Abstract
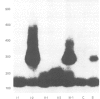
A new case of regression of the CTG copy number in the myotonic dystrophy allele was observed in a 7 year old boy. His affected father had an expanded allele of about 100 repeats in his lymphocyte DNA while the child showed a 60 repeat allele, of the same size as the present in the grandfather. Analysis of the father's sperm DNA allowed us to detect an expanded fragment of approximately the same size (62 repeats) as that present in the child's and grandfather's lymphocytes. This fragment was not detectable in the father's lymphocytes. Thus the regression is constitutive in the child, being already present in his father's germline. It is therefore likely that the regressed allele is present in all the tissues of the child, allowing a favourable prognosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barceló J. M., Mahadevan M. S., Tsilfidis C., MacKenzie A. E., Korneluk R. G. Intergenerational stability of the myotonic dystrophy protomutation. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jun;2(6):705–709. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.6.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. G., Jansen G., Nillesen W., Nelen M. R., de Die C. E., Höweler C. J., van Oost B. A., Wieringa B., Ropers H. H., Smeets H. J. Brief report: reverse mutation in myotonic dystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 18;328(7):476–480. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302183280705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H. G., Smeets H. J., Nillesen W., van Oost B. A., van den Biezenbos J. B., Joosten E. M., Pinckers A. J., Hamel B. C., Theeuwes A. G., Wieringa B. Myotonic dystrophy. Predictive value of normal results on clinical examination. Brain. 1991 Oct;114(Pt 5):2303–2311. doi: 10.1093/brain/114.5.2303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Fenwick R. G., Jr, King J., Rajnarayan S., Dunne P. W., Dubel J., Nasser G. A., Ashizawa T., de Jong P. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1256–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1546326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs R. C., Wood D. S. Criteria for establishing the validity of genetic recombination in myotonic dystrophy. Neurology. 1989 Mar;39(3):420–421. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.3.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S. Pre-symptomatic detection and genetic counselling in myotonic dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1973;4(2):134–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1973.tb01134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Sabourin L., Shutler G., Amemiya C., Jansen G., Neville C., Narang M., Barceló J., O'Hoy K. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1546325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulley J. C., Gedeon A. K., White S. J., Haan E. A., Richards R. I. Predictive diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy with flanking microsatellite markers. J Med Genet. 1991 Jul;28(7):448–452. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.7.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hoy K. L., Tsilfidis C., Mahadevan M. S., Neville C. E., Barceló J., Hunter A. G., Korneluk R. G. Reduction in size of the myotonic dystrophy trinucleotide repeat mutation during transmission. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):809–812. doi: 10.1126/science.8094260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelbourne P., Davies J., Buxton J., Anvret M., Blennow E., Bonduelle M., Schmedding E., Glass I., Lindenbaum R., Lane R. Direct diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy with a disease-specific DNA marker. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 18;328(7):471–475. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302183280704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelbourne P., Winqvist R., Kunert E., Davies J., Leisti J., Thiele H., Bachmann H., Buxton J., Williamson B., Johnson K. Unstable DNA may be responsible for the incomplete penetrance of the myotonic dystrophy phenotype. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Oct;1(7):467–473. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.7.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilfidis C., MacKenzie A. E., Mettler G., Barceló J., Korneluk R. G. Correlation between CTG trinucleotide repeat length and frequency of severe congenital myotonic dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1992 Jun;1(3):192–195. doi: 10.1038/ng0692-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]