Abstract
The modulation of macrophage phenotype from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state holds therapeutic potential in the treatment of inflammatory disease. We have previously shown that arginase-2 (Arg2), a mitochondrial enzyme, is a key regulator of the macrophage anti-inflammatory response. Here, we investigate the therapeutic potential of Arg2 enhancement via target site blockers (TSBs) in human macrophages. TSBs are locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotides that were specifically designed to protect specific microRNA recognition elements (MREs) in human ARG2 3′ UTR mRNA. TSBs targeting miR-155 (TSB-155) and miR-3202 (TSB-3202) MREs increased ARG2 expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages. This resulted in decreased gene expression and cytokine production of TNF-α and CCL2 and, for TSB-3202, in an increase in the anti-inflammatory macrophage marker, CD206. Proteomic analysis demonstrated that a network of pro-inflammatory responsive proteins was modulated by TSBs. In silico bioinformatic analysis predicted that TSB-3202 suppressed upstream pro-inflammatory regulators including STAT-1 while enhancing anti-inflammatory associated proteins. Proteomic data were validated by confirming increased levels of sequestosome-1 and decreased levels of phosphorylated STAT-1 and STAT-1 upon TSB treatment. In conclusion, upregulation of Arg2 by TSBs inhibits pro-inflammatory signaling and is a promising novel therapeutic strategy to modulate inflammatory signaling in human macrophages.
Keywords: MT: Oligonucleotides: Therapies and Applications, macrophages, arginase-2, miR-155, inflammation, microRNA, multiple sclerosis, target site blockers
Graphical abstract
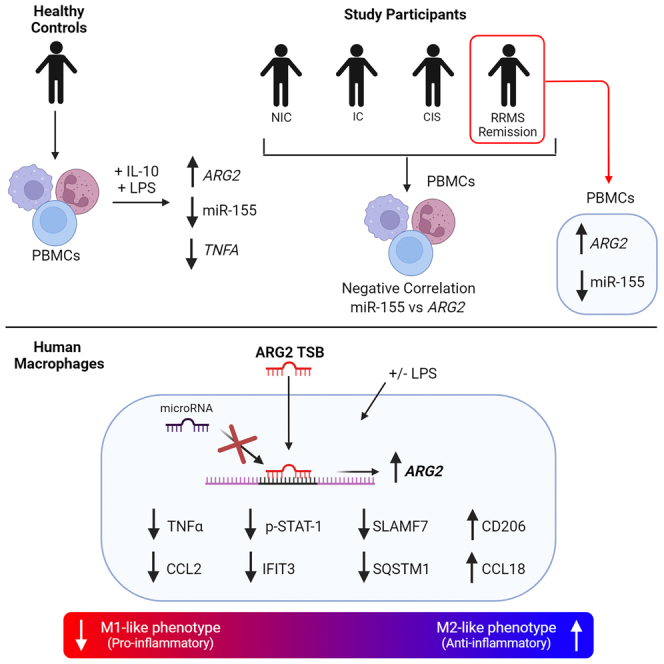
Fitzsimons and colleagues demonstrated that arginase-2 is increased by IL-10 in the presence of a pro-inflammatory stimulus in human primary macrophages. We designed oligonucleotides (target site blockers) that could block microRNA binding to arginase-2 messenger RNA. This led to enhancement of arginase-2 and a decrease in pro-inflammatory signaling.
Introduction
Macrophages are functionally heterogeneous innate immune cells that have plasticity, existing along a spectrum of activation depending on the stimuli within their microenvironment. Macrophages are activated in chronic inflammatory diseases,1,2 including multiple sclerosis,3 and are potential therapeutic targets4,5 as they are also involved in the resolution of inflammation, tissue repair and remodeling.6,7 The “M1”- and “M2”-like macrophage paradigm proposed that M1 and M2 responses can influence inflammation by opposing means.8 However, there are multiple subtypes that exist along a spectrum of macrophage activation with the M1 and M2 macrophages existing on opposing ends.9 Dampening the pro-inflammatory macrophage response is a promising therapeutic strategy to combat chronic inflammatory diseases. Markers of pro-inflammatory macrophages include the cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, CCL2, and IL-6, and the surface markers HLA-DR, CD80, and CD86.10,11,12 Anti-inflammatory macrophage markers include CD206 (MRC1), cluster of differentiation 163 (CD163), CCL18, and IL-10.11,13 In vivo, promoting anti-inflammatory M2-like macrophages represents a possible therapeutic strategy as they have been shown to be associated with regression of atherosclerosis,14,15 improved neurological outcome in an experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model,16 and can contribute to spinal cord repair.17,18
Targeting of microRNAs (miRNAs) is one strategy to modify the macrophage inflammatory phenotype as miRNAs are key regulators of macrophage polarization.19,20 There are multiple mechanisms to inhibit miRNA signaling21 but the most common strategy is the use of antagomirs. These small oligonucleotides are complementary to a specific miRNA, which results in binding and inhibition of the miRNA in question, thus allowing mRNA translation of the respective miRNA target genes. More recently the use of “blockmiRs” or target site blockers (TSBs) has emerged as a miRNA modulation strategy. These are custom-designed oligonucleotide sequences that can mask the miRNA recognition element (MRE) on a specific mRNA target sequence and are advantageous as only one miRNA target is modulated rather than a broader network of miRNA targets. TSB technology has been successfully employed in macrophages,22,23 endothelial cells,24,25 and in epithelial cells.26,27 For example, a TSB was used to block the interaction of miR-10a and ligand-dependent nuclear receptor corepressor (Lcor) mRNA in macrophages and was employed in vivo to demonstrate that miR-10a-Lcor interaction promotes oxidative metabolism and limits lesion formation in a murine model of atherosclerosis.23 Furthermore, specific TSBs have been shown to be efficacious in in vivo models of vascular leakage,25 cystic fibrosis,26 and atherosclerosis.23,24,28
Arginase-2 (Arg2) is a mitochondrial enzyme consisting of 354 amino acids and has ∼61% sequence identity to arginase-1 (Arg1).29 Both enzymes catalyze the conversion of L-arginine into urea and L-ornithine, which is a precursor for the synthesis of polyamines. While Arg1 has long been considered a canonical M2 marker, the role of Arg2 in macrophage polarization is still largely unexplored. We recently demonstrated that Arg2 is crucial for IL-10 metabolic reprogramming of inflammatory macrophages. IL-10-driven Arg2 expression modulated mitochondrial dynamics and enhanced oxidative phosphorylation in inflammatory macrophages. In addition, Arg2−/− bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) were unable to mediate the anti-inflammatory effects of IL-10 on IL-1β secretion.30
We have also shown that, in murine macrophages, Arg2 is a miRNA-155 (miR-155) target.30 Most recently, we have demonstrated that a TSB targeting the interaction of miR-155 and Arg2 is effective in enhancing Arg2 expression and inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion both in vitro, in murine macrophages, and in vivo, in a murine model of LPS-induced acute inflammation.31 However, much of this research was performed using murine models and cell lines, and the implications of modulating Arg2 need to be evaluated in human primary macrophages to be therapeutically viable. In this study, our focus was to employ TSBs to upregulate Arg2 in unstimulated human monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) and to investigate the macrophage response to a pro-inflammatory stimulus by assessing cytokines and markers of inflammation in conjunction with proteomic analysis. In addition, the relationship between miR-155 and Arg2 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) was assessed in the context of the remission phase of multiple sclerosis (MS), a chronic inflammatory condition.
Results
IL-10 increases Arg2 and suppresses TNFA in human macrophages treated with LPS, and miR-155 expression is negatively correlated with Arg2 expression in PBMCs
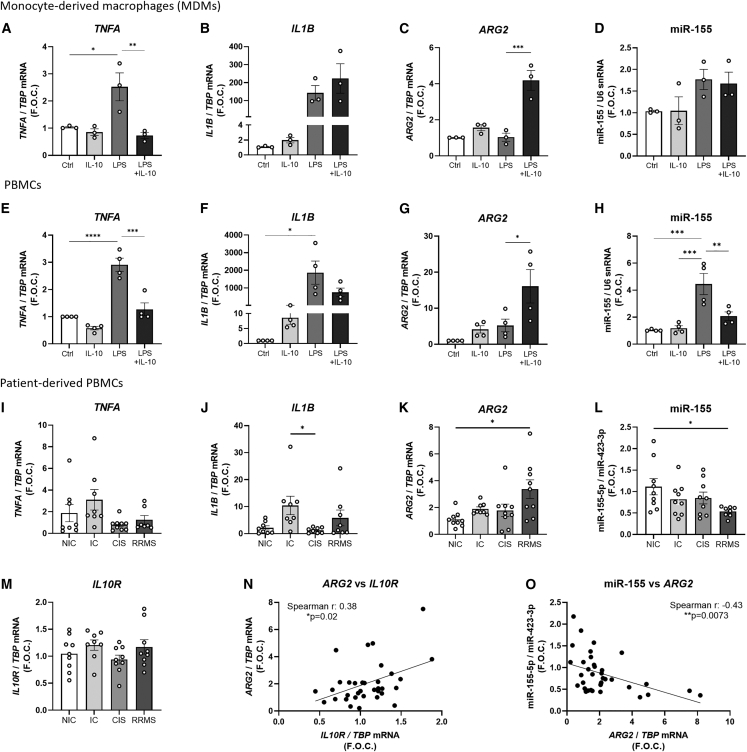
Our previous work has shown that IL-10 in combination with LPS inhibits IL-1β pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion, enhances arginase activity, and upregulates Arg2 in BMDMs.30 To investigate the translation of these results to human primary cells, human MDMs and human PBMCs were treated with this combination. In MDMs TNFA expression in macrophages was upregulated by LPS alone and decreased by combination of IL-10 and LPS (IL-10 + LPS) (LPS 2.52 ± 0.51 vs. IL-10 + LPS 0.73 ± 0.11 fold change, ∗∗p = 0.0069) (Figure 1A). There were no significant differences in Il1B (Figure 1B) or ARG1 (Figure S1A) expression between LPS and IL-10 + LPS. Enzymatic arginase activity was below the level of detection in these cells as determined chromogenically by the production of urea by the Arginase Assay Activity Kit from Sigma-Aldrich (data not shown). However, IL-10 + LPS significantly upregulated ARG2 expression when compared with control and LPS alone (LPS 1.04 ± 0.22 vs. IL-10 + LPS 4.19 ± 0.54 fold change, ∗∗∗p = 0.0004) (Figure 1C). We have previously shown that Arg2 is regulated by the pro-inflammatory miRNA, miR-155,30 which was therefore investigated here in MDMs, PBMCs, and patient-derived samples. In MDMs, despite the trending increase in the miR-155 in LPS stimulated macrophages, IL-10 + LPS did not suppress miR-155 (Figure 1D).
Figure 1.
Gene expression in stimulated human MDMs and PBMCs and in unstimulated patient-derived PBMCs
Expression levels of (A) TNFA, (B) IL1B, (C) ARG2, and (D) miR-155 in stimulated MDMs (n = 3) and of (E) TNFA, (F) IL1B, (G) ARG2, and (H) miR-155 in PBMCs isolated from buffy coat bags donated by healthy donors (n = 4) are shown. TBP was used as the endogenous control while U6 snRNA was used as the control for microRNA analysis and graphed as fold over control (F.O.C.). Expression levels of (I) TNFA, (J) IL1B, (K) ARG2, (L) miR-155, and (M) IL10R in four different participant groups, i.e., non-inflammatory controls (NIC) (n = 9), inflammatory controls (IC) (n = 9), clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) (n = 9), and in patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS) (n = 9) where samples were taken during the remission phase, are shown. TBP was used as the endogenous control while miR-423-3p was used as the endogenous microRNA control. Results were graphed as F.O.C. A Spearman’s correlation analysis was performed to analyze the correlation between the expression of ARG2 and (N) IL10R and (O) miR-155 in all PBMC samples. Graphs (A–H) were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test and graphs (I–N) were analyzed using a Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Correlation analysis was performed using a nonparametric Spearman correlation. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Error bars are representative of the standard error of the mean (SEM).
The effects of this combination on the heterogeneous white blood cell population of PBMCs was also analyzed. Similar to the results observed in the MDMs, LPS treatment significantly increased TNFA expression in PBMCs while the IL-10 + LPS suppressed TNFA compared with LPS treatment alone (LPS 2.91 ± 0.24 vs. IL-10 + LPS 1.27 ± 0.23 fold change, ∗∗∗∗p = 0.0001) (Figure 1E). LPS significantly increased Il1B when compared with the control (LPS 8.57 ± 2.16 fold change, ∗p < 0.012); however, combination treatment did not significantly suppress Il1B when compared with LPS (p = 0.6) (Figure 1F). ARG1 was unchanged across all treatment conditions (Figure S1B); however, ARG2 was significantly increased by IL-10 + LPS stimulation in comparison with LPS alone (LPS 5.22 ± 1.75 vs. IL-10 + LPS 16.1 ± 4.63 fold change, ∗p = 0.04) (Figure 1G). Furthermore, miR-155, was significantly upregulated by LPS treatment (CTRL 1.03 ± 0.03 vs. LPS 4.45 ± 0.77 fold change, ∗∗∗p = 0.0005) and downregulated by IL-10 + LPS (LPS 4.45 ± 0.77 vs. IL-10 + LPS 2.08 ± 0.31 fold change, ∗∗p = 0.009) (Figure 1H). These results highlight and support that IL-10 in the presence of LPS is a potent inhibitor of TNFA and induces ARG2 in both human macrophages and PBMCs.
