Abstract
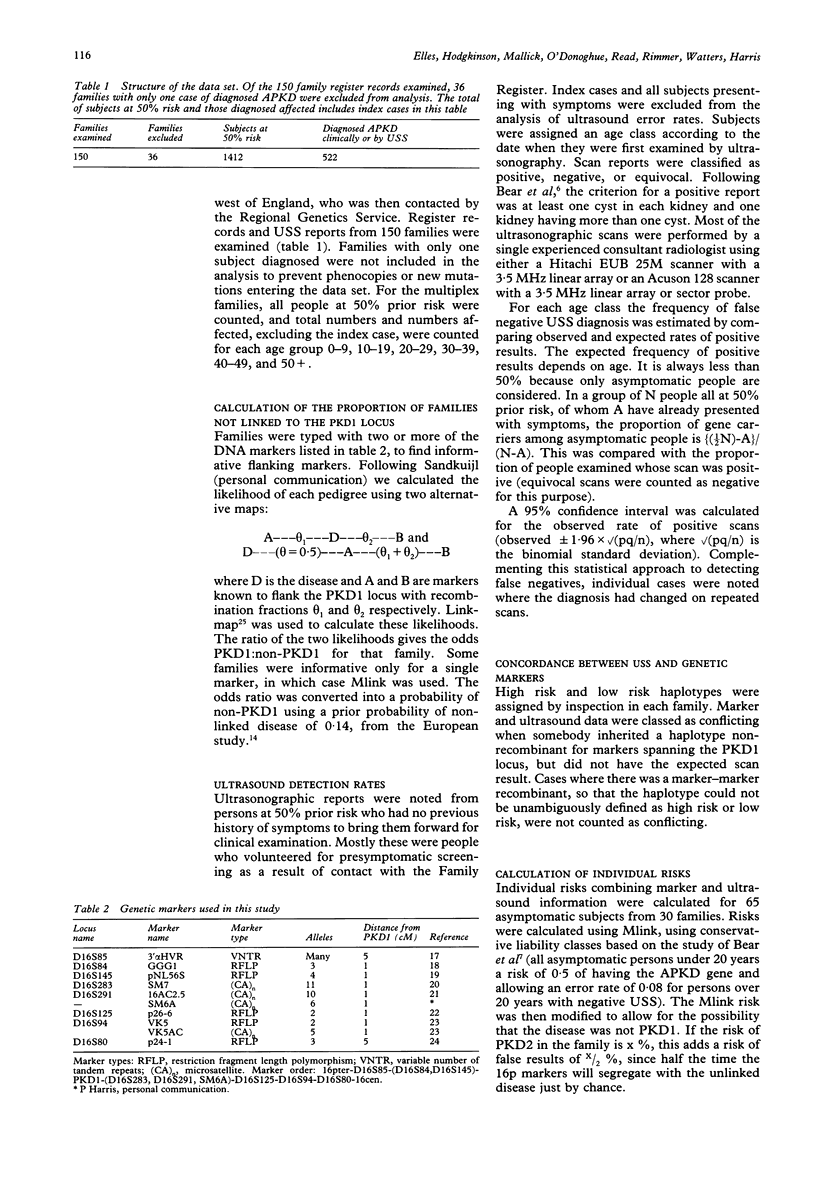
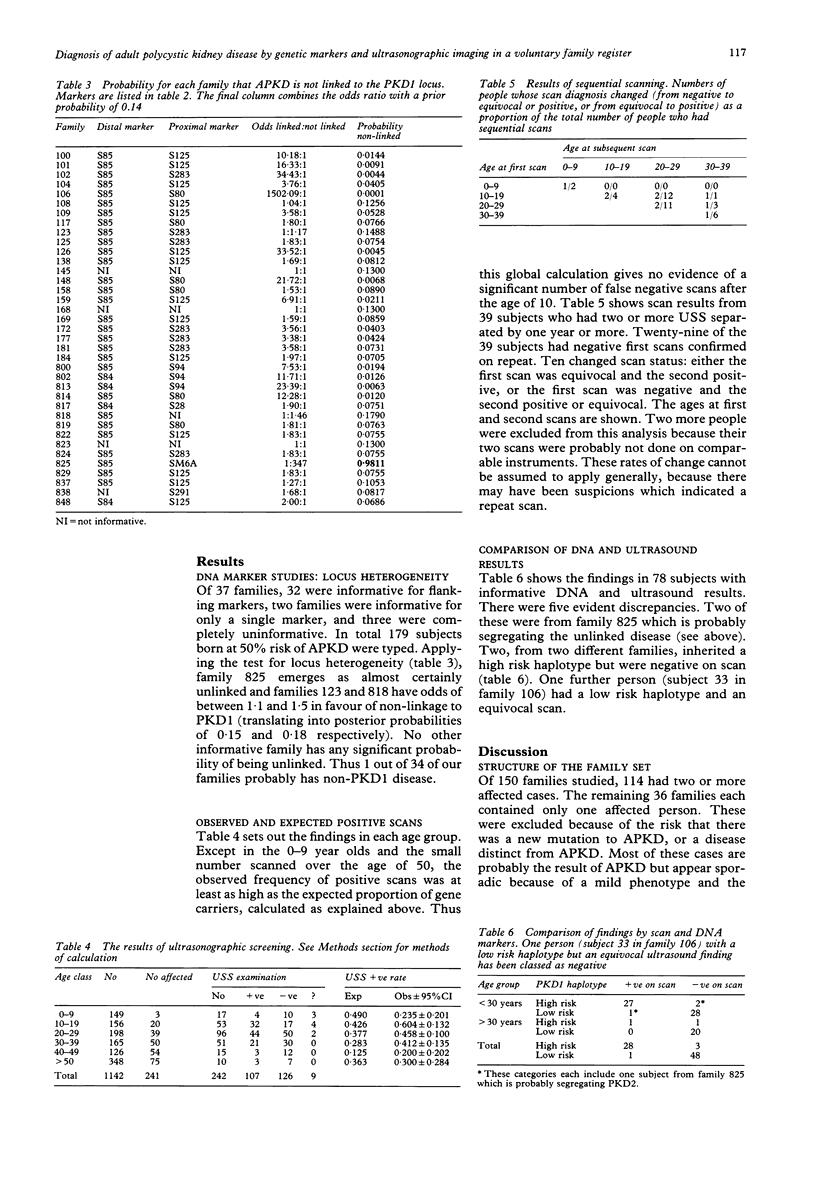
Diagnosis of autosomal dominant adult polycystic kidney disease (APKD) is possible by ultrasonographic scanning (USS) or by using DNA markers linked to the PKD1 locus. Ultrasonography is complicated by the age dependent penetrance of the gene and linkage studies are subject to recombination errors owing to meiotic crossing over and locus heterogeneity. This study draws on data collected from a voluntary family register of APKD over 10 years. Records of 150 families were examined, ultrasound reports were obtained from 242 people at 50% prior risk, and 37 families were typed for DNA markers. The fraction of APKD resulting from loci unlinked to PKD1 (designated PKD2 here) was calculated at 2.94% (upper confidence limit 8.62%). Some subjects who were negative on initial scan later gave a positive scan, but there was no example of a definite gene carrier aged over 30 giving a negative scan. In families large enough for linkage analysis, most people who were at 50% prior risk could be given a final risk below 5% or above 95%, by using combined ultrasound and DNA studies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bear J. C., McManamon P., Morgan J., Payne R. H., Lewis H., Gault M. H., Churchill D. N. Age at clinical onset and at ultrasonographic detection of adult polycystic kidney disease: data for genetic counselling. Am J Med Genet. 1984 May;18(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear J. C., Parfrey P. S., Morgan J. M., Martin C. J., Cramer B. C. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: new information for genetic counselling. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jun 1;43(3):548–553. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuning M. H., Reeders S. T., Brunner H., Ijdo J. W., Saris J. J., Verwest A., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Improved early diagnosis of adult polycystic kidney disease with flanking DNA markers. Lancet. 1987 Dec 12;2(8572):1359–1361. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91256-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuning M. H., Snijdewint F. G., Dauwerse J. G., Saris J. J., Bakker E., Pearson P. L., vanOmmen G. J. Two step procedure for early diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease with polymorphic DNA markers on both sides of the gene. J Med Genet. 1990 Oct;27(10):614–617. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.10.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breuning M. H., Snijdewint F. G., Smits J. R., Dauwerse J. G., Saris J. J., van Ommen G. J. A TaqI polymorphism identified by 26-6 (D16S125) proximal to the locus affecting adult polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) on chromosome 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3106–3106. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3106-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill D. N., Bear J. C., Morgan J., Payne R. H., McManamon P. J., Gault M. H. Prognosis of adult onset polycystic kidney disease re-evaluated. Kidney Int. 1984 Aug;26(2):190–193. