Abstract
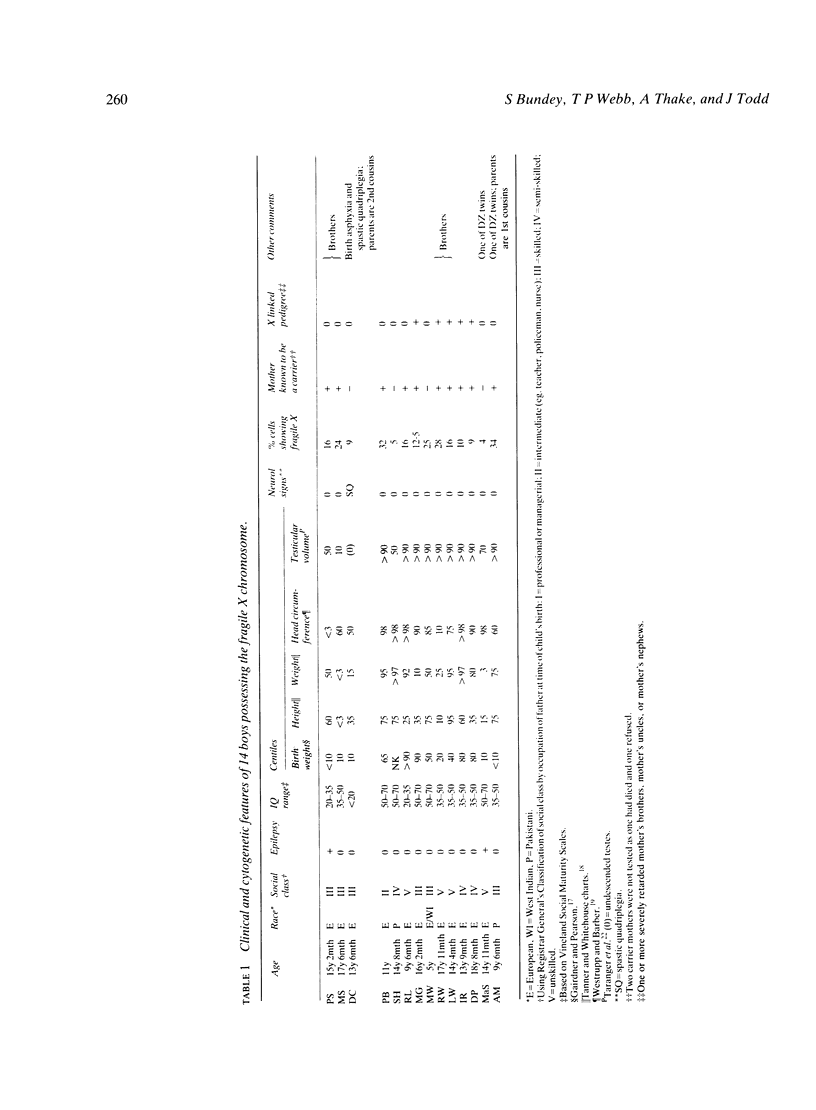
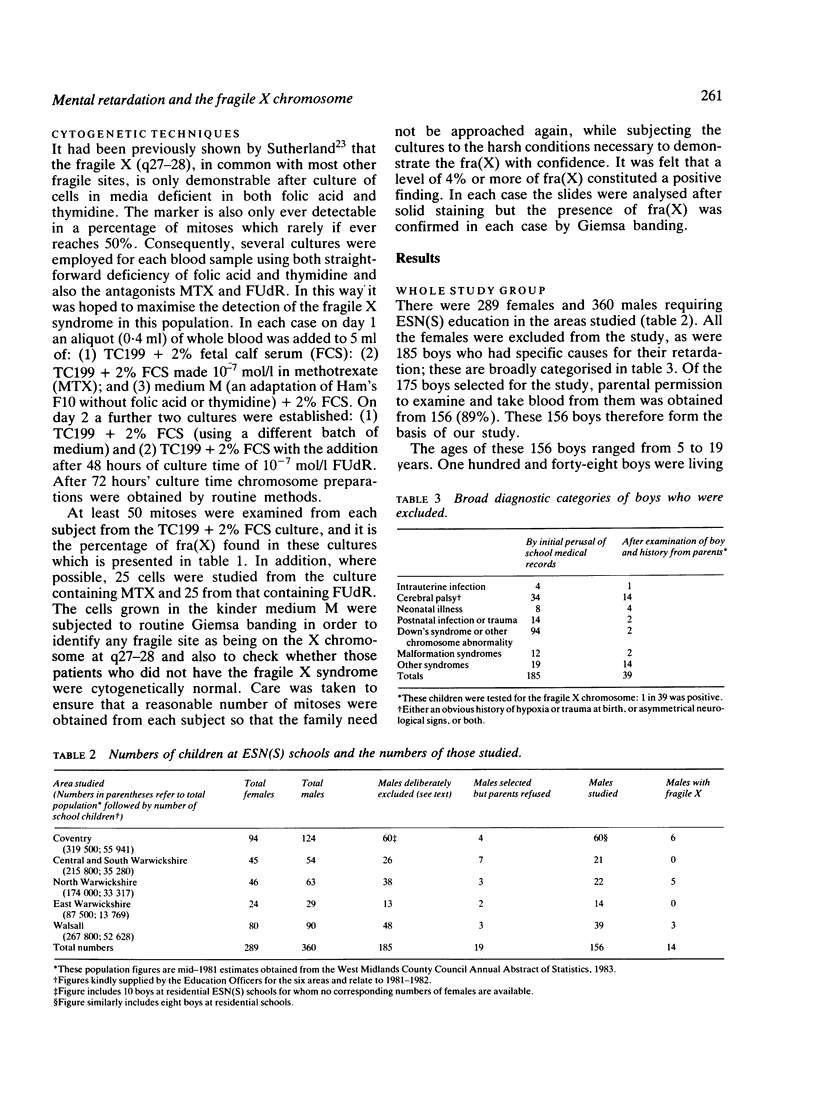
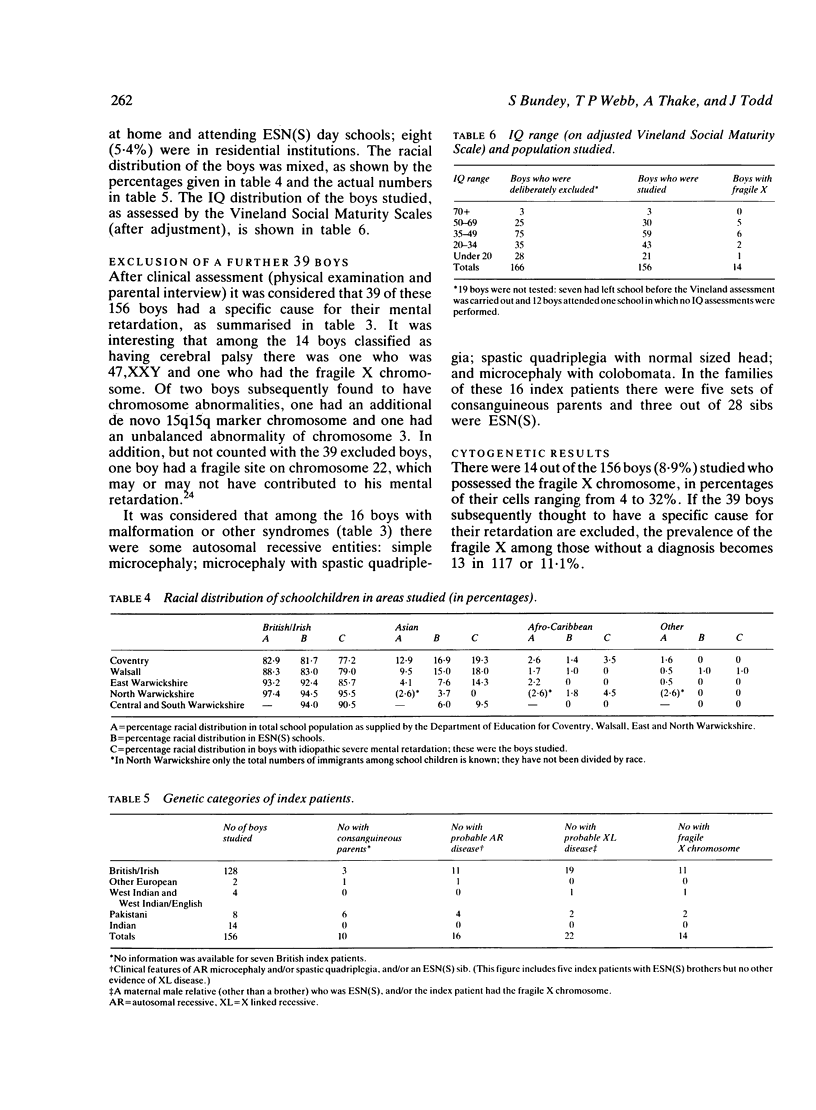
This paper describes a community based study of 156 boys with idiopathic, severe mental retardation. The boys were examined and a pedigree taken before the cytogenetic results were known. The prevalence of the fragile X chromosome among this group of boys was high: 9% in the whole group and 11% after 39 boys with specific features had been excluded. The fragile X syndrome is therefore an important cause of idiopathic, severe retardation. Its clinical features of large head, large testes, and IQ in the 35 to 70 range were often but not always present in the 14 boys identified in this study. In the whole group, the recurrence of severe mental subnormality was high: 1 in 8 for brothers and 1 in 25 for sisters. This high recurrence was partly due to the fragile X syndrome, partly to X linked mental retardation not accompanied by cytogenetic abnormalities, and partly due to autosomal recessive disease. Autosomal recessive disease was perhaps higher in the West Midlands than elsewhere (such as British Columbia, for example 1) because of the disproportionate contribution by Asian immigrants.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blomquist H. K., Gustavson K. H., Holmgren G., Nordenson I., Pålsson-Stråe U. Fragile X syndrome in mildly mentally retarded children in a northern Swedish county. A prevalence study. Clin Genet. 1983 Dec;24(6):393–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb00092.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist H. K., Gustavson K. H., Holmgren G., Nordenson I., Sweins A. Fragile site X chromosomes and X-linked mental retardation in severely retarded boys in a northern Swedish county. A prevalence study. Clin Genet. 1982 Mar;21(3):209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb00965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Jaye M., Mandel J. L. Close linkage of fragile X-mental retardation syndrome to haemophilia B and transmission through a normal male. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):701–704. doi: 10.1038/306701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chudley A. E., Knoll J., Gerrard J. W., Shepel L., McGahey E., Anderson J. Fragile (X) X-linked mental retardation I: relationship between age and intelligence and the frequency of expression of fragil (X)(q28). Am J Med Genet. 