We investigated the expression of these genes in PBMCs derived from patients with MS. MS is a chronic inflammatory disease that is driven in part by overactivation of pro-inflammatory signaling. Here we analyzed PBMCs donated from patients with relapsing remitting MS (RRMS) who were in the remission phase, while patients with clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) or with a non-neurological inflammatory condition (inflammatory controls [IC]) or with no inflammation (non-inflammatory controls [NIC]) were used as controls (Table 1). The secondary aim of this clinical analysis was to understand the relationship between miR-155 and ARG2 with key pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators across all clinical samples.
Table 1.
Clinical data overview
| Demographics |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | NIC (n = 9) | IC (n = 9) | CIS (n = 9) | RRMS (n = 9) | p value |
| Sex, n (%) | |||||
| Male | 2 (22) | 5 (55) | 2 (22) | 3 (33) | |
| Female | 7 (78) | 4 (45) | 7 (78) | 6 (66) | |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 45.6 ± 14.3 | 43.4 ± 14.9 | 36.1 ± 11.9 | 39.2 ± 7.3 | ns |
| Lesions T2 (mean ± SD) | 3.11 ± 6.8 | 0.63 ± 1.8 | 12.0 ± 6.5 | 23.8 ± 21.1 | NIC vs. RRMS∗∗, IC vs. RRMS∗∗ |
| EDSS (mean ± SD) | ND (n = 2) | 0.7 ± 0.9 (n = 5) | 1.8 ± 0.5 (n = 9) | 2.0 ± 0.6 (n = 9) | IC vs. CIS∗, IC vs. RRMS∗ |
| Gadolinium (Gd) enhancing lesions (n (%)) | |||||
| Gd-positive | 0 (0) | 0 | 5 (55) | 7 (78) | |
| Gd-negative | 9 (100) | 8 (89) | 4 (45) | 2 (8) | |
| Not assessed | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| Presence of IgG oligoclonal bands (OCB) (n (%)) | |||||
| OCB-positive | 4 (45) | 0 | 8 (89) | 9 (89) | |
| OCB-negative | 5 (55) | 9 (100) | 1 (11) | 0 (0) | |
| Not assessed | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Index IgG (mean ± SD) | 0.47 ± 0.19 (n = 7) | 0.67 ± 0.12 (n = 9) | 1.12 ± 0.52 (n = 9) | 1.00 ± 0.64 (n = 7) | NIC vs. CIS∗ |
| Vitamin D (mean ± SD) | 24.1 ± 14.3 (n = 6) | 31.8 ± 13.7 (n = 7) | 20.8 ± 8.4 (n = 8) | 19.0 ± 7.1 (n = 9) | ns |
| Smoking status, n (%) | |||||
| Yes/Ex | 4 (45) | 6 (66) | 6 (66) | 4 (45) | |
| No | 5 (55) | 3 (33) | 3 (33) | 5 (55) | |
Gd is used as a contrast agent to improve visualization of lesions during MRI. The Expanded Disability Status Score (EDSS) is a method used to quantify disability in multiple sclerosis. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. ns, not statistically significant; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
NIC, non-inflammatory control; IC, inflammatory control; CIS, clinically isolated syndrome; RRMS, relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis.
We observed a trending increase in the pro-inflammatory mediators TNFA and IL1B in the IC group but not in the RRMS group, although this was not significant (Figures 1I and 1J). ARG2 expression was significantly increased in the RRMS group by approximately 3-fold (NIC 1.15 ± 0.18 vs. RRMS 3.37 ± 0.69 fold change, ∗p = 0.013) (Figure 1K), while miR-155 was significantly decreased in the RRMS group (NIC 1.11 ± 0.18 vs. RRMS 0.54 ± 0.04 fold change, ∗p = 0.039) (Figure 1L). Although ARG1 (Figure S1C) and Il10R were unchanged across all groups (Figure 1M), there was a positive correlation identified between Il10R and ARG2 across all PBMC clinical samples (Spearman r = 0.39, ∗p = 0.024) (Figure 1N). Furthermore, we previously demonstrated that miR-155 can target Arg2 in vitro,30 hence we investigated the correlation between miR-155 and ARG2 expression in all PBMC clinical samples. There was a significant negative correlation between miR-155 and ARG2 (Spearman r = −0.44, ∗∗p = 0.0073) (Figure 1O). These results highlight that, during the remission phase, ARG2 is increased and miR-155 is decreased in PBMCs from patients with RRMS.
Arg2 TSB-155 and TSB-3202 increase Arg2 and inhibit TNF-α
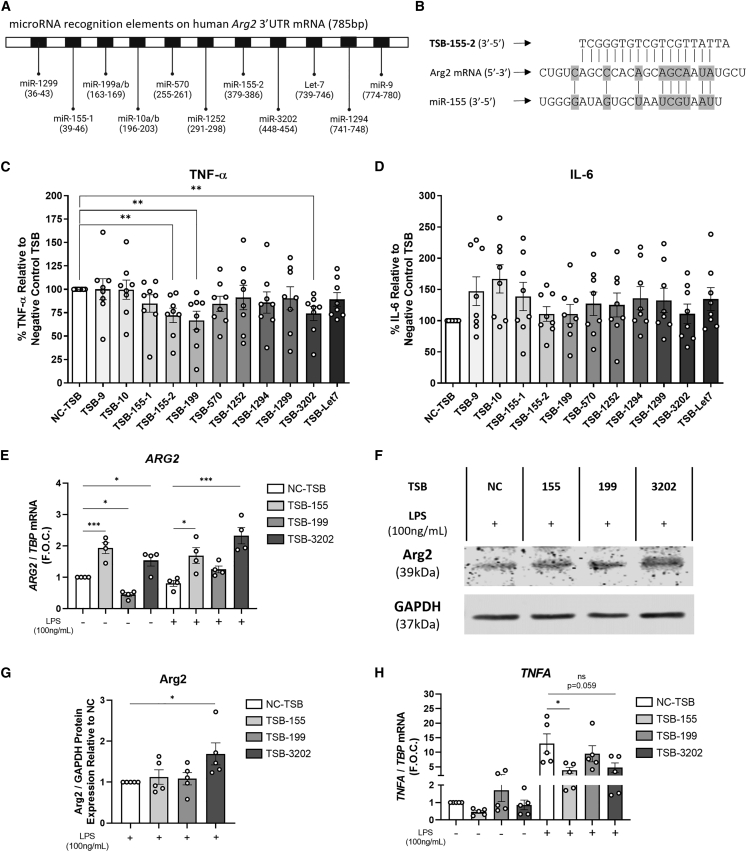
IL-10 is a potent anti-inflammatory mediator that mediates its effects in part via Arg2.30 Here we have demonstrated that IL-10 + LPS suppresses TNFA and enhances ARG2 expression in macrophages and, given the failure of recombinant IL-10 as a viable therapeutic clinical trial,32 we sought to develop methods of increasing the downstream mediator, Arg2, in human macrophages to inhibit inflammation. The human ARG2 3′ UTR messenger RNA was investigated to identify specific sites known as MREs that are complementary to specific miRNAs, and thus may participate in miRNA-mediated ARG2 repression (Figure 2A). Using miRNA predictive algorithm software, TargetScan, miRanda and DIANA-microT, 11 novel TSBs were designed and developed to bind to specific MREs on the ARG2 3′ UTR and block the miRNA interaction. An example of one such oligonucleotide interaction is illustrated in Figure 2B, which illustrates the sequence complementarity of TSB-155-2 and miR-155-5p with ARG2 mRNA. Flow cytometry was used to demonstrate the efficacy of transfection of TSBs into human MDMs using transfection reagent Lipofectamine 3000. On average, 89% of MDMs were positive for the fluorescent (FAM)-labeled TSB (Figure S2).
Figure 2.
Effects of human Arg2 TSBs on Arg2, TNF-α, and IL-6 in human MDMs
(A) Schematic of ARG2 3′ UTR mRNA consisting of 785 base pairs (bp) and the predicted miRNA binding sites to the microRNA recognition elements. (B) Schematic illustrating complimentary base pairing of TSB-155-2 and miR-155 with a region in of the 3′ UTR of ARG2 mRNA. Pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion by MDMs transfected with TSBs (100 nM) and stimulated with LPS was analyzed for (C) TNF-α and (D) IL-6 by ELISA and graphed as a percentage relative to the negative control TSB (NC-TSB) stimulated with LPS (n = 8 donors, using experimental triplicates). (E) ARG2 was analyzed by qRT-PCR using TBP as the endogenous control (n = 4). (F) Arg2 protein was analyzed in TSB and LPS stimulated cells by western blot using glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as the control. (G) Densitometry analysis was performed on the Arg2 western blots and normalized to GAPDH and graphed as relative expression to the NC-TSB with LPS (n = 5). Pro-inflammatory gene expression of (H) TNFA was analyzed by RT-PCR using TBP as the control (n = 5). Error bars are representative of the standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed using multiple independent unpaired t tests for (C and D) and using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test for (E–H). ns, not statistically significant, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
The effects of the 11 Arg2-modulating TSBs and negative control TSB (NC-TSB) on TNF-α and IL-6 cytokine secretion was assessed in human MDMs treated with LPS (100 ng/mL). Cytokine secretion was expressed as a percentage relative to NC-TSB stimulated with LPS due to the variance of TNF-α secretion across independent experiments (see Figure S3 for raw data). TNF-α secretion was significantly decreased by TSB-155-2 (72% ± 8%, ∗∗p = 0.0027), TSB-199 (67% ± 10%, ∗∗p = 0.0047), and TSB-3202 (75% ± 10%, ∗∗p = 0.0037) (Figure 2C). Inhibition of TNF-α secretion upon TSB transfection was dependent on LPS dose and treatment duration; however, overall, we found that TSB-155 and TSB-3202 were effective in suppressing TNF-α secretion across a series of LPS doses (0.1 and 1 ng/mL) and time points (Figure S4). Both TSBs had the most significant effect after 24 h of LPS stimulation (0.1 ng/mL) (NC-TSB 285% ± 104% vs. TSB-155 149% ± 47%, ∗p = 0.017), (NC-TSB 285% ± 104% vs. TSB-3202 147% ± 57%, ∗p = 0.016) (Figure S4). We also confirmed that the miR-155 mimic increases TNF-α secretion from human MDMs to further highlight the interaction between TNF-α and miR-155 (Figure S5). While IL-6 was elevated by several TSBs, it was not significantly induced by TSB-155-2, TSB-199, or TSB-3202 (Figure 2D). For simplicity, given that there were two separate TSBs designed for two distinct miR-155-5p MREs, from here on, TSB-155-2 will be referred to as TSB-155. These lead candidate TSBs (-155, -199, and -3202) were selected to further examine their efficacy on Arg2 by qRT-PCR, luciferase assay, and western blot. ARG2 gene expression was significantly increased by TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1 ± 0 vs. TSB-155 1.93 ± 0.17 fold change, ∗∗∗p = 0.0007) and TSB-3202 (NC-TSB 1 ± 0 vs. TSB-3202 1.53 ± 0.18 fold change, ∗p = 0.03) (Figure 2E). In the presence of LPS, ARG2 was also significantly increased by TSB-155 (NC-TSB + LPS 0.85 ± 0.09 vs. TSB-155 + LPS 1.69 ± 0.25 fold change, ∗p = 0.019) and TSB-3202 (NC-TSB + LPS 0.85 ± 0.09 vs. TSB-3202 + LPS 2.33 ± 0.26 fold change, ∗∗∗p = 0.0004) (Figure 2E). In contrast, ARG2 was downregulated by TSB-199 (NC-TSB 1 ± 0 vs. TSB-199 0.26 ± 0.06 fold change, ∗p = 0.03) and unchanged by TSB-199 in the presence of LPS. We demonstrated by luciferase assay that TSB-199 and TSB-3202 could target the ARG2 3′ UTR as the percentage of relative light units (RLUs) was significantly increased by TSB-199 (123% ± 4.7%, ∗∗p = 0.0073) and TSB-3202 (110% ± 3.3%, ∗p = 0.026) when compared with the NC-TSB (100%) (Figure S6). The representative western blot shows that Arg2 protein expression was increased by TSB-3202 (Figure 2F). Densitometry analysis of all western blot data for Arg2 generated from five independent experiments (Figures 2F and S7) showed that there was a significant increase in Arg2 after treatment with TSB-3202 (TSB-3202 1.69 ± 0.27, ∗p = 0.037) (Figure 2G). To assess the specificity of TSB-155 for Arg2 we investigated the gene expression of known miR-155 targets, inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase D (INPP5D also referred to as SHIP1)33 and suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS1).34 Neither target was increased by TSB-155 in the presence or absence of LPS (Figure S8).