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALGAARD O. Z. Bilateral polycystic disease of the kidneys; a follow-up of two hundred and eighty-four patients and their families. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1957;328:1–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies F., Coles G. A., Harper P. S., Williams A. J., Evans C., Cochlin D. Polycystic kidney disease re-evaluated: a population-based study. Q J Med. 1991 Jun;79(290):477–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elles R. G., Read A. P., Hodgkinson K. A., Watters A., Harris R. Recombination or heterogeneity: is there a second locus for adult polycystic kidney disease? J Med Genet. 1990 Jul;27(7):413–417. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.7.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino G. G., Barton N. J., Lamb J., Higgs D. R., Harris P., Xiao G. H., Scherer G., Nakamura Y., Reeders S. T. Identification of a locus which shows no genetic recombination with the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease gene on chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):925–933. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. C., Barton N. J., Higgs D. R., Reeders S. T., Wilkie A. O. A long-range restriction map between the alpha-globin complex and a marker closely linked to the polycystic kidney disease 1 (PKD1) locus. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):195–206. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90541-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. C., Thomas S., Ratcliffe P. J., Breuning M. H., Coto E., Lopez-Larrea C. Rapid genetic analysis of families with polycystic kidney disease 1 by means of a microsatellite marker. Lancet. 1991 Dec 14;338(8781):1484–1487. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92300-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkinson K. A., Kerzin-Storrar L., Watters E. A., Harris R. Adult polycystic kidney disease: knowledge, experience, and attitudes to prenatal diagnosis. J Med Genet. 1990 Sep;27(9):552–558. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.9.552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyland V. J., Suthers G. K., Friend K., MacKinnon R. N., Callen D. F., Breuning M. H., Keith T., Brown V. A., Phipps P., Sutherland G. R. Probe, VK5B, is located in the same interval as the autosomal dominant adult polycystic kidney disease locus, PKD1. Hum Genet. 1990 Feb;84(3):286–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00200577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarman A. P., Nicholls R. D., Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B., Higgs D. R. Molecular characterisation of a hypervariable region downstream of the human alpha-globin gene cluster. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1857–1863. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberling W. J., Fain P. R., Kenyon J. B., Goldgar D., Sujansky E., Gabow P. A. Linkage heterogeneity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 1988 Oct 6;319(14):913–918. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810063191405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfrey P. S., Bear J. C., Morgan J., Cramer B. C., McManamon P. J., Gault M. H., Churchill D. N., Singh M., Hewitt R., Somlo S. The diagnosis and prognosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 1990 Oct 18;323(16):1085–1090. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199010183231601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters D. J., Sandkuijl L. A. Genetic heterogeneity of polycystic kidney disease in Europe. Contrib Nephrol. 1992;97:128–139. doi: 10.1159/000421651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravine D., Walker R. G., Gibson R. N., Sheffield L. J., Kincaid-Smith P., Danks D. M. Treatable complications in undiagnosed cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 1991 Jan 19;337(8734):127–129. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90797-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T., Breuning M. H., Davies K. E., Nicholls R. D., Jarman A. P., Higgs D. R., Pearson P. L., Weatherall D. J. A highly polymorphic DNA marker linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):542–544. doi: 10.1038/317542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeders S. T., Keith T., Green P., Germino G. G., Barton N. J., Lehmann O. J., Brown V. A., Phipps P., Morgan J., Bear J. C. Regional localization of the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease locus. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romeo G., Devoto M., Costa G., Roncuzzi L., Catizone L., Zucchelli P., Germino G. G., Keith T., Weatherall D. J., Reeders S. T. A second genetic locus for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet. 1988 Jul 2;2(8601):8–11. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92943-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. D., Shen Y., Holman K., Sutherland G. R., Callen D. F., Richards R. I. Isolation and characterisation of (AC)n microsatellite genetic markers from human chromosome 16. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):402–408. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90260-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco A., Peissel B., Quaia P., Morandi R., Bovicelli L., Pignatti P. F. Prenatal diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease using flanking DNA markers and the polymerase chain reaction. Prenat Diagn. 1992 Jun;12(6):513–524. doi: 10.1002/pd.1970120606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. F., Teague P. W., Pound S. E., Pignatelli P. M., Macnicol A. M., Carothers A. D., De Mey R. J., Allan P. L., Watson M. L. A study of genetic linkage heterogeneity in 35 adult-onset polycystic kidney disease families. Hum Genet. 1993 Jan;90(5):569–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00217461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