1983 Apr;14(4):699–712. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishburn J., Turner G., Daniel A., Brookwell R. The diagnosis and frequency of X-linked conditions in a cohort of moderately retarded males with affected brothers. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Apr;14(4):713–724. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froster-Iskenius U., Felsch G., Schirren C., Schwinger E. Screening for fra(X)(q) in a population of mentally retarded males. Hum Genet. 1983;63(2):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00291535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gairdner D., Pearson J. A growth chart for premature and other infants. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Dec;46(250):783–787. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.250.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J., Judge C., Wiener S. Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):46–50. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst D. S., Baird P. A. Sib risks for nonspecific mental retardation in British Columbia. Am J Med Genet. 1982 Oct;13(2):197–208. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320130210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst D. S., Miller J. R. Nonspecific X-linked mental retardation II: the frequency in British Columbia. Am J Med Genet. 1980;7(4):461–469. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320070407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähkönen M., Leisti J., Wilska M., Varonen S. Marker X-associated mental retardation. A study of 150 retarded males. Clin Genet. 1983 Jun;23(6):397–404. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb01973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A. A marker X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 May;21(3):231–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellhaus G. Head circumference from birth to eighteen years. Practical composite international and interracial graphs. Pediatrics. 1968 Jan;41(1):106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. B., Tommerup N., Poulsen H., Mikkelsen M. X-linked mental retardation with fragile X. A pedigree showing transmission by apparently unaffected males and partial expression in female carriers. Hum Genet. 