Abstract
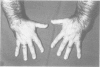
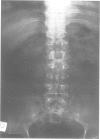
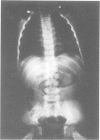
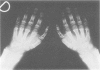
We report on a probably new form of spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia (SEMD) with an X linked inheritance pattern. Eight males were affected in the same family. We were able to examine three adult patients and we studied the skeletal radiological aspect of one of these patients at 2 years 6 months and at 9 years of age. The main clinical features are severe short trunked dwarfism, brachydactyly, normal facies, and normal intelligence. Radiologically, the diaphyses of all the long bones are short and broad. The epiphyses of the distal portion of the femora and those of the proximal and distal portions of the tibia are embedded in their metaphyses and there is marked narrowing of the intercondylar groove. There is moderate platyspondyly. Several vertebrae show an anterior tongue in infancy and severe irregularities of the upper and lower surfaces are present in adulthood. The 11th or 12th thoracic vertebra is wedge shaped. The pelvis is narrow. The distal ulnae and fibulae are disproportionately long. The hands show radial deviation and brachydactyly is present in the hands and feet. This X linked SEMD was not detectable at birth.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. E., Sillence D. O., Lachman R. S., Toomey K., Bull M., Dorst J., Rimoin D. L. Spondylometepiphyseal dysplasia, Strudwick type. Am J Med Genet. 1982 Nov;13(3):243–256. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arias S., Mota M., Pinto-Cisternas L'ostéochondrodysplasie spondylo-épiphyso-métaphysaire type Irapa. Nouveau nanisme avec rachis et métatarsiens courts. Nouv Presse Med. 1976 Feb 7;5(6):319–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beighton P., Gericke G., Kozlowski K., Grobler L. The manifestations and natural history of spondylo-epi-metaphyseal dysplasia with joint laxity. Clin Genet. 1984 Oct;26(4):308–317. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini F., Bardare M. Su un caso di disostosi periferica. Minerva Pediatr. 1966 Feb 4;18(3):106–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano F., Corso D., Basile G., Noto D., Orsi E., Chiappara G. M., Camera G. Pseudoacondroplasia (displasia spondiloepifisaria pseudoacondroplastica). Descrizione di due casi non famigliari. Pathologica. 1989 Nov-Dec;81(1076):627–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. G., Dorst J. P., Rotta J., McKusick V. A. Gonadal mosaicism in pseudoachondroplasia. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):143–151. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández A., Ramírez M. L., Nazará Z., Ocampo R., Ibarra B., Cantú J. M. Autosomal recessive spondylo-epi-metaphyseal dysplasia (Irapa type) in a Mexican family: delineation of the syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1980;5(2):179–188. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320050212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeffel J. C., Didier F., Chantereau D., Medoc J. M., Muller J. P. Metaphyseal dyschondroplasia with cone-shaped epiphyses. Br J Radiol. 1987 Jul;60(715):707–710. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-60-715-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jequier S., Bellini F., Mackenzie D. A. Metaphyseal chondrodysplasia with ectodermal dysplasia. Skeletal Radiol. 1981;7(2):107–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00347374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAROTEAUX P., LAMY M. Les formes pseudo-achondroplasiques des dysplasies spondylo-epiphysaires. Presse Med. 1959 Feb 25;67(10):383–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spranger J. W., Maroteaux P. Genetic heterogeneity of spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita? Am J Med Genet. 1982 Nov;13(3):241–242. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320130303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verloes A., Le Merrer M., Farriaux J. P., Maroteaux P. Metaphyseal acroscyphodysplasia. Clin Genet. 1991 May;39(5):362–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vichi G. F., Salti R., Galluzzi F., Corti S., Carbonai R. Spondylo-epiphyso-metaphyseal dysplasia: an atypical variant. Pediatr Radiol. 1990;21(1):78–79. doi: 10.1007/BF02010826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. P., Petersen D. J., McAlister W. H. Hypotrichosis with spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia in three generations: a new autosomal dominant syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Jul;36(3):288–291. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320360308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne-Davies R., Hall C. M., Young I. D. Pseudoachondroplasia: clinical diagnosis at different ages and comparison of autosomal dominant and recessive types. A review of 32 patients (26 kindreds). J Med Genet. 1986 Oct;23(5):425–434. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.5.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]