 10 | Malignant neoplasm of breast | 0.9242 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0096 | 0.0036 | 0.009 | 0.9323 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0090 | 0.0035 | 0.009 |
| 11 | Malignant neoplasms of female genital organs | 0.9347 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | 0.0010 | 0.0091 | 0.916 | 0.9423 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | 0.0009 | 0.0085 | 0.915 |
| 12 | Malignant neoplasm of cervix uteri, corpus uteri and part unspecified | 0.9315 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0022 | 0.0064 | 0.727 | 0.9392 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0021 | 0.0061 | 0.725 |
| 13 | Malignant tumour of the male genitalia | 0.9484 | 0.0115 | 0.000 | 0.0146 | 0.0115 | 0.202 | 0.9550 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | 0.0137 | 0.0106 | 0.196 |
| 14 | Malignant neoplasm of prostate | 0.9343 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.0044 | 0.904 | 0.9419 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.0042 | 0.903 |
| 15 | Malignant neoplasms of urinary tract | 0.9322 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0016 | 0.0066 | 0.804 | 0.9399 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0062 | 0.806 |
| 16 | Brain cancera | 0.9441 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | 0.0103 | 0.0064 | 0.108 | 0.9510 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.0097 | 0.0060 | 0.105 |
| 17 | Malignant neoplasms of ill-defined, secondary and unspecified sites, and of independent (primary) multiple sites | 0.9230 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0108 | 0.0056 | 0.055 | 0.9312 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0054 | 0.057 |
| 18 | Malignant neoplasms, stated or presumed to be primary, of lymphoid, haematopoietic and related tissue | 0.9328 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0010 | 0.0063 | 0.879 | 0.9405 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0009 | 0.0059 | 0.882 |
| 19 | In situ neoplasms | 0.9247 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0091 | 0.0050 | 0.068 | 0.9328 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0086 | 0.0048 | 0.070 |
| 20 | Haemolytic anaemias | 0.9548 | 0.0144 | 0.000 | 0.0210 | 0.0144 | 0.144 | 0.9608 | 0.0131 | 0.000 | 0.0194 | 0.0131 | 0.138 |
| 21 | Aplastic and other anaemias | 0.9243 | 0.0089 | 0.000 | − 0.0095 | 0.0089 | 0.283 | 0.9324 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0090 | 0.0084 | 0.285 |
| 22 | Other anaemias | 0.9278 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0060 | 0.0049 | 0.217 | 0.9357 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0057 | 0.0046 | 0.219 |
| 23 | Coagulation defects, purpura and other haemorrhagic conditions | 0.9404 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | 0.0066 | 0.0055 | 0.233 | 0.9476 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | 0.0062 | 0.0052 | 0.229 |
| 24 | Other diseases of blood and blood-forming organs | 0.9199 | 0.0113 | 0.000 | − 0.0138 | 0.0112 | 0.218 | 0.9282 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | − 0.0131 | 0.0108 | 0.222 |
| 25 | Certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | 0.9201 | 0.0097 | 0.000 | − 0.0137 | 0.0096 | 0.156 | 0.9284 | 0.0093 | 0.000 | − 0.0130 | 0.0092 | 0.160 |
| 26 | Diseases of the thyroida | 0.9261 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0077 | 0.0025 | 0.002 | 0.9341 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0072 | 0.0024 | 0.002 |
| 27 | Thyrotoxicosisa | 0.9291 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0047 | 0.0035 | 0.183 | 0.9369 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0044 | 0.0033 | 0.184 |
| 28 | Diabetes type 1a | 0.9246 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0092 | 0.0058 | 0.115 | 0.9327 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0087 | 0.0055 | 0.118 |
| 29 | Diabetes type 2a | 0.9292 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0045 | 0.0020 | 0.026 | 0.9371 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0043 | 0.0019 | 0.027 |
| 30 | Diabetes othersa | 0.9282 | 0.0217 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0217 | 0.797 | 0.9361 | 0.0206 | 0.000 | − 0.0053 | 0.0206 | 0.798 |
| 31 | Disorders of other endocrine glands | 0.9179 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0159 | 0.0056 | 0.005 | 0.9262 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0151 | 0.0054 | 0.005 |
| 32 | Metabolic disorders | 0.9137 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0200 | 0.0068 | 0.003 | 0.9223 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0191 | 0.0066 | 0.004 |
| 33 | Disturbances in lipoprotein circulation and other lipidsa | 0.9344 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | 0.0007 | 0.0014 | 0.647 | 0.9420 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | 0.0006 | 0.0013 | 0.641 |
| 34 | Cystic fibrosisa | 0.9092 | 0.0345 | 0.000 | − 0.0246 | 0.0345 | 0.477 | 0.9179 | 0.0333 | 0.000 | − 0.0235 | 0.0333 | 0.482 |
| 35 | Inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system | 0.9411 | 0.0117 | 0.000 | 0.0074 | 0.0117 | 0.530 | 0.9483 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | 0.0069 | 0.0109 | 0.526 |
| 36 | Systemic atrophies primarily affecting the central nervous system and other degenerative diseases | 0.9038 | 0.0142 | 0.000 | − 0.0300 | 0.0142 | 0.034 | 0.9126 | 0.0139 | 0.000 | − 0.0287 | 0.0138 | 0.037 |
| 37 | Parkinson’s diseasea | 0.9173 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0164 | 0.0047 | 0.001 | 0.9258 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0156 | 0.0045 | 0.001 |
| 38 | Extrapyramidal and movement disorders | 0.9192 | 0.0111 | 0.000 | − 0.0145 | 0.0110 | 0.187 | 0.9276 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | − 0.0138 | 0.0106 | 0.191 |
| 39 | Sclerosis | 0.8821 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | − 0.0516 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | 0.8913 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | − 0.0500 | 0.0094 | 0.000 |
| 40 | Demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system | 0.9160 | 0.0114 | 0.000 | − 0.0178 | 0.0114 | 0.118 | 0.9245 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | − 0.0169 | 0.0109 | 0.121 |
| 41 | Epilepsya | 0.9232 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0106 | 0.0043 | 0.015 | 0.9313 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0101 | 0.0041 | 0.015 |
| 42 | Migrainea | 0.9179 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0159 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | 0.9263 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0151 | 0.0021 | 0.000 |
| 43 | Other headache syndromes | 0.9221 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0117 | 0.0076 | 0.125 | 0.9303 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0111 | 0.0073 | 0.127 |
| 44 | Transient cerebral ischaemic attacks and related syndromes and vascular syndromes of brain in cerebrovascular diseases | 0.9343 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.0037 | 0.883 | 0.9419 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.0035 | 0.884 |
| 45 | Sleep disorders | 0.9256 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0082 | 0.0043 | 0.060 | 0.9337 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0077 | 0.0041 | 0.061 |
| 46 | Disorders of trigeminal nerve and facial nerve disorders | 0.9261 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0076 | 0.0065 | 0.238 | 0.9342 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0072 | 0.0061 | 0.241 |
| 47 | Disorders of other cranial nerves, cranial nerve disorders in diseases classified elsewhere, nerve root and plexus disorders and nerve root and plexus compressions in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.9189 | 0.0097 | 0.000 | − 0.0149 | 0.0096 | 0.122 | 0.9272 | 0.0093 | 0.000 | − 0.0141 | 0.0092 | 0.125 |
| 48 | Mononeuropathies of upper limb | 0.9251 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0087 | 0.0025 | 0.001 | 0.9332 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0082 | 0.0024 | 0.001 |
| 49 | Mononeuropathies of lower limb, other mononeuropathies and mononeuropathy in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.9217 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0121 | 0.0065 | 0.061 | 0.9299 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0115 | 0.0062 | 0.062 |
| 50 | Polyneuropathies and other disorders of the peripheral nervous system | 0.9144 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0194 | 0.0063 | 0.002 | 0.9229 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0185 | 0.0061 | 0.003 |
| 51 | Diseases of myoneural junction and muscle | 0.9147 | 0.0133 | 0.000 | − 0.0191 | 0.0132 | 0.149 | 0.9232 | 0.0128 | 0.000 | − 0.0182 | 0.0127 | 0.153 |
| 52 | Cerebral palsy and other paralytic syndromes | 0.8867 | 0.0121 | 0.000 | − 0.0470 | 0.0120 | 0.000 | 0.8959 | 0.0119 | 0.000 | − 0.0454 | 0.0119 | 0.000 |
| 53 | Other disorders of the nervous system | 0.9140 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0198 | 0.0064 | 0.002 | 0.9225 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0189 | 0.0062 | 0.002 |
| 54 | Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit | 0.9347 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | 0.0009 | 0.0053 | 0.859 | 0.9423 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | 0.0009 | 0.0049 | 0.860 |
| 55 | Corneal scars and opacities | 0.9232 | 0.0155 | 0.000 | − 0.0106 | 0.0155 | 0.495 | 0.9314 | 0.0148 | 0.000 | − 0.0100 | 0.0148 | 0.498 |
| 56 | Other disorders of cornea | 0.9464 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | 0.0126 | 0.0087 | 0.149 | 0.9531 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | 0.0118 | 0.0081 | 0.145 |
| 57 | Diseases of the eye lens (cataracts) | 0.9332 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0034 | 0.867 | 0.9409 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0032 | 0.870 |
| 58 | Disorders of the choroid and retina | 0.9264 | 0.0161 | 0.000 | − 0.0074 | 0.0161 | 0.645 | 0.9344 | 0.0153 | 0.000 | − 0.0070 | 0.0152 | 0.646 |
| 59 | Retinal vascular occlusions | 0.9460 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | 0.0122 | 0.0080 | 0.130 | 0.9527 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | 0.0113 | 0.0074 | 0.127 |
