Abstract
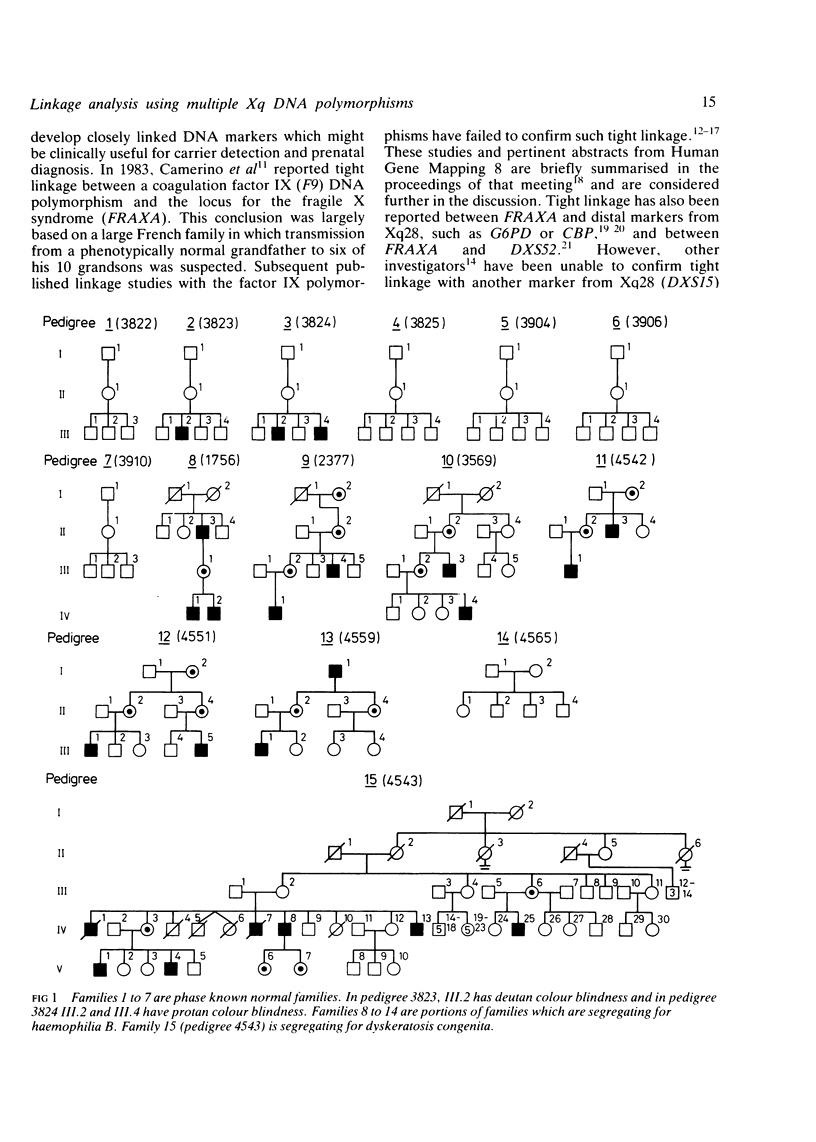
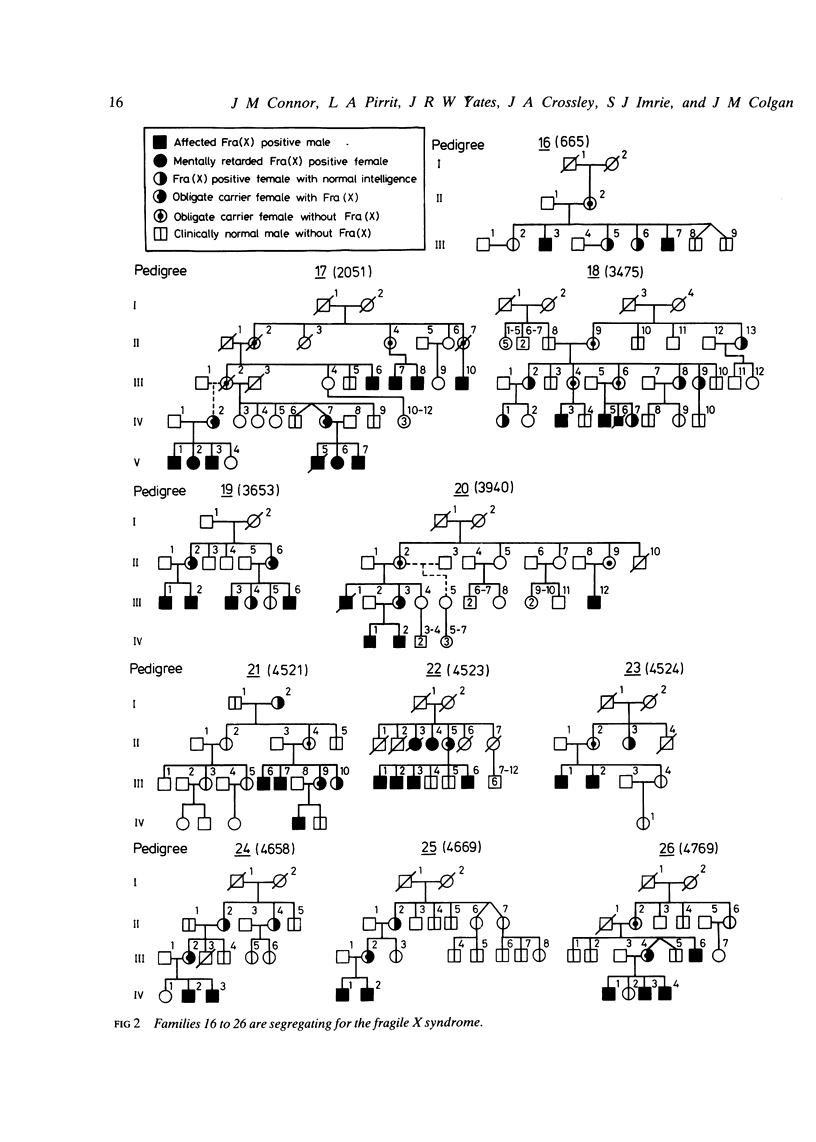
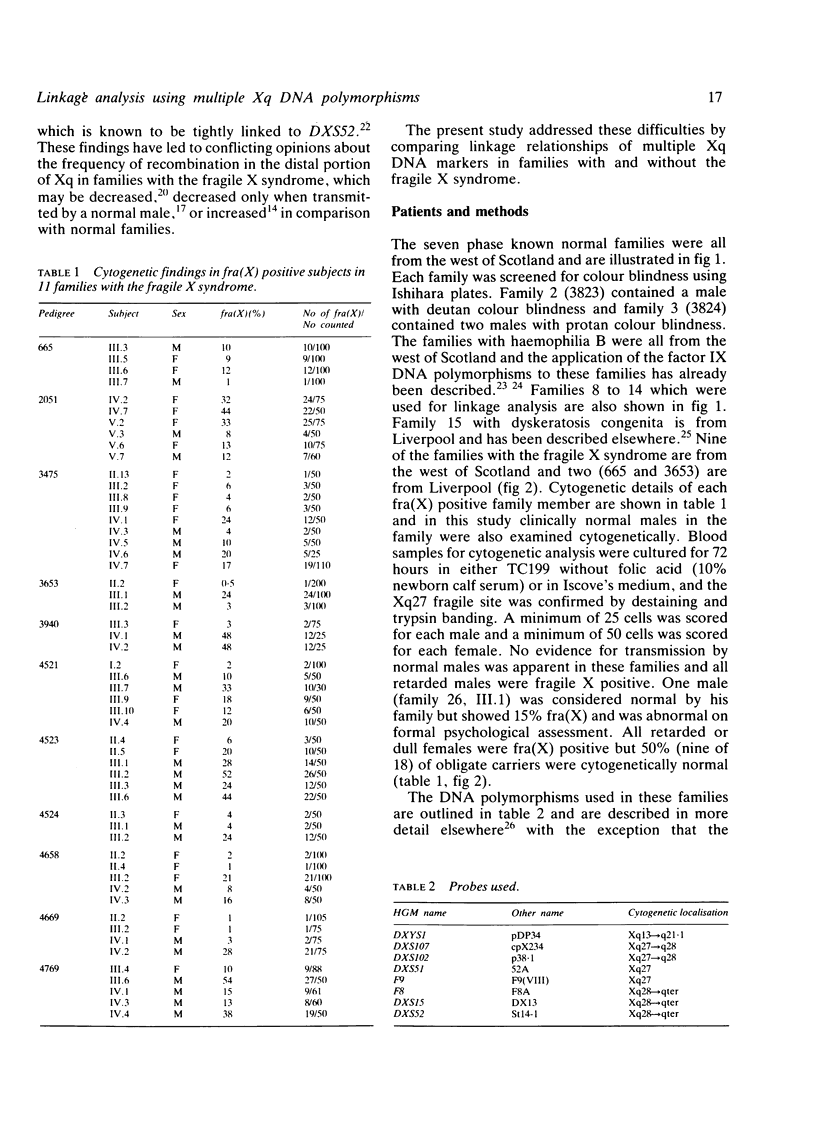
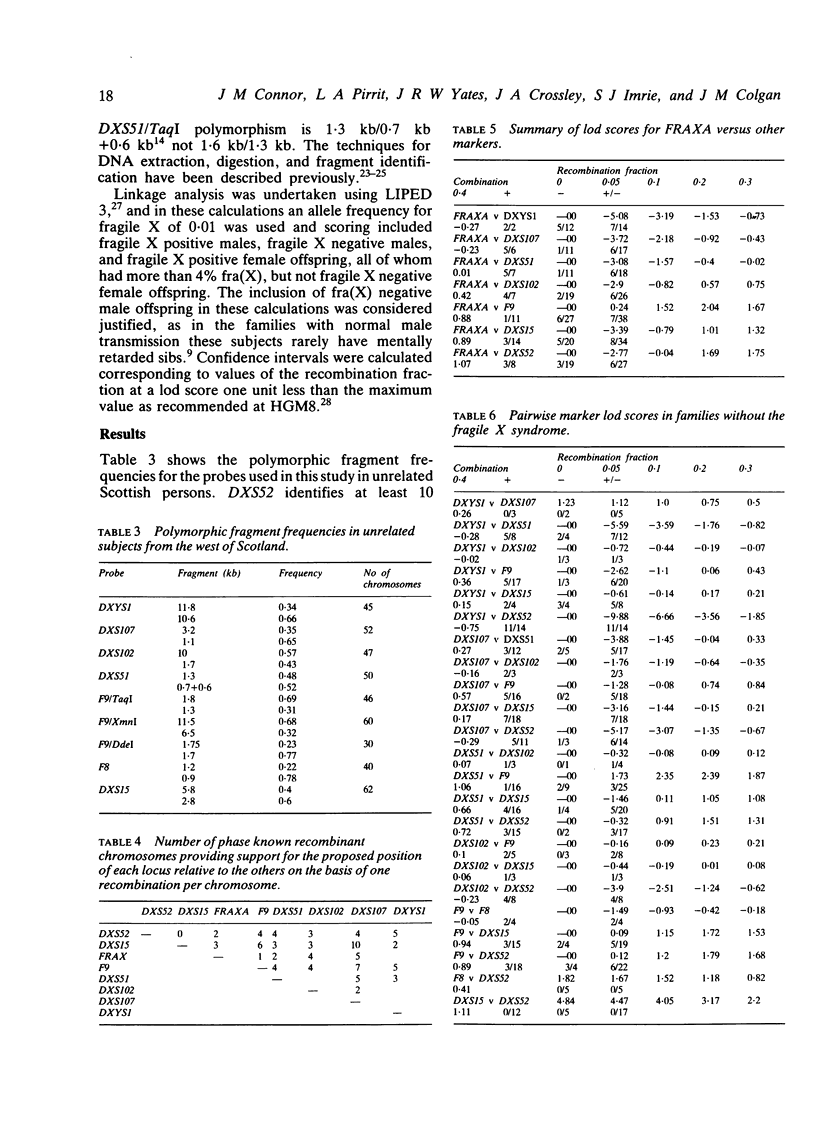
Multipoint linkage analysis was undertaken with eight Xq cloned DNA sequences which identify one or more restriction fragment length polymorphisms in 26 families. These families comprise seven phase known normal families with three or more males in the third generation, seven families segregating for haemophilia B, one large family with dyskeratosis congenita, and 11 families with the fragile X syndrome. Phase known meioses informative for three or more loci supported the order centromere--DXYS1--DXS107--DXS102, DXS51--F9--FRAXA--DXS15, DXS52, F8--Xqter in each group of families studied. One of the normal families was segregating for protan colour blindness and showed a phase known recombination which would support the order centromere--F9--DXS52--CBP--Xqter. With the exception of DXYS1, all of these sequences have been localised to Xq27----qter by in situ hybridisation or hybridisation to Xq fragment panels, and on this basis should lie within 20 cM of one another. No recombination was observed between the sequences localised to Xq28, namely DXS52, F8, and DXS15 (between DXS15 and DXS52 Z = 12.25 at theta = 0 with confidence limits of 0 to 5 cM). However, an excess of recombination was apparent in the region of FRAXA with maximal lod scores as follows: F9 versus FRAXA (Z = 2.05, theta = 0.19), DXS52 versus FRAXA (Z = 1.85, theta = 0.26), and DXS15 versus FRAXA (Z = 1.33, theta = 0.27). No consistent differences were observed in the frequency of recombination when families with the fragile X syndrome were compared with normal families or families segregating for other X linked conditions. These results are compared with other published work and support the conclusion that although measurable linkage exists between these flanking markers and FRAXA, the intervals as measured by the frequency of meiotic recombination will seriously limit their clinical usefulness.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Jenkins E. C. Genetic linkage heterogeneity in the fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1985;71(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00295659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Jaye M., Mandel J. L. Close linkage of fragile X-mental retardation syndrome to haemophilia B and transmission through a normal male. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):701–704. doi: 10.1038/306701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., George D., Filby G., Halliday J. L., Leversha M., Webb G., Danks D. M. Linkage analysis of X-linked mental retardation with and without fragile-X using factor IX gene probe. Lancet. 1984 Aug 11;2(8398):349–349. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92715-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conneally P. M., Edwards J. H., Kidd K. K., Lalouel J. M., Morton N. E., Ott J., White R. Report of the Committee on Methods of Linkage Analysis and Reporting. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):356–359. doi: 10.1159/000132186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. M., Gatherer D., Gray F. C., Pirrit L. A., Affara N. A. Assignment of the gene for dyskeratosis congenita to Xq28. Hum Genet. 1986 Apr;72(4):348–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00290963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. M., Pettigrew A. F., Hann I. M., Forbes C. D., Lowe G. D., Affara N. A. Application of an intragenic genomic probe to genetic counselling for haemophilia B in the west of Scotland. J Med Genet. 1985 Dec;22(6):441–446. doi: 10.1136/jmg.22.6.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. M., Pettigrew A. F., Shiach C., Hann I. M., Lowe G. D., Forbes C. D. Application of three intragenic DNA polymorphisms for carrier detection in haemophilia B. J Med Genet. 1986 Aug;23(4):300–309. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.4.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Veenema H., McGlade S., Harper K., Tommerup N., Nielsen K. B., Mikkelsen M., Beighton P. Linkage studies of X-linked mental retardation: high frequency of recombination in the telomeric region of the human X chromosome (fragile site/linkage/recombination/X chromosome). Hum Genet. 1985;70(3):249–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00273451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Arce M. A., Kearns A. The fragile X syndrome: the patients and their chromosomes. J Med Genet. 1984 Apr;21(2):84–91. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.2.