Abstract
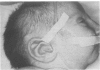
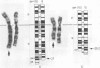
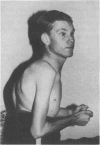
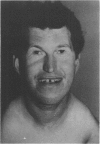
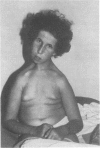
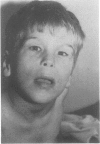
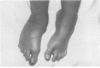
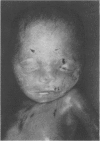
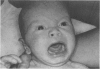
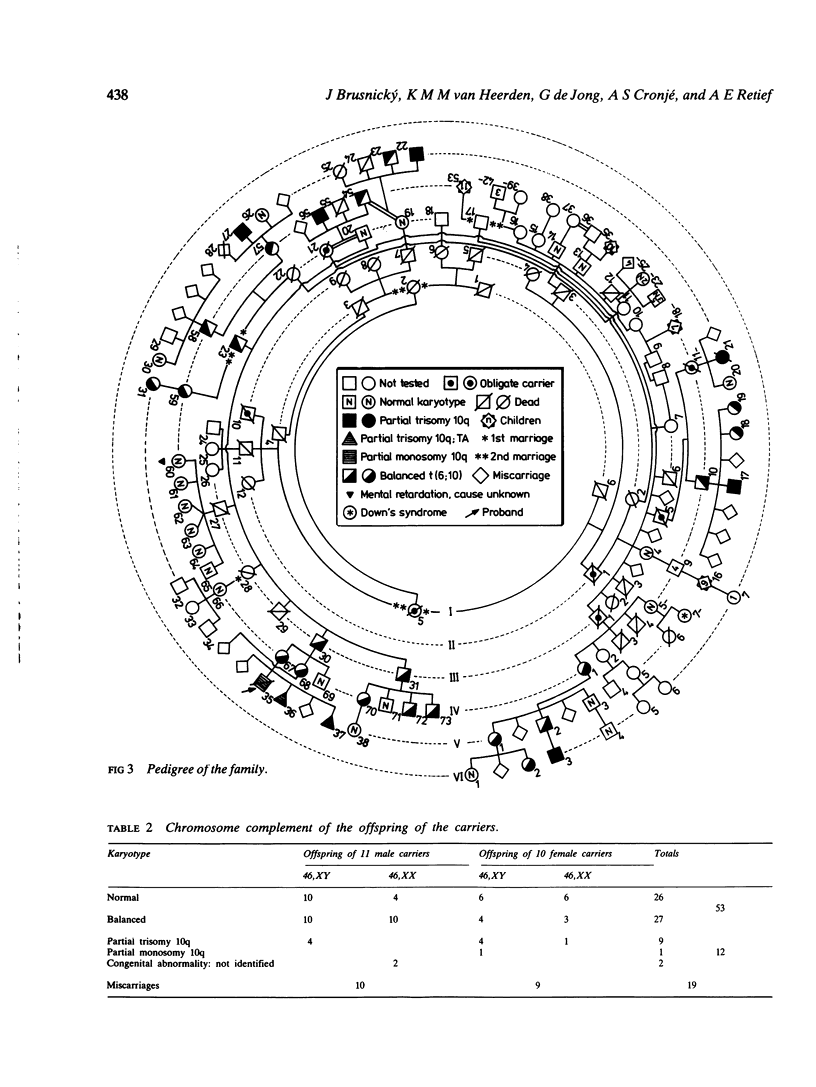
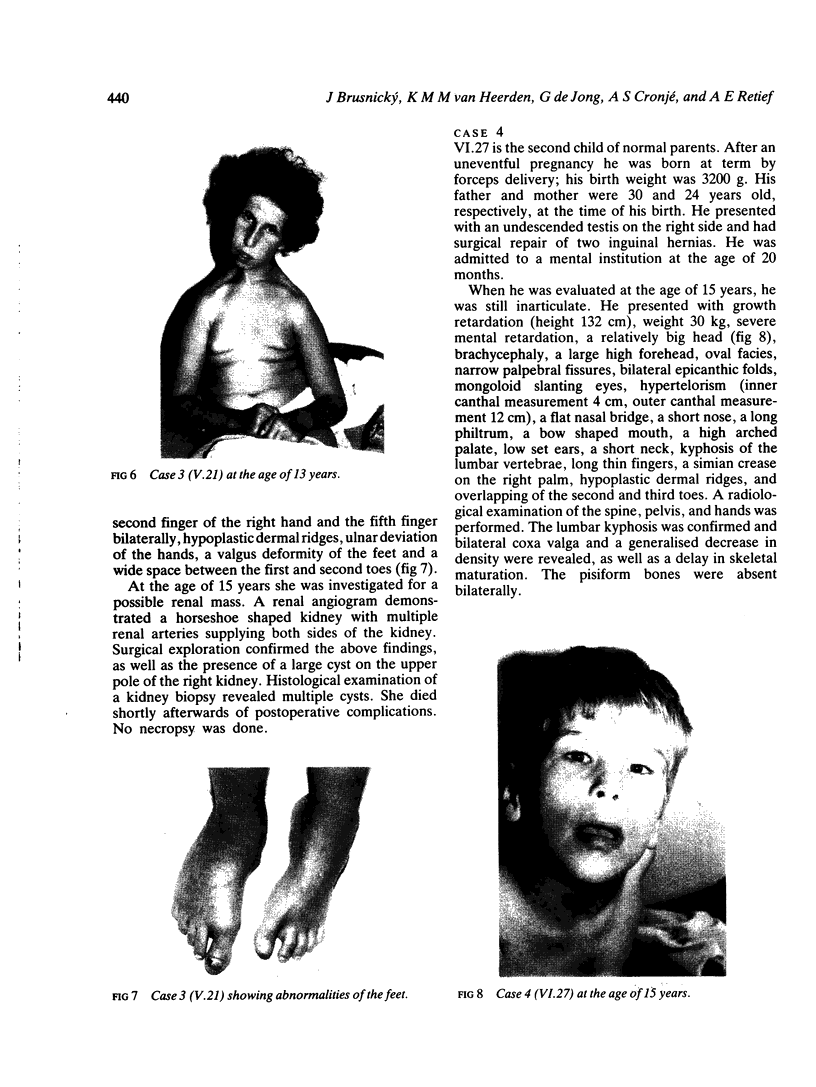
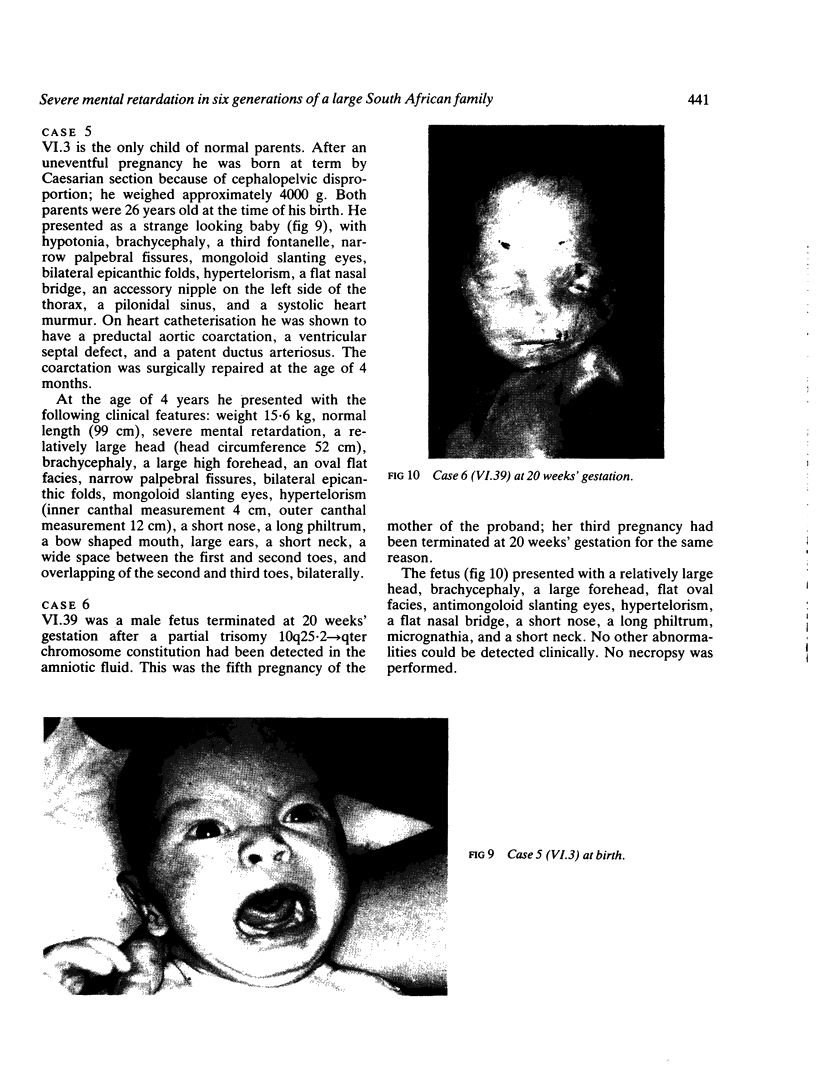
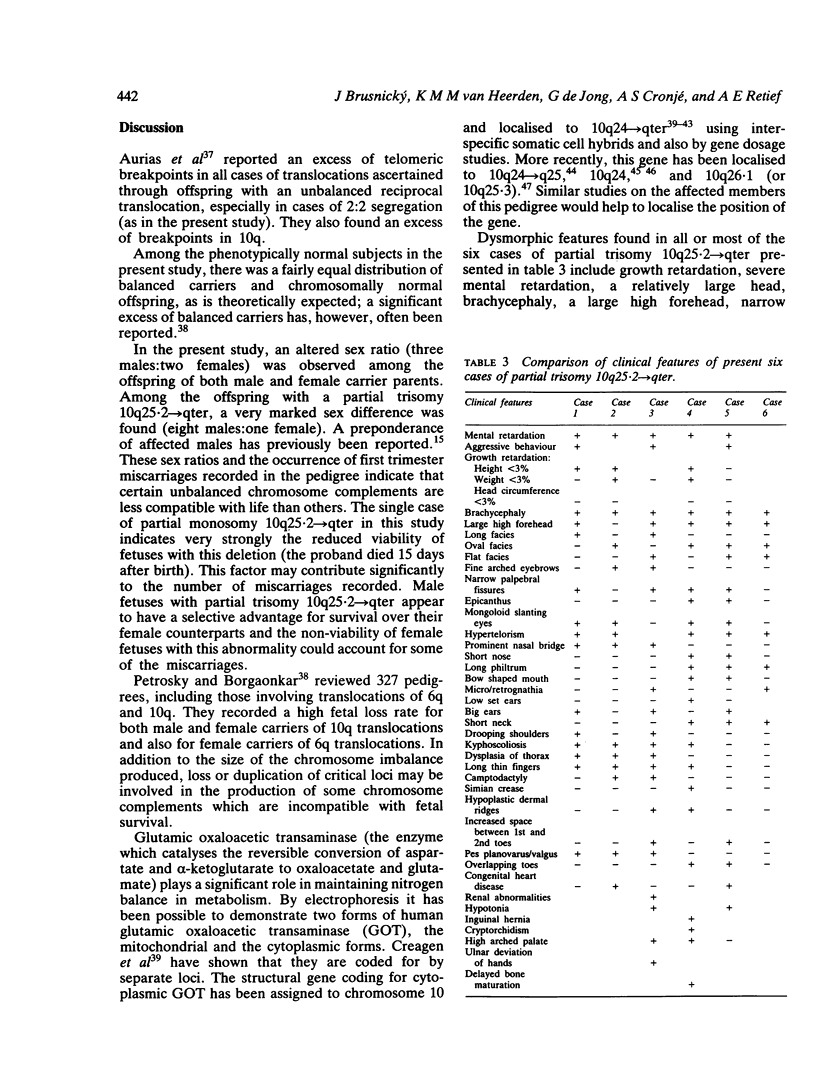
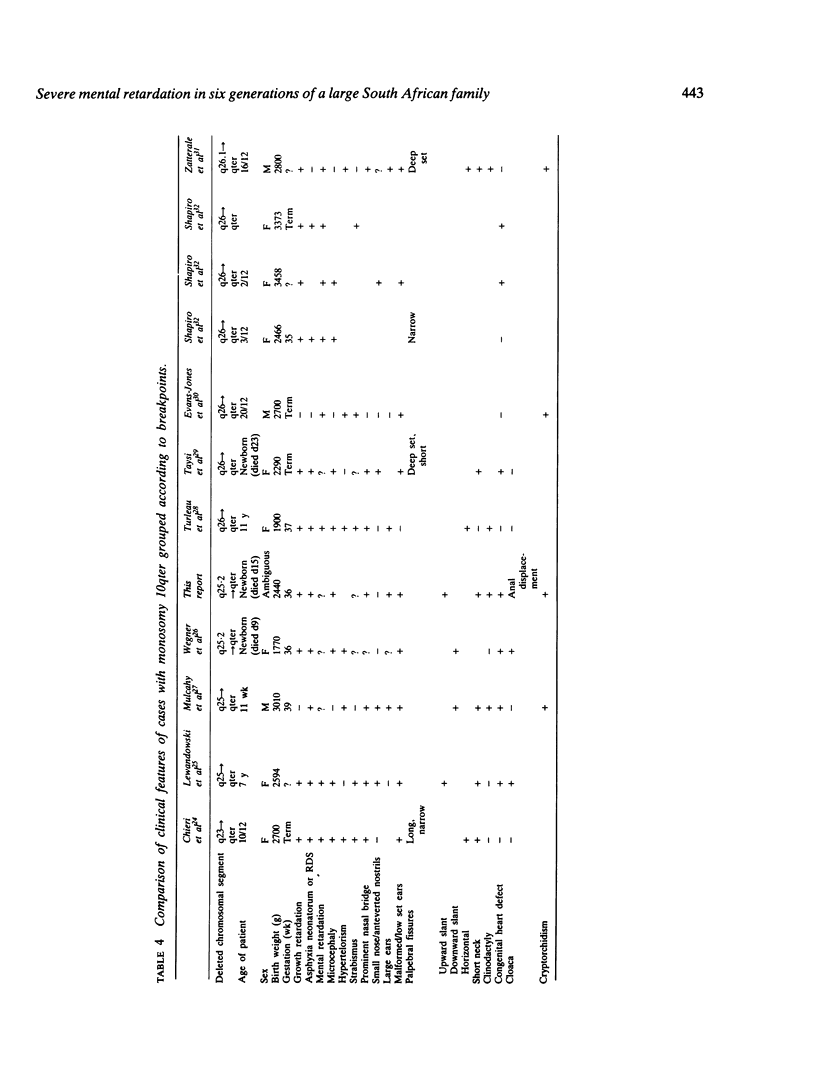
Partial monosomy 10q25.2----qter, detected in a newborn baby with multiple congenital abnormalities, was found to be derived from a balanced maternal translocation t(6;10)(q27;q25.2). The pedigree of six generations of the family is presented. In an extensive cytogenetic study of this family, the chromosome complements of 57 subjects, potentially capable of carrying some form of this translocation, were analysed. A total of 14 male carriers (four obligatory) and 14 female carriers (three obligatory) of this translocation was found. Partial trisomy 10q25.2----qter, associated with severe mental retardation, occurred in nine cases, eight males and one female. Two of these eight males were detected prenatally and subsequently therapeutically aborted. The phenotypes of the family members with partial trisomy 10q25.2----qter are compared to each other and to those reported in publications. No further cases of partial monosomy 10q25.2----qter were encountered. A review of published reports of partial monosomy and partial trisomy 10qter is given. The apparent absence of infertility, the occurrence of many first trimester miscarriages, and the marked sex ratio are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken D. A., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Gene dosage evidence for the regional assignment of the GOTS structural gene locus to 10q24 leads to 10q25. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):468–471. doi: 10.1159/000130999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aurias A., Prieur M., Dutrillaux B., Lejeune J. Systematic analysis of 95 reciprocal translocations of autosomes. Hum Genet. 1978 Dec 29;45(3):259–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00278725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back E., Kosmützky J., Schuwald A., Hameister H. Two cases of partial trisomy 10q in the same family caused by parental direct insertion [ins. (15;10) (q15;q24q26)]. Ann Genet. 1979;22(4):195–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger R., Derre J., Murawsky M., Amiel-Tison C. Trisomie 10 q partielle de novo. J Genet Hum. 1976 Dec;24(4):261–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Johansson C. Differential binding of alkylating fluorochromes in human chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Jun;60(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90523-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chieri P., Iölster N. Monosomy 10qter due to a balanced maternal translocation: t(10;8)(q23;p23). Clin Genet. 1983 Aug;24(2):147–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb02226.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creagan R., Tischfield J., McMorris F. A., Chen S., Hirschi M., Chen T. R., Ricciuti F., Ruddle F. H. Assignment of the genes for human peptidase A to chromosome 18 and cytoplasmic glutamic oxaloacetate transaminase to chromosome 10 using somatic-cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1973;12(3):187–198. doi: 10.1159/000130454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Laurent C., Bernasconi S., Lejeune J. La trisomie 10q24leads to10qter. Ann Genet. 