Abstract
Background and Objective
Bronchogenic cysts represent a rare form of cystic malformation of the respiratory tract. Primarily located in the mediastinum if occurring early in gestation as opposed to the thoracic cavity if arising later in development. However, they can arise from any site along the foregut. They exhibit a variety of clinical and radiologic presentations, representing a diagnostic challenge, especially in areas with endemic hydatid disease. Endoscopic drainage has emerged as a diagnostic and potentially therapeutic option but has been complicated by reports of infection. Surgical excision remains the standard of care allowing for symptomatic resolution and definitive diagnosis via pathologic examination; minimally invasive approaches such as robotic and thoracoscopic approaches aiding treatment. Following complete resection, prognosis is excellent with essentially no recurrence.
Methods
A review of the available electronic literature was performed from 1975 through 2022, using PubMed and Google Scholar, with an emphasis on more recent series. We included all retrospective series and case reports. A single author identified the studies, and all authors reviewed the selection until there was a consensus on which studies to include.
Key Content and Findings
The literature consisted of relatively small series, mixed between adult and pediatric patients, and the consensus remains that all symptomatic lesions should be excised via minimally invasive approach where feasible.
Conclusions
Surgical excision of symptomatic bronchogenic cysts remains the gold standard, with endoscopic drainage being reserved for diagnosis or as a temporizing measure in clinically unstable patients.
Keywords: Bronchogenic cyst, robotic surgery, mediastinum, mediastinal cyst
Introduction
Bronchogenic cysts, first described in 1859, are rare congenital cystic malformations of the respiratory tract, with an incidence of 1 per 42,000 to 68,000 hospital admissions in one hospital series (1,2). They comprise 10–15% of mediastinal tumors and between 50–60% of mediastinal cystic lesions (3). Bronchogenic cysts arise from the abnormal budding of the tracheobronchial tree or embryonic ventral lung bud, between the 26th–40th day of gestation (4). Their location is usually a function of their embryological development, with central (mediastinal) cysts arising earlier in development (Figures 1,2), and more peripheral development suggesting later formation (Figure 3) (4,5). Parenchymal bronchogenic cysts are reported to comprise 20–30% of all bronchogenic cysts (5,6). Histologically, bronchogenic cysts are typically unilocular and recapitulate elements of normal bronchial structures. The cyst wall is usually lined by respiratory-type epithelium (i.e., ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells with occasional mucin-filled goblet cells) and is comprised of variable amounts of hyaline cartilage, smooth muscle, and/or seromucinous bronchial glands (Figure 4) (7,8). Occasionally, bronchogenic cysts can undergo various histologic changes related to infarction, infection, and/or prior procedure. These changes include acute and chronic inflammation with epithelial denudation, hemorrhage with hemosiderin-laden macrophages, squamous metaplasia, cholesterol clefts, and fibrosis. Bronchogenic cysts typically develop into blind ending fluid-filled structures, though fistulization to adjacent organs and fatal air emboli have been reported (3,9-12). Malignant transformation is very rare but reported in the literature (13,14). The objective of our review is to summarize the historical management of bronchogenic cysts and the impact of evolving technologies including minimally invasive excision and endoscopic drainage. The article is presented in accordance with the Narrative Review reporting checklist (available at https://med.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/med-22-46/rc).
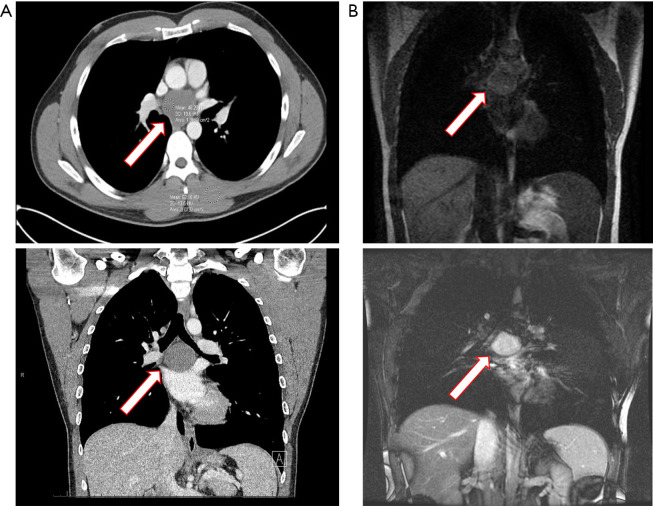
Figure 1.