In concordance with the previous TNF-α cytokine analysis, TNFA expression was significantly decreased by TSB-155 (NC-TSB + LPS 13.04 ± 3.3 vs. TSB-155 + LPS 3.81 ± 0.99 fold change, ∗p = 0.035) and there was also a decrease induced by TSB-3202 (NC-TSB + LPS 13.04 ± 3.3 vs. TSB-3202 + LPS 4.71 ± 1.64 fold change, ns, p = 0.059) although this was not statistically significant (Figure 2H). Notably, there were decreases in basal expression of TNFA after TSB-155 and TSB-3202 treatment, although these were not statistically significant (Figure 2H). Collectively, these results suggest that TSB-155 and TSB-3202 are most effective in increasing Arg2 and suppressing TNF-α and they therefore became the primary focus of subsequent experiments.
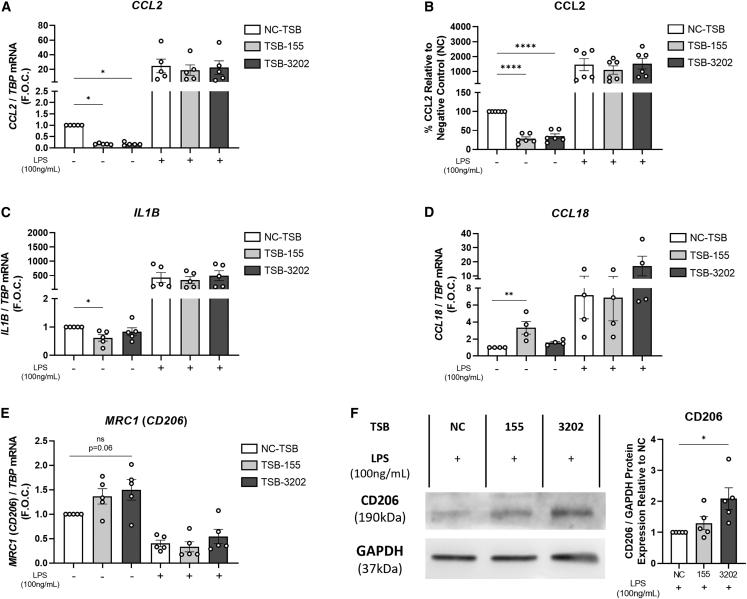
Arg2 TSB-155 and TSB-3202 alter pro- and anti-inflammatory macrophage cytokines and markers
Other pro- and anti-inflammatory macrophage markers were investigated following treatment with TSB-155 and TSB-3202. We noted that basally these unstimulated MDMs secreted an average of 333 pg/mL of the potent chemoattractant, CCL2 (Figure S9A), which is relevant as in unstimulated macrophages, TSB-155 and TSB-3202 significantly suppressed CCL2 expression (NC-TSB 1 ± 0 vs. TSB-155 0.17 ± 0.01 fold change, ∗p = 0.0175, vs. TSB-3202 0.17 ± 0.02, ∗p = 0.0173) (Figure 3A). At the cytokine level, basal CCL2 secretion was significantly decreased by TSB-155 and TSB-3202 treatment (NC-TSB 100% vs. TSB-155 28% ± 5%, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, vs. TSB-3202 35% ± 6%, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001) (Figure 3B). Although this decrease in CCL2 was not observed in the presence of LPS (100 ng/mL), it was significantly decreased after TSB-155 and TSB-3202 treatment in the presence of low dose LPS (0.1 ng/mL) (Figure S9B). In murine macrophages, Arg2 was shown to mediate the anti-inflammatory effects of IL-10 on the pro-inflammatory cytokine, IL-1β.30 Here in human MDMs, IL1B was significantly decreased by TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1 ± 0 vs. TSB-155 0.61 ± 0.11, ∗p = 0.04) (Figure 3C); however, it was unchanged by TSB-3202 and unchanged in the presence of LPS. In addition, IL-1β cytokine secretion was undetectable in the supernatant. To assess whether these TSBs had an effect on anti-inflammatory macrophage markers, the effects on CCL18 and MRC1 (CD206) were assessed.11 CCL18 was significantly increased by TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1 ± 0 vs. TSB-155 3.3 ± 0.75, ∗∗p = 0.0031); however, this effect was not observed in the presence of LPS (Figure 3D). Although there was a trending increase in MRC1 with TSB-3202 treatment this was not statistically significant (p = 0.06) (Figure 3E). However, when analyzed by western blot and densitometry, CD206 was significantly increased by TSB-3202 (NC-TSB 1 ± 0 vs. TSB-3202 1.88 ± 0.35, ∗p = 0.015) (Figure 3F). Flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess the effects of TSB-155 and TSB-3202 on macrophage markers HLA-DR, CD206, and CD16 (Figures S10A–S10C). Although there was a trending increase in unstimulated macrophages treated with TSB-3202, HLA-DR was reduced by approximately ∼15% by TSB-3202 in the presence of LPS (NC-TSB + LPS 115% ± 3.8% median fluorescence intensity [MFI] vs. TSB-3202 + LPS 99% ± 3.4% MFI, ∗∗p = 0.0082) (Figure S10D). TSB-3202 had been previously shown to significantly induce CD206 at the protein level and here there was a small (∼8%) trending increase in the percentage MFI of CD206 by flow cytometry; however, this was not statistically significant (Figure S10E). Interestingly, TSB-3202 significantly upregulated the IL-10-responsive macrophage marker, CD16, in resting cells (NC-TSB 100% ± 0% MFI vs. TSB-3202 108% ± 2%, ∗∗p = 0.0021) (Figure S10F).
Figure 3.
Effects of Arg2 TSBs in human MDMs on pro- and anti-inflammatory markers
(A) CCL2 was analyzed by RT-PCR using TBP as the control and graphed as F.O.C. in MDMs transfected with TSB-NC, TSB-155, and TSB-3202, in the presence or absence of LPS stimulation (n = 5). (B) Supernatants were analyzed by ELISA for CCL2 and graphed as a percentage relative to NC-TSB (n = 6). (C) IL1B pro-inflammatory gene expression was analyzed by RT-PCR using TBP as the control and graphed as F.O.C. (n = 5). The anti-inflammatory associated genes (D) CCL18 and (E) MRC1 (CD206) were analyzed by RT-PCR using TBP as the control and graphed as F.O.C. (4 ≤ n ≤ 5). (F) CD206 was analyzed in TSB-treated cells stimulated with LPS by western blot using GAPDH as the loading control. Densitometry analysis was performed on CD206 western blots and normalized to GAPDH and graphed as relative expression to the NC-TSB with LPS (n = 5). Error bars are representative of the SEM. Statistical analysis was performed on using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test on all graphs. ns, not statistically significant; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
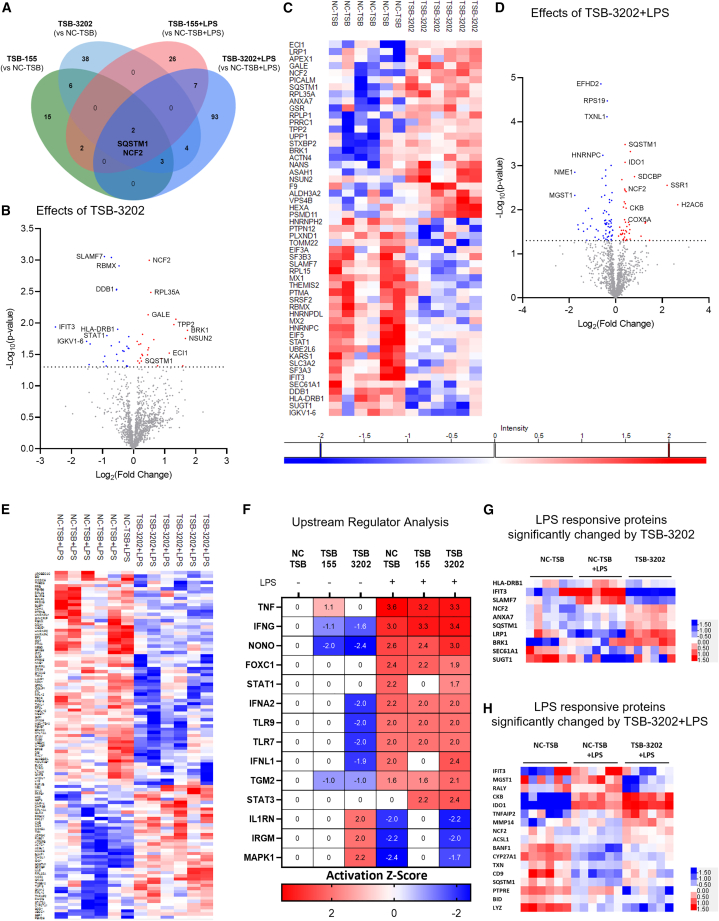
Arg2 TSB-155 and TSB-3202 regulate several inflammatory associated proteins and upstream regulators
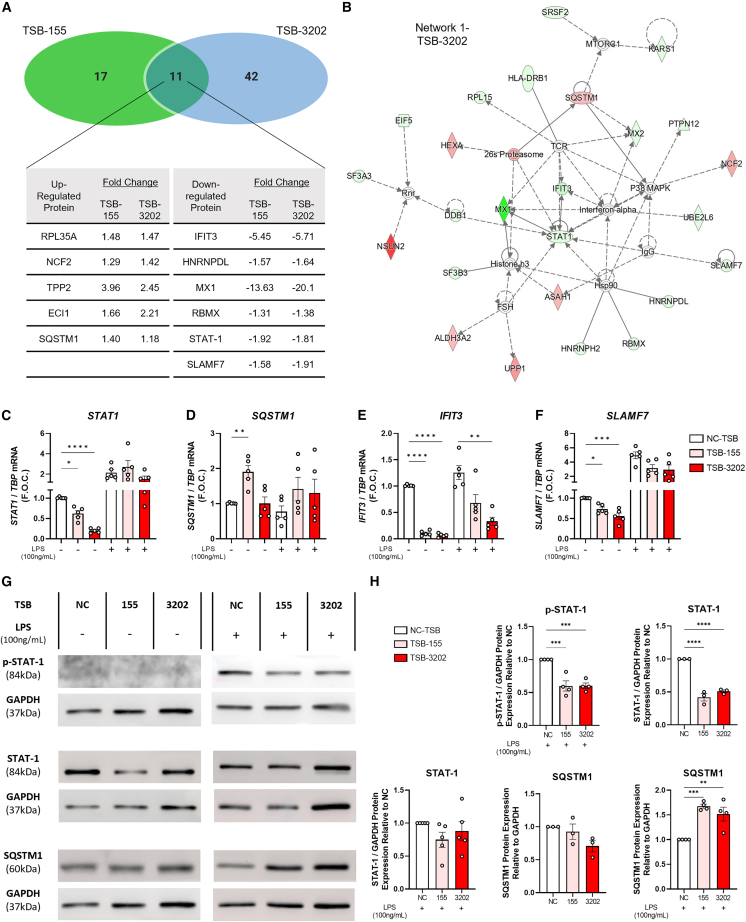
To further elucidate the key signaling proteins regulated by Arg2 induction, mass spectrometry-based proteomics was performed to comprehensively investigate the effects of TSB-155 and TSB-3202 on macrophages stimulated with and without LPS, using NC-TSB with and without LPS as the controls. The significantly changed proteins (p < 0.05) in each group were represented on a Venn diagram with sequestosome 1 (SQSTM1) and neutrophil cytosolic factor 2 (NCF2) significantly changed in all treatment conditions (Figure 4A). In the absence of LPS, TSB-3202 significantly changed (p < 0.05) 53 proteins as shown by volcano plot (Figure 4B) and by heatmap (Figure 4C). TSB-155 significantly changed (p < 0.05) 28 proteins as shown by volcano plot (Figure S11A) and heatmap (Figure S11B). Significantly changed protein lists are outlined in Table S7 (Excel file). In the presence of LPS, TSB-3202 significantly changed (p < 0.05) 109 proteins as shown by volcano plot (Figure 4D) and by heatmap (Figure 4E).
Figure 4.
Mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis of the effects of Arg2 TSBs in human MDMs
(A) A Venn diagram was used to illustrate the number and overlap of significantly differentially expressed proteins in MDMs transfected with TSB-NC, TSB-155, and TSB-3202, in the presence or absence of LPS stimulation (n = 3 independent experiments, performed in duplicate). Group comparisons made were included on the Venn diagram. (B) Volcano plot showing the effects of TSB-3202 compared with NC-TSB based on a Log2 (fold change) and –Log10 (p value). Proteins with a significant p value of <0.05 (–Log10 p > 1.3) are highlighted in red (increased fold change) and blue (decreased fold change). (C) Heatmap representing the effects of TSB-3202 compared with NC-TSB, where LFQ intensities of significantly changed proteins are represented as Z scores. (D) Volcano plot showing the effects of TSB-3202 + LPS compared with NC-TSB + LPS based on a Log2 (fold change) and –Log10 (p value). Proteins with a significant p value of <0.05 (-Log10 p value of >1.3) were highlighted in red and blue. (E) Heatmap representing the effects of TSB-3202 + LPS compared with NC-TSB + LPS (n = 3 independent experiments, performed in duplicate). (F) All treatment conditions were compared with NC-TSB and the lists of significantly changed proteins were analyzed by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software (QIAGEN) to determine the upstream regulators and their activation Z scores (p < 0.01). Upstream regulators with an activation Z score ≥1.6 or ≤ −1.6 modulated by NC-TSB + LPS were graphed alongside STAT-3 to highlight the upstream regulators of LPS. The corresponding activation Z scores of TSB-3202 and TSB-155 with and without LPS were included, the p value of overlap was p < 0.01. Comparison of the NC-TSB with NC-TSB + LPS was used to generate a list of LPS-responsive proteins, which was intersected with the proteins that were significantly changed by (G) TSB-3202 treatment (vs. TSB-NC) and (H) TSB-3202 + LPS treatment (vs. NC-TSB + LPS). Z scores were used to generate heatmaps. Error bars are representative of the standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was performed on proteomic data using a Student’s t test to identify the significantly changed proteins.
