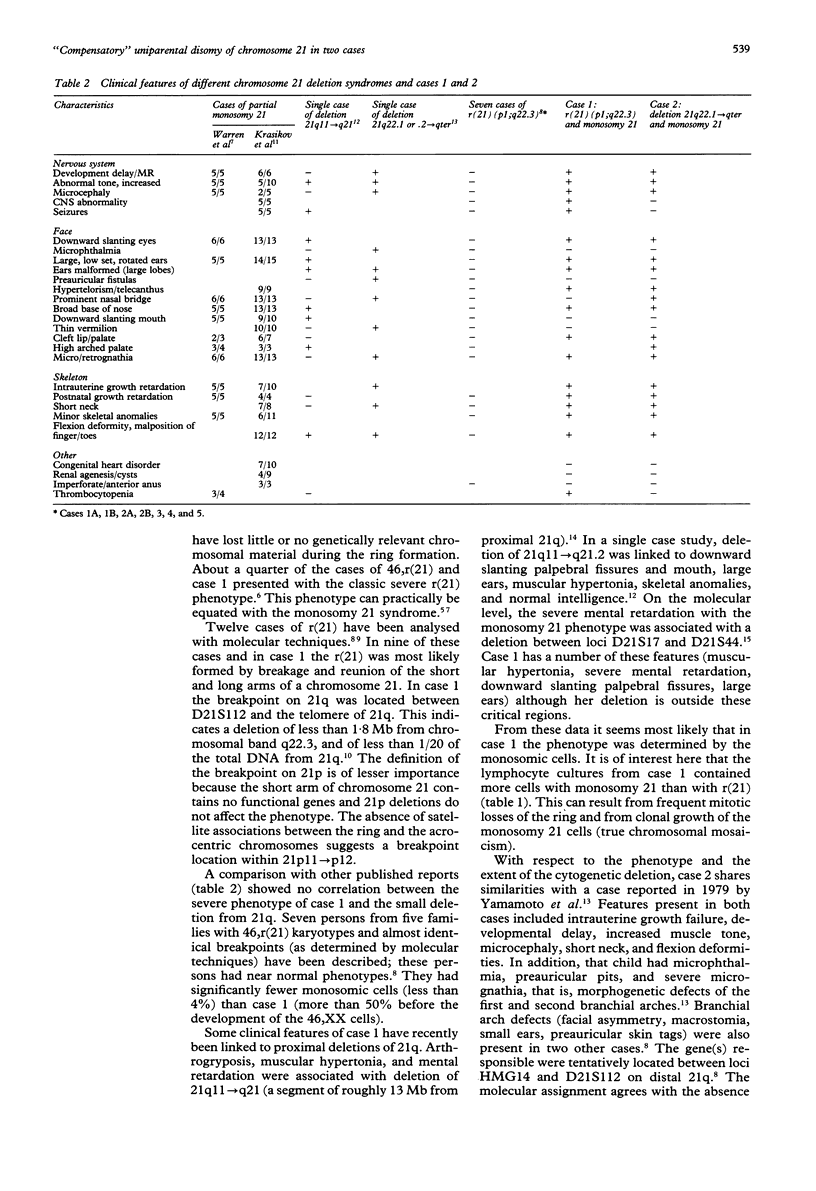
Abstract
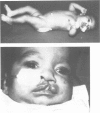
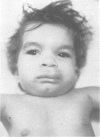
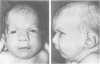
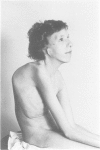
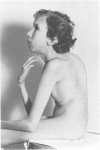
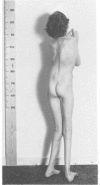
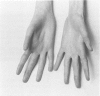
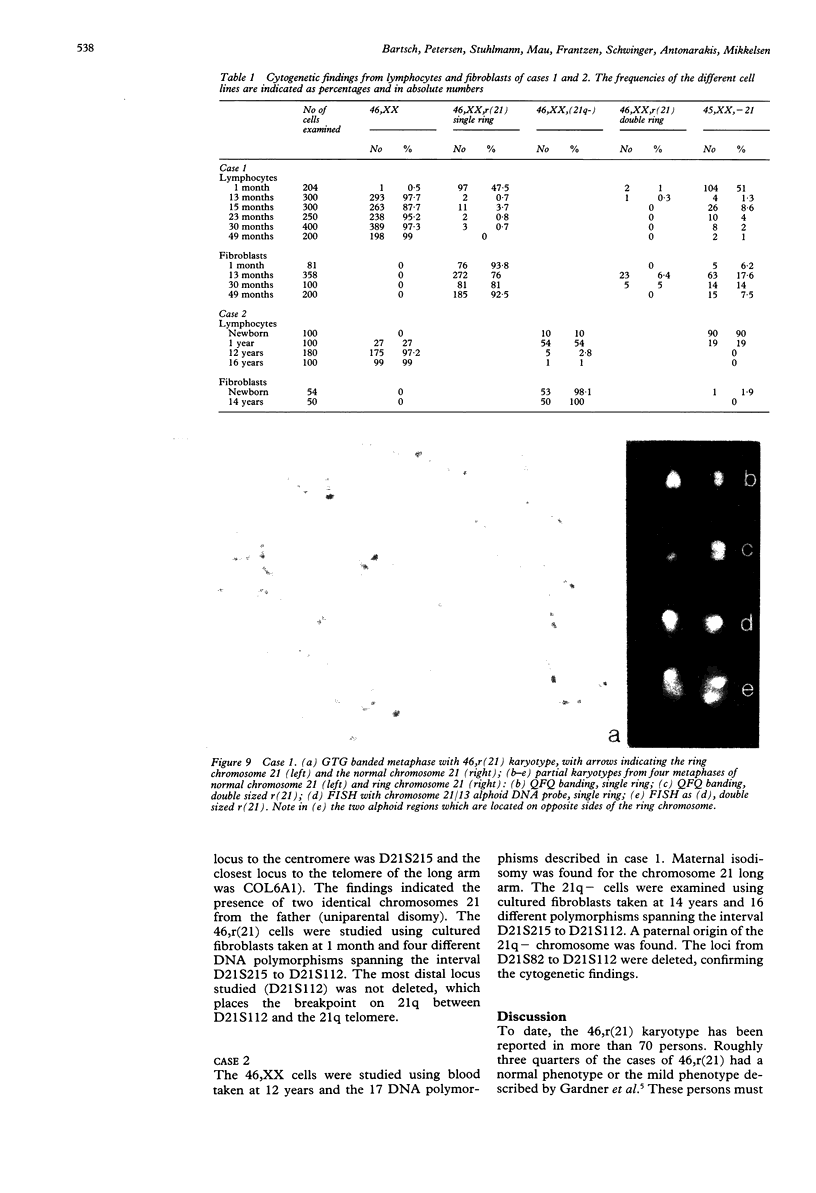
Two cases of growth failure, microcephaly, facial dysmorphism, muscular hypertonia, and severe psychomotor retardation are described. At birth, both cases had cytogenetic mosaicism in lymphocytes and skin fibroblasts, in case 1 ring chromosome 21 and monosomy 21 and in case 2, deletion of chromosome 21 and monosomy 21. At a later age the lymphocyte karyotype changed almost completely to 46,XX, but the fibroblast karyotype remained as before. DNA polymorphism analysis described elsewhere indicated that the 46,XX lymphocytes contained two identical chromosomes 21 (isodisomy), in case 1 inherited from the father and in case 2 from the mother. The isodisomy was the result of duplication of a chromosome in mitosis after the loss of the homologous abnormal chromosome ("compensatory isodisomy"). We report here that this cytogenetic mechanism can result in false normal cytogenetic findings. The phenotypes were attributed to the cells with monosomy 21 in case 1 and to the deletion and monosomy of chromosome 21 in case 2.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartsch O., Schwinger E. A simplified protocol for fluorescence in situ hybridization with repetitive DNA probes and its use in clinical cytogenetics. Clin Genet. 1991 Jul;40(1):47–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Kim S., Price E. R., de Lange T., Tantravahi U., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. A map of the distal region of the long arm of human chromosome 21 constructed by radiation hybrid mapping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrol C., Werner-Favre C., Wyss M., Pitmon D., Engel E. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in two children with a congenital chromosome anomaly: familial inv(11)(p15q13) in one and ring chromosome No. 21 in the other. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1983 Jan;8(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(83)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish R., Duckett D. P., Woodhouse M., Shannon R. S., Young I. D. Apparent monosomy 21 owing to a ring 21 chromosome: parental origin revealed by DNA analysis. J Med Genet. 1988 Dec;25(12):851–854. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.12.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Slagboom P., Cornelisse C. J., Pearson P. L. Sequence heterogeneity within the human alphoid repetitive DNA family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2059–2073. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchi A. M., Orofino M. G., Nucaro A. L., De Virgiliis S., Cao A. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a child with constitutional ring chromosome 21. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1987 Aug;27(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(87)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. J., Monk N. A., Clarkson J. E., Allen G. J. Ring 21 chromosome: the mild end of the phenotypic spectrum. Clin Genet. 