Abstract
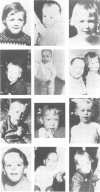
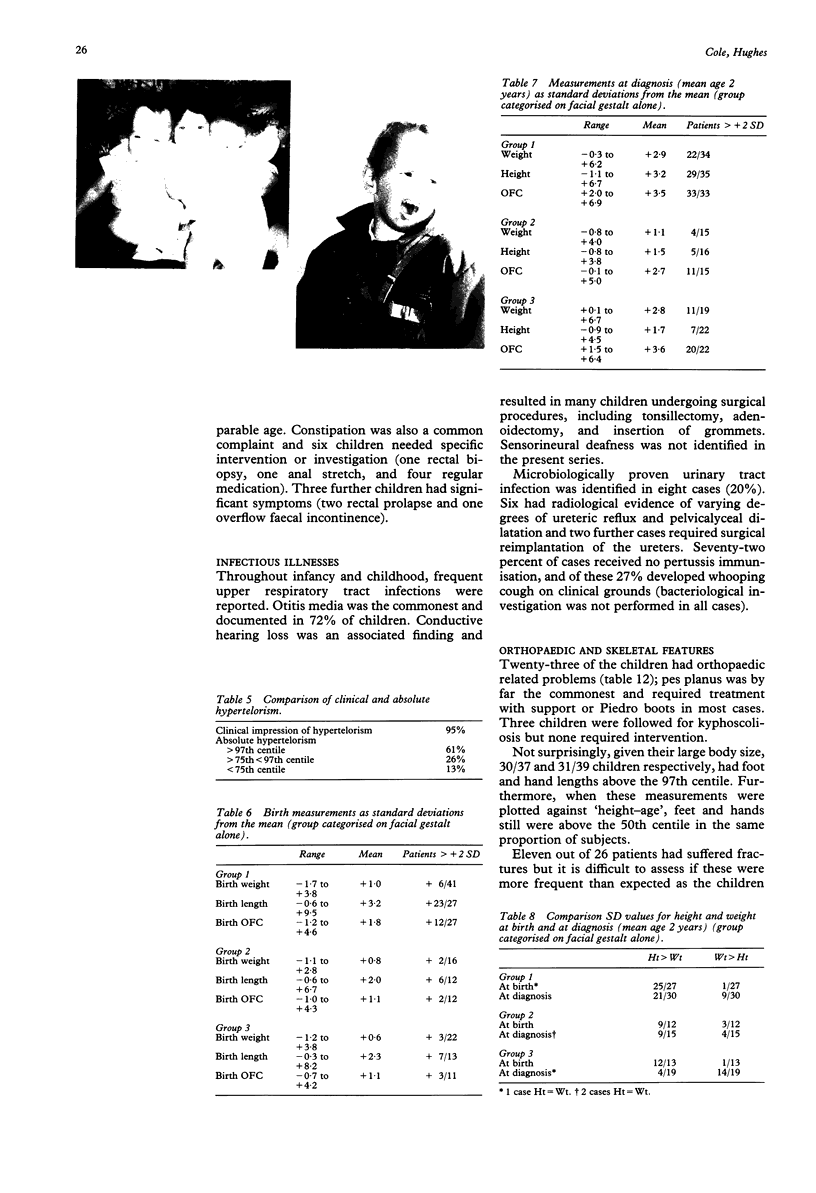
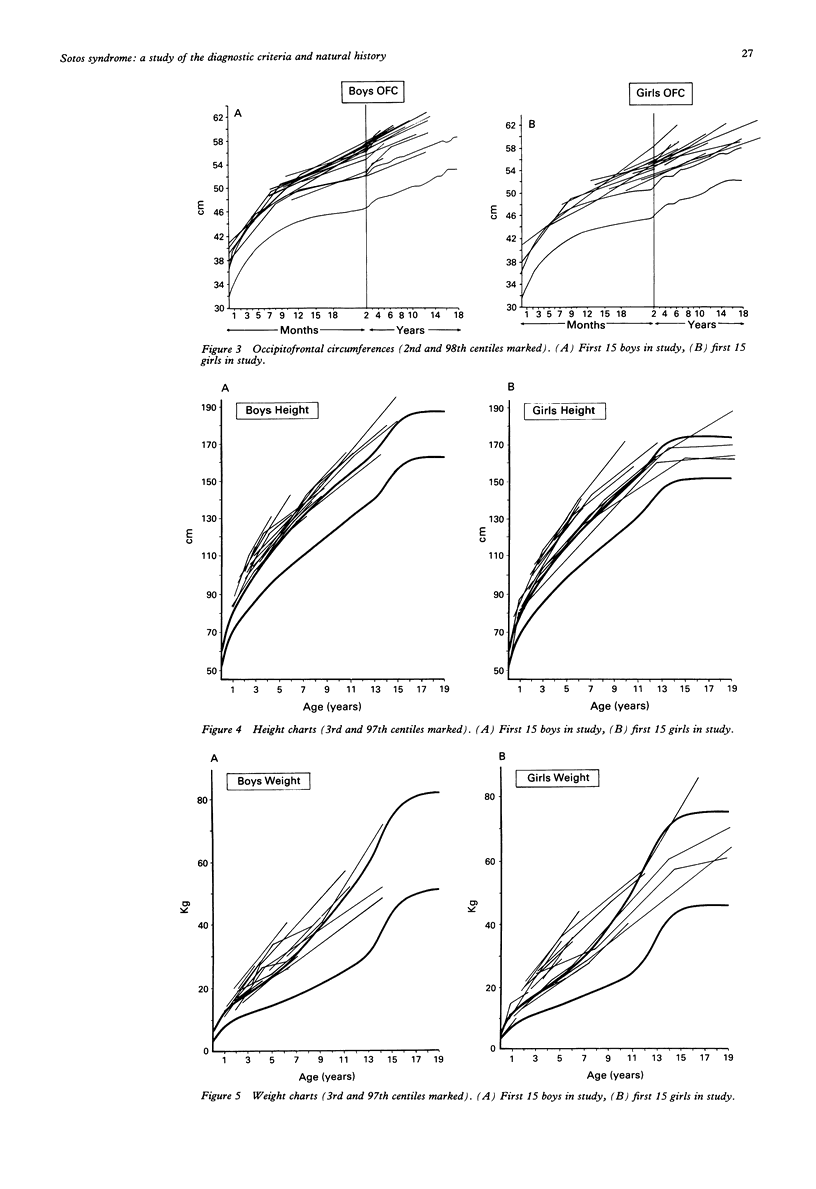
Seventy-nine patients with a provisional diagnosis of Sotos syndrome were clinically assessed, and their photographs between the ages of 1 and 6 years evaluated. These photographs, together with photographs of first degree relatives, also at ages 1 to 6 years, were reviewed by four clinical geneticists. Forty-one probands (but no first degree relatives) were identified in whom the facial gestalt was thought to be characteristic of Sotos syndrome. Comparison of anthropometric measurements, bone age, and developmental delay in these 41 probands showed marked differences between them and the remaining 38 probands, and allowed the formulation of guidelines for the diagnosis of Sotos syndrome. Length was identified as the most significantly increased prenatal parameter. In childhood occipitofrontal head circumference (OFC), height, and weight were all increased. OFC remained above the 97th centile in all but one case throughout childhood and adulthood, whereas height and weight had a tendency to return towards the mean. This 'normalisation' was more pronounced in females and was probably related to their early puberty. Early developmental delay and an advanced bone age, seen in 100% and 84% respectively of study cases, may be invariable in Sotos syndrome, but selection bias and limited data prevented confirmation of this supposition. The authors suggest that facial gestalt, growth pattern, bone age, and developmental delay are the major diagnostic criteria. Using these criteria, no affected first degree relatives were identified. There were few long term medical complications in the probands, but behavioural difficulties caused considerable parental concern.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. M., Snodgrass G. J. Sotos' syndrome of cerebral gigantism. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Apr;44(234):203–210. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.234.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardinger H. H., Hanson J. W., Harrod M. J., Cohen M. M., Jr, Tibbles J. A., Welch J. P., Young-Wee T., Sommer A., Goldberg R., Shprintzen R. J. Further delineation of Weaver syndrome. J Pediatr. 1986 Feb;108(2):228–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80988-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale A. E., Drum M. A., Parry D. M., Mulvihill J. J. Familial Sotos syndrome (cerebral gigantism): craniofacial and psychological characteristics. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Apr;20(4):613–624. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behmel A., Plöchl E., Rosenkranz W. A new X-linked dysplasia gigantism syndrome: follow up in the first family and report on a second Austrian family. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):275–285. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom A. S., Reese A., Hersh J. H., Podruch P. E., Weisskopf B., Dinno N. Cognition in cerebral gigantism: are the estimates of mental retardation too high? J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1983 Dec;4(4):250–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boman H., Nilsson D. Sotos syndrome in two brothers. Clin Genet. 1980 Dec;18(6):421–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb01787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
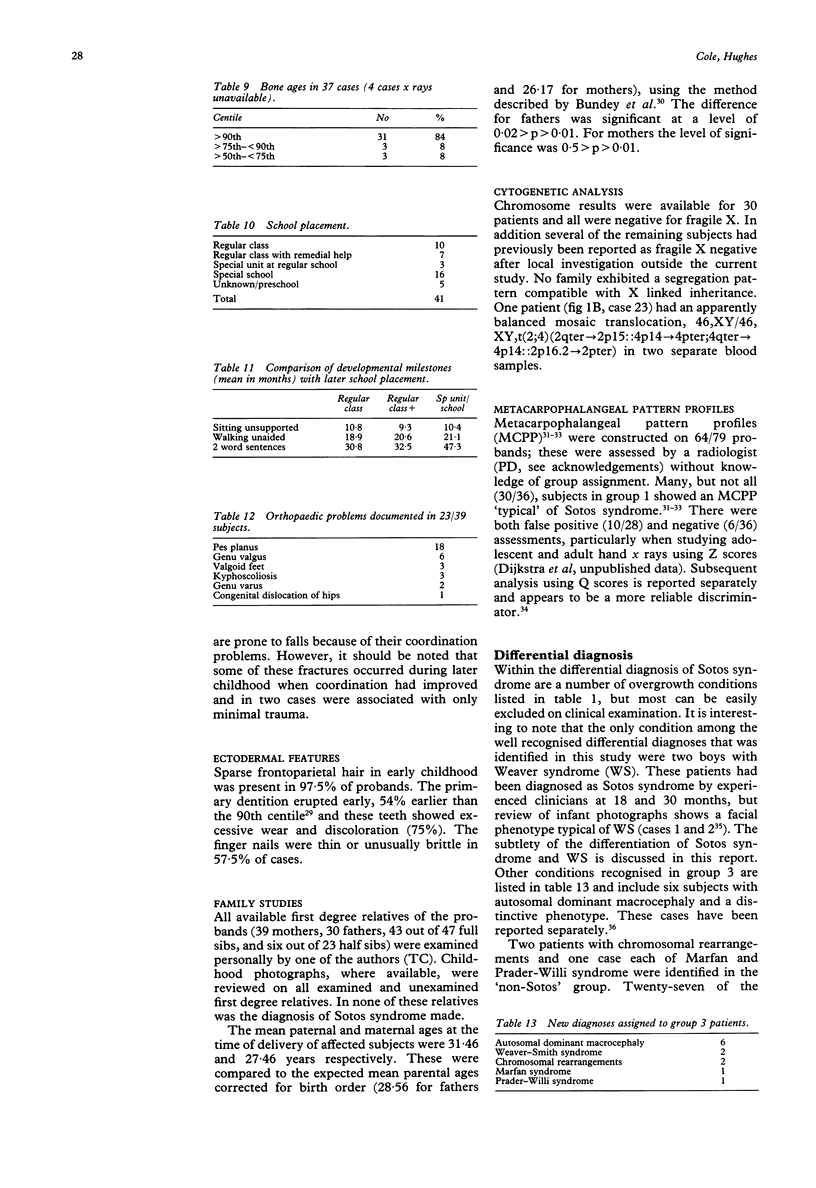
- Butler M. G., Dijkstra P. F., Meaney F. J., Gale D. D. Metacarpophalangeal pattern profile analysis in Sotos syndrome: a follow-up report on 34 subjects. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Jan;29(1):143–147. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G., Meaney F. J., Kittur S., Hersh J. H., Hornstein L. Metacarpophalangeal pattern profile analysis in Sotos syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Apr;20(4):625–629. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. D., Donnai D., Rogers J., Cooper J., Baraitser M. Proteus syndrome: an expanded phenotype. Am J Med Genet. 1987 May;27(1):99–117. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320270111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. R., Dennis N. R., Hughes H. E. Weaver syndrome. J Med Genet. 1992 May;29(5):332–337. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.5.332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. R., Hughes H. E. Autosomal dominant macrocephaly: benign familial macrocephaly or a new syndrome? Am J Med Genet. 1991 Oct 1;41(1):115–124. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320410128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole T. R., Hughes H. E., Jeffreys M. J., Williams G. T., Arnold M. M. Small cell lung carcinoma in a patient with Sotos syndrome: are genes at 3p21 involved in both conditions? J Med Genet. 1992 May;29(5):338–341. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.5.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer H., Niederdellmann H. Cerebral gigantism associated with jaw cyst basal cell naevoid syndrome in two families. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr (1970) 1983;233(2):111–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00343432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra P. F. Cerebral gigantism (Sotos' syndrome). Metacarpophalangeal pattern profiles. Rofo. 1985 Aug;143(2):183–185. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge P. R., Holmes S. J., Sotos J. F. Cerebral gigantism. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1983 Apr;25(2):248–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1983.tb13750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch N. The syndromes of Marshall and Weaver. J Med Genet. 1980 Jun;17(3):174–178. doi: 10.1136/jmg.17.3.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankenburg W. K., Dodds J. B. The Denver developmental screening test. J Pediatr. 1967 Aug;71(2):181–191. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(67)80070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemelli M., Carlo Stella N., Barberio G., Tortorella G., Mamì C., De Luca F. Sindrome di Sotos in due fratelli. Conferma di una ereditarietà autosomica recessiva? Minerva Pediatr. 1982 Nov 30;34(22):983–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginter D. N., Scott C. I. Cerebral gigantism. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(2):415–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goumy P., Malpuech G., Gannat M., Menut G. Gigantisme cérébral familial. Une nouvelle observation à transmission autosomique dominante? Pediatrie. 1979 Apr-May;34(3):249–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg F., Stein F., Gresik M. V., Finegold M. J., Carpenter R. J., Riccardi V. M., Beaudet A. L. The Perlman familial nephroblastomatosis syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1986 May;24(1):101–110. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320240112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen F. J., Friis B. Familial occurrence of cerebral gigantism, Sotos' syndrome. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 May;65(3):387–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry I., Bonaiti-Pellié C., Chehensse V., Beldjord C., Schwartz C., Utermann G., Junien C. Uniparental paternal disomy in a genetic cancer-predisposing syndrome. Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):665–667. doi: 10.1038/351665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. L., Smith D. W., Harvey M. A., Hall B. D., Quan L. Older paternal age and fresh gene mutation: data on additional disorders. J Pediatr. 1975 Jan;86(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80709-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko H., Tsukahara M., Tachibana H., Kurashige H., Kuwano A., Kajii T. Congenital heart defects in Sotos sequence. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Mar;26(3):569–576. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320260310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen D. V., Pearse R. G. Birthweight between 14 and 42 weeks' gestation. Arch Dis Child. 1985 May;60(5):440–446. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.5.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingood A. B., Borengasser M. A. Cerebral gigantism in infancy: implications for psychological and social development. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 1981 Fall;12(1):46–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00706673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. E., Graham C. B., Scott C. R., Smith D. W. Syndrome of accelerated skeletal maturation and relative failure to thrive: a newly recognized clinical growth disorder. J Pediatr. 1971 Jan;78(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80269-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevo S., Zeltzer M., Benderly A., Levy J. Evidence for autosomal recessive inheritance in cerebral gigantism. J Med Genet. 1974 Jun;11(2):158–165. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.2.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Butler M. G., Karam S., Lalande M. Genetic imprinting suggested by maternal heterodisomy in nondeletion Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):281–285. doi: 10.1038/342281a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman M., Goldberg G. M., Bar-Ziv J., Danovitch G. Renal hamartomas and nephroblastomatosis with fetal gigantism: a familial syndrome. J Pediatr. 1973 Sep;83(3):414–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80264-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettenati M. J., Haines J. L., Higgins R. R., Wappner R. S., Palmer C. G., Weaver D. D. Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome: presentation of clinical and cytogenetic data on 22 new cases and review of the literature. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):143–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00282078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyeritz R. E., McKusick V. A. The Marfan syndrome: diagnosis and management. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 5;300(14):772–777. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904053001406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter S. C., Cole T. R. Psychological characteristics of Sotos syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1991 Oct;33(10):898–902. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1991.tb14799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvalcaba R. H., Myhre S., Smith D. W. Sotos syndrome with intestinal polyposis and pigmentary changes of the genitalia. Clin Genet. 1980 Dec;18(6):413–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb01785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOTOS J. F., DODGE P. R., MUIRHEAD D., CRAWFORD J. D., TALBOT N. B. CEREBRAL GIGANTISM IN CHILDHOOD. A SYNDROME OF EXCESSIVELY RAPID GROWTH AND ACROMEGALIC FEATURES AND A NONPROGRESSIVE NEUROLOGIC DISORDER. N Engl J Med. 1964 Jul 16;271:109–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196407162710301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinzel A., Biró Z., Schmid W., Hayashi K. Trisomy 8 mosaicism syndrome. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1974 Dec;29(6):531–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J. L., Landey S., New M., German J. A previously unrecognized X-linked syndrome of dysmorphia. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(2):18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A., Farrar J. R., Silink M., Judzewitsch R. Dominant Sotos's syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Jul;55(7):579–579. doi: 10.1136/adc.55.7.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Daniel A., Frost M. X-linked mental retardation, macro-orchidism, and the Xq27 fragile site. J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):837–841. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80552-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEDEMANN H. R. COMPLEXE MALFORMATIF FAMILIAL AVEC HERNIE OMBILICALE ET MACROGLOSSIE--UN "SYNDROME NOUVEAU"? J Genet Hum. 1964 Sep;13:223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. D., Graham C. B., Thomas I. T., Smith D. W. A new overgrowth syndrome with accelerated skeletal maturation, unusual facies, and camptodactyly. J Pediatr. 1974 Apr;84(4):547–552. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80675-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedemann H. R., Burgio G. R., Aldenhoff P., Kunze J., Kaufmann H. J., Schirg E. The proteus syndrome. Partial gigantism of the hands and/or feet, nevi, hemihypertrophy, subcutaneous tumors, macrocephaly or other skull anomalies and possible accelerated growth and visceral affections. Eur J Pediatr. 1983 Mar;140(1):5–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00661895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigglesworth J. S. Lesions in the neonatal brain. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Dec;60(12):1202–1203. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.12.1202-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship I. M. Sotos syndrome--autosomal dominant inheritance substantiated. Clin Genet. 1985 Sep;28(3):243–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1985.tb00393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wit J. M., Beemer F. A., Barth P. G., Oorthuys J. W., Dijkstra P. F., Van den Brande J. L., Leschot N. J. Cerebral gigantism (Sotos syndrome). Compiled data of 22 cases. Analysis of clinical features, growth and plasma somatomedin. Eur J Pediatr. 1985 Jul;144(2):131–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00451898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zonana J., Sotos J. F., Romshe C. A., Fisher D. A., Elders M. J., Rimoin D. L. Dominant inheritance of cerebral gigantism. J Pediatr. 1977 Aug;91(2):251–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]