| 60 | Other retinal disorders | 0.9301 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0037 | 0.0036 | 0.312 | 0.9379 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0035 | 0.0034 | 0.314 |
| 61 | Retinal disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.9257 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0073 | 0.270 | 0.9337 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | − 0.0077 | 0.0070 | 0.271 |
| 62 | Glaucomac | 0.9281 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0057 | 0.0032 | 0.080 | 0.9360 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0054 | 0.0031 | 0.081 |
| 63 | Disorders of the vitreous body and globe | 0.9098 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | − 0.0240 | 0.0095 | 0.012 | 0.9185 | 0.0093 | 0.000 | − 0.0229 | 0.0092 | 0.013 |
| 64 | Disorders of optic nerve and visual pathways | 0.9323 | 0.0123 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0123 | 0.900 | 0.9399 | 0.0116 | 0.000 | − 0.0014 | 0.0116 | 0.901 |
| 65 | Disorders of ocular muscles, binocular movement, accommodation and refraction | 0.9355 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | 0.0017 | 0.0048 | 0.729 | 0.9430 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | 0.0016 | 0.0045 | 0.724 |
| 66 | Visual disturbances | 0.9434 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | 0.0096 | 0.0051 | 0.059 | 0.9503 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | 0.0090 | 0.0047 | 0.058 |
| 67 | Blindness and partial sight | 0.9464 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | 0.0127 | 0.0106 | 0.232 | 0.9531 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | 0.0117 | 0.0098 | 0.229 |
| 68 | Nystagmus and other irregular eye movements and other disorders of eye and adnexa | 0.9432 | 0.0089 | 0.000 | 0.0094 | 0.0089 | 0.289 | 0.9502 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | 0.0088 | 0.0082 | 0.286 |
| 69 | Otosclerosis | 0.9431 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | 0.0093 | 0.0062 | 0.133 | 0.9501 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | 0.0087 | 0.0057 | 0.130 |
| 70 | Ménière’s diseasea | 0.9147 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0191 | 0.0079 | 0.016 | 0.9232 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0181 | 0.0076 | 0.017 |
| 71 | Other diseases of the inner ear | 0.9332 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0035 | 0.869 | 0.9408 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0033 | 0.870 |
| 72 | Conductive and sensorineural hearing loss | 0.9331 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0039 | 0.860 | 0.9407 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0006 | 0.0037 | 0.862 |
| 73 | Other hearing loss and other disorders of ear, not elsewhere classified | 0.9268 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | − 0.0070 | 0.0082 | 0.394 | 0.9347 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0066 | 0.0078 | 0.396 |
| 74 | Presbycusis (age-related hearing loss) | 0.9329 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0009 | 0.0028 | 0.749 | 0.9405 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0008 | 0.0026 | 0.749 |
| 75 | Hearing loss, unspecified | 0.9364 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | 0.0026 | 0.0030 | 0.372 | 0.9439 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | 0.0025 | 0.0028 | 0.370 |
| 76 | Tinnitus | 0.9241 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0097 | 0.0037 | 0.010 | 0.9322 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0092 | 0.0036 | 0.010 |
| 77 | Other specified disorders of ear | 0.9322 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0016 | 0.0050 | 0.756 | 0.9399 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0047 | 0.758 |
| 78 | Aortic and mitral valve diseasea | 0.9300 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0038 | 0.0048 | 0.428 | 0.9378 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0036 | 0.0045 | 0.430 |
| 79 | Hypertensive diseasesa | 0.9278 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | − 0.0060 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | 0.9358 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0012 | 0.000 |
| 80 | Heart failurea | 0.9296 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0042 | 0.0065 | 0.519 | 0.9374 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0039 | 0.0061 | 0.519 |
| 81 | Angina pectoris | 0.9236 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0032 | 0.002 | 0.9317 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0097 | 0.0031 | 0.002 |
| 82 | Acute myocardial infarction and subsequent myocardial infarction | 0.9430 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | 0.0092 | 0.0047 | 0.047 | 0.9500 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | 0.0086 | 0.0043 | 0.046 |
| 83 | AMI complex/other | 0.9036 | 0.0156 | 0.000 | − 0.0302 | 0.0156 | 0.053 | 0.9124 | 0.0153 | 0.000 | − 0.0289 | 0.0152 | 0.057 |
| 84 | Chronic ischaemic heart disease | 0.9279 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0059 | 0.0037 | 0.114 | 0.9358 | 0.0037 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0035 | 0.116 |
| 85 | Pulmonary heart disease and diseases of pulmonary circulation | 0.9333 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0090 | 0.959 | 0.9409 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0085 | 0.959 |
| 86 | Acute pericarditis | 0.9428 | 0.0113 | 0.000 | 0.0090 | 0.0112 | 0.422 | 0.9498 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | 0.0084 | 0.0104 | 0.418 |
| 87 | Other forms of heart disease | 0.9143 | 0.0117 | 0.000 | − 0.0195 | 0.0117 | 0.095 | 0.9228 | 0.0113 | 0.000 | − 0.0185 | 0.0113 | 0.100 |
| 88 | Atrioventricular and left bundle-branch block | 0.9345 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | 0.0007 | 0.0066 | 0.918 | 0.9420 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | 0.0007 | 0.0062 | 0.916 |
| 89 | Other conduction disorders | 0.9281 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | − 0.0057 | 0.0086 | 0.507 | 0.9360 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | − 0.0054 | 0.0081 | 0.509 |
| 90 | Paroxysmal tachycardia | 0.9253 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0084 | 0.0039 | 0.031 | 0.9334 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0037 | 0.032 |
| 91 | Atrial fibrillation and flutter | 0.9295 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0043 | 0.0030 | 0.153 | 0.9373 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0041 | 0.0029 | 0.156 |
| 92 | Other cardiac arrhythmias | 0.9249 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0089 | 0.0045 | 0.049 | 0.9330 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0084 | 0.0043 | 0.050 |
| 93 | Complications and ill-defined descriptions of heart disease and other heart disorders in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.9221 | 0.0191 | 0.000 | − 0.0117 | 0.0191 | 0.540 | 0.9303 | 0.0183 | 0.000 | − 0.0111 | 0.0182 | 0.544 |
| 94 | Stroke | 0.9276 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0062 | 0.0043 | 0.151 | 0.9355 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0059 | 0.0041 | 0.152 |
| 95 | Cerebrovascular diseases | 0.9140 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0198 | 0.0076 | 0.009 | 0.9225 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | − 0.0189 | 0.0073 | 0.010 |
| 96 | Sequelae of cerebrovascular disease | 0.9258 | 0.0064 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0063 | 0.208 | 0.9339 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0075 | 0.0060 | 0.210 |
| 97 | Atherosclerosis | 0.9202 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0136 | 0.0060 | 0.024 | 0.9285 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0129 | 0.0058 | 0.025 |
| 98 | Aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection | 0.9096 | 0.0101 | 0.000 | − 0.0242 | 0.0100 | 0.016 | 0.9183 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0231 | 0.0097 | 0.018 |
| 99 | Diseases of arteries, arterioles and capillaries | 0.9341 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | 0.0003 | 0.0060 | 0.965 | 0.9416 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | 0.0002 | 0.0057 | 0.966 |
| 100 | Other peripheral vascular diseases | 0.9124 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0214 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.9210 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0204 | 0.0058 | 0.001 |
| 101 | Phlebitis, thrombosis of the portal vein and others | 0.9293 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0045 | 0.0046 | 0.323 | 0.9371 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0042 | 0.0043 | 0.326 |
| 102 | Varicose veins of lower extremities | 0.9377 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | 0.0039 | 0.0039 | 0.317 | 0.9451 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | 0.0037 | 0.0037 | 0.317 |
| 103 | Haemorrhoidsa | 0.9266 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0072 | 0.0028 | 0.011 | 0.9346 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0068 | 0.0027 | 0.011 |
| 104 | Oesophageal varices (chronic), varicose veins of other sites, other disorders of veins, nonspecific lymphadenitis, other noninfective disorders of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes and other and unspecified disorders of the circulatory system | 0.9333 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0077 | 0.949 | 0.9409 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0073 | 0.950 |
| 105 | Respiratory allergya | 0.9287 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0051 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9366 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0048 | 0.0011 | 0.000 |
| 105A | Chronic lower respiratory diseasesa | 0.9307 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0031 | 0.0018 | 0.091 | 0.9384 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | − 0.0029 | 0.0017 | 0.092 |
| 106 | Bronchitis, not specified as acute or chronic, simple and mucopurulent chronic bronchitis and unspecified chronic bronchitis | 0.9310 | 0.0077 | 0.000 | − 0.0028 | 0.0076 | 0.712 | 0.9387 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0026 | 0.0072 | 0.713 |
| 107 | Emphysema | 0.9409 | 0.0117 | 0.000 | 0.0071 | 0.0117 | 0.545 | 0.9480 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | 0.0066 | 0.0109 | 0.543 |
| 108 | Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD)a | 0.9266 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0072 | 0.0024 | 0.003 | 0.9346 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0068 | 0.0023 | 0.003 |
