Abstract
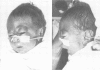
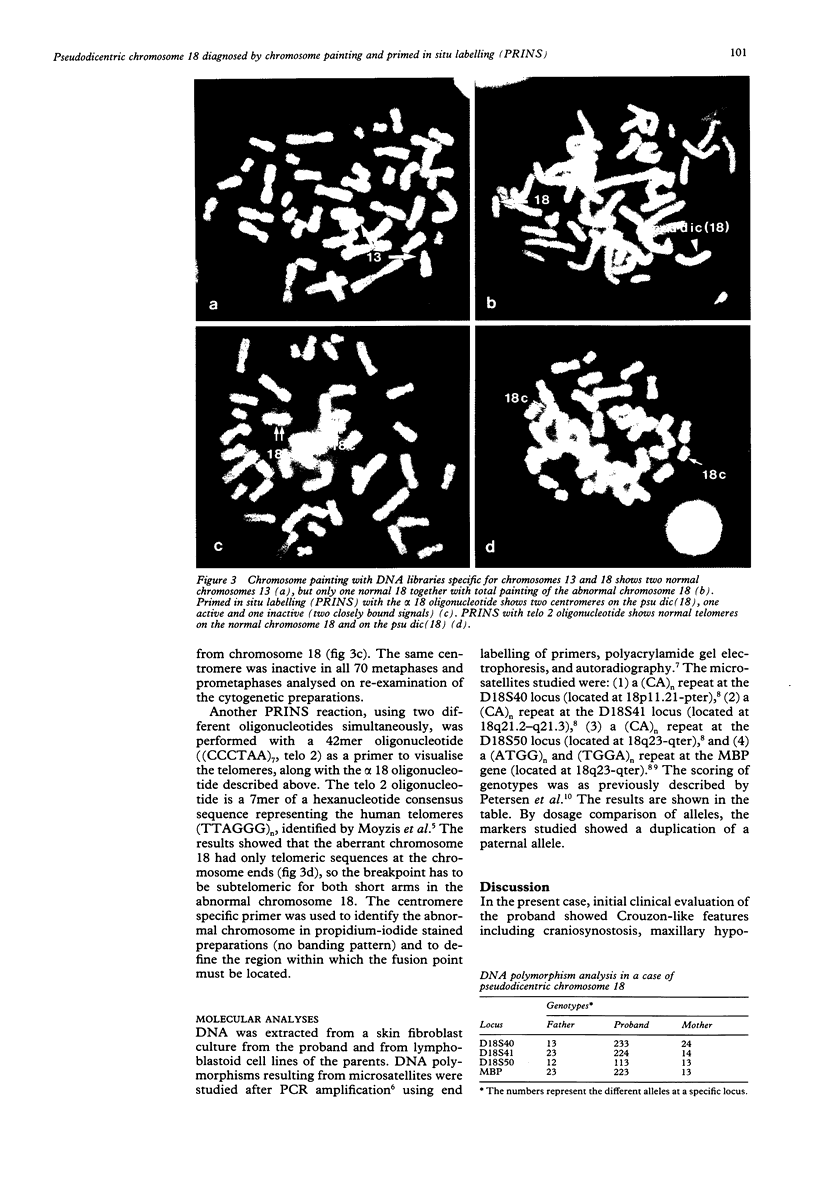
We report on a newborn white male infant with marked dysmorphic features and various congenital malformations. The initial clinical evaluation showed Crouzon-like features as well as some features of trisomy 18 syndrome and trisomy 13 syndrome. The results from conventional cytogenetic analysis showed a structurally abnormal chromosome replacing one normal chromosome 18, but only by applying molecular cytogenetic methods could the architecture of this abnormal chromosome be characterised clearly. The primed in situ labelling (PRINS) technique, using a newly synthesised alpha 18 oligonucleotide, showed the dicentric pattern and direct chromosome painting established the origin to be from chromosome 18. The combination of conventional cytogenetics and molecular cytogenetics showed the karyotype in the proband to be 45,XY,-14,-18,-21,+t(14;21),+psu dic(18) (qter-->cen-->p11.3: :p11.3-->psu cen-->qter). This was supported by molecular analysis using chromosome 18 specific DNA markers, which showed the paternal origin of the abnormal chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass H. N., Sparkes R. S., Miller A. A. Features of trisomy 18 and 18p- syndromes in an infant with 45,XY,i(18q). Clin Genet. 1979 Sep;16(3):163–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb00986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fioretti G., Stabile M., Pagano L., Rinaldi A., Rolando D., Trapassi C., de Tollis G., Ventruto V. A case of Edward's syndrome with pseudodicentric isochromosome 18: 46,XY,i dic(18) (p11::p11). Ann Genet. 1982;25(2):116–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froster-Iskenius U., Coerdt W., Rehder H., Schwinger E. Isochromosome 18q with karyotype 46,XX,i(18q). Cytogenetics and pathology. Clin Genet. 1984 Dec;26(6):549–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch J. E., Kølvraa S., Petersen K. B., Gregersen N., Bolund L. Oligonucleotide-priming methods for the chromosome-specific labelling of alpha satellite DNA in situ. Chromosoma. 1989 Oct;98(4):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00327311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch J., Hindkjaer J., Mogensen J., Kølvraa S., Bolund L. An improved method for chromosome-specific labeling of alpha satellite DNA in situ by using denatured double-stranded DNA probes as primers in a primed in situ labeling (PRINS) procedure. Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1991 Sep;8(6):171–178. doi: 10.1016/1050-3862(91)90058-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meguid N. A., Habibian R. Isodicentric chromosome 18 in an abnormal infant using chromosome specific DNA probe. Clin Genet. 1992 May;41(5):225–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyzis R. K., Buckingham J. M., Cram L. S., Dani M., Deaven L. L., Jones M. D., Meyne J., Ratliff R. L., Wu J. R. A highly conserved repetitive DNA sequence, (TTAGGG)n, present at the telomeres of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Schinzel A. A., Binkert F., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Collins F. A., Economou E. P., Antonarakis S. E. Use of short sequence repeat DNA polymorphisms after PCR amplification to detect the parental origin of the additional chromosome 21 in Down syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):65–71. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. B., Frantzen M., Antonarakis S. E., Warren A. C., Van Broeckhoven C., Chakravarti A., Cox T. K., Lund C., Olsen B., Poulsen H. Comparative study of microsatellite and cytogenetic markers for detecting the origin of the nondisjoined chromosome 21 in Down syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Sep;51(3):516–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Xiao H., Merril C. R. Tetranucleotide repeat polymorphism at the human myelin basic protein gene (MBP). Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Nov;1(8):658–658. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.8.658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Speer M. C., Luo Y., Rojas K., Overhauser J., Ott J., Gilliam T. C. A microsatellite genetic linkage map of human chromosome 18. Genomics. 1993 Jan;15(1):48–56. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]