Abstract
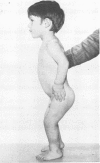
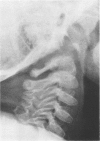
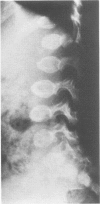
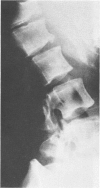
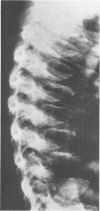
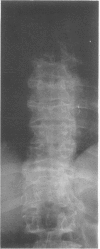
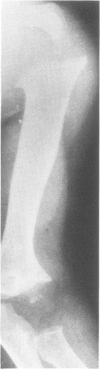
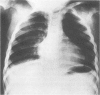
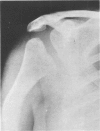
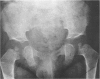
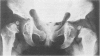
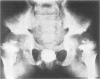
This survey reviews the diagnosis (predominantly radiological) of 32 cases of pseudoachondroplasia from 26 kindreds and illustrates the natural history and varying appearance of the disordered bone growth from infancy to adult life. In addition, an attempt has been made to detect phenotypic differences between autosomal dominant and recessive types (excluding isolated cases), analysing 10 kindreds of dominant inheritance (three in the current survey, seven from published reports) and six of recessive inheritance (three in the current survey, three from published reports). There appears to be no clinical or radiographical feature which clearly distinguishes them, but, using height as a criterion of severity, among those with autosomal recessive inheritance there was a disproportionate number of the most severely affected cases and there also appears to be very little intrafamilial variation. It is possible that pseudoachondroplasia can be subdivided into autosomal dominant mild and severe and autosomal recessive mild and severe, but full delineation must await elucidation of the basic defect at biochemical and molecular levels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crossan J. F., Wynne-Davies R., Fulford G. E. Bilateral failure of the capital femoral epiphysis: bilateral Perthes disease, multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, pseudoachondroplasia, and spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita and tarda. J Pediatr Orthop. 1983 Jul;3(3):297–301. doi: 10.1097/01241398-198307000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis N. R., Renton P. The severe recessive form of pseudoachondroplastic dysplasia. Pediatr Radiol. 1975 Jun 13;3(3):169–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01006905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORD N., SIL VERMAN F. N., KOZLOWSKI K. Spondylo-epiphyseal dysplasia (pseudo-achondroplastic type). Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1961 Sep;86:462–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine G., Gourguechon A., Smith M. La dysplasie pseudoachondroplasique à forme dominante. Une observation familiale. Presse Med. 1979 Dec 10;8(48):3961–3963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grether P., Vidales C., Carnevale A., López Marure E. Pseudoacondroplasia tipo II, presentación de una familia. Rev Invest Clin. 1983 Jul-Sep;35(3):241–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heselson N. G., Cremin B. J., Beighton P. Pseudoachondroplasia, a report of 13 cases. Br J Radiol. 1977 Jul;50(595):473–482. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-50-595-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton W. A., Hall J. G., Scott C. I., Pyeritz R. E., Rimoin D. L. Growth curves for height for diastrophic dysplasia, spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita, and pseudoachondroplasia. Am J Dis Child. 1982 Apr;136(4):316–319. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970400034010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski K. Pseudoachondroplastic dysplasia (Maroteaux-Lamy): a critical analysis. Australas Radiol. 1976 Sep;20(3):255–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1673.1976.tb02033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman R. S., Rimoin D. L., Hall J. G., Kozlowski K., Langer L. O., Jr, Scott C. I., Jr, Spranger J. Difficulties in the classification of the epiphyseal dysplasias. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(6):231–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindstrom J. A. Type III psuedoachondroplastic dysplasia (dominant inheritance). Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1974;10(12):368–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAROTEAUX P., LAMY M. Les formes pseudo-achondroplasiques des dysplasies spondylo-epiphysaires. Presse Med. 1959 Feb 25;67(10):383–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux P., Stanescu R., Stanescu V., Fontaine G. The mild form of pseudoachondroplasia. Identity of the morphological and biochemical alterations of growth cartilage with those of typical pseudoachondroplasia. Eur J Pediatr. 1980 May;133(3):227–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00496081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoin D. L. Variable expressivity in the skeletal dysplasias. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1979;15(5B):91–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu V., Maroteaux P., Stanescu R. The biochemical defect of pseudoachondroplasia. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 May;138(3):221–225. doi: 10.1007/BF00441206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöss H., Pesch H. J., Spranger J. Different morphologic findings and genetic heterogeneity in pseudoachondroplasia: light- and electron-microscopic observations in iliac crest bioptic material. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1982;104:379–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. D., Moore J. R. Severe pseudoachondroplasia with parental consanguinity. J Med Genet. 1985 Apr;22(2):150–153. doi: 10.1136/jmg.22.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]