| 109 | Asthma, status asthmaticusa | 0.9281 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0057 | 0.0020 | 0.006 | 0.9360 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0054 | 0.0019 | 0.006 |
| 110 | Bronchiectasis | 0.9541 | 0.0104 | 0.000 | 0.0203 | 0.0104 | 0.050 | 0.9602 | 0.0095 | 0.000 | 0.0189 | 0.0095 | 0.046 |
| 111 | Other diseases of the respiratory system | 0.9289 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0049 | 0.0069 | 0.479 | 0.9367 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0046 | 0.0066 | 0.481 |
| 112 | Ulcersa | 0.9170 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0167 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | 0.9255 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0159 | 0.0022 | 0.000 |
| 113 | Inguinal hernia | 0.9283 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0055 | 0.0042 | 0.186 | 0.9362 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0052 | 0.0039 | 0.189 |
| 114 | Ventral hernia | 0.9354 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | 0.0016 | 0.0078 | 0.837 | 0.9429 | 0.0074 | 0.000 | 0.0015 | 0.0073 | 0.838 |
| 115 | Crohn’s diease | 0.9139 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0199 | 0.0072 | 0.006 | 0.9224 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0189 | 0.0069 | 0.006 |
| 116 | Ulcerative colitis | 0.9234 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | − 0.0104 | 0.0052 | 0.047 | 0.9316 | 0.0051 | 0.000 | − 0.0098 | 0.0050 | 0.048 |
| 117 | Other noninfective gastroenteritis and colitis | 0.9259 | 0.0068 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0067 | 0.242 | 0.9339 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0074 | 0.0064 | 0.245 |
| 118 | Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) | 0.9213 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0125 | 0.0039 | 0.001 | 0.9295 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0119 | 0.0037 | 0.001 |
| 119 | Other functional intestinal disorders | 0.9190 | 0.0045 | 0.000 | − 0.0148 | 0.0044 | 0.001 | 0.9273 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0141 | 0.0042 | 0.001 |
| 120 | Diseases of liver, biliary tract and pancreas | 0.9120 | 0.0059 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | 0.9206 | 0.0057 | 0.000 | − 0.0208 | 0.0056 | 0.000 |
| 121 | Psoriasisa | 0.9310 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0028 | 0.0034 | 0.410 | 0.9387 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0027 | 0.0032 | 0.407 |
| 122 | Infectious arthropathies | 0.9217 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | − 0.0121 | 0.0105 | 0.248 | 0.9299 | 0.0101 | 0.000 | − 0.0115 | 0.0100 | 0.252 |
| 123 | Rheumatoid arthritisa | 0.9093 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0244 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | 0.9180 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0233 | 0.0036 | 0.000 |
| 124 | Inflammatory polyarthropathies, except rheumatoid arthritisa | 0.9192 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0146 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.9275 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0139 | 0.0028 | 0.000 |
| 125 | Polyarthrosis (arthrosis) | 0.9070 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0268 | 0.0087 | 0.002 | 0.9157 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0256 | 0.0084 | 0.002 |
| 126 | Coxarthrosis (arthrosis of hip) | 0.9110 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0228 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | 0.9196 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 127 | Gonarthrosis (arthrosis of knee) | 0.9073 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0265 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | 0.9161 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0253 | 0.0021 | 0.000 |
| 128 | Arthrosis of first carpometacarpal joint and other arthrosis | 0.9148 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0190 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | 0.9233 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0181 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 129 | Acquired deformities of fingers and toes | 0.9258 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0079 | 0.0038 | 0.037 | 0.9339 | 0.0038 | 0.000 | − 0.0075 | 0.0036 | 0.039 |
| 130 | Other acquired deformities of limbs | 0.9190 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0148 | 0.0057 | 0.009 | 0.9273 | 0.0056 | 0.000 | − 0.0141 | 0.0054 | 0.010 |
| 131 | Disorders of patella (kneecap) | 0.9163 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0174 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | 0.9248 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0166 | 0.0040 | 0.000 |
| 132 | Internal derangement of knee | 0.9011 | 0.0083 | 0.000 | − 0.0327 | 0.0082 | 0.000 | 0.9100 | 0.0081 | 0.000 | − 0.0313 | 0.0080 | 0.000 |
| 133 | Derangement of meniscus due to old tear or injury | 0.9230 | 0.0043 | 0.000 | − 0.0108 | 0.0042 | 0.010 | 0.9312 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0040 | 0.011 |
| 134 | Internal derangement of knee, unspecified | 0.9093 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0245 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | 0.9180 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0234 | 0.0048 | 0.000 |
| 135 | Other specific joint derangements | 0.9071 | 0.0145 | 0.000 | − 0.0267 | 0.0144 | 0.064 | 0.9158 | 0.0141 | 0.000 | − 0.0255 | 0.0140 | 0.068 |
| 136 | Other joint disorders, not elsewhere classified | 0.8955 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0383 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | 0.9045 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0369 | 0.0065 | 0.000 |
| 137 | Systemic connective tissue disorders | 0.9234 | 0.0046 | 0.000 | − 0.0104 | 0.0044 | 0.019 | 0.9315 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | − 0.0099 | 0.0042 | 0.020 |
| 138 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | 0.9433 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | 0.0096 | 0.0108 | 0.376 | 0.9503 | 0.0101 | 0.000 | 0.0089 | 0.0100 | 0.374 |
| 139 | Dermatopolymyositis | 0.9495 | 0.0217 | 0.000 | 0.0157 | 0.0217 | 0.470 | 0.9560 | 0.0200 | 0.000 | 0.0146 | 0.0199 | 0.463 |
| 140 | Systemic sclerosis | 0.8932 | 0.0293 | 0.000 | − 0.0406 | 0.0293 | 0.167 | 0.9023 | 0.0288 | 0.000 | − 0.0390 | 0.0288 | 0.175 |
| 141 | Kyphosis, lordosis | 0.9028 | 0.0131 | 0.000 | − 0.0310 | 0.0130 | 0.017 | 0.9117 | 0.0127 | 0.000 | − 0.0297 | 0.0127 | 0.019 |
| 142 | Scoliosis | 0.8989 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0349 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | 0.9078 | 0.0084 | 0.000 | − 0.0335 | 0.0083 | 0.000 |
| 143 | Spinal osteochondrosis | 0.8874 | 0.0147 | 0.000 | − 0.0464 | 0.0146 | 0.002 | 0.8965 | 0.0145 | 0.000 | − 0.0449 | 0.0145 | 0.002 |
| 144 | Other deforming dorsopathies | 0.8976 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0362 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | 0.9066 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0348 | 0.0064 | 0.000 |
| 145 | Other inflammatory spondylopathies | 0.9140 | 0.0128 | 0.000 | − 0.0198 | 0.0128 | 0.121 | 0.9225 | 0.0124 | 0.000 | − 0.0188 | 0.0123 | 0.126 |
| 146 | Spondylosis | 0.8979 | 0.0041 | 0.000 | − 0.0358 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | 0.9069 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0344 | 0.0038 | 0.000 |
| 147 | Other spondylopathies and spondylopathies in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.9127 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0211 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | 0.9213 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0201 | 0.0051 | 0.000 |
| 148 | Cervical disc disorders | 0.9155 | 0.0088 | 0.000 | − 0.0183 | 0.0088 | 0.037 | 0.9240 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | − 0.0174 | 0.0084 | 0.039 |
| 149 | Other intervertebral disc disorders | 0.8939 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0398 | 0.0053 | 0.000 | 0.9030 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0384 | 0.0053 | 0.000 |
| 150 | Other dorsopathies, not elsewhere classified | 0.8942 | 0.0107 | 0.000 | − 0.0396 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | 0.9033 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | − 0.0381 | 0.0105 | 0.000 |
| 151 | Dorsalgia | 0.8824 | 0.0049 | 0.000 | − 0.0514 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | 0.8915 | 0.0048 | 0.000 | − 0.0498 | 0.0047 | 0.000 |
| 152 | Soft tissue disorders | 0.9153 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | − 0.0185 | 0.0078 | 0.018 | 0.9238 | 0.0076 | 0.000 | − 0.0176 | 0.0075 | 0.019 |
| 153 | Synovitis and tenosynovitis | 0.9188 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0150 | 0.0053 | 0.005 | 0.9271 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0143 | 0.0051 | 0.005 |
| 154 | Disorders of synovium and tendon | 0.9191 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0146 | 0.0060 | 0.014 | 0.9275 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0139 | 0.0057 | 0.015 |
| 155 | Soft tissue disorders related to use, overuse and pressure | 0.9090 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0248 | 0.0071 | 0.001 | 0.9177 | 0.0070 | 0.000 | − 0.0237 | 0.0069 | 0.001 |
| 156 | Fibroblastic disorders | 0.9295 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0043 | 0.0041 | 0.288 | 0.9373 | 0.0039 | 0.000 | − 0.0041 | 0.0038 | 0.287 |
| 157 | Shoulder lesions | 0.9042 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0296 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | 0.9131 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | − 0.0283 | 0.0030 | 0.000 |
| 158 | Enthesopathies of lower limb, excluding foot | 0.9120 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0218 | 0.0097 | 0.025 | 0.9206 | 0.0094 | 0.000 | − 0.0208 | 0.0094 | 0.026 |
| 159 | Other enthesopathies | 0.9008 | 0.0080 | 0.000 | − 0.0330 | 0.0079 | 0.000 | 0.9097 | 0.0078 | 0.000 | − 0.0316 | 0.0077 | 0.000 |
| 160 | Rheumatism, unspecified | 0.8938 | 0.0170 | 0.000 | − 0.0400 | 0.0170 | 0.019 | 0.9028 | 0.0168 | 0.000 | − 0.0386 | 0.0168 | 0.022 |
| 161 | Myalgia | 0.9104 | 0.0089 | 0.000 | − 0.0234 | 0.0088 | 0.008 | 0.9190 | 0.0086 | 0.000 | − 0.0223 | 0.0085 | 0.009 |