1975 Dec;18(4):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutrillaux B., Laurent C., Robert J. M., Lejeune J. Inversion péricentrique, inv(10), chez la mére et aneusomie de recombinaison, inv(10),rEC(10), chez son fils. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1973;12(4):245–253. doi: 10.1159/000130460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans-Jones G., Walker S., Howard P. J. A further case of monosomy 10qter. Clin Genet. 1983 Sep;24(3):216–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb02242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraisse J., Lauras B., La Selve A., Freycon F. Deux nouveaux cas de trisomie 10q24 à 10qter chez deux sceurs par translocation paternelle t(9;10) (q34;q24). Ann Genet. 1977 Jun;20(2):128–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U. Quinacrine mustard fluorescence of human chromosomes: characterization of unusual translocations. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Mar;24(2):189–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellkuhl B., Grzeschik K. H. Regional mapping of human chromosome 10: assignment of the gene for cytoplasmic glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase to 10q24 leads to qter. Hum Genet. 1976 Jul 27;33(2):109–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00281884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junien C., Despoisse S., Turleau C., de Grouchy J., Bucher T., Fundele R. Assignment of phosphoglycerate mutase (PGAMA) to human chromosome 10. Regional mapping of GOT1 and PGAMA to subbands 10q26.1 (or q25.3). Ann Genet. 