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Davies K., Hartley D., Mandel J. L., Camerino G., Williamson R., White R. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome by using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi G., Rinaldi A., Archidiacono N., Rocchi M., Balazs I., Siniscalco M. Brief report: linkage between G6PD and fragile-X syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1983 May;15(1):113–119. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320150115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippi G., Rinaldi A., Palmarino R., Seravalli E., Siniscalco M. Linkage disequilibrium for two X-linked genes in Sardinia and its bearing on the statistical mapping of the human X chromosome. Genetics. 1977 May;86(1):199–212. doi: 10.1093/genetics/86.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster-Gibson C. J., Mulligan L. M., Partington M. W., Simpson N. E., Holden J. J., White B. N. The genetic distance between the coagulation factor IX gene and the locus for the fragile X syndrome: clinical implications. J Neurogenet. 1985 Jun;2(3):231–237. doi: 10.3109/01677068509100152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froster-Iskenius U., Felsch G., Schirren C., Schwinger E. Screening for fra(X)(q) in a population of mentally retarded males. Hum Genet. 1983;63(2):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00291535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P. The fragile X syndrome. A study of 83 families. Clin Genet. 1984 Dec;26(6):497–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):296–352. doi: 10.1159/000132178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison C. J., Jack E. M., Allen T. D., Harris R. The fragile X: a scanning electron microscope study. J Med Genet. 1983 Aug;20(4):280–285. doi: 10.1136/jmg.20.4.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley D. A., Davies K. E., Drayna D., White R. L., Williamson R. A cytological map of the human X chromosome--evidence for non-random recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5277–5285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janco R. L., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Orlando P., Davies K. E., Old J., Antonarakis S. E. Carrier testing strategy in haemophilia A. Lancet. 1986 Jan 18;1(8473):148–149. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keats B. Genetic mapping: X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1983;64(1):28–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00289474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawczun M. S., Jenkins E. C., Brown W. T. Analysis of the fragile-X chromosome: localization and detection of the fragile site in high resolution preparations. Hum Genet. 1985;69(3):209–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00293026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie D. A., Palmer R. W., Hultén M. A. Chiasma derived genetic lengths and recombination fractions: chromosomes 2 and 9. Ann Hum Genet. 1982 Jul;46(Pt 3):233–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1982.tb00715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Baeteman M. A., Heilig R., Oberlé I., Davies K., Mandel J. L., Mattei J. F. Localization by in situ hybridization of the coagulation factor IX gene and of two polymorphic DNA probes with respect to the fragile X site. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):327–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00291650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz J. M., Sutherland G. R. Conference report: International Workshop on the fragile X and X-linked mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Jan;17(1):5–94. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320170103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pembrey M. E., Winter R. M., Davies K. E. A premutation that generates a defect at crossing over explains the inheritance of fragile X mental retardation. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Aug;21(4):709–717. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320210413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purrello M., Alhadeff B., Esposito D., Szabo P., Rocchi M., Truett M., Masiarz F., Siniscalco M. The human genes for hemophilia A and hemophilia B flank the X chromosome fragile site at Xq27.3. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):725–729. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03689.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purrello M., Nussbaum R., Rinaldi A., Filippi G., Traccis S., Latte B., Siniscalco M. Old and new genetics help ordering loci at the telomere of the human X-chromosome long arm. Hum Genet. 