| 162 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified | 0.9055 | 0.0102 | 0.000 | − 0.0283 | 0.0102 | 0.005 | 0.9143 | 0.0099 | 0.000 | − 0.0271 | 0.0099 | 0.006 |
| 163 | Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified: pain in limb | 0.9070 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0268 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | 0.9157 | 0.0061 | 0.000 | − 0.0256 | 0.0060 | 0.000 |
| 164 | Fibromyalgia | 0.8852 | 0.0301 | 0.000 | − 0.0486 | 0.0301 | 0.107 | 0.8944 | 0.0299 | 0.000 | − 0.0470 | 0.0299 | 0.116 |
| 165 | Osteoporosisa | 0.9181 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0157 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | 0.9265 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0149 | 0.0025 | 0.000 |
| 166 | Osteoporosis in diseases classified elsewhere | 0.9388 | 0.0238 | 0.000 | 0.0050 | 0.0238 | 0.834 | 0.9460 | 0.0222 | 0.000 | 0.0046 | 0.0221 | 0.835 |
| 167 | Adult osteomalacia and other disorders of bone density and structure | 0.9230 | 0.0042 | 0.000 | − 0.0107 | 0.0040 | 0.008 | 0.9312 | 0.0040 | 0.000 | − 0.0102 | 0.0039 | 0.008 |
| 168 | Disorders of continuity of bone | 0.9241 | 0.0167 | 0.000 | − 0.0097 | 0.0167 | 0.560 | 0.9322 | 0.0159 | 0.000 | − 0.0092 | 0.0158 | 0.561 |
| 169 | Other osteopathies | 0.9200 | 0.0075 | 0.000 | − 0.0138 | 0.0075 | 0.064 | 0.9283 | 0.0072 | 0.000 | − 0.0131 | 0.0071 | 0.067 |
| 170 | Other disorders of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | 0.9207 | 0.0063 | 0.000 | − 0.0131 | 0.0062 | 0.036 | 0.9290 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | − 0.0124 | 0.0059 | 0.037 |
| 171 | Chronic renal failure (CRF)a | 0.9392 | 0.0071 | 0.000 | 0.0054 | 0.0070 | 0.443 | 0.9464 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | 0.0051 | 0.0066 | 0.440 |
| 172 | Congenital malformations: of the nervous, circulatory, respiratory system; cleft palate and cleft lip, urinary tract, bones and muscles, other and chromosomal abnormalities not elsewhere classified | 0.9251 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0087 | 0.0035 | 0.013 | 0.9332 | 0.0035 | 0.000 | − 0.0082 | 0.0033 | 0.014 |
| 173 | Congenital malformations of eye, ear, face and neck | 0.9342 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | 0.0005 | 0.0054 | 0.932 | 0.9418 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | 0.0004 | 0.0051 | 0.930 |
| 174 | Other congenital malformations of the digestive system | 0.9335 | 0.0097 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0097 | 0.978 | 0.9411 | 0.0091 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0091 | 0.977 |
| 175 | Congenital malformations of the sexual organs | 0.9295 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | 0.0043 | 0.0061 | 0.485 | 0.9374 | 0.0058 | 0.000 | − 0.0040 | 0.0058 | 0.487 |
| 176 | Dementiaa | 0.9272 | 0.0127 | 0.000 | − 0.0066 | 0.0127 | 0.602 | 0.9351 | 0.0121 | 0.000 | − 0.0063 | 0.0120 | 0.601 |
| 177 | Organic, including symptomatic, mental disorders | 0.9212 | 0.0096 | 0.000 | − 0.0126 | 0.0096 | 0.189 | 0.9294 | 0.0092 | 0.000 | − 0.0120 | 0.0092 | 0.192 |
| 178 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to use of alcohol | 0.9263 | 0.0055 | 0.000 | − 0.0075 | 0.0054 | 0.161 | 0.9343 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0071 | 0.0051 | 0.163 |
| 179 | Mental and behavioural disorders due to psychoactive substance use | 0.9349 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | 0.0011 | 0.0046 | 0.810 | 0.9424 | 0.0044 | 0.000 | 0.0010 | 0.0043 | 0.814 |
| 180 | Schizophreniaa | 0.9200 | 0.0098 | 0.000 | − 0.0138 | 0.0097 | 0.155 | 0.9283 | 0.0093 | 0.000 | − 0.0131 | 0.0093 | 0.159 |
| 181 | Schizotypal and delusional disorders | 0.9551 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | 0.0214 | 0.0066 | 0.001 | 0.9612 | 0.0060 | 0.000 | 0.0198 | 0.0060 | 0.001 |
| 182 | Bipolar affective disordera | 0.9278 | 0.0106 | 0.000 | − 0.0059 | 0.0105 | 0.572 | 0.9358 | 0.0100 | 0.000 | − 0.0056 | 0.0100 | 0.575 |
| 183 | Depressiona | 0.9018 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0319 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | 0.9107 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | − 0.0306 | 0.0018 | 0.000 |
| 184 | Mood (affective) disorders | 0.9329 | 0.0189 | 0.000 | − 0.0009 | 0.0188 | 0.961 | 0.9405 | 0.0178 | 0.000 | − 0.0009 | 0.0177 | 0.962 |
| 185 | Phobic anxiety disorders | 0.9161 | 0.0114 | 0.000 | − 0.0176 | 0.0114 | 0.121 | 0.9246 | 0.0110 | 0.000 | − 0.0168 | 0.0109 | 0.125 |
| 186 | Other anxiety disorders | 0.9285 | 0.0065 | 0.000 | − 0.0053 | 0.0064 | 0.412 | 0.9364 | 0.0062 | 0.000 | − 0.0050 | 0.0061 | 0.412 |
| 187 | Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD)a | 0.9195 | 0.0112 | 0.000 | − 0.0142 | 0.0112 | 0.203 | 0.9279 | 0.0108 | 0.000 | − 0.0135 | 0.0107 | 0.208 |
| 188 | Post-traumatic stress disorder | 0.9104 | 0.0180 | 0.000 | − 0.0234 | 0.0179 | 0.193 | 0.9191 | 0.0174 | 0.000 | − 0.0223 | 0.0174 | 0.199 |
| 189 | Reactions to severe stress and adjustment disorders | 0.9324 | 0.0050 | 0.000 | − 0.0014 | 0.0049 | 0.776 | 0.9401 | 0.0047 | 0.000 | − 0.0013 | 0.0046 | 0.777 |
| 190 | Dissociative (conversion) disorders, somatoform disorders and other neurotic disorders | 0.9156 | 0.0076 | 0.000 | − 0.0182 | 0.0075 | 0.015 | 0.9241 | 0.0073 | 0.000 | − 0.0173 | 0.0072 | 0.017 |
| 191 | Eating disorders | 0.9407 | 0.0093 | 0.000 | 0.0070 | 0.0093 | 0.453 | 0.9478 | 0.0087 | 0.000 | 0.0065 | 0.0086 | 0.453 |
| 192 | Behavioural syndromes associated with physiological disturbances and physical factors | 0.9245 | 0.0122 | 0.000 | − 0.0093 | 0.0122 | 0.446 | 0.9326 | 0.0116 | 0.000 | − 0.0088 | 0.0116 | 0.449 |
| 193 | Emotionally unstable personality disorder | 0.9189 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | − 0.0148 | 0.0108 | 0.171 | 0.9273 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | − 0.0141 | 0.0104 | 0.176 |
| 194 | Specific personality disorders | 0.9216 | 0.0054 | 0.000 | − 0.0121 | 0.0053 | 0.022 | 0.9299 | 0.0052 | 0.000 | − 0.0115 | 0.0051 | 0.023 |
| 195 | Disorders of adult personality and behaviour | 0.9353 | 0.0090 | 0.000 | 0.0015 | 0.0090 | 0.866 | 0.9428 | 0.0085 | 0.000 | 0.0014 | 0.0084 | 0.865 |
| 196 | Mental retardation | 0.9410 | 0.0176 | 0.000 | 0.0072 | 0.0175 | 0.683 | 0.9481 | 0.0163 | 0.000 | 0.0067 | 0.0163 | 0.682 |
| 197 | Disorders of psychological development | 0.9281 | 0.0118 | 0.000 | − 0.0057 | 0.0118 | 0.630 | 0.9360 | 0.0112 | 0.000 | − 0.0053 | 0.0112 | 0.632 |
| 198 | Hyperkinetic disorders (ADHD)a | 0.9172 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0166 | 0.0068 | 0.015 | 0.9256 | 0.0067 | 0.000 | − 0.0158 | 0.0065 | 0.016 |
| 199 | Behavioural and emotional disorders with onset usually occurring in childhood and adolescence | 0.9299 | 0.0069 | 0.000 | − 0.0039 | 0.0068 | 0.569 | 0.9377 | 0.0066 | 0.000 | − 0.0037 | 0.0065 | 0.571 |
| Denmark sample (base) | 0.9353 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | 0.9428 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | |||||||
| North Denmark Region (sample 2–3) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0009 | 0.074 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0014 | 0.0008 | 0.073 | |
| Specific ages (dydx) | |||||||||||||
| Age 16 | 0.9420 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | 0.0006 | 0.0003 | 0.034 | 0.9487 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | 0.0006 | 0.0003 | 0.027 | |
| Age 20 | 0.9434 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.335 | 0.9502 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.273 | |
| Age 25 | 0.9434 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.179 | 0.9502 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.239 | |
| Age 30 | 0.9422 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9492 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | − 0.0003 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 35 | 0.9404 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9475 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 40 | 0.9382 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9455 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 45 | 0.9360 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9434 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 50 | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 55 | 0.9317 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9394 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 60 | 0.9297 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | 0.9375 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.000 | |
| Age 65 | 0.9277 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9357 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 70 | 0.9257 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9338 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | − 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 75 | 0.9234 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9316 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0005 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 80 | 0.9204 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | 0.9287 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0007 | 0.0001 | 0.000 | |
| Age 85 | 0.9161 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0011 | 0.0002 | 0.000 | 0.9246 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0010 | 0.0002 | 0.000 | |
| Education | |||||||||||||
| No education (base) | 0.9303 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | 0.9381 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Student | 0.9368 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | 0.0065 | 0.0020 | 0.001 | 0.9442 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | 0.0061 | 0.0019 | 0.001 | |
| Short | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0035 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | 0.0033 | 0.0009 | 0.000 | |
| Middle (bsc eq) | 0.9403 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | 0.0100 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9475 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | 0.0094 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |
| Higher (msc+) | 0.9469 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | 0.0165 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | 0.9536 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | 0.0155 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | |
| Ethnicity | |||||||||||||
| Danish (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Western | 0.9192 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0146 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | 0.9275 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | − 0.0139 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | |
| Non-western | 0.9194 | 0.0033 | 0.000 | − 0.0144 | 0.0030 | 0.000 | 0.9277 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | − 0.0136 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | |
| Income | |||||||||||||
| 0.19 (25%) | 0.9334 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0042 | 0.0018 | 0.019 | 0.9410 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0039 | 0.0017 | 0.019 | |
| 0.26 (50%) | 0.9337 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0042 | 0.0018 | 0.018 | 0.9413 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | 0.0040 | 0.0017 | 0.018 | |
| 0.33 (75%) | 0.9341 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0042 | 0.0018 | 0.017 | 0.9416 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | 0.0040 | 0.0017 | 0.017 | |
| Marriage/partner | |||||||||||||
| Partner/married (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| No partner | 0.9323 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | − 0.0015 | 0.0008 | 0.050 | 0.9400 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0014 | 0.0007 | 0.050 | |
| Children | |||||||||||||
| No children < 15 (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Children < 15 | 0.9362 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | 0.0024 | 0.0010 | 0.014 | 0.9436 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0022 | 0.0009 | 0.015 | |
| Loneliness | |||||||||||||
| Not/seldom lonely (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Often lonely | 0.9107 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0231 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | 0.9194 | 0.0026 | 0.000 | − 0.0220 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | |
| Stress | |||||||||||||
| 80% least stressed (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 20% most stressed | 0.8630 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | − 0.0708 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | 0.8722 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0692 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | |
| BMI | |||||||||||||
| BMI < 18.5 | 0.9286 | 0.0029 | 0.000 | − 0.0052 | 0.0027 | 0.057 | 0.9364 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0050 | 0.0026 | 0.056 | |
| BMI 18.5–25 (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| BMI > 25 < 30 | 0.9273 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | − 0.0065 | 0.0009 | 0.000 | 0.9352 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | − 0.0061 | 0.0008 | 0.000 | |
| BMI ≥ 30 < 35 | 0.9188 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | − 0.0150 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | 0.9271 | 0.0016 | 0.000 | − 0.0143 | 0.0013 | 0.000 | |
| BMI ≥ 35 | 0.9042 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | − 0.0296 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | 0.9131 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | − 0.0283 | 0.0022 | 0.000 | |
| Smoking | |||||||||||||
| Do not smoke daily (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Smoke daily | 0.9253 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | − 0.0085 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | 0.9333 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | − 0.0081 | 0.0010 | 0.000 | |
| Drinking | |||||||||||||
| Do not exceed recommendations (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Exceed recommendations | 0.9258 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0080 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | 0.9338 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | − 0.0076 | 0.0014 | 0.000 | |
| Exercise | |||||||||||||
| Exercise at least 4 hrs/day (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Do not exercise | 0.9176 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | − 0.0162 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9260 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | − 0.0154 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | |
| Fruit intake | |||||||||||||
| Do not meet recommendations (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 5 or more portions | 0.9372 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | 0.0034 | 0.0015 | 0.022 | 0.9446 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | 0.0032 | 0.0014 | 0.022 | |
| SF-12 General Health (self-reported) | |||||||||||||
| Excellent | 0.9386 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0048 | 0.0005 | 0.000 | 0.9460 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | 0.0046 | 0.0004 | 0.000 | |
| Very good | 0.9382 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.0045 | 0.0004 | 0.000 | 0.9456 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | 0.0042 | 0.0004 | 0.000 | |
| Good (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Fair | 0.8939 | 0.0036 | 0.000 | − 0.0399 | 0.0032 | 0.000 | 0.9033 | 0.0034 | 0.000 | − 0.0380 | 0.0031 | 0.000 | |
| Poor | 0.7688 | 0.0109 | 0.000 | − 0.1650 | 0.0107 | 0.000 | 0.7808 | 0.0107 | 0.000 | − 0.1606 | 0.0105 | 0.000 | |
| Missing | 0.9244 | 0.0028 | 0.000 | − 0.0094 | 0.0025 | 0.000 | 0.9325 | 0.0027 | 0.000 | − 0.0089 | 0.0024 | 0.000 | |
| Long-term illness or disability (self-reported) | |||||||||||||
| No long-term illness (base) | 0.9338 | 0.0012 | 0.000 | 0.9414 | 0.0011 | 0.000 | |||||||
| Long-term illness | 0.9141 | 0.0023 | 0.000 | − 0.0197 | 0.0018 | 0.000 | 0.9226 | 0.0021 | 0.000 | − 0.0187 | 0.0017 | 0.000 | |
| Missing | 0.9272 | 0.0020 | 0.000 | − 0.0066 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | 0.9352 | 0.0019 | 0.000 | − 0.0062 | 0.0015 | 0.000 | |
Note: n = 55,616 in all models
aComplex defined condition
Chronic conditions from groups M, G and F have some of the largest estimated disutilities in the base UK model. Some examples of large disutilities are (ICD-10 code and ME for male/female in brackets): fibromyalgia (M797; ME − 0.1999/− 0.1900), sclerosis (G35; − 0.1379/− 0.1273), rheumatism, unspecified (M790; ME − 0.1336/− 0.1236), dorsalgia (M54; ME − 0.1041/− 0.0954), cerebral palsy (G80–G83; ME − 0.1034/− 0.0945), post-traumatic stress disorder (F431 − 0.0919/− 0.0837), HIV (B20–24; ME − 0.0833/− 0.0772), other intervertebral disc disorders (M51; ME − 0.0829/− 0.0754), diseases of myoneural junction and muscle (G70–G73; ME − 0.081/− 0.0742), dementia (F00–2, G30–32; ME −0.0806/−0.0744), spinal osteochondrosis (M42; ME − 0.0804/− 0.0733) and depression (F32, F33, F34.1, F06.32; ME − 0.0787/− 0.0716). When controlling for additional variables in the full model, the disutilities of the chronic conditions tend to decrease in size, probably due to the inclusion of the SF-12 question, which will be correlated to some extent with the presence of chronic conditions. One exception is fibromyalgia, where the disutility appears to be higher than in the base model (− 0.1999/− 0.1900); however, the sample has very few individuals with this chronic condition, and it is atypical to have fibromyalgia on its own; the median number of chronic conditions in these individuals is eight.
The disutilities of chronic conditions estimated using the US base model are generally smaller than in the UK model, reflecting the differences in the US/UK value sets. The largest disutilities correspond to chronic viral hepatitis (B18; ME − 0.1024/− 0.1040), sclerosis (G35; ME − 0.0842/− 0.0816), post-traumatic stress disorder (F431; ME − 0.0739/− 0.0717), dorsalgia (M54; ME − 0.0716/− 0.0695) and rheumatism (M790; ME − 0.0671/− 0.0650). Chronic diseases of group M show relatively higher marginal disutilities in the US model.
Both base models include age as a covariate for adjustment, and the full UK and US models also include other socioeconomic, lifestyle and health risk variables. For all four models, an increase in age is associated with a decrease in utility. The decrease per year is relatively small after controlling for chronic conditions and other covariates, and the rate of decrease increases with age. For example, in the base UK model, males with no chronic conditions at age 20 are estimated to have an average utility of 0.9121 (0.9270 for females); at age 80, the average utility declines to 0.8719 (0.8920 for females), with a difference of 0.0402 (0.0350 for females). In the US base model, the corresponding average disutility for that group is 0.0246 (0.0231 for females). This decrease is much smaller at younger ages, with an increase of 1 year expected to decrease utility for males by 0.0003 at age 20 but by a much larger 0.0037 at age 80.
We found relatively large decreases in marginal utilities within the single SF-12 general health question, stress, self-reported long-standing illness, high BMI and loneliness. The largest single disutilities were found for the SF-12 question of poor general health (UK − 0.2369/− 0.2260 for males/females; USA − 0.1650/− 0.1606 for male/females) followed by perceived stress (UK − 0.0595/− 0.0535 for males/females; USA − 0.0708/− 0.0692 for males/females), self-reported long-standing illness or injury (UK around − 0.073 for both sexes; USA around − 0.020 both sexes), BMI > 35 (UK − 0.0129/− 0.0113 for males/females; USA − 0.0296/− 0.0283 for males/females) and a sense of feeling loneliness often (UK − 0.0152/− 0.0136 for males/females; USA − 0.0231/− 0.0220 for males/females). Finally, higher education showed a relatively high positive difference relative to the baseline of no education (UK 0.0252/0.0244 for males/females) but less for the US models (0.0165/0.0155 for males/females).
Finally, estimates of socioeconomic disparities provide potential health improvements and have become increasingly important to public health assessments, interventions, researchers, healthcare decision-makers, and the industry [36, 70–72]. Hence, Appendices 3 and 4 in the online Supplementary Material 1 present easily available, off-the-shelf health inequality UK and US EQ-5D-3L average sample scores based on subgroups of educational, income, socioeconomic, age, gender, BMI groups across the 199+ chronic conditions and covariates.
