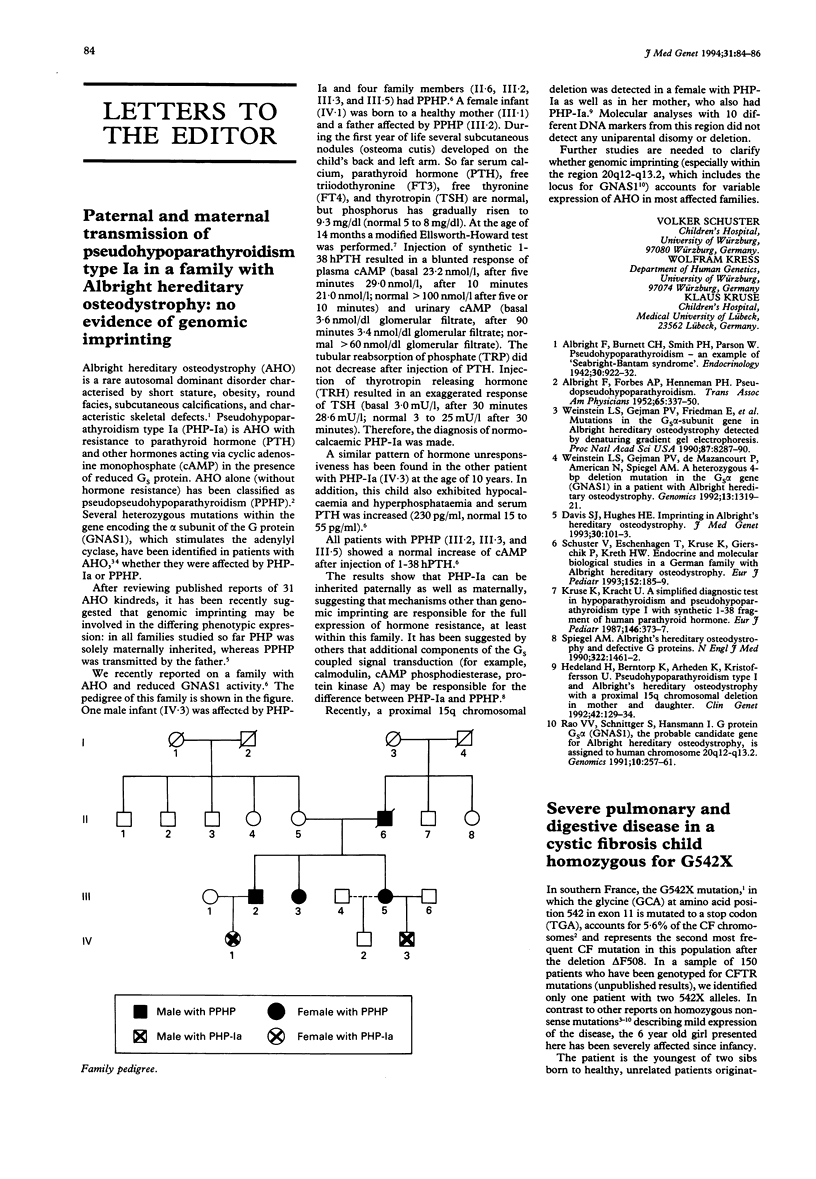
Full text
PDFPage 84
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBRIGHT F., FORBES A. P., HENNEMAN P. H. Pseudo-pseudohypoparathyroidism. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1952;65:337–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. J., Hughes H. E. Imprinting in Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy. J Med Genet. 1993 Feb;30(2):101–103. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedeland H., Berntorp K., Arheden K., Kristoffersson U. Pseudohypoparathyroidism type I and Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy with a proximal 15q chromosomal deletion in mother and daughter. Clin Genet. 1992 Sep;42(3):129–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1992.tb03224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse K., Kracht U. A simplified diagnostic test in hypoparathyroidism and pseudohypoparathyroidism type I with synthetic 1-38 fragment of human parathyroid hormone. Eur J Pediatr. 1987 Jul;146(4):373–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00444941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. V., Schnittger S., Hansmann I. G protein Gs alpha (GNAS 1), the probable candidate gene for Albright hereditary osteodystrophy, is assigned to human chromosome 20q12-q13.2. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90508-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V., Eschenhagen T., Kruse K., Gierschik P., Kreth H. W. Endocrine and molecular biological studies in a German family with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Mar;152(3):185–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01956140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy and defective G proteins. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 17;322(20):1461–1462. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005173222010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L. S., Gejman P. V., Friedman E., Kadowaki T., Collins R. M., Gershon E. S., Spiegel A. M. Mutations of the Gs alpha-subunit gene in Albright hereditary osteodystrophy detected by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8287–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein L. S., Gejman P. V., de Mazancourt P., American N., Spiegel A. M. A heterozygous 4-bp deletion mutation in the Gs alpha gene (GNAS1) in a patient with Albright hereditary osteodystrophy. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1319–1321. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