Posterior mediastinal bronchogenic cyst. Subcarinal bronchogenic cyst detected by CT scan of chest with intravenous contrast to investigate complaints of mild dysphagia and nonspecific back pain in a 35-year-old healthy man. (A) Axial and coronal CT images demonstrates a smooth-bordered 4.5 cm cystic lesion in the subcarinal location. The cyst has high density with HU of 48 and thick proteinaceous fluid was drained at the time of robotic thoracoscopic resection. Red bordered arrow marks the cyst. (B) Coronal CT MRIs image delineates the bronchogenic cyst with the MRI image, T1-weighted image shows liquid nature of the cyst contents, demonstrating dark contents consistent with fluid. T2-weighted confirms these findings as illustrated by cyst bright finding. Complete resection was achieved by right robotic thoracoscopic approach, and the cyst was filled with thick proteinaceous fluid. Red bordered arrow marks the cyst. CT, computed tomography; HU, Houndsfield units; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
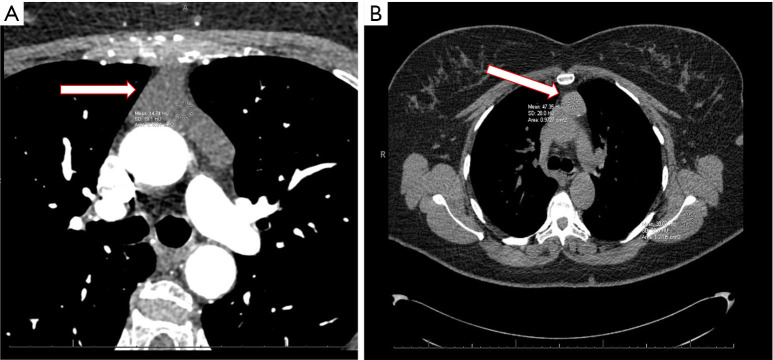
Figure 2.
Anterior mediastinal bronchogenic cyst. (A) Incidental finding on cardiac CT scan for coronary artery calcium scoring in a 75-year-old asymptomatic woman. The cyst has low density with HU of 14 and clear fluid was found in the cyst at the time of robotic thoracoscopic resection. Red bordered arrow marks the cyst. (B) Incidental finding of anterior mediastinal cystic lesions by CT scan of the chest for investigation of non-specific chest discomfort in a 45-year-old woman. The cyst content had a high density with HU of 47 and proteinaceous fluid was drained that the time of robotic thoracoscopic resection. Red bordered arrow marks the cyst. CT, computed tomography; HU, Houndsfield units.
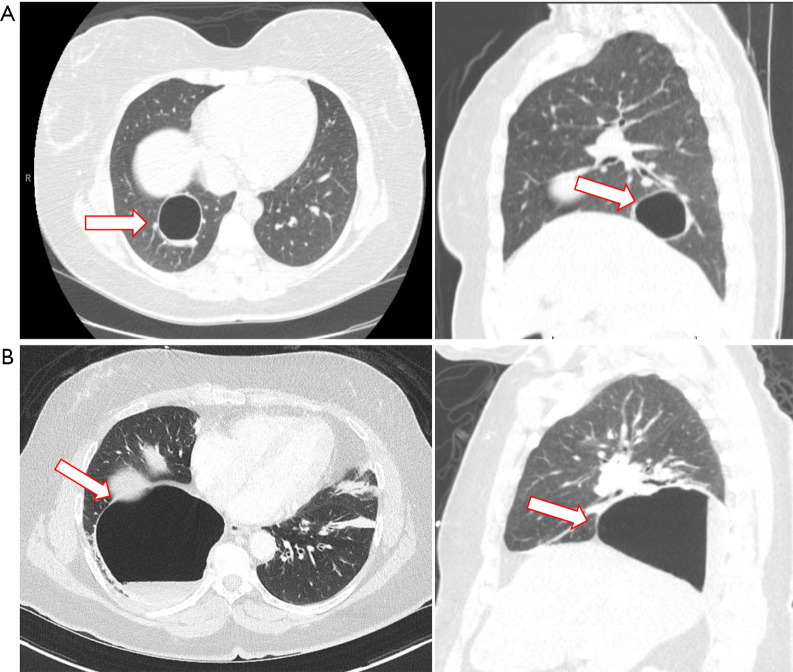
Figure 3.