1981;59(1):23–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00278849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards B. W., Sylvester P. E., Brooker C. Fragile X-linked mental retardation: the Martin-Bell syndrome. J Ment Defic Res. 1981 Dec;25(Pt 4):253–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1981.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Morton N. E., Jacobs P. A., Turner G. The marker (X) syndrome: a cytogenetic and genetic analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;48(Pt 1):21–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Heritable fragile sites on human chromosomes. III. Detection of fra(X)(q27) in males with X-linked mental retardation and in their female relatives. Hum Genet. 1979;53(1):23–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00289445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taranger J., Engström I., Lichtenstein H., Svennberg- Redegren I. VI. Somatic pubertal development. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1976;(258):121–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Brookwell R., Daniel A., Selikowitz M., Zilibowitz M. Heterozygous expression of X-linked mental retardation and X-chromosome marker fra(X)(q27). N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 18;303(12):662–664. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009183031202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Turner B. X-linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1974 Jun;11(2):109–113. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.2.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waaler P. E., Thorsen T., Stoa K. F., Aarskog D. Studies in normal male puberty. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1974;(249):1–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1974.tb07587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vijver L. M., Lötter A. P. The constituents in the roots of Plumbago auriculata Lam. and Plumbago zeylanica L. responsible for antibacterial activity. Planta Med. 1971 Jul;20(1):8–13. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1099658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


