Abstract
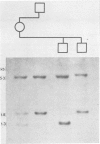
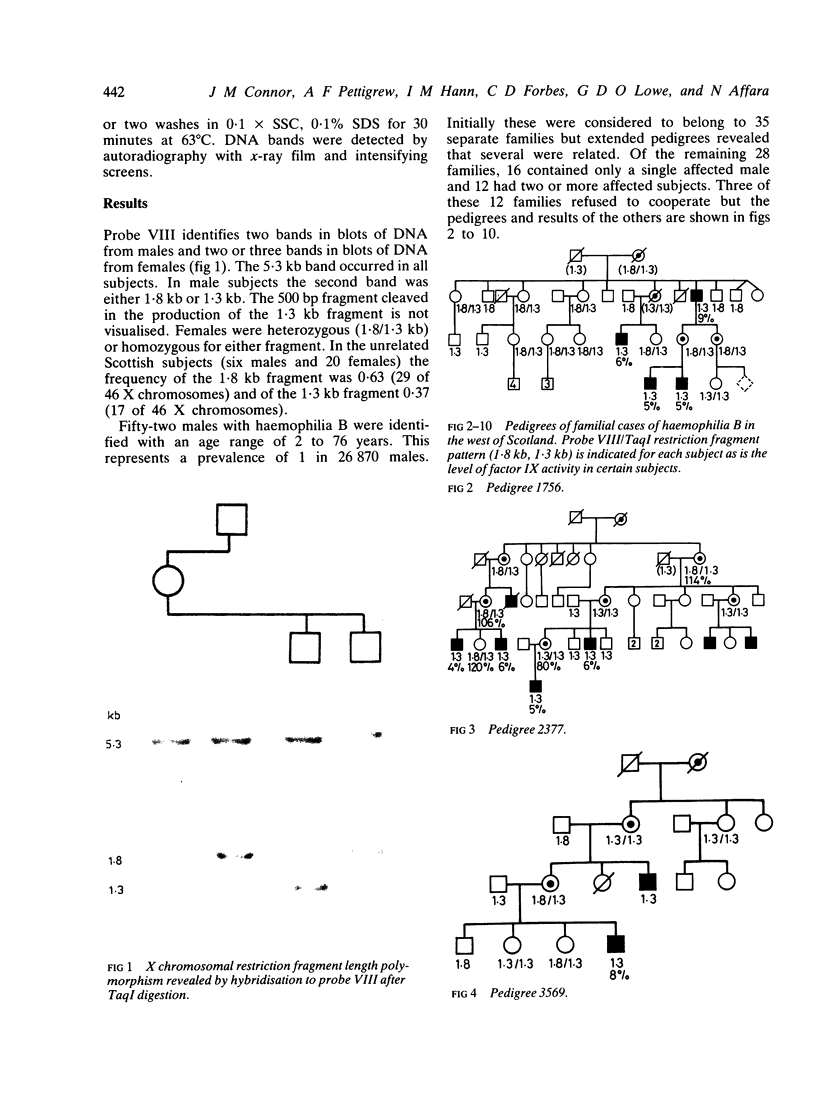
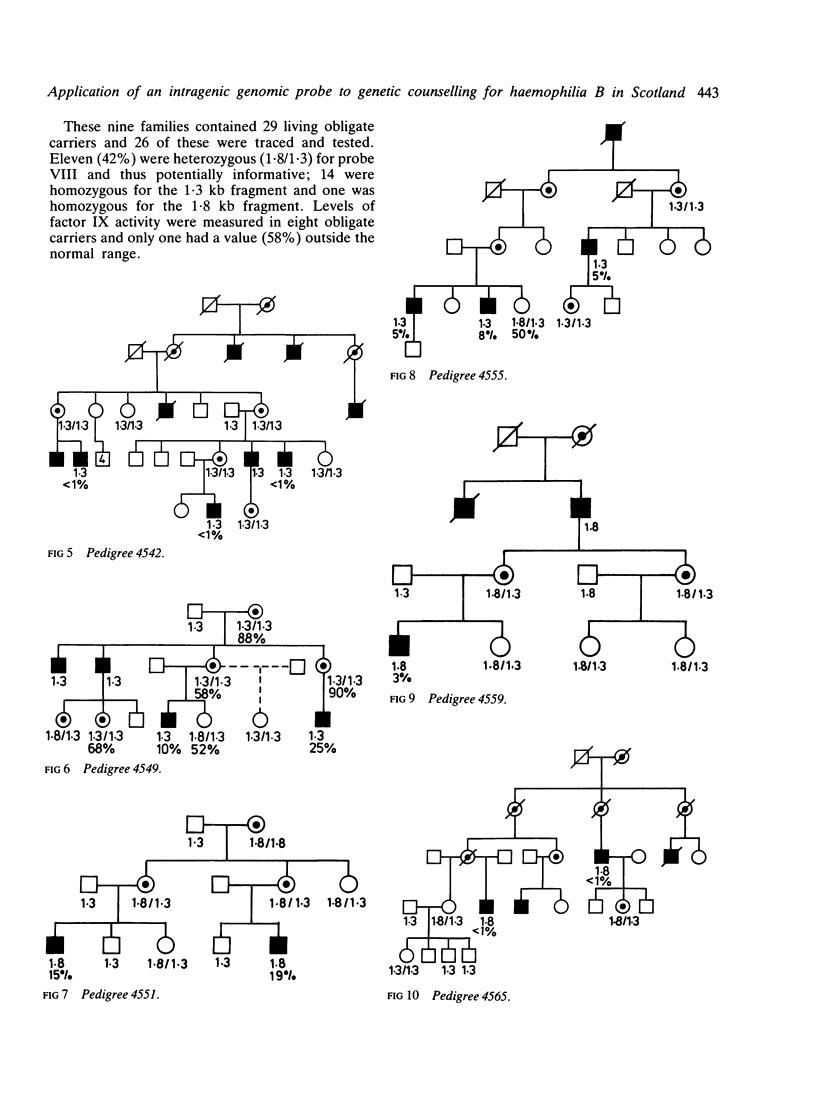
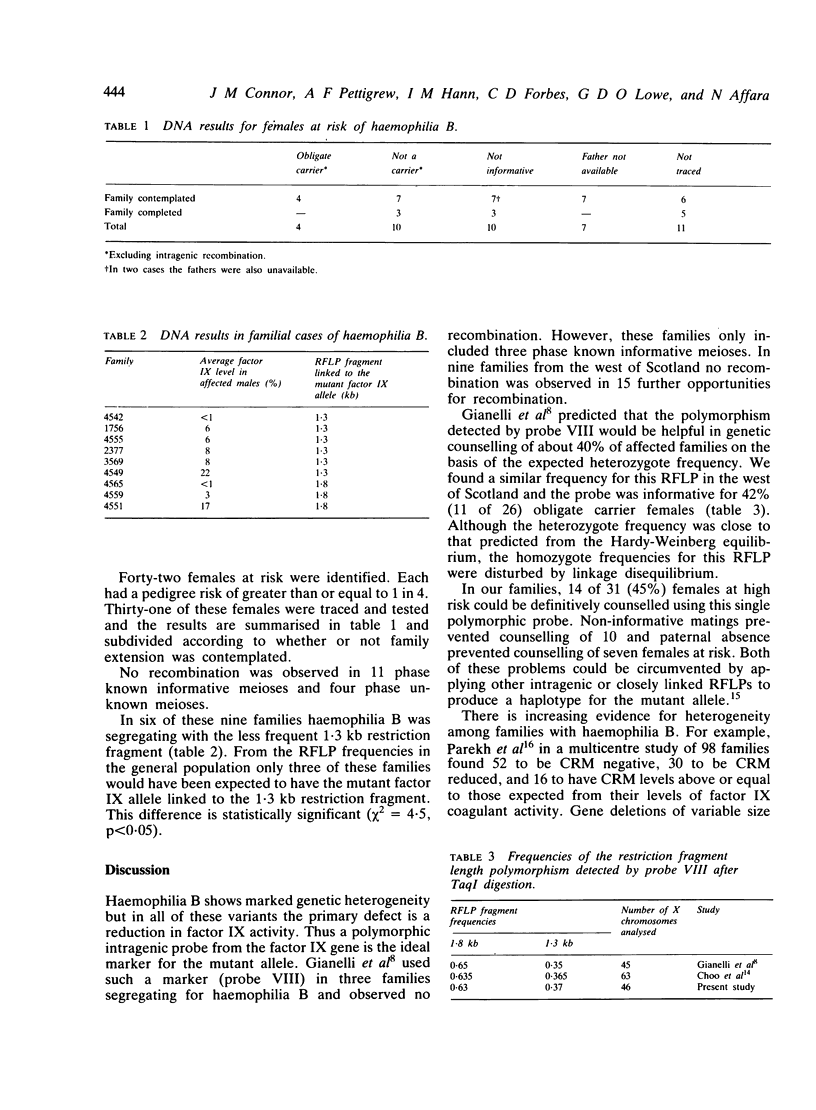
Total ascertainment revealed 28 families with haemophilia B in the west of Scotland (prevalence 1/26 870 males). In 12 of these families more than one person was affected and 26 living obligate carriers were identified and tested. Of these, 42% were heterozygous for a DNA polymorphism recognised by a factor IX genomic probe. No recombination was observed in 11 phase known and four phase unknown informative meioses. Definitive genetic counselling was possible for 14 of 42 females at risk, 11 could not be traced, in 10 the probe was not informative, and in seven paternal absence prevented interpretation. Linkage disequilibrium was apparent for this restriction fragment length polymorphism and haemophilia B in the west of Scotland.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Giannelli F., Gould K., Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. The gene structure of human anti-haemophilic factor IX. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1053–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravarti A. Utility and efficiency of linked marker genes for genetic counseling. III. Proportion of informative families under linkage disequilibrium. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Jul;35(4):592–610. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., George D., Filby G., Halliday J. L., Leversha M., Webb G., Danks D. M. Linkage analysis of X-linked mental retardation with and without fragile-X using factor IX gene probe. Lancet. 1984 Aug 11;2(8398):349–349. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92715-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Gould K. G., Rees D. J., Brownlee G. G. Molecular cloning of the gene for human anti-haemophilic factor IX. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):178–180. doi: 10.1038/299178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. H. Population genetics of C4 with the use of complementary DNA probes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):405–417. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. I., Shaw A. Attitudes of Haemophilia carrier to fetoscopy and amniocentesis. Lancet. 1979 Dec 22;2(8156-8157):1371–1371. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92856-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Winship P. R., Ferrari N., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Characterisation and use of an intragenic polymorphic marker for detection of carriers of haemophilia B (factor IX deficiency). Lancet. 1984 Feb 4;1(8371):239–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannelli F., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Boyd Y., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Gene deletions in patients with haemophilia B and anti-factor IX antibodies. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):181–182. doi: 10.1038/303181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Gustavii B., Cordesius E., Kristoffersson A. C., Ljung R., Löfberg L., Strömberg P., Nilsson I. M. Prenatal diagnosis of hemophilia B by an immunoradiometric assay of factor IX. Blood. 1980 Sep;56(3):397–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper C. K., Osterud B., Minami J. Y., Shonick W., Rapaport S. I. Hemophilia B: characterization of genetic variants and detection of carriers. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):351–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mibashan R. S., Rodeck C. H., Thumpston J. K., Edwards R. J., Singer J. D., White J. M., Campbell S. Plasma assay of fetal factors VIIIC and IX for prenatal diagnosis of haemophilia. Lancet. 1979 Jun 23;1(8130):1309–1311. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91946-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orstavik K. H., Veltkamp J. J., Bertina R. M., Hermans J. Detection of carriers of haemophilia B. Br J Haematol. 1979 Jun;42(2):293–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb01133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh V. R., Mannucci P. M., Ruggeri Z. M. Immunological heterogeneity of haemophilia B: a multicentre study of 98 kindreds. Br J Haematol. 1978 Dec;40(4):643–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb05840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake I. R., Furlong B. L., Bloom A. L. Carrier detection by direct gene analysis in a family with haemophilia B (factor IX deficiency). Lancet. 1984 Feb 4;1(8371):242–243. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON N. E., BIGGS R. The inheritance of Christmas factor. Br J Haematol. 1962 Jul;8:191–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1962.tb06512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R., Anson D. S., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Carrier detection in haemophilia B using two further intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8861–8872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]