Intraparenchymal bronchogenic cyst. (A) Axial and sagittal images of a chest CT scan with intravenous contrast of a 34-year-old woman demonstrating a large peripherally located cyst in the right lower lobe, adjacent to segmental pulmonary vessels. She had a history an enlarging cystic lesion once complicated by an infection that was treated with a month-course of oral antibiotic. A complete resection was achieved by right robotic thoracoscopy and enucleation of the lung cyst separating the cyst wall from the underlying vessels and bronchus thus avoiding a pulmonary segmentectomy. Pathologic examination determined this lesion being a benign bronchogenic cyst. Red bordered arrow marks the cyst. (B) Axial and sagittal cuts of a CT scan with intravenous contrast of a 63-year-old woman admitted to the hospital with fever/chills and leukocytosis showing a cystic lesion in the right lower lobe with air-fluid level suggestive of an infected intrapulmonary bronchogenic cyst. This was her first presentation of a bronchogenic cyst. The cyst was completely resected by a right robotic thoracoscopy and wedge resection of the cyst. Final pathology report shows: Respiratory-lined cyst with fibrosis, adjacent fibrinopurulent exudate, granulation tissue and reactive mesothelial hyperplasia. Red bordered arrow marks the cyst. CT, computed tomography.
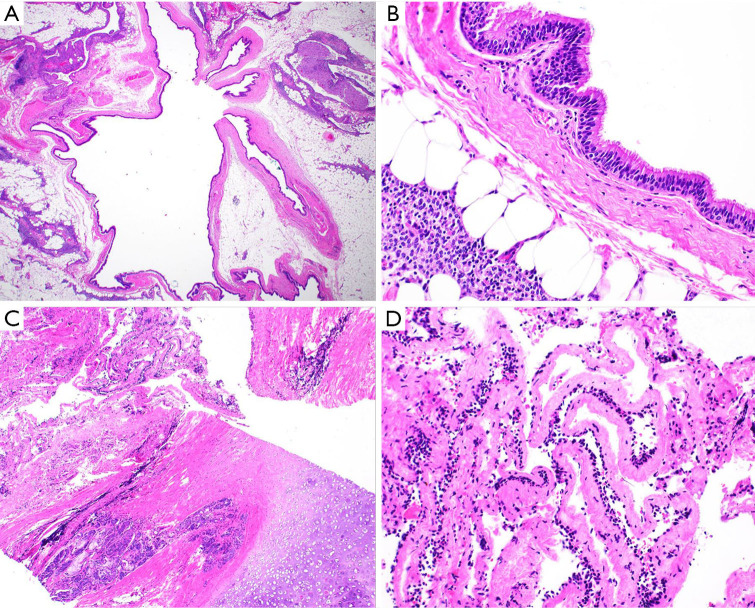
Figure 4.
Histologic findings of bronchogenic cysts corresponding with imaging (hemoxylin & eosin stain). (A) Low power magnification (×12.5) reveals a thin-walled cyst with adjacent adipose and thymic tissue. (B) Higher power magnification (×400) demonstrates that the epithelial lining consists of ciliated pseudostratified columnar respiratory-type epithelium. The cyst wall lacks other features typical of a mature bronchogenic cyst. (C) Medium power magnification (×40) corresponding with images shown in Figure 2A,2B demonstrating an epithelial-lined cyst wall (upper lefthand corner) with adjacent seromucinous glands and mature hyaline cartilage (bottom righthand corner). (D) Higher power magnification (×200) demonstrates that the cyst wall is lined by an attenuated flat-to-cuboidal epithelium.
