Abstract
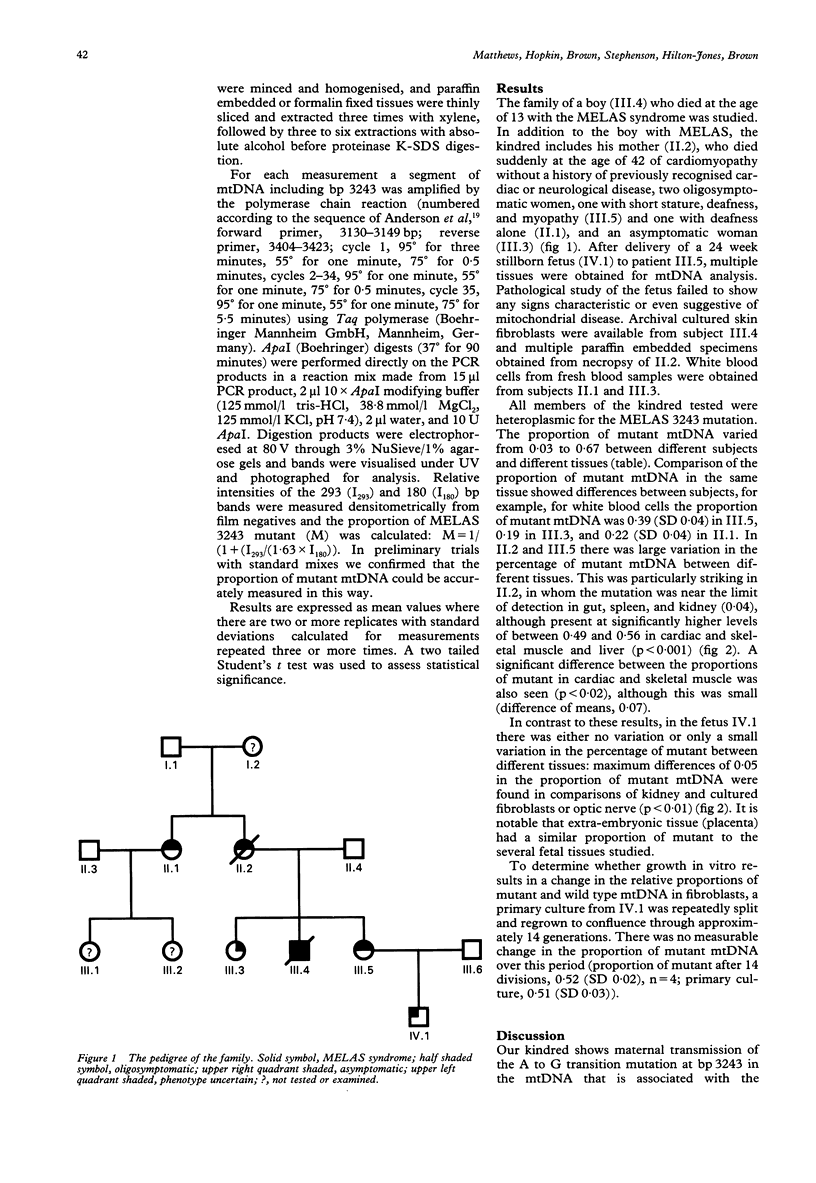
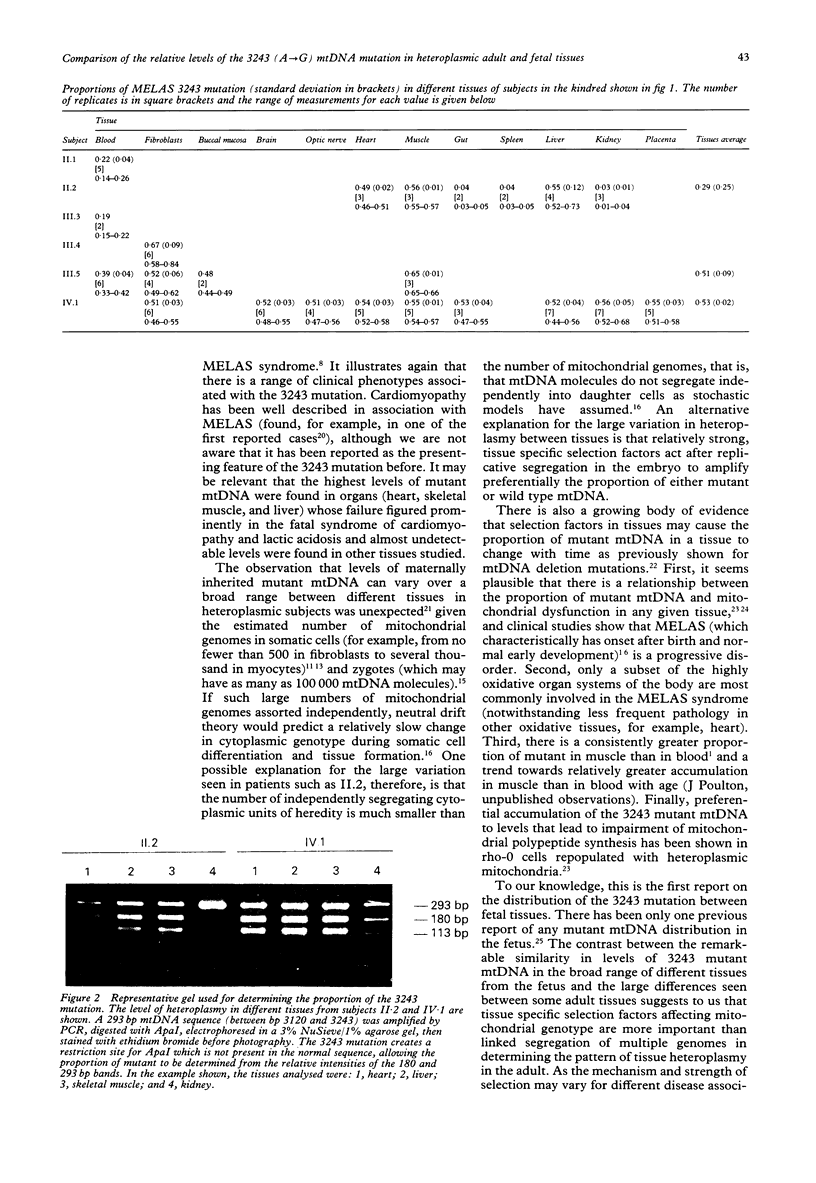
In this report, levels of the 3243 A to G mtDNA mutation associated with the mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) syndrome were measured in different heteroplasmic tissues of subjects in a kindred including adults with variable clinical phenotypes and a fetus. The relative proportions of mutant mtDNA varied widely (0.03 to 0.67) between identical tissues of the six different subjects and between different tissues of the same subjects. In the one adult for whom sufficient data were available there was an apparent correlation between the distribution of mutant mtDNA and clinical presentation. A woman without neurological symptoms who died prematurely with a cardiomyopathy and lactic acidosis had higher proportions of mutant in heart (0.49, SD 0.02), skeletal muscle (0.56, SD 0.01), and liver (0.55, SD 0.12) than in other tissues studied (for example, kidney, 0.03, SD 0.01). A strikingly different result was found in a 24 week old fetus in whom there was little variation in heteroplasmy in different tissues (average proportion of mutant mtDNA in six tissues, 0.53, SD 0.02). These observations add cardiomyopathy to the growing list of presenting features of the 3243 mtDNA mutation. The unique results from the fetus suggest also that selection pressures acting on either wild type or 3243 mutant mtDNA (rather than variation from replicative segregation of the heteroplasmic mtDNA) may be responsible primarily for the variable levels of 3243 mutant mtDNA in different heteroplasmic tissues of adults.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S., Bankier A. T., Barrell B. G., de Bruijn M. H., Coulson A. R., Drouin J., Eperon I. C., Nierlich D. P., Roe B. A., Sanger F. Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):457–465. doi: 10.1038/290457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkovic S. F., Carpenter S., Evans A., Karpati G., Shoubridge E. A., Andermann F., Meyer E., Tyler J. L., Diksic M., Arnold D. Myoclonus epilepsy and ragged-red fibres (MERRF). 1. A clinical, pathological, biochemical, magnetic resonance spectrographic and positron emission tomographic study. Brain. 1989 Oct;112(Pt 5):1231–1260. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.5.1231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomyn A., Martinuzzi A., Yoneda M., Daga A., Hurko O., Johns D., Lai S. T., Nonaka I., Angelini C., Attardi G. MELAS mutation in mtDNA binding site for transcription termination factor causes defects in protein synthesis and in respiration but no change in levels of upstream and downstream mature transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4221–4225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciafaloni E., Ricci E., Shanske S., Moraes C. T., Silvestri G., Hirano M., Simonetti S., Angelini C., Donati M. A., Garcia C. MELAS: clinical features, biochemistry, and molecular genetics. Ann Neurol. 