Using the two types of catalogues
The sections above provide two separate catalogues that may be of interest. The first one provides population-based estimates of utility; the second one provides utility estimates adjusted for covariates for a representative individual so that comparisons across chronic conditions adjusted for other covariates can be made for UK and US EQ-5D-3L norms. Catalogue one, the population estimates, are useful when interest lies in EQ-5D-3L in the general population. The estimated regressions used to construct catalogue two may be used to calculate utility estimates in samples other than the general population sample used here, for example, when using it to appraise interventions with different age and sex distributions or lower baseline health than the general population. For this purpose, a technical guide on how to use the model estimates to predict EQ-5D-3L scores has been provided in the online Supplementary Material 2, along with Stata data and programming files to do so.3
Discussion
EQ-5D is one of the most widely used measures of benefit for CEA. However, EQ-5D is not always collected in trials, and when it is, different populations, methodologies and value sets make comparisons across trials difficult. Utility catalogues of chronic diseases which use a standardised methodology can help to ensure meaningful comparisons can be made. This paper presents newer, standardised catalogues of mean-based EQ-5D-3L preference scores for 199 doctor-reported chronic conditions in the UK and the USA. Two versions of the catalogues are included, one based on a model controlling for chronic conditions, age and sex, and a second, more comprehensive one, which controls for additional socioeconomic, lifestyle and health risk variables. The study provides evidence of the association between different chronic conditions, health risks and lifestyle factors with HRQoL and their differences. This may be useful for benchmarking, and comparisons, including identifying what factors, such as conditions and/or health risks, are associated with the lowest HRQoL, of interest for policy- and decision-makers, health professionals, and researchers. The catalogue may also be of use to inform evidence in Public Health interventions designed to reduce the prevalence of some chronic conditions.
This study has several methodological strengths. First, it uses registry records to determine chronic conditions instead of self-reported data. Second, it includes 199 chronic conditions on the basis of the newer ICD-10 classification. Third, we use statistical models developed specifically to model the characteristics of generic preference-based measures such as EQ-5D-3L.
The study also has some limitations. Despite the large number of chronic conditions and other controls included in the models, heterogeneity within the chronic conditions can be large. Being able to control for other chronic conditions goes some way in alleviating this problem, as the estimates can be tailored to different populations, but when using the estimates in economic evaluations, analysts would need to make additional assumptions regarding the impact of new treatments in the long run.
We use a Danish data sample to estimate HRQoL models for the UK and USA by applying the respective value sets to the EQ-5D-3L instrument data. As earlier pointed out by Sullivan and colleagues (2011), this is not an ideal approach [28] but a practical one. Despite efforts to produce EQ-5D-3L versions that are comparable across countries, there still remains the possibility that the dimension descriptors are interpreted slightly differently in different countries, leading to differences in both the distribution of responses to the individual dimensions and the value sets. Furthermore, as confirmed in the current study, issues such as country differences in health risks, for example, BMI, may impact HRQoL. Differences in BMI across the USA and Europe are well documented. For instance, WHO estimated the mean BMI in Denmark to be 25.3 in 2016, while both the UK and US estimates are larger, 27.1 and 28.9 for the UK and the USA, respectively [73]. Other research also finds similar patterns in BMI, with the UK slightly closer to the Danish population than the USA [74].
Another factor that may contribute to differences might be educational attainment. Educational levels in the USA are the highest and closest to the Danish population, although some have also argued that the three countries have similar high educational population levels compared with other countries [75]. We find that the EQ-5D-3L educational sample means of the current study (Table 2) are similar to the older MEPS used for the previous catalogues: no degree 0.814 versus 0.83 and master’s degree 0.919 versus 0.91. Overall, US EQ-5D-3L population means are also similar between the current sample and the MEPS, with 0.869 versus 0.867 in the MEPS for the overall mean; 0.883 versus 0.880 for men and 0.854 versus 0.850 for women. A similar pattern emerges across age groups [24, 26]. However, the differences across some conditions are slightly larger: diabetes 0.779–0.758, asthma 0.803–0.820 and hypertension 0.801–0.787, respectively [26]. We expect some differences between conditions because the current catalogue is based on doctor-reported conditions instead of the MEPS self-reports. Nevertheless, it is difficult to know to what extent the differences are due to the chronic conditions reporting methodology versus other reasons.
Moreover, other studies have found country population differences regarding mortality and ethnic, income and education composition [76, 77]. Thus, it cannot be ruled out that the US and partly UK unadjusted estimates of the current study could be larger (overestimated) than they would have been using ‘native’ samples, although the precise impact is unclear. Nevertheless, we might get some indication of the possible size of the impact from other studies. For example, research has shown that the UK VAS ratings (83) are close to the Danish estimates (84), compared with 81 in the USA.
Similarly, a cross-country mean EQ-5D-3L comparison based on the European value set gave close estimates between DK (0.866) and the UK (0.856) and less so for the USA (0.825). Although these studies are based on older datasets, this might be the pattern we expect to see due to population differences, whether they are due to health directly or any socioeconomic differences. Thus, given this evidence, we can expect the DK sample to be closer to the UK population-based scores than the US sample. At the same time, the US EQ-5D-3L estimates might be slightly overestimated on the basis of a Danish population than if we had used a US population. Furthermore, using foreign-based sample estimates, although not ideal, might still be more acceptable than other alternatives, such as not having any baseline or reference condition estimates or using other more unreliable sources [28]. Moreover, all regression models adjusted for sex and age, as well as the full regression model for socio-economic variables and health risks, including BMI, thus reducing the impact of possible population differences.
Finally, the present study includes the latest national EQ-5D-3L data available, but the age of data might be a concern due to possible changes in HRQoL and treatments if improvements in technology and treatments, for example, lead to higher HRQoL. However, there does not seem to be evidence of positive changes in HRQoL across years or even decades. For example, comparing the latest available EQ-5L-3L population scores of 2010, 2013 and 2017, there is a slight decline from 0.85 to 0.83 (Danish norms) [78]. Another Danish study identified a slight decline from 0.89 in 2000 to 0.87 in 2010, suggestively due to an ageing population [56]. Other more recent Danish reports also suggest national declines in HRQoL. For instance, HRQoL measured by the SF-12 showed varying and slightly worsening national population health from 2010 to 2021 for physical health (10.0–11.3% having bad health in 2017 and 11.0% in 2021) and mental health dimensions (from 10.0% in 2010 to 13.2% having bad health in 2017, increasing to 17.4% in 2021) [79, 80]. This may indicate that population-based HRQoL is still slightly declining over time, although there seems to be an impact of COVID-19 around 2021 on mental health, in which long-lasting impacts on the population HRQoL are currently unknown. However, if anything, the estimates provided in the current study may be slightly conservative, e.g., lower, compared with the present time. Finally, any decline in HRQoL due to ageing populations over time can be factored in when modelling the population of interest using the provided regression estimates in catalogue two.
Conclusion
Along with the rapidly growing burden of chronic diseases in both prevalence, personal health and economic terms [33, 81–85], the future holds an increasing need for policy and decision-makers to prioritise and ensure most ‘health per pound or dollar’. The current study provides updated, larger catalogues of EQ-5D-3L preference scores for the UK and the USA. The catalogues describe aspects of disease burden, including identifying diseases with the lowest HRQoL and which can be used in CEA to allocate healthcare resources. To our knowledge, this is the largest and most comprehensive mean-based regression modelling of EQ-5D-3L scores for chronic conditions for these two countries. The models enable valid comparisons and assessments of the impact of HRQoL between 199 chronic conditions, socioeconomic factors, health risks and lifestyle factors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Author contributions
MFH made the underlying data management and the first draft of the paper, as well as Supplementary Material 1. MHA made first draft of all Supplementary Material 2 including guideline, data and Stata do files. MFH and MHA equally made the study rationale and design, data modelling, critical evaluation and interpretation, and all revisions of the paper, supplementary materials and others.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
MFH and MHA declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Participants gave informed consent for the survey data. No other consent was required.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and material
All data are kept on a secure server at Statistics Denmark, and due to legal requirements, the micro data underlying the present study cannot be made freely available. However, the estimated utilities and regression models are made freely available for analysts through Stata .ster files and the result presented in paper.
Code availability
Stata do file code is available in Supplementary Material 2.
Footnotes
The ethnicity variable defined as Danish, western or non-western used Danish standard programming based on register variables agreed on in the joint collaboration regarding the national health profiles between the five Danish regions and the National Institute of Public health (Christensen et al. [53]).
A third model including similar covariates to Sullivan et al.’s work [26, 28] was also estimated. This model is not discussed here as the fit was similar to the base model, but can be provided by the authors on request.
Furthermore, a simplified example of how to use the estimates has been provided in an earlier publication using the Danish value set in the results section [32].
References
- 1.The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Guide to the methods of technology appraisal. Process and methods [Internet]. NICE. 2013. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/process/pmg9/resources/guide-to-the-methods-of-technologyappraisal-2013-pdf-2007975843781. [PubMed]
- 2.ICER. Overview of the ICER value framework and proposals for an update for 2017–2018. 2018.
- 3.Drummond M, Sculpher JM, Glaxton K, Stoddart LG, Torrance WG. Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. 4th edition. [Internet]. Oxford University Press; 2015. Available from: https://global.oup.com/academic/product/methods-for-the-economic-evaluation-of-health-care-programmes-9780199665877?cc=dk&lang=en&.
- 4.Brazier J, Ratcliffe J, Saloman J, Tsuchiya A. Measuring and valuing health benefits for economic evaluation [Internet]. Pharmacoeconomics. Oxford University Press; 2016. Available from: http://www.oxfordmedicine.com/view/10.1093/med/9780198725923.001.0001/med-9780198725923.
- 5.Gerlinger C, Bamber L, Leverkus F, Schwenke C, Haberland C, Schmidt G, et al. Comparing the EQ-5D-5L utility index based on value sets of different countries: impact on the interpretation of clinical study results 11 Medical and Health Sciences 1117 Public Health and Health Services. BMC Res Notes. 2019;12:4–9. doi: 10.1186/s13104-019-4067-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Devlin N. EuroQol G. 5 things you should do with EQ-5D Data [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2022 Feb 5]. p. 1–4. Available from: https://www.ohe.org/news/5-things-you-should-do-eq-5d-data.
