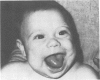
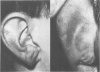
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews M. W., Amparo E. G. Wilms' tumor in a patient with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: onset detected with 3-month serial sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993 Jan;160(1):139–140. doi: 10.2214/ajr.160.1.8380110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird P. A., MacDonald E. C. An epidemiologic study of congenital malformations of the anterior abdominal wall in more than half a million consecutive live births. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 May;33(3):470–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartolomei M. S., Zemel S., Tilghman S. M. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):153–155. doi: 10.1038/351153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannan C. I., Dees E. C., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. W., Gardner A., Williams J. C., Mott M. G., McDermott A., Maitland N. J. Paternal origin of 11p15 duplications in the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. A new case and review of the literature. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1992 Jan;58(1):66–70. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(92)90136-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Efstratiadis A., Robertson E. J. A growth-deficiency phenotype in heterozygous mice carrying an insulin-like growth factor II gene disrupted by targeting. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):78–80. doi: 10.1038/345078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChiara T. M., Robertson E. J., Efstratiadis A. Parental imprinting of the mouse insulin-like growth factor II gene. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90513-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström W., Lindham S., Schofield P. Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 1988 Jun;147(5):450–457. doi: 10.1007/BF00441965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith A. C., Cattanach B. M., Barton S. C., Beechey C. V., Surani M. A. Embryological and molecular investigations of parental imprinting on mouse chromosome 7. Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):667–670. doi: 10.1038/351667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith A. C., Sasaki H., Cattanach B. M., Surani M. A. Parental-origin-specific epigenetic modification of the mouse H19 gene. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):751–755. doi: 10.1038/362751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini P., Guala A., Vardeu M. P., Franceschini D. Monozygotic twinning and Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1993 May 15;46(3):353–354. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy R. G., Pritchard J., Baraitser M., Risdon A., Robards M. Perlman and Wiedemann-Beckwith syndromes: two distinct conditions associated with Wilms' tumour. Eur J Pediatr. 1992 Dec;151(12):895–898. doi: 10.1007/BF01954125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao Y., Crenshaw T., Moulton T., Newcomb E., Tycko B. Tumour-suppressor activity of H19 RNA. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):764–767. doi: 10.1038/365764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry I., Bonaiti-Pellié C., Chehensse V., Beldjord C., Schwartz C., Utermann G., Junien C. Uniparental paternal disomy in a genetic cancer-predisposing syndrome. Nature. 1991 Jun 20;351(6328):665–667. doi: 10.1038/351665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry I., Puech A., Riesewijk A., Ahnine L., Mannens M., Beldjord C., Bitoun P., Tournade M. F., Landrieu P., Junien C. Somatic mosaicism for partial paternal isodisomy in Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome: a post-fertilization event. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(1):19–29. doi: 10.1159/000472384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higurashi M., Iijima K., Sugimoto Y., Ishikawa N., Hoshina H., Watanabe N., Yoneyama K. The birth prevalence of malformation syndromes in Tokyo infants: a survey of 14,430 newborn infants. Am J Med Genet. 1980;6(3):189–194. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes-Benzie R. M., Hunter A. G., Allanson J. E., Mackenzie A. E. Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome associated with renal dysplasia and embryonal tumor: localization of the gene to Xqcen-q21. 1992 Apr 15-May 1Am J Med Genet. 43(1-2):428–435. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320430165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junien C. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, tumourigenesis and imprinting. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Jun;2(3):431–438. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80154-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koufos A., Grundy P., Morgan K., Aleck K. A., Hadro T., Lampkin B. C., Kalbakji A., Cavenee W. K. Familial Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome and a second Wilms tumor locus both map to 11p15.5. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):711–719. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutou C., Junien C., Henry I., Bonaïti-Pellié C. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome: a demonstration of the mechanisms responsible for the excess of transmitting females. J Med Genet. 1992 Apr;29(4):217–220. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.4.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa O., Becroft D. M., Morison I. M., Eccles M. R., Skeen J. E., Mauger D. C., Reeve A. E. Constitutional relaxation of insulin-like growth factor II gene imprinting associated with Wilms' tumour and gigantism. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):408–412. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa O., Eccles M. R., Szeto J., McNoe L. A., Yun K., Maw M. A., Smith P. J., Reeve A. E. Relaxation of insulin-like growth factor II gene imprinting implicated in Wilms' tumour. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):749–751. doi: 10.1038/362749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson R., Nyström A., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Töhönen V., Hedborg F., Schofield P., Flam F., Ekström T. J. IGF2 is parentally imprinted during human embryogenesis and in the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Nat Genet. 1993 May;4(1):94–97. doi: 10.1038/ng0593-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettenati M. J., Haines J. L., Higgins R. R., Wappner R. S., Palmer C. G., Weaver D. D. Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome: presentation of clinical and cytogenetic data on 22 new cases and review of the literature. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):143–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00282078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ping A. J., Reeve A. E., Law D. J., Young M. R., Boehnke M., Feinberg A. P. Genetic linkage of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome to 11p15. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):720–723. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainier S., Johnson L. A., Dobry C. J., Ping A. J., Grundy P. E., Feinberg A. P. Relaxation of imprinted genes in human cancer. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):747–749. doi: 10.1038/362747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viljoen D., Ramesar R. Evidence for paternal imprinting in familial Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. J Med Genet. 1992 Apr;29(4):221–225. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.4.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIEDEMANN H. R. COMPLEXE MALFORMATIF FAMILIAL AVEC HERNIE OMBILICALE ET MACROGLOSSIE--UN "SYNDROME NOUVEAU"? J Genet Hum. 1964 Sep;13:223–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waziri M., Patil S. R., Hanson J. W., Bartley J. A. Abnormality of chromosome 11 in patients with features of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. J Pediatr. 1983 Jun;102(6):873–876. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksberg R., Shen D. R., Fei Y. L., Song Q. L., Squire J. Disruption of insulin-like growth factor 2 imprinting in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Nat Genet. 1993 Oct;5(2):143–150. doi: 10.1038/ng1093-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksberg R., Teshima I., Williams B. R., Greenberg C. R., Pueschel S. M., Chernos J. E., Fowlow S. B., Hoyme E., Anderson I. J., Whiteman D. A. Molecular characterization of cytogenetic alterations associated with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) phenotype refines the localization and suggests the gene for BWS is imprinted. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 May;2(5):549–556. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.5.549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieacker P., Wilhelm C., Greiner P., Schillinger H. Prenatal diagnosis of Wiedemann-Beckwith syndrome. J Perinat Med. 1989;17(5):351–355. doi: 10.1515/jpme.1989.17.5.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Tycko B. Monoallelic expression of the human H19 gene. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):40–44. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]