Methods
We systematically searched the available electronic literature, PubMed and Google Scholar to identify relevant case series in the adult and pediatric peer reviewed literature focusing on diagnosis and management of bronchogenic cysts. We searched the following terms ‘bronchogenic cyst’, ‘bronchogenic parenchymal cysts’, ‘bronchogenic mediastinal cysts’, ‘drainage bronchogenic cyst’, ‘pediatric bronchogenic cysts’ and ‘VATS bronchogenic cyst’ (Table 1).
Table 1. Search strategy summary.
| Items | Specification |
|---|---|
| Date of search | 7/1/2022–8/29/2022 |
| Databases and other sources searched | PubMed, Google Scholar |
| Search terms used | ‘Bronchogenic cyst’, ‘bronchogenic parenchymal cysts’, ‘bronchogenic mediastinal cysts’, ‘drainage bronchogenic cyst’, ‘pediatric bronchogenic cysts’, ‘VATS bronchogenic cyst’ |
| Timeframe | 1975–2022 |
| Inclusion and exclusion criteria | Inclusion: retrospective studies, meta-analyses, case studies |
| Exclusion: thoracic duct cyst, necrotic | |
| Selection process | One author compiled a list of eligible studies followed by review by the entire authorship team to determine suitability |
VATS, video assisted thoracoscopic surgery.
Discussion
Clinical presentations
Bronchogenic cysts are frequently incidental findings on ultrasound or chest radiograph in the neonatal period (4). Symptoms in neonates are usually related to mass effect on the involved structure or infection (15). Major bronchus obstruction is rare but has been reported in the setting of a subcarinal cyst (16). More commonly, the presentation mimics centrilobular emphysema secondary to air trapping of the smaller airways (17). The presentation of bronchogenic cysts in the adult population ranges from an asymptomatic incidental finding of computed tomography (CT) of the chest to a clinical presentation of hemoptysis, pneumothorax, pneumonia (bronchogenic cyst in the lung parenchyma) or chest pain, dysphagia, central venous compression due to mass effecting the mediastinum. Imaging diagnosis is typically made using CT scan, demonstrating a smooth mass with sharp borders (occasionally lobulated), with cystic components (3,18). Masses can occasionally appear solid on CT, and in this setting, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can serve as an adjunctive role to highlight the cystic nature of these lesions. Fluid-filled cystic lesion demonstrates high T2 intensity without enhancement with contrast, T1 weighted imaging is variable depending upon cystic contents and their relative tissue composition (Figure 1) (3). Fiberoptic bronchoscopy with endoscopic bronchial ultrasound (EBUS) has been used to further characterize peri-bronchial cystic masses and can serve a dual therapeutic role by allowing for aspiration in cases of compressive symptoms while providing a pathologic diagnosis, albeit with an increased risk of infection secondary to bacterial contamination of the cyst content by the transbronchial needle (19-22).
Treatment
Surgical excision remains the mainstay of therapy (23-25). Surgery in the neonate can be safely delayed allowing for weight gain. Symptomatic adult patients should undergo resection after immediate stabilization (26). Aspiration is a temporizing measure only for compressive symptoms and should be shortly followed by resection as there is a significant risk of infection following biopsy/aspiration, with very high incidence of short-term recurrence of the lesion, though some series are emerging advocating for drainage as a definitive means of therapy (19-21). Mediastinal bronchogenic cysts resection must ensure complete removal of the epithelium-lined cyst wall via resection or ablation to prevent the accumulation of fluid or recurrence (27,28). In the case of intrapulmonary bronchogenic cysts within lung parenchyma, lobectomy has been the historical gold standard though more recently parenchymal sparing approaches, such as non-anatomic wedge resection or segmentectomy, have been advocated by some surgeons (29). Thoracotomy has traditionally been the standard approach given their location and inflammation of surrounding tissues, with the vast majority of older series being exclusively completed via an open approach (14,26). With the emergence of minimally invasive platforms, resection of bronchogenic cysts either mediastinal or intraparenchymal variants can frequently be performed via thoracoscopic approach (25). Our own institutional experience follows more recent trends of adopting a robotic thoracoscopic platform for resection of these lesions (30,31). There are few long-term sequelae following resection of bronchogenic cysts, although recent literature still reports a combined morbidity and mortality rate of 9.8% in a mixed series comprising bronchogenic and other cystic lesions of the lung (32).