1982;25(1):25–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klep-de Pater J. M., Bijlsma J. B., de France H. F., Leschot N. J., Duijndam-van den Berge M., van Hemel J. O. Partial trisomy 10q: a recognizable syndrome. Hum Genet. 1979 Jan 19;46(1):29–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00278899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroyer S., Niebuhr E. Partial trisomy 10q occurring in a family with a reciprocal translocation t(10;18)(q25;q23). Ann Genet. 1975 Mar;18(1):50–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent C., Bovier-Lapierre M., Dutrillaux B. Trisomie 10 partielle par translocation familiale t(1;10)(q44;q22. Humangenetik. 1973;18(4):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00291129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski R. C., Jr, Kukolich M. K., Sears J. W., Mankinen C. B. Partial deletion 10q. Hum Genet. 1978 Jun 27;42(3):339–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00291317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miró R., Templado C., Ponsá M., Serradell J., Marina S., Egozcue J. Balanced translocation (10;13) in a father, ascertained through the study of meiosis in semen, and partial trisomy 10q in his son. Characterization of the region responsible for the partial trisomy 10q syndrome. Hum Genet. 1980 Feb;53(2):179–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00273492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Fuenmayor H., Zackai E. H., Mellman W. J., Aronson M. Familial partial trisomy of the long arm of chromosome 10 (q24-26). Pediatrics. 