1992 Apr;31(4):391–398. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuhara N., Tokiguchi S., Shirakawa K., Tsubaki T. Myoclonus epilepsy associated with ragged-red fibres (mitochondrial abnormalities ): disease entity or a syndrome? Light-and electron-microscopic studies of two cases and review of literature. J Neurol Sci. 1980 Jul;47(1):117–133. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(80)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto Y., Nonaka I., Horai S. A mutation in the tRNA(Leu)(UUR) gene associated with the MELAS subgroup of mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Nature. 1990 Dec 13;348(6302):651–653. doi: 10.1038/348651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding A. E., Holt I. J., Sweeney M. G., Brockington M., Davis M. B. Prenatal diagnosis of mitochondrial DNA8993 T----G disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Mar;50(3):629–633. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano M., Ricci E., Koenigsberger M. R., Defendini R., Pavlakis S. G., DeVivo D. C., DiMauro S., Rowland L. P. Melas: an original case and clinical criteria for diagnosis. Neuromuscul Disord. 1992;2(2):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0960-8966(92)90045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt I. J., Harding A. E., Petty R. K., Morgan-Hughes J. A. A new mitochondrial disease associated with mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Mar;46(3):428–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEARNS T. P., SAYRE G. P. Retinitis pigmentosa, external ophthalmophegia, and complete heart block: unusual syndrome with histologic study in one of two cases. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1958 Aug;60(2):280–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Ichihashi K., Ohta S., Nihei K., Kagawa Y., Yanagisawa M., Momoi M. Y. The mutant mitochondrial genes in mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) were selectively amplified through generations. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1992;15(5):803–808. doi: 10.1007/BF01800025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson N. G., Holme E., Kristiansson B., Oldfors A., Tulinius M. Progressive increase of the mutated mitochondrial DNA fraction in Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Pediatr Res. 1990 Aug;28(2):131–136. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199008000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lott M. T., Voljavec A. S., Wallace D. C. Variable genotype of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy patients. Am J Ophthalmol. 1990 Jun 15;109(6):625–631. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)72429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyabayashi S., Hanamizu H., Nakamura R., Endo H., Tada K. Defects of mitochondrial respiratory enzymes in cloned cells from MELAS fibroblasts. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1992;15(5):797–802. doi: 10.1007/BF01800024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moraes C. T., Schon E. A., DiMauro S., Miranda A. F. Heteroplasmy of mitochondrial genomes in clonal cultures from patients with Kearns-Sayre syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):765–771. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92499-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obermaier-Kusser B., Paetzke-Brunner I., Enter C., Müller-Höcker J., Zierz S., Ruitenbeek W., Gerbitz K. D. Respiratory chain activity in tissues from patients (MELAS) with a point mutation of the mitochondrial genome [tRNA(Leu(UUR))]. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 29;286(1-2):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80942-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlakis S. G., Phillips P. C., DiMauro S., De Vivo D. C., Rowland L. P. Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes: a distinctive clinical syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1984 Oct;16(4):481–488. doi: 10.1002/ana.410160409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. K., Harding A. E., Morgan-Hughes J. A. The clinical features of mitochondrial myopathy. Brain. 1986 Oct;109(Pt 5):915–938. doi: 10.1093/brain/109.5.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robin E. D., Wong R. Mitochondrial DNA molecules and virtual number of mitochondria per cell in mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Sep;136(3):507–513. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M., Kuroiwa T. Organization of multiple nucleoids and DNA molecules in mitochondria of a human cell. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Sep;196(1):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90467-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoffner J. M., Lott M. T., Lezza A. M., Seibel P., Ballinger S. W., Wallace D. C. Myoclonic epilepsy and ragged-red fiber disease (MERRF) is associated with a mitochondrial DNA tRNA(Lys) mutation. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):931–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90059-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C. Diseases of the mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1175–1212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner R. J., Rüegg J. C., Morano I. Counting target molecules by exponential polymerase chain reaction: copy number of mitochondrial DNA in rat tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):553–559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90517-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