Conclusions
Bronchogenic cysts are a relatively rare congenital malformation. Aspiration and EBUS potentially serve as useful adjuncts for compression relief and potential diagnosis but are plagued by high recurrence and risk of infection. The gold standard remains surgical excision with excellent long-term outcomes free of recurrence and low peri-operative morbidity/mortality. Video-assisted thoracoscopic resection has emerged as a viable approach and with the adoption of the robotic platform for minimally invasive thoracic surgery, thoracoscopic resection has become more feasible. The transition from open to video assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) to robotic-assisted thoracoscopy has followed the authors’ experience and has been associated with few complications. Therefore, we advocate for minimally invasive resection as a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure in a single setting with relatively few complications in our own institutional experience.
Supplementary
The article’s supplementary files as
Acknowledgments
Funding: None.
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Footnotes
Provenance and Peer Review: This article was commissioned by the Guest Editor (Nestor Villamizar) for the series “Mediastinal Cysts” published in Mediastinum. The article has undergone external peer review.
Reporting Checklist: The authors have completed the Narrative Review reporting checklist. Available at https://med.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/med-22-46/rc
Peer Review File: Available at https://med.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/med-22-46/prf
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://med.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/med-22-46/coif). The series “Mediastinal Cysts” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
References
- 1.Meyer H. Ueber angeborene blasige Missbildung der Lungen, nebst einigen Bemerkungen über Cyanose aus Lungenleiden. Archiv f pathol Anat 1859;16:78-95.
- 2.Coselli MP, de Ipolyi P, Bloss RS, et al. Bronchogenic cysts above and below the diaphragm: report of eight cases. Ann Thorac Surg 1987;44:491-4. 10.1016/S0003-4975(10)62106-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McAdams HP, Kirejczyk WM, Rosado-de-Christenson ML, et al. Bronchogenic cyst: imaging features with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiology 2000;217:441-6. 10.1148/radiology.217.2.r00nv19441 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Di Lorenzo M, Collin PP, Vaillancourt R, et al. Bronchogenic cysts. J Pediatr Surg 1989;24:988-91. 10.1016/S0022-3468(89)80199-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.St-Georges R, Deslauriers J, Duranceau A, et al. Clinical spectrum of bronchogenic cysts of the mediastinum and lung in the adult. Ann Thorac Surg 1991;52:6-13. 10.1016/0003-4975(91)91409-O [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Suen HC, Mathisen DJ, Grillo HC, et al. Surgical management and radiological characteristics of bronchogenic cysts. Ann Thorac Surg 1993;55:476-81. 10.1016/0003-4975(93)91022-F [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bailey PV, Tracy T, Jr, Connors RH, et al. Congenital bronchopulmonary malformations. Diagnostic and therapeutic considerations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1990;99:597-603. 10.1016/S0022-5223(19)36931-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Limaïem F, Ayadi-Kaddour A, Djilani H, et al. Pulmonary and mediastinal bronchogenic cysts: a clinicopathologic study of 33 cases. Lung 2008;186:55-61. 10.1007/s00408-007-9056-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sarper A, Ayten A, Golbasi I, et al. Bronchogenic cyst. Tex Heart Inst J 2003;30:105-8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zaugg M, Kaplan V, Widmer U, et al. Fatal air embolism in an airplane passenger with a giant intrapulmonary bronchogenic cyst. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;157:1686-9. 10.1164/ajrccm.157.5.9706040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Closon M, Vivier E, Breynaert C, et al. Air embolism during an aircraft flight in a passenger with a pulmonary cyst: a favorable outcome with hyperbaric therapy. Anesthesiology 2004;101:539-42. 10.1097/00000542-200408000-00037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pages ON, Rubin S, Baehrel B. Intra-esophageal rupture of a bronchogenic cyst. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2005;4:287-8. 10.1510/icvts.2005.108050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Whooley J, White A, Soo A. Bronchogenic cyst: a rare case of malignant transformation. BMJ Case Rep 2022;15:e248916. 