All treatment combinations were then compared with the unstimulated NC-TSB (Table S8 (Excel file)) and these significantly changed protein lists were analyzed by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software to identify the predicted upstream regulators with a predicted activation Z score based on fold change and p value. As illustrated by the heatmap, NC-TSB + LPS was predicted to induce several pro-inflammatory associated proteins including TNF, interferon-γ (IFNG), forkhead box C1 (FOXC1), signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT-1), and interferon α2 (IFNA2) while repressing IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL1RN) (activation Z score cutoff applied was ≥1.6 or ≤ −1.6). In the presence of LPS, FOXC1, TNF, and STAT-1 were the three upstream regulators predicted to be decreased by TSB-155 and TSB-3202 treatment (TNF: NC-TSB activation Z score = 3.6 vs. TSB-155 activation Z score = 3.2 vs. TSB-3202 activation Z score = 3.3; STAT-1: NC-TSB activation Z score = 2.2 vs. TSB-155 activation Z score = 0 vs. TSB-3202 activation Z score = 1.7). In addition, anti-inflammatory associated STAT-335,36 was predicted to be upregulated by both TSBs and TSB-155 + LPS did not inhibit the anti-inflammatory-associated protein, IL1RN. In the absence of LPS, IFNG was predicted to be suppressed by TSB-155 (activation Z score = −1.14, p value of overlap = 0.001) and by TSB-3202 (activation Z score = −1.62, p value of overlap = 0.0003) when compared with NC-TSB. In addition, IL1RN, predicted to be suppressed by LPS (activation Z score = −1.98, p value of overlap = 0.0003), was predicted to be activated by TSB-3202 (activation Z score = 2.00, p value of overlap = <0.0001) (Figure 4F). Next the LPS-responsive proteins were identified through analysis of NC-TSB comparison with NC-TSB + LPS (NC-TSB vs. NC-TSB + LPS). This protein list was intersected with proteins significantly changed by TSB-3202 (Figure 4G) and TSB-3203 + LPS (Figure 4H) and visualized using a heatmap with some of the most notable visual changes across conditions being in interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3 (IFIT3), SLAM family member 7 (SLAMF7), and SQSTM1.
Arg2 TSB-155 and TSB-3202 commonly upregulate SQSTM1 and downregulate STAT-1, IFIT3, and SLAMF7
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics identified 11 proteins in common that were basally regulated by both TSB-155 and TSB-3202. Interestingly, the level and directionality of the fold change in these proteins was similar for both TSBs (Figure 5A). For example, STAT-1, a critical pro-inflammatory signaling molecule associated with M1-like macrophages, which was identified as a predicted upstream regulator by IPA, was significantly downregulated by TSB-155 (−1.92 signed fold change, ∗p = 0.011) and TSB-3202 (−1.81 signed fold change, ∗p = 0.015) when compared with the NC-TSB (Figure 5A). The top network identified by in silico analysis of the TSB-3202 proteomic dataset contained STAT-1, IFNA, SLAMF7, SQSTM1, and IFIT3 (Figure 5B). IFIT3, IFNA, SQSTM1, and STAT-1 were also shown to be part of one of the networks collated from the protein dataset significantly regulated by TSB-155 (Figure S12). Next qRT-PCR was performed to investigate whether these significantly changed proteins were altered at a transcriptional level. Basally, these TSBs suppressed STAT1 expression with TSB-3202 causing the greatest inhibitory effect (NC-TSB 1.01 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-3202 0.20 ± 0.02 fold change, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001) (Figure 5C). SQSTM1, an inhibitor of IL-1β secretion in macrophages,37 was significantly increased by TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1.01 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-155 1.91 ± 0.18 fold change, ∗∗p = 0.0015) (Figure 5D). In addition, IFIT3, which is upregulated in M1-like macrophages,38 was significantly downregulated by both TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1.01 ± 0.01 vs. TSB-155 0.11 ± 0.02 fold change, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001) and TSB-3202 (NC-TSB 1.01 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-3202 0.06 ± 0.02 fold change, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001) (Figure 5E). SLAMF7, which is associated with super-activated macrophages in inflammatory disease,39 was also significantly decreased by TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1.00 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-155 0.73 ± 0.05 fold change, ∗p = 0.02), while TSB-3202 was most effective in suppressing SLAMF7 (NC-TSB 1.00 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-3202 0.55 ± 0.07 fold change, ∗∗∗p = 0.0004) (Figure 5F). In the presence of LPS, although there was a trending decrease in STAT1 and SLAMF7, IFIT3 was the only significantly downregulated gene following TSB-3202 treatment (NC-TSB + LPS 1.26 ± 0.13 vs. TSB-3202 + LPS 0.33 ± 0.08 fold change, ∗∗p = 0.002).
Figure 5.
Validation of the effects of Arg2 TSBs on inflammatory signaling targets identified by mass spectrometry analysis
(A) Venn diagram representing the overlap between the effects of TSB-155 and TSB-3202 on protein expression with a table showing the signed fold change of significantly upregulated and downregulated proteins altered by TSB-155 and TSB-3202 as analyzed by mass spectrometry. (B) Interactive IPA network of the effects of TSB-3202. Genes with red (upregulated) nodes and green (downregulated) nodes are the significantly changed proteins in the TSB-3202 dataset, others (clear nodes) are generated/predicted through the network analysis from the IPA QIAGEN Knowledge Base. (C) STAT1, (D) SQSTM1, (E) IFIT3, and (F) SLAMF7 were analyzed by RT-PCR using TBP as the endogenous control and graphed as F.O.C. in MDMs transfected with TSB-NC, TSB-155, and TSB-3202, in the presence or absence of LPS stimulation (n = 5). (G) Phosphorylated STAT-1 (p-STAT-1), STAT-1, and SQSTM1 were analyzed by western blot using GAPDH as the endogenous control in MDMs transfected with TSB-NC, TSB-155, and TSB-3202, in the presence or absence of LPS stimulation (n = 3–5). (H) Densitometry analysis was performed on the protein of interest and normalized to GAPDH and graphed as relative expression to the NC-TSB with and without LPS. Please note that in the absence of LPS, membranes were re-probed for SQSTM1 hence the same GAPDH western blot was used as the control for both p-STAT-1 and SQSTM1. Error bars are representative of the SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
IPA software was used to highlight proteins that were suppressed by TSBs in the STAT-1 signaling pathway and phosphorylation of STAT-1 is an essential component of this pathway, which mediates the effects of pro-inflammatory signaling (Figure S13). Western blotting and densitometry analysis was used to further validate the proteomic analysis and the effects of TSBs on the key signaling mediators, total STAT-1, phosphorylated-STAT-1 (p-STAT-1), and SQSTM1 were analyzed (additional representative blots were included in Figure S14). As can be observed in the representative western blot, p-STAT-1 was induced by LPS (Figure 5G). In the presence of LPS, p-STAT-1 was significantly downregulated by TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1.00 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-155 0.59 ± 0.08 fold change, ∗∗∗∗p = 0.0007) and TSB-3202 (NC-TSB 1.00 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-3202 0.60 ± 0.04 fold change, ∗∗∗∗p = 0.0007) (Figures 5G and 5H). In the absence of LPS, total STAT-1 was significantly downregulated by TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1.00 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-155 0.41 ± 0.05 fold change, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001) and TSB-3202 (NC-TSB 1.00 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-3202 0.51 ± 0.02 fold change, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001); however, total STAT-1 was unchanged in the presence of LPS (Figures 5G and 5H). There was no significant change in SQSTM1 following TSB treatment; however, in the presence of LPS, SQSTM1 was significantly upregulated by both TSB-155 (NC-TSB 1.00 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-155 1.67 ± 0.04 fold change, ∗∗∗p = 0.0006) and TSB-3202 (NC-TSB 1.00 ± 0.00 vs. TSB-3202 1.52 ± 0.14 fold change, ∗∗p = 0.0036) (Figures 5G and 5H).
Discussion
Previously we demonstrated that Arg2 was upregulated by the combination of IL-10 and LPS in THP-1 and murine macrophages.30 Here, we have demonstrated that these findings translate to human PBMCs and primary human macrophages, further highlighting that ARG2 is significantly induced in the presence of this combination. This increase in ARG2 with the IL-10 + LPS combination, coincided with an inhibition of TNF-α secretion and miR-155 expression. Previously, we have shown that Arg2 is a key regulator of the anti-inflammatory response as it plays an essential role in mediating the effects of IL-10 signaling.30 Analysis of all clinical PBMC samples identified a positive correlation between ARG2 and IL10R, highlighting their association as anti-inflammatory signaling mediators. Furthermore, we found that ARG2 is elevated and miR-155 is reduced in PBMCs obtained from patients in the remission stage of MS. The remission stage of MS, characterized as a period of functional recovery from neurological disability (relapse), is associated with remyelination and resolution of inflammation and edema.40 Aberrant immune cell signaling drives periods of relapse and it has been suggested that further investigation of remission may aid in the identification of novel therapeutic targets for MS.41 Previous studies have shown differences in T cells during remission42,43 and analysis of the PBMC transcriptome has also been shown to be capable of distinguishing between different subtypes of MS.44 Furthermore, as Dowling et al.30 demonstrated that Arg2 is a miR-155 target in macrophages, analysis of all clinical samples revealed a negative correlation between miR-155 and ARG2. Collectively these results suggest that, as miR-155 levels increase, ARG2 is suppressed, and that enhancing ARG2, as it is upregulated during remission, may be a strategy to limit pro-inflammatory responses. We propose that Arg2 is a critical regulator of inflammation, which could be induced via using oligonucleotide TSB technology to alter the signaling of TNF-α, CCL2, and other pro-inflammatory mediators in human MDMs.
TNF-α is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that is elevated in the context of chronic diseases such as MS and targeted suppression of TNF-α may be a viable therapeutic strategy. TNF-α is elevated in active lesions of patients with MS at autopsy45,46 and peripheral levels of TNF-α are increased in the blood, mononuclear cells, and T cells from patients with MS.47 Specifically, patients with progressive MS have higher serum TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-10 than controls, with elevations in these cytokines being associated with disease progression.48 In a murine model of progressive EAE, this pro-inflammatory cytokine has been shown to be sustained in infiltrating macrophages.49
Previous studies have shown that loss of Arg2 enhances the pro-inflammatory response. For example, deletion of Arg2 in mice led to induction of pro-inflammatory responses and M1 macrophage activation in the presence of Helicobacter pylori.50 In addition, Arg2 deficiency in a murine model of neuroinflammation caused more severe pain behaviors following nerve injury, increased M1 pro-inflammatory cytokines, and decreased M2 anti-inflammatory cytokines.51 Our previous work in vivo and in murine macrophages demonstrated that a TSB designed to inhibit miR-155 interaction with Arg2 was an effective strategy to enhance Arg2, which led to the suppression of pro-inflammatory signaling.31 Arg2 activation by liver X receptor agonists in macrophages inhibited nitrite production in response to inflammatory stimuli.52 In addition, TSBs designed to target miR-155 interaction with RhoA and human antigen receptor were successfully used in the context of cancer.53,54 Here, we identified 11 MREs in the 3′ UTR of human ARG2 mRNA and designed TSBs to inhibit potential miRNA binding. Specifically, TSB-155 and TSB-3202, were the most effective in enhancing ARG2 expression and suppressing TNF-α secretion. TNFA suppression by TSB-155 and TSB-3202 was confirmed at the gene level in LPS-activated macrophages. Furthermore, this inhibition of TNF-α cytokine secretion was sustained using lower doses of LPS with a significant reduction in TNF-α after 24 h.
