Abstract
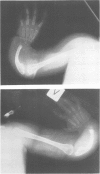
Rothmund-Thomson syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive syndrome characterised by poikiloderma of the face and extremities, alopecia, short stature, and skeletal defects. We report a patient with the characteristic features of Rothmund-Thomson syndrome who also had lymphocyte chromosome abnormalities. She has a small flat face with short palpebral fissures and micrognathia together with severe skeletal abnormalities of the upper extremities with absence of both radii, short dysmorphic ulnae, a rudimentary right thumb, and aplasia of the left thumb. She also has anal atresia with a rectovaginal fistula. From the age of 3 months she developed poikiloderma skin changes on the face and extensor surfaces of the extremities. Mental development seems to be normal. Lymphocyte chromosomes in the neonatal period showed an unidentified marker chromosome in eight of a total of 32 cells. A repeat analysis at the age of 10 months showed three abnormal cells out of 100 analysed: 47,XX,-7,+i(7q),+7p, 46,XX,t(3;18)(p14.2;q22), and 49,XX,+del(3)(p11.2),+mar,+mar. A skin biopsy from an affected area showed poor growth and five of 48 cells analysed had structural abnormalities. The father had one of 48 cells with an additional marker chromosome and two cells with different 7;14 translocations. The abnormal chromosome complements in lymphocytes indicate that there may be in vivo chromosome instability in Rothmund-Thomson syndrome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaustein H. S., Stevens A. W., Stevens P. D., Grossman M. E. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome associated with annular pancreas and duodenal stenosis: a case report. Pediatr Dermatol. 1993 Jun;10(2):159–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1993.tb00046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der Kaloustian V. M., McGill J. J., Vekemans M., Kopelman H. R. Clonal lines of aneuploid cells in Rothmund-Thomson syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Nov;37(3):336–339. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320370308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. E., Campisano L. C., Callen J. P., Hersh J. H., Yusk J. W. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome: a case report. Pediatr Dermatol. 1989 Dec;6(4):321–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.1989.tb00918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinya A., Nishigori C., Moriwaki S., Takebe H., Kubota M., Ogino A., Imamura S. A case of Rothmund-Thomson syndrome with reduced DNA repair capacity. Arch Dermatol. 1993 Mar;129(3):332–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennos E. M., Collins M., James W. D. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome: review of the world literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992 Nov;27(5 Pt 1):750–762. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(92)70249-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ying K. L., Oizumi J., Curry C. J. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome associated with trisomy 8 mosaicism. J Med Genet. 1990 Apr;27(4):258–260. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.4.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]