1984;65(3):295–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00286521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Jacobs P. A., Morton N. E., Froster-Iskenius U., Howard-Peebles P. N., Nielsen K. B., Partington M. W., Sutherland G. R., Turner G., Watson M. Further segregation analysis of the fragile X syndrome with special reference to transmitting males. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):289–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00291644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Morton N. E., Jacobs P. A., Turner G. The marker (X) syndrome: a cytogenetic and genetic analysis. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;48(Pt 1):21–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb00830.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo P., Purrello M., Rocchi M., Archidiacono N., Alhadeff B., Filippi G., Toniolo D., Martini G., Luzzatto L., Siniscalco M. Cytological mapping of the human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene distal to the fragile-X site suggests a high rate of meiotic recombination across this site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7855–7859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Brookwell R., Daniel A., Selikowitz M., Zilibowitz M. Heterozygous expression of X-linked mental retardation and X-chromosome marker fra(X)(q27). N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 18;303(12):662–664. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009183031202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Jacobs P. Marker (X)-linked mental retardation. Adv Hum Genet. 1983;13:83–112. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8342-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. T., Glover T. W., Davidson R. L., Jagadeeswaran P. Linkage and recombination between fragile X-linked mental retardation and the factor IX gene. Hum Genet. 1985;69(1):44–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00295528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoll B., Arnemann J., Krawczak M., Cooper D. N., Pescia G., Wahli W., Steinbach P., Schmidtke J. Evidence against close linkage of the loci for fraXq of Martin-Bell syndrome and for factor IX. Hum Genet. 1985;71(2):122–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00283366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