Inhibition of TNF-α has been an effective therapeutic strategy for the treatment of chronic inflammatory disease. Monoclonal antibodies designed to inhibit TNF-α signaling have been approved as treatments for diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and psoriasis.55 Furthermore, anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody treatment in a murine model of EAE reduced clinical disability, demyelination, and mortality rate and restored blood-brain barrier integrity.49 However, a clinical trial investigating TNF-α inhibition in MS patients was terminated due to exacerbation of disease and increased severity of neurological deficits.56 It must be noted that TNF-α and TNFR1 are critical to remyelination and oligodendrocyte regeneration, respectively.57 Thus, non-selective TNF-α inhibition is detrimental in MS; however, evidence suggests that selective targeting and modulation of TNF-α in specific cell types may be a more promising strategy. For example, myeloid cells and T cells are critical sources of TNF-α in models of EAE, and knockout of TNF-α in myeloid and T cells has been shown to reduce EAE and facilitate Th1 cell development.58
Following our analysis of several pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators, we found that the expression and secretion of CCL2, a potent chemoattractant, was significantly decreased by TSB-155 and TSB-3202 in the absence and presence of low-dose LPS. CCL2 is secreted by multiple cells including monocytes and macrophages and functions to recruit myeloid and lymphoid cells, and its role in the promotion of the pro-inflammatory response has been extensively reviewed.59 The effects of TSB on CCL2 may be a downstream effect of TNF-α suppression as CCL2 is regulated by TNF-α60,61 and IFN-γ.62 In contrast, treatment of human PBMC-derived monocytes with CCL2 did not alter TNF-α but did induce pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion of IL-1 and IL-6.63 There is some evidence to suggest that CCL2 modulates macrophage phenotype toward an M1 or M2; however, this is often dependent on the cells and model used.59 Pharmacological inhibition of the receptor for CCL2, CCR2, has been shown to be effective in in vivo models of chronic inflammatory pain.64 In the context of MS, CCR2−/− mice have impaired CNS macrophage infiltration and decreased clinical score in an EAE model.65,66 Targeting of CCL2/CCR2 signaling has been shown to be effective in reducing inflammatory monocyte/macrophage/myeloid infiltration in conjunction with suppressing hepatocellular carcinoma development in vivo.67,68
In acute MS brain lesions, CCL2 was expressed by hyperactive astrocytes and macrophages.69,70 As extensively reviewed by Mahad et al., CSF levels of CCL2 have been demonstrated to be reduced while there is no consensus on the directionality of CCL2 levels in MS serum.71 Interestingly, both CCL2 and TNF-α secretion was increased in PBMCs from stable untreated MS patients when compared with stable IFN-β-treated MS patients.72 Our work indicates that TSB-155 and TSB-3202 could be a viable option for dampening both TNF-α and CCL2 simultaneously in inflammatory macrophages.
Furthermore, we aimed to analyze specific pro- and anti-inflammatory markers to assess the macrophage phenotype. Notably, in resting macrophages TSB-155 significantly decreased the pro-inflammatory gene, IL1B, and increased CCL18, a chemokine that primes monocytes toward an M2-like anti-inflammatory macrophage with CD206 expression and a high capacity for phagocytosis.73 In addition, CCL18 is elevated in IL-4- or IL-13-activated M2 macrophages.11,74 However, only TSB-3202 increased MRC1/CD206 gene and protein expression. Collectively these results highlight that TSB-3202 induces a reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine production (TNF-α and CCL2) and M1 marker expression coinciding with an increase in the anti-inflammatory markers, CD206, suggesting a priming effect toward an M2-like macrophage.
Furthermore, we sought to comprehensively understand the key signaling proteins modulated by TSB-155 and TSB-3202 through unbiased mass spectrometry-based proteomics. This analysis provided an abundance of insights into the downstream effects of Arg2 enhancement. Most interestingly, there were several key inflammatory mediators that were downregulated by both TSBs, these included STAT-1, which has been shown to be a regulator of pro-inflammatory macrophage signaling.75 STAT-1 signaling involves phosphorylation of STAT-1, dimerization, nuclear translocation, and DNA binding to gamma-activated sequence elements upstream of IFN-γ-induced genes76 and its role in macrophages has been extensively reviewed.77 STAT-1 activity is essential for M1 macrophage polarization and LPS-stimulated macrophages from Stat1−/− mice have impaired induction of interferon-γ-induced protein 10 (IP-10), interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1), and iNOS.78 Here, we showed that TSB-155 and TSB-3202 caused a significant decrease in STAT1 gene expression in concert with a significant decrease in protein levels of total STAT-1 in resting macrophages and phosphorylated STAT-1 in LPS-stimulated macrophages. The effects of TSBs on STAT-1 suppression may be a primary mechanism by which these TSBs decrease TNF-α as previously STAT-1 deficiency resulted in suppression of TNF-α and IL-12 secretion following macrophage TLR stimulation.75 STAT-1 is activated in response to IFN-α and IFN-γ receptor activation and LPS and is a crucial mediator downstream of IFN-γ signaling.79 IPA also revealed that TSB-155 and TSB-3202 are predicted to downregulate IFN signaling in the absence of LPS.
To further validate the proteomic and pathway analysis we confirmed at the transcript level that IFN-γ-associated genes, IFIT3 and SLAMF7, were downregulated in the presence of both TSBs. IFIT3 has been recently proposed as a useful marker for M1 macrophage polarization as proteomic analysis showed it was strongly upregulated in human primary M1 pro-inflammatory macrophages38 and it is known to be activated in response to viral infection.80 Notably exogenous expression of IFIT3 causes the induction of IRF3-responsive genes (IFNB, ISG56, and RANTES) and NF-κB-including responsive genes (IL8, NFKBIA, and TNFA), while IFIT3 knockdown inhibited these genes.81 In addition, the predicted upregulation of the anti-inflammatory mediators, IL1RN (without LPS) and STAT3 (with LPS) by TSB-3202 suggests that, in conjunction with a reduction in the pro-inflammatory response, the anti-inflammatory response may be activated in these macrophages.
The suppression of SLAMF7 and TNF-α by the TSBs may be linked, as SLAMF7 was shown to increase macrophage activation via a TNF-α autocrine loop.39 SLAMF7 is a receptor on macrophages previously shown to be upregulated by IFN-γ.39 Furthermore it was found that SLAMF7 was increased on macrophages from patients with rheumatoid arthritis39 and is a viable therapeutic target as, elotuzumab, an anti-SLAMF7 antibody, is clinically used for the treatment of multiple myeloma.82 Activation of SLAMF7 in macrophages caused an induction of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-12B) and chemokines (CCL3, CCL4, CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL8).39 Furthermore, SLAMF7 is an interesting target for chronic inflammatory diseases as it was increased in unstable atherosclerotic plaques and enriched in CD68+ macrophages. Depletion of SLAMF7 in plaque-derived CD14+ cells decreased TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-12.83 Collectively, this literature and the data presented here suggest that suppression of SLAMF7 via Arg2 TSBs may be a potential strategy in treating chronic inflammatory disease.
SQSTM1, also known as p62, a ubiquitin binding protein involved in autophagy, was upregulated by both TSBs in resting and LPS-stimulated macrophages. In resting macrophages, SQSTM1 was significantly increased by TSB-155, and in LPS-stimulated macrophages we observed that SQSTM1 was increased at the protein level. Critically, LPS induced SQSTM1 expression via NF-κB in macrophages and ablation of SQSTM1 in macrophages prevented mitophagy and enhanced NLRP3-inflammasome activation.37 Also, SQSTM1/p62 indirectly contributes to the activity of nuclear factor erythroid 2-like 2, which upregulates several antioxidant and anti-inflammatory proteins.84 Interestingly, ApoE−/− Arg2+/+ mice had increased levels of aortic SQSTM1 in comparison with ApoE−/−Arg2−/− mice, highlighting the link between SQSTM1 and Arg2.85 The suppression of CCL2 by TSBs may be driven in part by the induction of SQSTM1 as previous studies report that silencing of SQSTM1 enhances CCL2 in retinal epithelial cells86 and that rapamycin, which induces SQSTM1, downregulates CCL2 expression in THP-1 macrophages.87 Peritoneal macrophages from SQSTM1/p62 knockout mice had increased levels of IL-1β and these mice had increased atherosclerotic plaque burden,88 suggesting that sequestering of cytotoxic ubiquitinated proteins is crucial in the prevention of atherogenesis. Further investigation is required to fully elucidate the relationship between Arg2 and SQSTM1. There were several limitations in this paper, which include the low numbers of clinical PBMC samples for each group and an absence of testing these TSBs in patient-derived samples. Future work will therefore explore the effects of these TSBs in macrophages derived from patients with MS and other inflammatory disorders.
In conclusion, we have shown that miR-155 correlates with Arg2 expression in human patient PBMCs and that IL-10 enhances Arg2 in the presence of a pro-inflammatory stimulus. In addition, Arg2 can be enhanced by specifically designed TSBs that suppressed TNF-α and CCL2 expression and secretion while downregulating markers such as STAT-1 and IFIT3, which are associated with the pro-inflammatory M1-macrophage phenotype. The suppression of the pro-inflammatory macrophage phenotype is likely mediated in part via a STAT-1- and/or SLAMF7-dependent mechanism as both molecules were confirmed to be inhibited following TSB treatment. Therefore, enhancing Arg2 through use of TSBs is a promising therapeutic strategy for diseases driven by chronic macrophage inflammation.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Human buffy coat blood bags were obtained from the Irish Blood Transfusion Service (IBTS). Written approval was obtained from the IBTS, which provides de-identified blood components and by-products of the donation process, pro bono, to academic researchers.
In brief, blood was diluted in a ratio of 1:2 in PBS (Gibco, cat. no. 10010015) and then layered onto Histopaque-1077 (Sigma, cat. no. 10771) in a ratio of 1:1. The layered solution was centrifuged in a Sorvall ST40R centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at 400 × g for 30 min at room temperature (RT). The PBMC layer was removed and washed three times in PBS. PBMCs were resuspended in cell separation buffer (0.5% w/v BSA [Sigma, cat. no. A2153], 0.4% EDTA [(pH 8.0) 0.5 M; Thermo Fisher, cat. no. 1021]) in PBS. PBMCs were incubated with human CD14 MicroBeads (Miltenyi Biotech, cat. no. 130-050-201) at 4°C for 15 min. Solution was passed through an LS Columns (Miltenyi Biotech, cat. no. 130042401) attached to the magnetic QuadroMACS Separator (Miltenyi Biotech, cat. no. 130090976). Columns were washed using cell separation buffer and CD14-positive monocytes were isolated. Monocytes were resuspended in RPMI (RPMI 1640 Medium with GlutaMAX Supplement [Sigma, cat. no. 61870010] containing 10% human serum from human male AB plasma [Sigma, cat. no. H4522] and 1% penicillin/streptomycin [100 U/mL; Sigma, cat. P4333]), seeded at 1.5 × 105 cells per well in 48-well Falcon Polystrene Microplates (Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 10199391) and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO2. After 4 days in culture the medium was replaced with RPMI containing 10% human serum and 1% penicillin/streptomycin and cells were allowed to continue to differentiate into macrophages for a further 6 days. On day 10, MDMs were ready for cell treatments. PBMCs were seeded in serum-free RPMI (1% penicillin/streptomycin [100 U/mL]) at 1 × 106 cells per well in a 12-well plate. Macrophages were imaged and were positive for the pan-macrophage marker, CD68, and had low expression of the monocyte marker, CD14, when compared with monocytes (Figure S15). Furthermore, flow cytometry analysis of MDMs showed that 97% were positive for CD68 (Figure S16).
HEK293T cells were maintained in complete DMEM (10% fetal bovine serum [Sigma, cat. F9665] and 1% penicillin/streptomycin [100 U/mL]) and passaged once a week. Cells were seeded at 2 × 104 cells per well in a 96-well plate.
Cell treatments
IL-10 and LPS stimulation
PBMCs and MDMs were treated with IL-10 (100 ng/mL) (R&D Systems, cat. no. 217-IL), ultrapure LPS, E. coli 0111:B4 (100 ng/mL) (InvivoGen, cat. no. Tlrl-3pelps) and IL-10 + LPS for 24 h in complete RPMI. Supernatants were stored at −20°C and RNA was harvested and isolated using the TRI Reagent (Sigma, cat. no. T9424) RNA isolation method.
TSB transfection
In vivo ready miRCURY LNA Power Target Site Blocker arginase-2 TSBs (QIAGEN, cat. no. 339199) were synthesized with custom design to facilitate binding to the 3′ UTR of arginase-2, which is complementary to the binding site of miR-9, miR-10, miR-155-1 (canonical), miR-155-2 (non-canonical), miR-199, miR-570, miR-1252, miR-1294, miR-1299, miR-3202, and Let7 (Table S1). The individual TSBs (TSB-9, TSB-10, TSB-155-1, TSB-155-2, TSB-199, TSB-570, TSB-1252, TSB-1294, TSB-1299, TSB-3202, and TSB-Let7) and their respective oligonucleotide sequences are listed in Table S2. Negative Control A (QIAGEN, cat. no. 339199), a scrambled sequence (Table S2), was used as the NC-TSB. To assess transfection efficacy, Negative Control A was conjugated to FAM (QIAGEN, cat. no. YT0070993). Macrophages were transfected with TSBs (100 nM) using 0.5% Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen L3000008) for 5 h in serum-free RPMI. Cells were rested overnight in complete RPMI and then stimulated with and without ultrapure LPS, E. coli 0111:B4 (0.1, 1, 10, and 100 ng/mL) (InvivoGen, cat. no. Tlrl-3pelps) for 24 h. Supernatants were stored at −20°C and cells were harvested using TRI Reagent for RNA extraction, low-stringency lysis buffer for protein extraction, urea (8 M) for mass spectrometry, and FACS buffer (0.02% bovine serum albumin [BSA] in PBS without Ca2+ and Mg2+) for flow cytometry analysis.
For macrophage polarization experiments, MDMs were stimulated for 48 h with cytokines in complete RPMI. Macrophages were treated with LPS (100 ng/mL) and IFN-γ (20 ng/mL) (R&D Systems, cat. no. 285-IF) to induce a pro-inflammatory, M1-like phenotype. Macrophages were pre-stimulated with IL-10 (100 ng/mL) for 5 min prior to the addition of LPS and IFN-γ to assess the impact of an anti-inflammatory stimulus in the presence of LPS and IFN-γ. Macrophages were treated with IL-4 (20 ng/mL) (R&D Systems, cat. no. 204-IL) to induce an anti-inflammatory, M2-like phenotype.