1975 Nov;56(5):756–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy M. T., Jenkyn J., Masters P. L. A familial 10/13 translocation: partial trisomy C in an infant associated with familial 10/13 translocation. Clin Genet. 1974;6(5):335–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb02256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy M. T., Pemberton P. J., Thompson E., Watson M. Is there a monosomy 10qter syndrome? Clin Genet. 1982 Jan;21(1):33–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb02076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrosky D. L., Borgaonkar D. S. Segregation analysis in reciprocal translocation carriers. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Sep;19(1):137–159. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320190115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux C., Taillemite J. L., Baheux-Morlier G. Trisomie partielle 10q par translocation familiale t(10q-; 22p-plus) Ann Genet. 1974 Mar;17(1):59–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. D., Hansen K. L., Pasztor L. M., DiLiberti J. H., Jorgenson R. J., Young R. S., Moore C. M. Deletions of the long arm of chromosome 10. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jan;20(1):181–196. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sills J. A., Buckton K. E., Raeburn J. A. Severe mental retardation in a boy with partial trisomy 10q and partial monosomy 2q. J Med Genet. 1976 Dec;13(6):507–510. doi: 10.1136/jmg.13.6.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taysi K., Strauss A. W., Yang V., Padmalatha C., Marshall R. E. Terminal deletion of the long arm of chromosome 10 : q26 to qter. Case report and review of literature. Ann Genet. 1982;25(3):141–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turleau C., de Grouchy J., Ponsot G., Bouygues D. Monosomy 10qter. Hum Genet. 