- 7.Devlin NJ, Brooks R. EQ-5D and the EuroQol Group: past, present and future. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2017;15:127–137. doi: 10.1007/s40258-017-0310-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jiang R, Janssen MFB, Pickard AS. US population norms for the EQ-5D-5L and comparison of norms from face-to-face and online samples. Qual Life Res. 2021;30:803–816. doi: 10.1007/s11136-020-02650-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.EuroQol Research Foundation. EQ-5D-3L user guide [Internet]. 2018. Available from: https://euroqol.org/publications/user-guides.
- 10.EuroQol Research Foundation. EQ-5D-5L user guide [Internet]. 2019. Available from: https://euroqol.org/publications/user-guides.
- 11.Dolan P. Modeling valuations for EuroQol health states. Med Care. 1997;35:1095–108. Available from: http://journals.lww.com/00005650-199711000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 12.Shaw JW, Johnson JA, Coons SJ. US valuation of the EQ-5D health states: development and testing of the D1 valuation model. Med Care. 2005;43:203–220. doi: 10.1097/00005650-200503000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dolan P, Gudex C, Kind P, Williams A. A social tariff for EuroQol: results from a UK general population survey [Internet]. Work. Pap. 1995. Available from: http://ideas.repec.org/p/chy/respap/138chedp.html.
- 14.Devlin NJ, Shah KK, Feng Y, Mulhern B, van Hout B. Valuing health-related quality of life: An EQ-5D-5L value set for England. Heal Econ (United Kingdom). 2018;27:7–22. Available from: https://eq-5dpublications.euroqol.org/download?id=0_63315&fileId=63073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Pickard AS, Law EH, Jiang R, Pullenayegum E, Shaw JW, Xie F, et al. United States valuation of EQ-5D-5L health states using an international protocol. Value Health. 2019;22:931–941. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2019.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kajang, Cheung, Mandy, Oemar, Mark, Oppe, et al. EQ-5D-3L user guide v2.0. [Internet]. EuroQol. Rotterdam, Netherlands; 2009. Available from: https://euroqol.org/publications/user-guides/.
- 17.National Institute for Care and Excellence. Position statement on use of the EQ-5D-5L value set for England (updated October 2019) [Internet]. Nice. 2019. p. 2018–20. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/about/what-we-do/our-programmes/nice-guidance/technology-appraisal-guidance/eq-5d-5l.
- 18.Hernández Alava M, Pudney S, Wailoo A. Estimating the relationship between EQ-5D-5L and EQ-5D-3L: results from a UK population study. Pharmacoeconomics. 2023;41:199–207. doi: 10.1007/s40273-022-01218-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hernández-Alava M, Pudney S. eq5dmap: a command for mapping between EQ-5D-3L and EQ-5D-5L. Stata J. 2018;18:395–415. doi: 10.1177/1536867X1801800207. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Dickman PW, Coviello E. Software updates. Stata J Promot Commun Stat Stata. 2022;22:238–241. doi: 10.1177/1536867X221083931. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), National Institute of Clinical Excellence (NICE). Guide to the methods of technology appraisal 2013. [Internet]. Natl. Inst. Heal. Care Excell. London, England; 2013 [cited 2016 Jun 30]. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/about/what-we-do/our-programmes/nice-guidance/nice-technology-appraisal-guidance.
- 22.National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Guide to the methods of technology appraisal (2008) [Internet]. London; 2008. Available from: https://heatinformatics.com/sites/default/files/images-videosFileContent/UKNHS_NICEHTA2008.pdf. [PubMed]
- 23.National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Guide to the processes of technology appraisal (2018) [Internet]. Natl. Inst. Heal. Care Excell. 2018. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/Media/Default/About/what-we-do/NICE-guidance/NICE-technology-appraisals/technology-appraisal-processes-guide-apr-2018.pdf. [PubMed]
- 24.Sullivan PW, Ghushchyan V. Preference-based EQ-5D index scores for chronic conditions in the United States. Med Decis Mak [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2012 Apr 23];26:410–20. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2634296&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Wilson KCM, Copeland JRM, Taylor S, Donoghue J, Mccracken CFM. Natural history of pharmacotherapy of older depressed community residents. The MRC-ALPHA Study. Br J Psychiatry. 1999;175:439–443. doi: 10.1192/bjp.175.5.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sullivan PW, Lawrence WF, Ghushchyan V. A national catalog of preference-based scores for chronic conditions in the United States. Med Care. 2005;43(7):736–749. doi: 10.2307/3768375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sullivan, Patrick W Ghushchyan V. “How to Use the Estimates”. Appendix to: Preference-based EQ-5D Index scores for chronic conditions in the United States (2006). Med Decis Mak [Internet]. 2006 [cited 2023 Apr 18];003:1–5. Available from: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/0272989X06290495?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub0pubmed#supplementary-materials. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Sullivan PW, Slejko JF, Sculpher MJ, Ghushchyan V. Catalogue of EQ-5D scores for the United Kingdom. Med Decis Mak. 2011;31:800–804. doi: 10.1177/0272989X11401031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Saarni SI, Härkänen T, Sintonen H, Suvisaari J, Koskinen S, Aromaa A, et al. The impact of 29 chronic conditions on health-related quality of life: a general population survey in Finland using 15D and EQ-5D. Qual Life Res. 2006;15:1403–1414. doi: 10.1007/s11136-006-0020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kang E-J, Ko S-K. A catalogue of EQ-5D utility weights for chronic diseases among noninstitutionalized community residents in Korea. Value Health. 2009;12:S114–S117. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2009.00642.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Van Wilder L, Rammant E, Clays E, Devleesschauwer B, Pauwels N, De Smedt D. A comprehensive catalogue of EQ-5D scores in chronic disease: results of a systematic review. Qual Life Res. 2019;28:3153–3161. doi: 10.1007/s11136-019-02300-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hvidberg MF, Petersen KD, Davidsen M, Witt Udsen F, Frølich A, Ehlers L, et al. Catalog of EQ-5D-3L Health-related quality-of-life scores for 199 chronic conditions and health risks in Denmark. MDM Policy Pract. 2023;8:238146832311590. doi: 10.1177/23814683231159023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hvidberg MF. A framework for identifying disease burden and estimating health-related quality of life and prevalence rates for 199 medically defined conditions [Internet]. 2016. Available from: http://vbn.aau.dk/da/persons/michael-falk-hvidberg(e8cf2d66-764b-44ca-a54b-6b3e25647fc7)/publications.html.
- 34.Hvidberg MF, Johnsen SP, Davidsen M, Ehlers L. A nationwide study of prevalence rates and characteristics of 199 chronic conditions in Denmark. PharmacoEconomics Open. 2020;4:361–380. doi: 10.1007/s41669-019-0167-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hvidberg MF, Frølich A, Lundstrøm SL, Kamstrup-Larsen N. Catalogue of multimorbidity mean based severity and associational prevalence rates between 199+ chronic conditions—a nationwide register-based population study. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0273850. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hvidberg MF, Frølich A, Lundstrøm SL. Catalogue of socioeconomic disparities and characteristics of 199+ chronic conditions—a nationwide register-based population study. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0278380. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hvidberg MF, Frølich A, Ryom P, Lundstrøm SL. [In peer review] Catalogue of eight health risks—stress, loneliness, sleep, obesity/BMI, smoking, physical exercise, alcohol consumption, fruit intake—and related disparities among 199+ chronic conditions. 2023.
- 38.Bergmann MM, Byers T, Freedman DS, Mokdad A. Validity of self-reported diagnoses leading to hospitalization : a comparison of self-reports with hospital records in a prospective study of american adults. Am J Epidemiol [Internet]. 1998;147:969–77. Available from: http://aje.oxfordjournals.org/content/147/10/969.short. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 39.Martin LM, Leff M, Calonge N, Garrett C, Nelson DE. Validation of self-reported chronic conditions and health services in a managed care population. Am J Prev Med. 2000;18:215–218. doi: 10.1016/S0749-3797(99)00158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kriegsman DMW, Perminx BWH, Eijk JM, Boeke AJP, Deeg DJH. Self-reports and general practitioner information on the presence of chronic diseases in community dwelling elderly. J Clin Epidemiol. 1996;49:1407–1417. doi: 10.1016/S0895-4356(96)00274-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Okura Y, Urban LH, Mahoney DW, Jacobsen SJ, Rodeheffer RJ. Agreement between self-report questionnaires and medical record data was substantial for diabetes, hypertension, myocardial infarction and stroke but not for heart failure. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004;57:1096–1103. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Maheswaran H, Petrou S, Rees K, Stranges S. Estimating EQ-5D utility values for major health behavioural risk factors in England. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2013;67:172–180. doi: 10.1136/jech-2012-201019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hernández Alava M, Wailoo AJ, Ara R. Tails from the peak district: adjusted limited dependent variable mixture models of EQ-5D questionnaire health state utility values. Value Health. 2012;15:550–561. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2011.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hernández Alava M, Wailoo A. Fitting adjusted limited dependent variable mixture models to EQ-5D. Stata J [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2015 Oct 28];15:737–50. Available from: http://www.stata-journal.com/article.html?article=st0401.
- 45.Hernandez Alava M, Wailoo A, Wolfe F, Michaud K. A comparison of direct and indirect methods for the estimation of health utilities from clinical outcomes. Med Decis Mak [Internet]. 2014;34:919–30. Available from: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/74543/. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Basu A, Manca A. Regression estimators for generic health-related quality of life and quality-adjusted life years. Med Decis Mak [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2013 Aug 21];32:56–69. Available from: http://mdm.sagepub.com/content/32/1/56.abstract. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 47.Wailoo A, Hernández M, Philips C, Brophy S, Siebert S. Modeling health state utility values in ankylosing spondylitis: comparisons of direct and indirect methods. Value Health. 2015;18:425–431. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2015.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wailoo A, Hernandez Alava M, Escobar MA. Modelling the relationship between the WOMAC osteoarthritis index and EQ-5D. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014;12:37. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-12-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ara R, Brazier J. Comparing EQ-5D scores for comorbid health conditions estimated using 5 different methods. Med Care. 2012;50:452–459. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e318234a04a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.McIntosh CN. Utility scores for comorbid conditions: methodological issues and advances. Handb Dis Burdens Qual Life Meas New York Springer [Internet]. 2010;2010:360–378. Available from: http://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007%2F978-0-387-78665-0_20.