HEK293T cells were transfected for 5 h in serum-free high-glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Sigma, cat. no. D5796) with human Arg2 plasmid (25 ng) and TSB-155, TSB-199, and TSB-3202 (100 nM) using 0.3% TransIT-X2 Dynamic Delivery System Reagent (Mirus, cat. no. MIR6003). Cells were rested in DMEM with 10% fetal bovine serum (Sigma, cat. no. F9665) overnight and the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega, cat. no. E1910) was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
miR mimic transfection
miR-155 mimic (40 nM) (Ambion, cat. no. 4464066, ID: MC28440) and miR-3202 mimic (40 nM) (Ambion, cat. no. 4464066, ID: MC16446) were transfected into human MDMs using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen L3000008) for 5 h using the negative control mimic (40 nM) (Ambion, cat. no. 4464058) as the control. The medium was changed, and cells were rested overnight. Cells were stimulated with 1 ng/mL of LPS and 10 ng/mL of LPS for 24 h.
Patient samples
Participants were recruited into this study involving the collaboration of Dr. Josep Trueta University Hospital and the Girona Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBGI), Salt, Girona, Spain. This study received ethical approval from The Ethics Committee and the Committee of Clinical Investigation at Dr. Josep Trueta University Hospital (ethical approval study identification: BioEM: 157/13 and miEM: 003/18). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Participants were grouped into four groups based on their diagnosis: NIC, IC, CIS, or RRMS. Blood samples were obtained from patients with RRMS during a remission phase and these patients were not on any disease-modifying therapies at the time of sample collection. Participant demographic information and relevant clinical data are outlined in Table 1. Blood was collected in BD Vacutainer CPT Mononuclear Cell Preparation tubes containing sodium citrate (Sanbio, cat. no. 362782) and centrifuged at 1,800 × g for 25 min. Cells and plasma were collected and centrifuged at 800 × g for 15 min. Plasma was discarded, and isolated PBMCs were washed in physiologically enriched sera, centrifuged again at 950 × g for 10 min, and then 5 × 106 PBMCs were frozen in RPMI medium supplemented with 3% DMSO and 3% fetal bovine serum. Following collection of all samples, downstream analysis was performed en masse on participant PBMC samples from all groups. RNA was isolated via the TRI Reagent method and 200 ng of RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA.
Protein analysis-western blotting
Protein was quantified using a bicinchoninic acid assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis using a 10% polyacrylamide resolving gel. Using a transfer cassette, gels were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (GE Healthcare Amersham Protran, Life Sciences, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Ireland). Skim milk (5%) (Sigma, cat. no. 70166) was used to block the membranes, which were then incubated with diluted primary antibody overnight at 4°C. The details of the primary and secondary antibodies used are outlined in Table S3. Secondary antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology) were applied for 1 h at RT. Membranes were developed using Supersignal West Pico PLUS Chemiluminescent Substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 34580) on a Vilber Fusion Fx Imaging System (Vilber). Membranes incubated with fluorescent antibodies were analyzed using the Odyessy CLx imaging system. Either β-actin or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) were used as loading/housekeeping controls for densitometry analysis, which was performed using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health). All targets of interest were normalized to the control treatment or control group and then normalized to the loading/housekeeping control and represented as protein expression relative to control.
Gene expression analysis-real-time qPCR
For mRNA analysis, RNA was reverse transcribed to cDNA using the Applied Biosystems High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 4368814). Real-time PCR was performed using the Applied Biosystems PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. A25778) and the sequences of SYBR Primers listed in Table S4. TATA-box-binding protein (TBP) was used as the endogenous control. Gene expression was analyzed using a 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems).
For miRNA analysis, two methods were performed. For experiments that involved the analysis of <2 miRNAs, 15 ng of total RNA was reverse transcribed to miRNA cDNA specific for the TaqMan hydrolysis probes, miR-155-5p (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 4427975, assay ID: 002623) and U6 snRNA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 4427975, assay ID: 001973) using the Applied Biosystems TaqMan miRNA reverse transcription kit (Thermo Fisher, cat. no. 4366596). For experiments that involved the analysis of >2 miRNAs, 10 ng of RNA was reverse transcribed using the Applied Biosystems TaqMan Advanced miRNA cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. A28007). miRNA analysis was performed using TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 4444557) and the following advanced miRNA Assays (Applied Biosystems): hsa-miR-155-5p (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. A25576, 483064_miR), hsa-miR-199a-3p (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. A25576, 477961_miR), hsa-miR-3202 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. A25576, 479675_mir), and hsa-miR-423-3p (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 4427975, 002626) was used as the endogenous control (Table S5). miRNA expression was analyzed using a 7500 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). mRNA and miRNA RT-PCR results were analyzed using the delta delta Ct (2–ΔΔCt) method to calculate the relative fold gene expression of samples in comparison with the control. This was represented on graphs as fold over control.
Flow cytometry analysis
Treated macrophages were analyzed by flow cytometry using the Attune NxT Flow Cytometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Cells were gently scraped in filtered FACS buffer (0.02% BSA in PBS without Ca2+ and Mg2+).
For polarization experiments, cell surface receptors were analyzed. Firstly, cells were blocked for 20 min on ice using Fc receptor binding inhibitor polyclonal antibody (100 μg/mL) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. 14-9161-73). Cells were then stained with human leukocyte antigen-DR isotype (HLA-DR), mannose receptor C-type 1 (MRC1), and CD16 for 30 min at 4°C. Cells were washed and then stained with Live/Dead Fixable Near-IR Dead Cell Stain Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, cat. no. L10119) for 30 min at 4°C. For characterization of MDMs, cells were stained with CD68 (see Table S6 for antibody details and dilutions).
For TSB experiments, both surface and intracellular proteins were analyzed. Cells were stained with Live/Dead Fixable Near-IR Dead Cell Stain Kit for 30 min at 4°C and then washed and blocked for 20 min on ice using Fc receptor binding inhibitor polyclonal antibody (100 μg/mL). Cells were then stained with CD16 (surface receptor) for 30 min at 4°C. Cells were washed and then permeabilized and fixed using the Cryo-Fast Fix/Perm Buffer Set (BioLegend, cat. no. 426803). Cells were then stained with CD206 and HLA-DR for 30 min at 4°C.
Fluorescent minus one (FMO) controls and unstained cells were used to set and check the gating strategy. A representative flow cytometry gating strategy and FMO controls are outlined in Figure S17. A total of 10,000 live cell events were analyzed per sample at a flow rate of 100 μL/min using the Attune NxT Acoustic Flow Cytometer. Fluorescence signal was detected using the violet laser 1 (filter wavelength: 440/50; BV421), the blue laser 1 (filter wavelength: 530/30 nm; FITC signal), the red laser 1 (filter wavelength: 670/14; APC signal), and the red laser 3 (filter wavelength: 780/60; Fixable Near IR signal). Data were analyzed using the flow cytometry software FlowJo V10 (BD Biosciences). MFI value and the percentage of MFI relative to the control were determined for each independent experiment and graphed using GraphPad Prism 10. Representative histograms were also constructed.
Cytokine analysis-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
PBMC-derived macrophage supernatants were analyzed using MCP-1/CCL2 human ELISA kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, UK, cat. no. 88-7399-86), human IL-6 DuoSet ELISA (R&D Systems, Abingdon, UK, cat. no. DY206-05), and human TNF-α DuoSet ELISA (R&D Systems, cat. no. DY210-05) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Mass spectrometry
Treated macrophages were harvested in urea (6 M) (Fisher Scientific, cat. no. U/0450/53) and protein concentration was determined by Bradford Assay. Dithiothreitol (5 mM) (Sigma, cat. no. 43819) was added to 50 μg of protein sample in urea and samples were incubated in a Thermomixer for 30 min at 37°C. Iodoacetemide solution (10 mM) (Sigma, cat. no. I1149) was added to each sample and incubated in the dark for 30 min at RT. An ammonium bicarbonate solution (50 mM) was added to dilute the urea concentration to <2 M. Trypsin (0.5 μg) (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. no. T7575) was added to the samples. Samples were incubated overnight in a Thermomixer at 37°C, after which acetic acid (AA) was added in a ratio of 1:100.
C18 Stage Tips were prepared as per Rappsilber et al.89 Stage tips were activated with 80% acetonitrile (ACN) + 0.5% AA solution. Samples were centrifuged through the Stage Tip. Stage tips containing samples were washed with 0.5% AA. Peptides were eluted from the Stage Tips in 80% ACN + 0.5% AA. Sample flow through was then evaporated in a SpeedVac Concentrator for ∼30 min at 45°C. Peptides were resuspended in mass spectrometry-grade water containing 0.5% AA + 2.5% ACN. The peptides were quantified using a DeNovix DS-11 Fx Spectrophotometer, normalized to a peptide concentration of 0.2 mg/mL, and then transferred to mass spectrometry vials.
Peptides from macrophages were analyzed on a Q-Exactive mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific), which was fitted with a reversed-phase NanoLC UltiMate 3000 high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system (Thermo Scientific). In brief, peptides were separated on a reverse-phase column (10 cm × 75 μm inner diameter) packed in-house with 3 μm C18 particles (Dr. Maisch, Germany) using a 2 h gradient at a flow rate of 250 nL/min. Mobile phases were 0.5% (v/v) AA with 2.5% ACN in water (phase A) and 0.5% (v/v) AA in 97% ACN (phase B). The peptides were separated by a gradient starting from 1% of mobile phase B and increased linearly to 28% for 118 min. This was increased to 95% of mobile phase B where it was maintained for 10 min. The volume injected was 5 μL. The Orbitrap, operating in data-dependent mode, automatically altered between mass spectrometry and mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry acquisition. Survey full-scan mass spectrometry spectra (m/z 350–1,600) had a resolution of 70,000. Mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry spectra had a resolution of 17,500. The 12 most intense ions were sequentially isolated and fragmented via higher-energy C-trap dissociation.
Raw data from the Q-Exactive were processed using the MaxQuant90,91 (version 1.6.10.43) incorporating the Andromeda search engine.92 To identify peptides and proteins, mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry spectra were matched against UniProt Homo sapiens database (2021_03) containing 78,120 entries. All searches were performed using the default setting of MaxQuant, with trypsin as specified enzyme allowing two missed cleavages and a false discovery rate of 1% on the peptide and protein level. The database searches were performed with carbamidomethyl (C) as fixed modification and acetylation (protein N terminus) and oxidation (M) as variable modifications. For the generation of label-free quantitative (LFQ) ion intensities for protein profiles, signals of corresponding peptides in different nano-HPLC mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry runs were matched by MaxQuant in a maximum time window of 1 min.93 The mass spectrometry proteomics data were deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium94 via the PRIDE95 partner repository with the dataset identifiers PXD035018 and 10.6019/PXD035018.
The Perseus statistical software (version 1.6.15.0)96 was used to analyze the ion intensities from the MaxQuant results. A filter was applied to remove any protein identifications from the “reverse” database, “only identified by site,” and “common contaminants.” LFQ intensities for each protein identification were log2 transformed and filtered for at least four valid values in at least one group. Missing values were imputed with values from the normal distribution. Scatterplots were generated to visualize the data. A Student’s t test was performed (p < 0.05) comparing TSB treatment to NC-TSB to further filter the data. For heatmap visualization of significantly changed proteins, the values were first Z score normalized prior to hierarchical clustering, which was carried out using Euclidean distance measures and average linkage. Corresponding gene ID for the differentially regulated proteins were used for graphical representation of the data.
IPA
Lists of proteins and their p values (p < 0.05) identified by proteomic analysis were analyzed by QIAGEN IPA software (QIAGEN Inc., https://digitalinsights.qiagen.com/IPA) using their gene IDs to determine the networks and upstream regulators altered in macrophages following the treatment of TSBs and LPS.
The effects of all TSB combinations were analyzed in comparison with the NC-TSB. The upstream regulators were identified by the IPA software Z score algorithm (p < 0.01) (Ingenuity Systems, QIAGEN) based on lists of significantly differentially expressed proteins. A cutoff activation Z score of ≥1.6 or ≤ −1.6 and a p value of overlap of p < 0.001 were implemented for the NC-TSB + LPS group to identify the upstream regulators activated and inhibited by LPS in comparison with the NC-TSB. Despite not being altered by NC-TSB + LPS, STAT3 was also included in the analysis following its unique upregulation by TSB-155 and TSB-3202 in the presence of LPS. The corresponding effects of TSB-155, TSB-3202, TSB-155 + LPS, and TSB-3202 + LPS on these LPS-regulated upstream regulators identified were then included and displayed on a heatmap (p value of overlap of p < 0.001 was deemed statistically significant). Differentially expressed protein lists were used to generate the top network interaction diagrams, which were also exported.
Human Arg2 plasmid design and dual luciferase reporter assay
A 525 base pair segment of human Arg2 3′ UTR was amplified using Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (NEB) and inserted into XhoI-digested pmirGLO vector (Promega) downstream of the firefly luciferase (luc2) reporter gene using the GenBuilder Cloning Kit (GenScript, cat. no. L00701). Plasmids were amplified and isolated in E. coli DH5α using the Plasmid Midi Kit (QIAGEN, cat. no. 12143) followed by sequence verification using the Arg2 3′ UTR primers listed in Table S4.