1979 Apr 5;47(3):233–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00321014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner R. D., Kunze J., Paust H. Monosomy 10qter due to a balanced familial translocation: t(10;16)(q25.2;q24). Clin Genet. 1981 Feb;19(2):130–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb00683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. S., Fidone G. S., Reider-Garcia P. A., Hansen K. L., McCombs J. L., Moore C. M. Deletions of the long arm of chromosome 6: two new cases and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jan;20(1):21–29. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J., Sanchez O. A new syndrome resulting from partial trisomy for the distal third of the long arm of chromosome 10. J Pediatr. 1974 Apr;84(4):567–570. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80683-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackai E., Mellman W., Aronson M., Miller R. C., Greene A. E., Coriell L. L. A (10;17) translocation, unbalanced, 46 chromosomes. Repository identification No. GM-217. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):90–91. doi: 10.1159/000130327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatterale A., Pagano L., Fioretti G., Caniglia M., Festa B., Renda S., Rinaldi M. M., Ventruto V. Clinical features of monosomy 10qter. Ann Genet. 1983;26(2):106–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vooren M. J., Planteydt H. T., Hagemeijer A., Peters-Slough M. F., Timmerman M. J. Familial balanced insertion (5;10) and monosomy and trisomy (10) (q24.2----q25.3). Clin Genet. 1984 Jan;25(1):52–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb00462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]