- 51.Fu AZ, Kattan MW, Fu AZ, Kattan MW. Utilities should not be multiplied: evidence from the preference-based scores in the United States. Med Care [Internet]. 2008;46:984–90. Available from: https://www.jstor.org/stable/pdf/40221766.pdf. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 52.Hu B, Fu AZ. Predicting utility for joint health states: a general framework and a new nonparametric estimator. Med Decis Mak. 2010;30:E29–39. doi: 10.1177/0272989X10374508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Christensen AI, Ekholm O, Glumer C, Andreasen AH, Hvidberg MF, Kristensen PL, The Danish National Health Survey et al. Study design and respondent characteristics. Scand J Public Health. 2010;2012(40):391–397. doi: 10.1177/1403494812451412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hvidberg MF, Johnsen SP, Glümer C, Petersen KD, Olesen A V., Ehlers L. Catalog of 199 register-based definitions of chronic conditions. Scand J Public Health [Internet]. 2016;44:462–79. Available from: http://sjp.sagepub.com/content/early/2016/04/19/1403494816641553.full. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 55.Hvidberg HMF, Johnsen SP, Glumer C, Petersen KD, Olesen A V., Ehlers L. Supplementary material: process, content and considerations of the medical review and ratification regarding register-based definitions of chronic conditions (to “Catalog of 199 register-based definitions of chronic conditions”). Scand J Public Health [Internet]. 2016;44:462–79. Available from: http://sjp.sagepub.com/content/early/2016/04/19/1403494816641553/suppl/DC1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 56.Christensen AI, Ekholm O, Davidsen M, Juel K. Sundhed og sygelighed i DK 2010 & udviklingen siden 1987 [Health and morbidity in Denmark 2010 - and development since 1987] [Internet]. Natl. Inst. Public Heal. Oester Farimagsgade 5 A, 2. 1353 Copenhagen K, Denmark; 2012. Available from: https://www.sdu.dk/sif/-/media/images/sif/sidste_chance/sif/udgivelser/2012/sundhed_og_sygelighed_2010.pdf.
- 57.Pedersen J, Friis K, Asferg AR, Hvidberg MF, Vinding AL, Jensen K. Sundhedsprofil 2010—Trivsel, sundhed og sygdom i Nordjylland [Health Profile 2010—well-being, health and disease in North Jutland] Niels Bohrs vej. 2011;30:9220. doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.35227.95526. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Hayes VS, Cristoffanini SL, Kraemer SR, Johnsen SB, Vinding AL. Sundhedsprofil 2013—trivsel, sundhed og sygdom i Region Nordjylland [Health profile 2013 - well-being, health and disease in North Jutland] [Internet]. Niels Bohrs vej 30, 9220 Aalborg OE, Denmark, Denmark; 2014. Available from: https://rn.dk/sundhedsprofil.
- 59.Petersson F, Baadsgaard M, Thygesen LC. Danish registers on personal labour market affiliation. Scand J Public Health [Internet]. 2011;39:95–8. Available from: http://sjp.sagepub.com/content/39/7_suppl/95.short. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 60.Jensen VM, Rasmussen AW. Danish education registers. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:91–94. doi: 10.1177/1403494810394715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lynge E, Sandegaard JL, Rebolj M. The Danish National Patient Register. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:30–33. doi: 10.1177/1403494811401482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Mors O, Perto GP, Mortensen PB. The Danish Psychiatric Central Research Register. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:54–57. doi: 10.1177/1403494810395825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sahl Andersen J, De Fine Olivarius N, Krasnik A. The Danish National Health Service Register. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:34–37. doi: 10.1177/1403494810394718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wallach Kildemoes H, Toft Sørensen H, Hallas J. The Danish National Prescription Registry. Scand J Public Health. 2011;39:38–41. doi: 10.1177/1403494810394717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Pedersen CB, Gøtzsche H, Møller JO, Mortensen PB. The Danish Civil Registration System. A cohort of eight million persons. Dan Med Bull. 2006;53:441–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Hernández Alava M, Wailoo A, Pudney S, Gray L, Manca A. Mapping clinical outcomes to generic preference-based outcome measures: development and comparison of methods. Health Technol Assess (Rockv). 2020;24:1–68. doi: 10.3310/hta24340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ware JE, Kosinski M, Keller SD. SF-12: How to score the SF-12 Physica and Mental Health Summary Scales [Internet]. 2nd ed. Boston: The Health Insitute, New England Medical Center; 1995. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242636950.
- 68.Wailoo AJ, Hernandez-Alava M, Manca A, Mejia A, Ray J, Crawford B, et al. Mapping to estimate health-state utility from non-preference-based outcome measures: an ISPOR Good Practices for Outcomes Research task force report. Value Health. 2017;20:18–27. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2016.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hvidberg MF, Petersen KD, Davidsen M, Witt Udsen F, Frølich A, Ehlers L, et al. Supplementary materials 1–3 and appendices to: catalog of EQ-5D-3L health-related quality of life scores for 199 chronic conditions and health risks in Denmark. MDM Policy Pract. 2023;8:1–114. doi: 10.1177/23814683231159023#supplementary-materials. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.World Health Organization (WHO). Closing the gap in a generation—health equity through action on the social determinants [Internet]. WHO. The world; 2008. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/43943/9789241563703_eng.pdf;jsessionid=B8A6DC72E16E0A4F1F825160EDC7CCF2?sequence=1.
- 71.Nordahl H. Social inequality in chronic disease outcomes. Dan Med J. 2014;61:B4943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Vos T, Allen C, Arora M, Barber RM, Brown A, Carter A, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1545–1602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.World Health Organization (WHO). The Global Health Observatory. Mean BMI. [Internet]. 2021. p. 9–11. Available from: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/indicators/indicator-details/GHO/mean-bmi-(kg-m-)-(age-standardized-estimate).
- 74.Di Cesare M, Bentham J, Stevens GA, Zhou B, Danaei G, Lu Y, et al. Trends in adult body-mass index in 200 countries from 1975 to 2014: a pooled analysis of 1698 population-based measurement studies with 19.2 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387:1377–1396. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30054-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.OECD. OECD Family Database. CO3 . 1 : Educational attainment by gender [Internet]. 2019. Available from: https://www.oecd.org/els/family/CO3_1_Educational_attainment_by_gender.pdf.
- 76.Karlsson JA, Nilsson JÅ, Neovius M, Kristensen LE, Gülfe A, Saxne T, et al. National EQ-5D tariffs and quality-adjusted life-year estimation: comparison of UK, US and Danish utilities in south Swedish rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann Rheum Dis [Internet]. 2011;70:2163–6. Available from: https://ard.bmj.com/content/annrheumdis/70/12/2163.full.pdf. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 77.Oksuzyan A, Crimmins E, Saito Y, O’Rand A, Vaupel JW, Christensen K. Cross-national comparison of sex differences in health and mortality in Denmark, Japan and the US. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25:471–480. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9460-6.pdf. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Kyed H, Johnsen B, Mejlby M, Vinding L. Hvordan har du det? Sundhedsprofil for Nordjylland 2017 [How are you? Health Profile 2017 in North Jutland] [Internet]. Reg. Nord. 2018. Available from: https://rn.dk/sundhedsprofil.
- 79.Rosendahl Jensen HA, Davidsen M, Ekholm O, Christensen AI. Danskernes Sundhed - Den Nationale Sundhedsprofil 2017 [Danes health - the national health profile 2017] [Internet]. Sundhedsstyrelsen [National Board Heal. Copenhagen K; 2018. Available from: http://www.si-folkesundhed.dk/Udgivelser/Bøgerograpporter/2018/DanskernesSundhed.DenNationaleSundhedsprofil2017.aspx.
- 80.Amalie H, Jensen R, Davidsen M, Møller SR, Ellegaard J, Román I. Danskernes sundhed—Den Nationale Sundhedsprofil 2021 [Danes Health - The National Health Profile 2021] [Internet]. 2021. Available from: https://www.sst.dk/-/media/Udgivelser/2022/Sundhedsprofil/Sundhedsprofilen.ashx.
- 81.US Department of Health and Human Services. Multiple chronic conditions—a strategic framework: optimum health and quality of life for individuals with multiple chronic conditions [Internet]. … DC, Dep. Heal. …. 2010. Available from: http://www.pined.info/pdf/framework/6.pdf.
- 82.Raghupathi W, Raghupathi V. An empirical study of chronic diseases in the United States: a visual analytics approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:10–12. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15030431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Fried LP. America’s health and health care depend on preventing chronic disease [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2020 Aug 7]. p. 1–11. Available from: https://www.huffpost.com/entry/americas-health-and-healthcare-depends-on-preventing_b_58c0649de4b070e55af9eade?guccounter=1.
- 84.Gurenlian JR. The power of prevention: chronic disease the public health challenge of the 21st century [Internet]. Natl. Cent. Chronic Dis. Prev. Heal. Promot. 2009. Available from: www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/pdf/2009-Power-of-Prevention.pdf.
- 85.Tinker A. How to improve patient outcomes for chronic diseases and comorbidities [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2020 Aug 7]. p. 1–5. Available from: http://www.healthcatalyst.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/How-to-Improve-Patient-Outcomes.pdf.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.