1986 Dec;30(6):466–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Kalousek D. K., Anneren G., Pulst S. M., Hall J. G., Epstein C. J., Cox D. R. Deletion of chromosome 21 and normal intelligence: molecular definition of the lesion. Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;87(2):112–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00204163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasikov N., Takaesu N., Hassold T., Knops J. F., Finley W. H., Scarbrough P. Molecular and cytogenetic investigation of complex tissue-specific duplication and loss of chromosome 21 in a child with a monosomy 21 phenotype. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jun 1;43(3):554–560. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinniss M. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Stetten G., Petersen M. B., Boman H., Engel E., Greenberg F., Hertz J. M., Johnson A., Laca Z. Mechanisms of ring chromosome formation in 11 cases of human ring chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;50(1):15–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen M., Vestermark S. Karyotype 45,XX,-21/46,XX,21q-in an infant with symptoms of G-deletion syndrome I. J Med Genet. 1974 Dec;11(4):389–393. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen M. B., Bartsch O., Adelsberger P. A., Mikkelsen M., Schwinger E., Antonarakis S. E. Uniparental isodisomy due to duplication of chromosome 21 occurring in somatic cells monosomic for chromosome 21. Genomics. 1992 Jun;13(2):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90242-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pui C. H., Williams D. L., Scarborough V., Jackson C. W., Price R., Murphy S. Acute megakaryoblastic leukaemia associated with intrinsic platelet dysfunction and constitution ring 21 chromosome in a young boy. Br J Haematol. 1982 Feb;50(2):191–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1982.tb01909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richer C. L., Fitch N., Sitahal S., Murer-Orlando M., Jean P. Analysis of banding patterns in a case of ring chromosome 21. Am J Med Genet. 1981;10(4):323–331. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320100404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond H. G., MacArthur P., Hunter D. A "G" deletion syndrome anti-mongolism. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1973 Mar;62(2):216–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1973.tb08096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R. J., Rimoin D. L. The G deletion syndromes. J Pediatr. 1970 Oct;77(4):658–663. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Stetten G., Earnshaw W. C., Van Keuren M. L., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular mechanism in the formation of a human ring chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1914–1918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Ogasawara N., Gotoh A., Komiya H., Nakai H., Kuroki Y. A case of 21q--syndrome with normal SOD-1 activity. Hum Genet. 1979 May 10;48(3):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00272832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]