10.1136/bcr-2022-248916 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cuypers P, De Leyn P, Cappelle L, et al. Bronchogenic cysts: a review of 20 cases. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1996;10:393-6. 10.1016/S1010-7940(96)80103-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Haller JA, Shermeta DW, Donahoo JS, et al. Life-threatening respiratory distress from mediastinal masses in infants. Ann Thorac Surg 1975;19:365-70. 10.1016/S0003-4975(10)64035-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Funakoshi Y, Takeda S, Kadota Y, et al. Mediastinal bronchogenic cyst with respiratory distress from airway and vascular compression. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;55:53-4. 10.1055/s-2006-924002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lucaya J, Baert AL, Strife JL. Pediatric Chest Imaging: Chest Imaging in Infants and Children. Heidelberg: Springer Berlin; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yoon YC, Lee KS, Kim TS, et al. Intrapulmonary bronchogenic cyst: CT and pathologic findings in five adult patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002;179:167-70. 10.2214/ajr.179.1.1790167 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Bukamur HS, Alkhankan E, Mezughi HM, et al. The role and safety of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis and management of infected bronchogenic mediastinal cysts in adults. Respir Med Case Rep 2018;24:46-9. 10.1016/j.rmcr.2018.04.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Onuki T, Kuramochi M, Inagaki M. Mediastinitis of bronchogenic cyst caused by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration. Respirol Case Rep 2014;2:73-5. 10.1002/rcr2.53 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rajmane R, Adams AM, Rajmane O, et al. Cyst Rupture After Endobronchial Ultrasound-guided Transbronchial Needle Aspiration. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol 2016;23:e20-2. 10.1097/LBR.0000000000000277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Singh A, Singh S, Malpani A, et al. Treatment of bronchogenic cyst surgical versus transbronchial drainage? J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol 2011;18:359-61. 10.1097/LBR.0b013e31823575c5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bolton JW, Shahian DM. Asymptomatic bronchogenic cysts: what is the best management? Ann Thorac Surg 1992;53:1134-7. 10.1016/0003-4975(92)90412-W [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Martinod E, Pons F, Azorin J, et al. Thoracoscopic excision of mediastinal bronchogenic cysts: results in 20 cases. Ann Thorac Surg 2000;69:1525-8. 10.1016/S0003-4975(99)01438-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Weber T, Roth TC, Beshay M, et al. Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery of mediastinal bronchogenic cysts in adults: a single-center experience. Ann Thorac Surg 2004;78:987-91. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.03.092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Patel SR, Meeker DP, Biscotti CV, et al. Presentation and management of bronchogenic cysts in the adult. Chest 1994;106:79-85. 10.1378/chest.106.1.79 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gharagozloo F, Dausmann MJ, McReynolds SD, et al. Recurrent bronchogenic pseudocyst 24 years after incomplete excision. Report of a case. Chest 1995;108:880-3. 10.1378/chest.108.3.880 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hasegawa T, Murayama F, Endo S, et al. Recurrent bronchogenic cyst 15 years after incomplete excision. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 2003;2:685-7. 10.1016/S1569-9293(03)00204-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mestan H, Ceylan KC, Kaya ŞÖ. Surgery outcomes of the bronchogenic cysts. Eur Respir J 2019;54:PA1094. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Caterino U, Amore D, Cicalese M, et al. Anterior bronchogenic mediastinal cyst as priority procedure for robotic thoracic surgery. J Thorac Dis 2017;9:E674-6. 10.21037/jtd.2017.07.39 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xu S, Liu B, Wang X, et al. Robotic thoracic surgery of the anterior superior mediastinal bronchogenic cyst. Ann Transl Med 2015;3:57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Makhija Z, Moir CR, Allen MS, et al. Surgical management of congenital cystic lung malformations in older patients. Ann Thorac Surg 2011;91:1568-73; discussion 1573. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.01.080 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The article’s supplementary files as