For the luciferase assay experiments, HEK293T cells were seeded at a density of 2 × 104 cells per well in 100 μL of complete DMEM and incubated for 24 h. Cells were then transfected with TSB-155/-199/-3202 (100 nM) or NC-TSB (100 nM) and 25 ng of pmir_Arg2 luciferase reporter plasmid. Transfection mixes were prepared using serum-free DMEM with 0.3% TransIT-X2 Dynamic Delivery System Transfection reagent (Myrus, cat. no. MIR 6004) and incubated for 5 h. After 24 h, the luciferase activity was assessed using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay (Promega, cat. no. E1910) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Luciferase activity was measured using a luminometer (in RLUs). The RLUs of the firefly luciferase/renilla luciferase ratio were calculated for each triplicate and then averaged. A minimum of three independent experiments were performed. The RLU average was then graphed as a percentage relative to the NC-TSB.
Statistical analysis
Results generated were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 9.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA) with the exception of the proteomic data, which were analyzed by Student’s t test using the Perseus software version 1.6.15.0.96 Data are presented as mean ± SEM, which is represented on each graph using an error bar. On graphs, each individual data point is representative of an independent experiment obtained from the average of biological replicates. On graphs involving clinical samples, each individual data point is representative of an individual participant in the study obtained from the average of technical replicates. A normal distribution test was conducted to determine whether the data would be analyzed as parametric data or non-parametric data. For cell culture data analysis, where condition comparisons were greater than two, an ordinary one-way ANOVA was performed. A Dunnett’s (parametric data) or a Dunn’s (non-parametric data) multiple comparisons’ post-test was performed comparing the mean of each column to the mean of the control column. In cases of comparisons of only two conditions, an unpaired t test (parametric data) or a Mann-Whitney t test (nonparametric data) was performed.
Clinical study participant data were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA with a Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Clinical correlation analysis was performed using a nonparametric Spearman correlation test. Statistical significance was defined as ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Every p value displayed is two tailed. Further details of statistical analysis and details of “n” numbers, where n represents the number of independent experiments performed, are outlined under the corresponding figures.
Data and code availability
The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium94 via the PRIDE95 partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD035018 and 10.6019/PXD035018. PRIDE website: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Science Foundation Ireland (grant no. FRL/16/3855), Enterprise Ireland and Knowledge Transfer Ireland (SI 2020 3049), FutureNeuro seed fund, and the Irish Research Council (GOIPD/2018/575). We would like to thank all patients who donated blood samples at Dr. Josep Trueta University Hospital. We would also like to acknowledge the UCD Proteomic Core and the Irish Blood Transfusion Service.
Author contribution
Conception and design of experiments, S.F., C.E.M.., and C.D.S.; data collection, S.F., C.D.S., F.N., M.M.-S.M., and L.R.-T.; data analysis and interpretation, S.F.; data analysis, F.N., I.A.F., and E.D.; drafting of manuscript, S.F., C.E.M.., C.D.S., and M.J.S.; final approval of manuscript, C.E.M. and C.D.S.; drafting of manuscript and data interpretation, J.K.D.
Declaration of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2023.08.023.
Contributor Information
Stephen Fitzsimons, Email: sfitzsimons08@gmail.com.
Chiara De Santi, Email: chiaradesanti@rcsi.ie.
Supplemental information
References
- 1.Schultze J.L., Schmieder A., Goerdt S. Macrophage activation in human diseases. Semin. Immunol. 2015;27:249–256. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2015.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Parisi L., Gini E., Baci D., Tremolati M., Fanuli M., Bassani B., Farronato G., Bruno A., Mortara L. Macrophage Polarization in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Killers or Builders? J. Immunol. Res. 2018;2018:8917804. doi: 10.1155/2018/8917804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chu F., Shi M., Zheng C., Shen D., Zhu J., Zheng X., Cui L. The roles of macrophages and microglia in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2018;318:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Peterson K.R., Cottam M.A., Kennedy A.J., Hasty A.H. Macrophage-Targeted Therapeutics for Metabolic Disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018;39:536–546. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2018.03.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ponzoni M., Pastorino F., Di Paolo D., Perri P., Brignole C. Targeting Macrophages as a Potential Therapeutic Intervention: Impact on Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19:1953. doi: 10.3390/ijms19071953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mantovani A., Biswas S.K., Galdiero M.R., Sica A., Locati M. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling. J. Pathol. 2013;229:176–185. doi: 10.1002/path.4133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Schett G., Neurath M.F. Resolution of chronic inflammatory disease: universal and tissue-specific concepts. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:3261. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05800-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mills C.D., Kincaid K., Alt J.M., Heilman M.J., Hill A.M. M-1/M-2 Macrophages and the Th1/Th2 Paradigm. J. Immunol. 2000;164:6166–6173. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.12.6166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nahrendorf M., Swirski F.K. Abandoning M1/M2 for a Network Model of Macrophage Function. Circ. Res. 2016;119:414–417. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fitzsimons S., Oggero S., Bruen R., McCarthy C., Strowitzki M.J., Mahon N.G., Ryan N., Brennan E.P., Barry M., Perretti M., Belton O. microRNA-155 Is Decreased During Atherosclerosis Regression and Is Increased in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles During Atherosclerosis Progression. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:576516. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.576516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Raggi F., Pelassa S., Pierobon D., Penco F., Gattorno M., Novelli F., Eva A., Varesio L., Giovarelli M., Bosco M.C. Regulation of Human Macrophage M1–M2 Polarization Balance by Hypoxia and the Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells-1. Front. Immunol. 2017;8:1097. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Murray P.J., Allen J.E., Biswas S.K., Fisher E.A., Gilroy D.W., Goerdt S., Gordon S., Hamilton J.A., Ivashkiv L.B., Lawrence T., et al. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41:14–20. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Unuvar Purcu D., Korkmaz A., Gunalp S., Helvaci D.G., Erdal Y., Dogan Y., Suner A., Wingender G., Sag D. Effect of stimulation time on the expression of human macrophage polarization markers. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0265196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McCarthy C., Duffy M.M., Mooney D., James W.G., Griffin M.D., Fitzgerald D.J., Belton O. IL-10 mediates the immunoregulatory response in conjugated linoleic acid-induced regression of atherosclerosis. Faseb. J. 2013;27:499–510. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-215442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bi Y., Chen J., Hu F., Liu J., Li M., Zhao L. M2 Macrophages as a Potential Target for Antiatherosclerosis Treatment. Neural Plast. 2019;2019:6724903. doi: 10.1155/2019/6724903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Denney L., Kok W.L., Cole S.L., Sanderson S., McMichael A.J., Ho L.-P. Activation of Invariant NKT Cells in Early Phase of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Results in Differentiation of Ly6Chi Inflammatory Monocyte to M2 Macrophages and Improved Outcome. J. Immunol. 2012;189:551–557. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kigerl K.A., Gensel J.C., Ankeny D.P., Alexander J.K., Donnelly D.J., Popovich P.G. Identification of two distinct macrophage subsets with divergent effects causing either neurotoxicity or regeneration in the injured mouse spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 2009;29:13435–13444. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3257-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shechter R., Miller O., Yovel G., Rosenzweig N., London A., Ruckh J., Kim K.W., Klein E., Kalchenko V., Bendel P., et al. Recruitment of beneficial M2 macrophages to injured spinal cord is orchestrated by remote brain choroid plexus. Immunity. 2013;38:555–569. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Self-Fordham J.B., Naqvi A.R., Uttamani J.R., Kulkarni V., Nares S. MicroRNA: Dynamic Regulators of Macrophage Polarization and Plasticity. Front. Immunol. 2017;8:1062. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang N., Liang H., Zen K. Molecular Mechanisms That Influence the Macrophage M1–M2 Polarization Balance. Front. Immunol. 2014;5:614. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Beavers K.R., Nelson C.E., Duvall C.L. MiRNA inhibition in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015;88:123–137. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Niespolo C., Johnston J.M., Deshmukh S.R., Satam S., Shologu Z., Villacanas O., Sudbery I.M., Wilson H.L., Kiss-Toth E. Tribbles-1 Expression and Its Function to Control Inflammatory Cytokines, Including Interleukin-8 Levels are Regulated by miRNAs in Macrophages and Prostate Cancer Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:574046. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wei Y., Corbalán-Campos J., Gurung R., Natarelli L., Zhu M., Exner N., Erhard F., Greulich F., Geißler C., Uhlenhaut N.H., et al. Dicer in Macrophages Prevents Atherosclerosis by Promoting Mitochondrial Oxidative Metabolism. Circulation. 2018;138:2007–2020. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hartmann P., Zhou Z., Natarelli L., Wei Y., Nazari-Jahantigh M., Zhu M., Grommes J., Steffens S., Weber C., Schober A. Endothelial Dicer promotes atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation by miRNA-103-mediated suppression of KLF4. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:10521. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Young J.A., Ting K.K., Li J., Moller T., Dunn L., Lu Y., Moses J., Prado-Lourenço L., Khachigian L.M., Ng M., et al. Regulation of vascular leak and recovery from ischemic injury by general and VE-cadherin-restricted miRNA antagonists of miR-27. Blood. 2013;122:2911–2919. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-12-473017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sonneville F., Ruffin M., Coraux C., Rousselet N., Le Rouzic P., Blouquit-Laye S., Corvol H., Tabary O. MicroRNA-9 downregulates the ANO1 chloride channel and contributes to cystic fibrosis lung pathology. Nat. Commun. 2017;8:710. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00813-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.De Santi C., Fernández Fernández E., Gaul R., Vencken S., Glasgow A., Oglesby I.K., Hurley K., Hawkins F., Mitash N., Mu F., et al. Precise Targeting of miRNA Sites Restores CFTR Activity in CF Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Mol. Ther. 2020;28:1190–1199. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Natarelli L., Geißler C., Csaba G., Wei Y., Zhu M., di Francesco A., Hartmann P., Zimmer R., Schober A. miR-103 promotes endothelial maladaptation by targeting lncWDR59. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:2645. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05065-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.S Clemente G., van Waarde A., F Antunes I., Dömling A., H Elsinga P. Arginase as a Potential Biomarker of Disease Progression: A Molecular Imaging Perspective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:5291. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dowling J.K., Afzal R., Gearing L.J., Cervantes-Silva M.P., Annett S., Davis G.M., De Santi C., Assmann N., Dettmer K., Gough D.J., et al. Mitochondrial arginase-2 is essential for IL-10 metabolic reprogramming of inflammatory macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:1460. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21617-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.De Santi C., Nally F.K., Afzal R., Duffy C.P., Fitzsimons S., Annett S.L., Robson T., Dowling J.K., Cryan S.-A., McCoy C.E. Enhancing arginase 2 expression using target site blockers as a strategy to modulate macrophage phenotype. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2022;29:643–655. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fioranelli M., Roccia M.G. Twenty-five years of studies and trials for the therapeutic application of IL-10 immunomodulating properties. From high doses administration to low dose medicine new paradigm. J Integr Cardiol. 2014;1:2–6. [Google Scholar]
- 33.O'Connell R.M., Chaudhuri A.A., Rao D.S., Baltimore D. Inositol phosphatase SHIP1 is a primary target of miR-155. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:7113–7118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0902636106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang P., Hou J., Lin L., Wang C., Liu X., Li D., Ma F., Wang Z., Cao X. Inducible microRNA-155 feedback promotes type I IFN signaling in antiviral innate immunity by targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 1. J. Immunol. 2010;185:6226–6233. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hutchins A.P., Diez D., Miranda-Saavedra D. The IL-10/STAT3-mediated anti-inflammatory response: recent developments and future challenges. Brief. Funct. Genomics. 2013;12:489–498. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elt028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yin Z., Ma T., Lin Y., Lu X., Zhang C., Chen S., Jian Z. IL-6/STAT3 pathway intermediates M1/M2 macrophage polarization during the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018;119:9419–9432. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zhong Z., Umemura A., Sanchez-Lopez E., Liang S., Shalapour S., Wong J., He F., Boassa D., Perkins G., Ali S.R., et al. NF-κB Restricts Inflammasome Activation via Elimination of Damaged Mitochondria. Cell. 2016;164:896–910. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Huang C., Lewis C., Borg N.A., Canals M., Diep H., Drummond G.R., Goode R.J., Schittenhelm R.B., Vinh A., Zhu M., et al. Proteomic Identification of Interferon-Induced Proteins with Tetratricopeptide Repeats as Markers of M1 Macrophage Polarization. J. Proteome Res. 2018;17:1485–1499. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Simmons D.P., Nguyen H.N., Gomez-Rivas E., Jeong Y., Jonsson A.H., Chen A.F., Lange J.K., Dyer G.S., Blazar P., Earp B.E., et al. SLAMF7 engagement superactivates macrophages in acute and chronic inflammation. Sci. Immunol. 2022;7:eabf2846. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abf2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Trapp B.D., Nave K.A. Multiple sclerosis: an immune or neurodegenerative disorder? Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008;31:247–269. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.30.051606.094313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Steinman L. Immunology of relapse and remission in multiple sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014;32:257–281. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Verma N.D., Lam A.D., Chiu C., Tran G.T., Hall B.M., Hodgkinson S.J. Multiple sclerosis patients have reduced resting and increased activated CD4+CD25+FOXP3+T regulatory cells. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:10476. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88448-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Fransson M.E., Liljenfeldt L.S.E., Fagius J., Tötterman T.H., Loskog A.S.I. The T-cell pool is anergized in patients with multiple sclerosis in remission. Immunology. 2009;126:92–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Acquaviva M., Menon R., Di Dario M., Dalla Costa G., Romeo M., Sangalli F., Colombo B., Moiola L., Martinelli V., Comi G., Farina C. Inferring Multiple Sclerosis Stages from the Blood Transcriptome via Machine Learning. Cell Rep. Med. 2020;1:100053. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hofman F.M., Hinton D.R., Johnson K., Merrill J.E. Tumor necrosis factor identified in multiple sclerosis brain. J. Exp. Med. 1989;170:607–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Selmaj K., Raine C.S., Cannella B., Brosnan C.F. Identification of lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor in multiple sclerosis lesions. J. Clin. Invest. 1991;87:949–954. doi: 10.1172/JCI115102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fresegna D., Bullitta S., Musella A., Rizzo F.R., De Vito F., Guadalupi L., Caioli S., Balletta S., Sanna K., Dolcetti E., et al. Re-Examining the Role of TNF in MS Pathogenesis and Therapy. Cells. 2020;9:2290. doi: 10.3390/cells9102290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kallaur A.P., Oliveira S.R., Simão A.N.C., Alfieri D.F., Flauzino T., Lopes J., de Carvalho Jennings Pereira W.L., de Meleck Proença C., Borelli S.D., Kaimen-Maciel D.R., et al. Cytokine Profile in Patients with Progressive Multiple Sclerosis and Its Association with Disease Progression and Disability. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017;54:2950–2960. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9846-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Valentin-Torres A., Savarin C., Hinton D.R., Phares T.W., Bergmann C.C., Stohlman S.A. Sustained TNF production by central nervous system infiltrating macrophages promotes progressive autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflammation. 2016;13:46. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0513-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hardbower D.M., Asim M., Murray-Stewart T., Casero R.A., Jr., Verriere T., Lewis N.D., Chaturvedi R., Piazuelo M.B., Wilson K.T. Arginase 2 deletion leads to enhanced M1 macrophage activation and upregulated polyamine metabolism in response to Helicobacter pylori infection. Amino Acids. 2016;48:2375–2388. doi: 10.1007/s00726-016-2231-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yin Y., Phạm T.L., Shin J., Shin N., Kang D.W., Lee S.Y., Lee W., Kim C.S., Kim S.R., Hong J., et al. Arginase 2 Deficiency Promotes Neuroinflammation and Pain Behaviors Following Nerve Injury in Mice. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:302. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Marathe C., Bradley M.N., Hong C., Lopez F., Ruiz de Galarreta C.M., Tontonoz P., Castrillo A. The Arginase II Gene Is an Anti-inflammatory Target of Liver X Receptor in Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:32197–32206. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605237200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Al-Haidari A.A., Syk I., Thorlacius H. MiR-155-5p positively regulates CCL17-induced colon cancer cell migration by targeting RhoA. Oncotarget. 2017;8:14887–14896. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Al-Haidari A., Algaber A., Madhi R., Syk I., Thorlacius H. MiR-155-5p controls colon cancer cell migration via post-transcriptional regulation of Human Antigen R (HuR) Cancer Lett. 2018;421:145–151. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.02.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kalliolias G.D., Ivashkiv L.B. TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016;12:49–62. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2015.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.The Lenercept Multiple Sclerosis Study, G., and The University of British Columbia, M.S.M.R.I.A.G TNF neutralization in MS. Neurology. 1999;53:457–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Arnett H.A., Mason J., Marino M., Suzuki K., Matsushima G.K., Ting J.P. TNF alpha promotes proliferation of oligodendrocyte progenitors and remyelination. Nat. Neurosci. 2001;4:1116–1122. doi: 10.1038/nn738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kruglov A.A., Lampropoulou V., Fillatreau S., Nedospasov S.A. Pathogenic and Protective Functions of TNF in Neuroinflammation Are Defined by Its Expression in T Lymphocytes and Myeloid Cells. J. Immunol. 2011;187:5660–5670. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Gschwandtner M., Derler R., Midwood K.S. More Than Just Attractive: How CCL2 Influences Myeloid Cell Behavior Beyond Chemotaxis. Front. Immunol. 2019;10:2759. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ping D., Jones P.L., Boss J.M. TNF regulates the in vivo occupancy of both distal and proximal regulatory regions of the MCP-1/JE gene. Immunity. 1996;4:455–469. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Ping D., Boekhoudt G., Zhang F., Morris A., Philipsen S., Warren S.T., Boss J.M. Sp1 binding is critical for promoter assembly and activation of the MCP-1 gene by tumor necrosis factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:1708–1714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.3.1708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bauermeister K., Burger M., Almanasreh N., Knopf H.P., Schumann R.R., Schollmeyer P., Dobos G.J. Distinct regulation of IL-8 and MCP-1 by LPS and interferon-gamma-treated human peritoneal macrophages. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1998;13:1412–1419. doi: 10.1093/ndt/13.6.1412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Jiang Y., Beller D.I., Frendl G., Graves D.T. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 regulates adhesion molecule expression and cytokine production in human monocytes. J. Immunol. 1992;148:2423–2428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dansereau M.-A., Midavaine É., Bégin-Lavallée V., Belkouch M., Beaudet N., Longpré J.M., Mélik-Parsadaniantz S., Sarret P. Mechanistic insights into the role of the chemokine CCL2/CCR2 axis in dorsal root ganglia to peripheral inflammation and pain hypersensitivity. J. Neuroinflammation. 2021;18:79. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02125-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Huang D.R., Wang J., Kivisakk P., Rollins B.J., Ransohoff R.M. Absence of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 in mice leads to decreased local macrophage recruitment and antigen-specific T helper cell type 1 immune response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 2001;193:713–726. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.6.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dogan R.-N.E., Elhofy A., Karpus W.J. Production of CCL2 by Central Nervous System Cells Regulates Development of Murine Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis through the Recruitment of TNF- and iNOS-Expressing Macrophages and Myeloid Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2008;180:7376–7384. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.11.7376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Teng K.Y., Han J., Zhang X., Hsu S.H., He S., Wani N.A., Barajas J.M., Snyder L.A., Frankel W.L., Caligiuri M.A., et al. Blocking the CCL2-CCR2 Axis Using CCL2-Neutralizing Antibody Is an Effective Therapy for Hepatocellular Cancer in a Mouse Model. Mol. Cancer Therapeut. 2017;16:312–322. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Li X., Yao W., Yuan Y., Chen P., Li B., Li J., Chu R., Song H., Xie D., Jiang X., Wang H. Targeting of tumour-infiltrating macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 signalling as a therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2017;66:157–167. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Simpson J.E., Newcombe J., Cuzner M.L., Woodroofe M.N. Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and other β-chemokines by resident glia and inflammatory cells in multiple sclerosis lesions. J. Neuroimmunol. 1998;84:238–249. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(97)00208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.McManus C., Berman J.W., Brett F.M., Staunton H., Farrell M., Brosnan C.F. MCP-1, MCP-2 and MCP-3 expression in multiple sclerosis lesions: an immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization study. J. Neuroimmunol. 1998;86:20–29. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(98)00002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mahad D.J., Ransohoff R.M. The role of MCP-1 (CCL2) and CCR2 in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) Semin. Immunol. 2003;15:23–32. doi: 10.1016/s1044-5323(02)00125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Iarlori C., Reale M., De Luca G., Di Iorio A., Feliciani C., Tulli A., Conti P., Gambi D., Lugaresi A. Interferon β-1b modulates MCP-1 expression and production in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002;123:170–179. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(01)00487-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Schraufstatter I.U., Zhao M., Khaldoyanidi S.K., Discipio R.G. The chemokine CCL18 causes maturation of cultured monocytes to macrophages in the M2 spectrum. Immunology. 2012;135:287–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Kodelja V., Müller C., Politz O., Hakij N., Orfanos C.E., Goerdt S. Alternative macrophage activation-associated CC-chemokine-1, a novel structural homologue of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha with a Th2-associated expression pattern. J. Immunol. 1998;160:1411–1418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kim H.S., Kim D.C., Kim H.-M., Kwon H.-J., Kwon S.J., Kang S.-J., Kim S.C., Choi G.-E. STAT1 deficiency redirects IFN signalling toward suppression of TLR response through a feedback activation of STAT3. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:13414. doi: 10.1038/srep13414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Schneider W.M., Chevillotte M.D., Rice C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: a complex web of host defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014;32:513–545. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lawrence T., Natoli G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011;11:750–761. doi: 10.1038/nri3088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ohmori Y., Hamilton T.A. Requirement for STAT1 in LPS-induced gene expression in macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001;69:598–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Kovarik P., Stoiber D., Novy M., Decker T. Stat1 combines signals derived from IFN-gamma and LPS receptors during macrophage activation. EMBO J. 1998;17:3660–3668. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.13.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Zhou X., Michal J.J., Zhang L., Ding B., Lunney J.K., Liu B., Jiang Z. Interferon induced IFIT family genes in host antiviral defense. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013;9:200–208. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Liu X.-Y., Chen W., Wei B., Shan Y.-F., Wang C. IFN-Induced TPR Protein IFIT3 Potentiates Antiviral Signaling by Bridging MAVS and TBK1. J. Immunol. 2011;187:2559–2568. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Malaer J.D., Mathew P.A. CS1 (SLAMF7, CD319) is an effective immunotherapeutic target for multiple myeloma. Am J Cancer Rs. 2017;7:1637–1641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Xia Z., Gu M., Jia X., Wang X., Wu C., Guo J., Zhang L., Du Y., Wang J. Integrated DNA methylation and gene expression analysis identifies SLAMF7 as a key regulator of atherosclerosis. Aging (Albany NY) 2018;10:1324–1337. doi: 10.18632/aging.101470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Jain A., Lamark T., Sjøttem E., Larsen K.B., Awuh J.A., Øvervatn A., McMahon M., Hayes J.D., Johansen T. p62/SQSTM1 is a target gene for transcription factor NRF2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:22576–22591. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.118976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Xiong Y., Yepuri G., Forbiteh M., Yu Y., Montani J.P., Yang Z., Ming X.F. ARG2 impairs endothelial autophagy through regulation of MTOR and PRKAA/AMPK signaling in advanced atherosclerosis. Autophagy. 2014;10:2223–2238. doi: 10.4161/15548627.2014.981789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Korhonen E., Piippo N., Hytti M., Hyttinen J.M.T., Kaarniranta K., Kauppinen A. SQSTM1/p62 regulates the production of IL-8 and MCP-1 in IL-1β-stimulated human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cytokine. 2019;116:70–77. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Ko J.H., Yoon S.O., Lee H.J., Oh J.Y. Rapamycin regulates macrophage activation by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-p38 MAPK-NFκB pathways in autophagy- and p62-dependent manners. Oncotarget. 2017;8:40817–40831. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Sergin I., Bhattacharya S., Emanuel R., Esen E., Stokes C.J., Evans T.D., Arif B., Curci J.A., Razani B. Inclusion bodies enriched for p62 and polyubiquitinated proteins in macrophages protect against atherosclerosis. Sci. Signal. 2016;9:ra2. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aad5614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Rappsilber J., Mann M., Ishihama Y. Protocol for micro-purification, enrichment, pre-fractionation and storage of peptides for proteomics using StageTips. Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:1896–1906. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Cox J., Mann M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:1367–1372. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Tyanova S., Temu T., Cox J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016;11:2301–2319. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Cox J., Neuhauser N., Michalski A., Scheltema R.A., Olsen J.V., Mann M. Andromeda: A Peptide Search Engine Integrated into the MaxQuant Environment. J. Proteome Res. 2011;10:1794–1805. doi: 10.1021/pr101065j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Cox J., Hein M.Y., Luber C.A., Paron I., Nagaraj N., Mann M. Accurate proteome-wide label-free quantification by delayed normalization and maximal peptide ratio extraction, termed MaxLFQ. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2014;13:2513–2526. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.031591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Deutsch E.W., Bandeira N., Sharma V., Perez-Riverol Y., Carver J.J., Kundu D.J., García-Seisdedos D., Jarnuczak A.F., Hewapathirana S., Pullman B.S., et al. The ProteomeXchange consortium in 2020: enabling 'big data' approaches in proteomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:D1145–D1152. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Perez-Riverol Y., Bai J., Bandla C., García-Seisdedos D., Hewapathirana S., Kamatchinathan S., Kundu D.J., Prakash A., Frericks-Zipper A., Eisenacher M., et al. The PRIDE database resources in 2022: a hub for mass spectrometry-based proteomics evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:D543–D552. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Tyanova S., Temu T., Sinitcyn P., Carlson A., Hein M.Y., Geiger T., Mann M., Cox J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods. 2016;13:731–740. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium94 via the PRIDE95 partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD035018 and 10.6019/PXD035018. PRIDE website: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/