Abstract
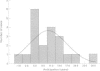
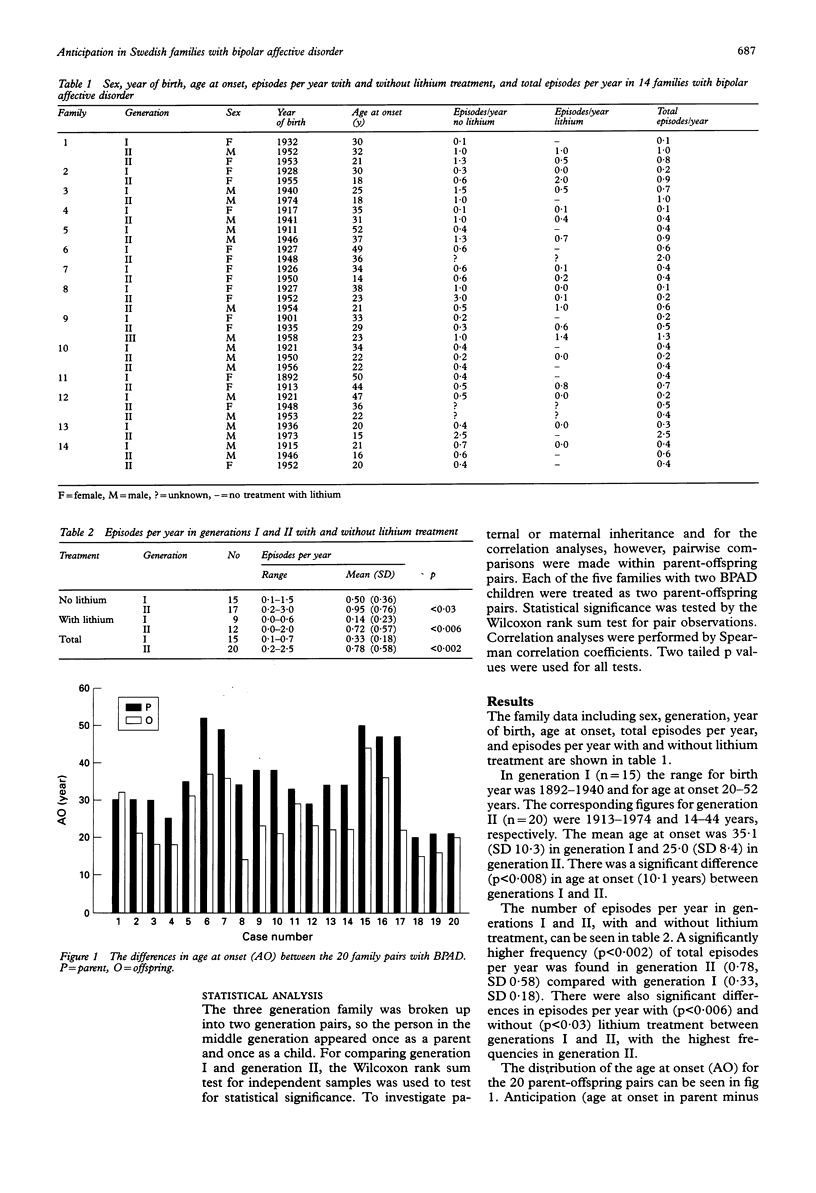
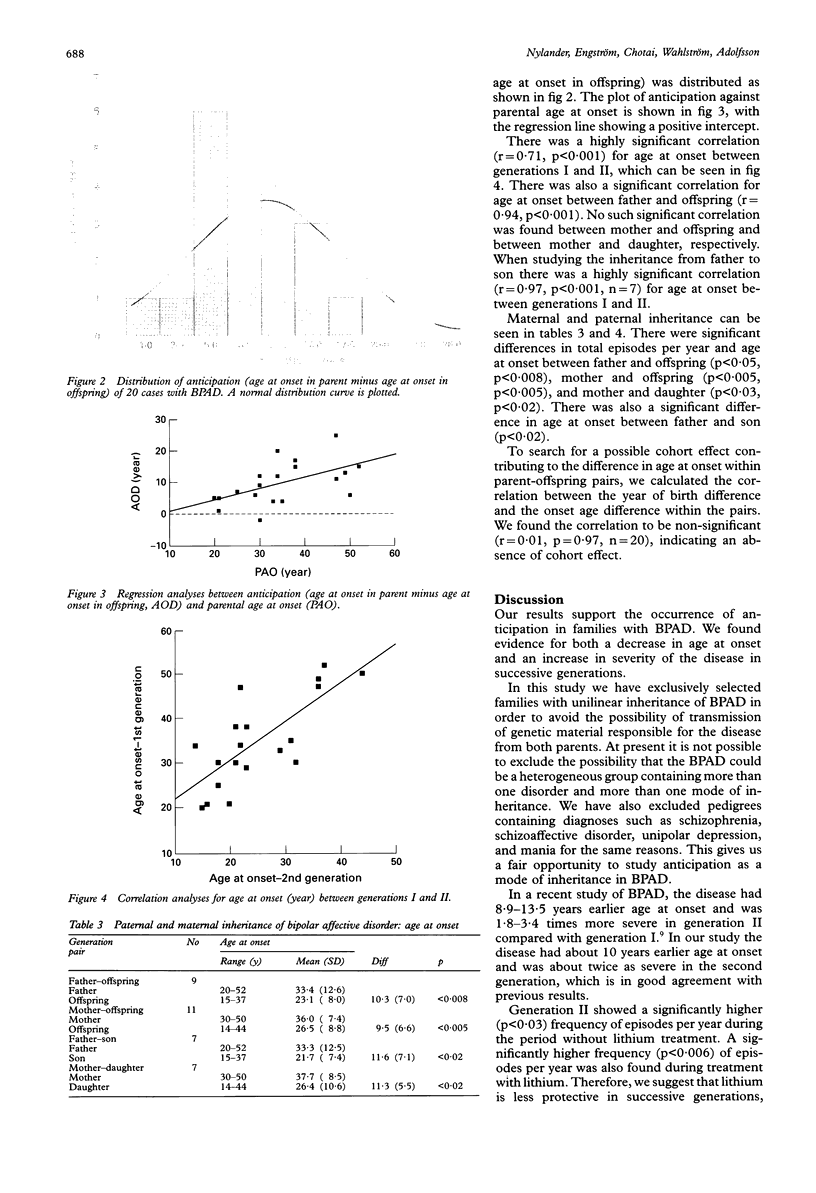
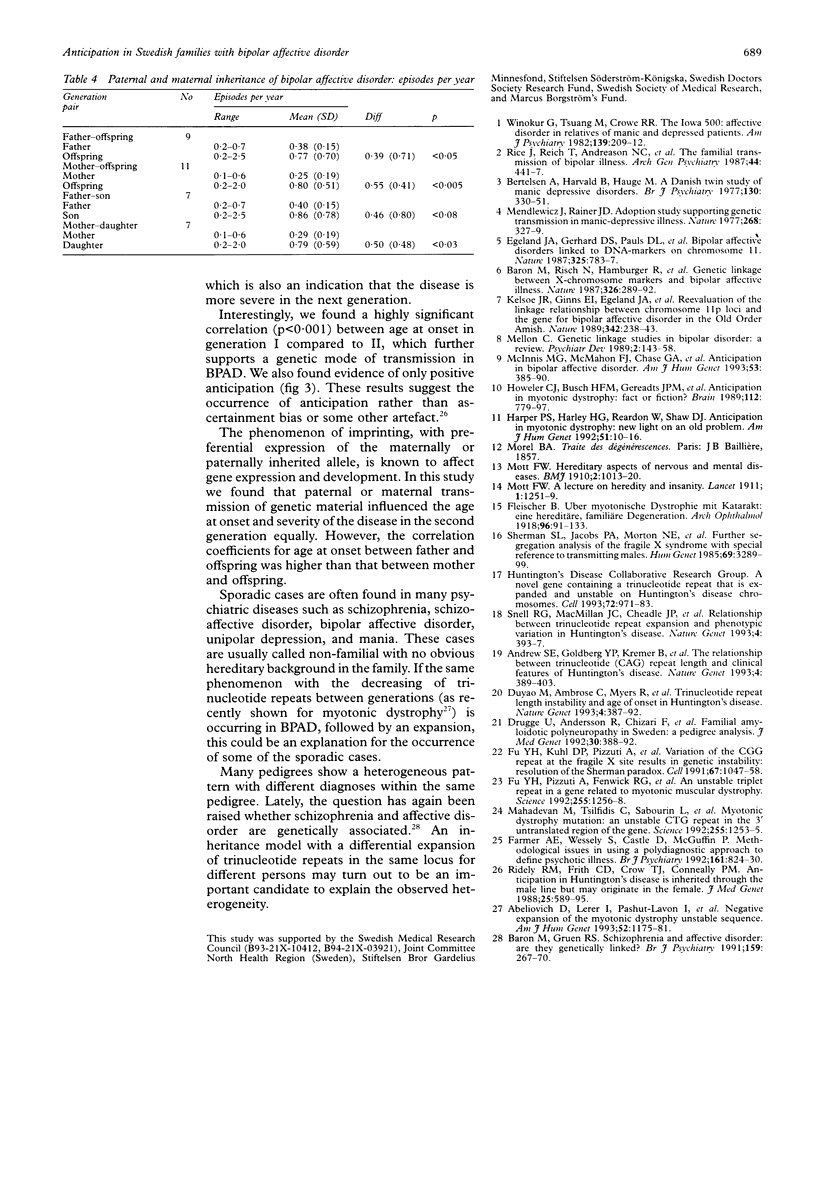
Anticipation describes an inheritance pattern within a pedigree with an increase in disease severity or decrease in age at onset or both in successive generations. The phenomenon of anticipation has recently been shown to be correlated with the expansion of trinucleotide repeat sequences in different disorders. We have studied differences of age at onset and disease severity between two generations in 14 families with unilinear inheritance of bipolar affective disorder (BPAD). There was a significant difference in age at onset (p < 0.008), in episodes per year with (p < 0.006) and without (p < 0.03) lithium treatment, and in total episodes per year (p < 0.002) between generations I and II. Furthermore, there was a highly significant correlation (p < 0.001) in age at onset between generations I and II. No evidence for specific paternal or maternal inheritance was found. We found evidence of anticipation and could rule out ascertainment bias or some other artefact. Anticipation is thus an inheritance pattern in BPAD which suggests that the expansion of trinucleotide repeat sequences is a possible mode of inheritance in BPAD.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeliovich D., Lerer I., Pashut-Lavon I., Shmueli E., Raas-Rothschild A., Frydman M. Negative expansion of the myotonic dystrophy unstable sequence. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jun;52(6):1175–1181. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew S. E., Goldberg Y. P., Kremer B., Telenius H., Theilmann J., Adam S., Starr E., Squitieri F., Lin B., Kalchman M. A. The relationship between trinucleotide (CAG) repeat length and clinical features of Huntington's disease. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):398–403. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Gruen R. S. Schizophrenia and affective disorder: are they genetically linked? Br J Psychiatry. 1991 Aug;159:267–270. doi: 10.1192/bjp.159.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M., Risch N., Hamburger R., Mandel B., Kushner S., Newman M., Drumer D., Belmaker R. H. Genetic linkage between X-chromosome markers and bipolar affective illness. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):289–292. doi: 10.1038/326289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsen A., Harvald B., Hauge M. A Danish twin study of manic-depressive disorders. Br J Psychiatry. 1977 Apr;130:330–351. doi: 10.1192/bjp.130.4.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drugge U., Andersson R., Chizari F., Danielsson M., Holmgren G., Sandgren O., Sousa A. Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy in Sweden: a pedigree analysis. J Med Genet. 1993 May;30(5):388–392. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.5.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyao M., Ambrose C., Myers R., Novelletto A., Persichetti F., Frontali M., Folstein S., Ross C., Franz M., Abbott M. Trinucleotide repeat length instability and age of onset in Huntington's disease. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):387–392. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeland J. A., Gerhard D. S., Pauls D. L., Sussex J. N., Kidd K. K., Allen C. R., Hostetter A. M., Housman D. E. Bipolar affective disorders linked to DNA markers on chromosome 11. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):783–787. doi: 10.1038/325783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer A. E., Wessely S., Castle D., McGuffin P. Methodological issues in using a polydiagnostic approach to define psychotic illness. Br J Psychiatry. 1992 Dec;161:824–830. doi: 10.1192/bjp.161.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Kuhl D. P., Pizzuti A., Pieretti M., Sutcliffe J. S., Richards S., Verkerk A. J., Holden J. J., Fenwick R. G., Jr, Warren S. T. Variation of the CGG repeat at the fragile X site results in genetic instability: resolution of the Sherman paradox. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Pizzuti A., Fenwick R. G., Jr, King J., Rajnarayan S., Dunne P. W., Dubel J., Nasser G. A., Ashizawa T., de Jong P. An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1256–1258. doi: 10.1126/science.1546326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S., Harley H. G., Reardon W., Shaw D. J. Anticipation in myotonic dystrophy: new light on an old problem. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jul;51(1):10–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höweler C. J., Busch H. F., Geraedts J. P., Niermeijer M. F., Staal A. Anticipation in myotonic dystrophy: fact or fiction? Brain. 1989 Jun;112(Pt 3):779–797. doi: 10.1093/brain/112.3.779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsoe J. R., Ginns E. I., Egeland J. A., Gerhard D. S., Goldstein A. M., Bale S. J., Pauls D. L., Long R. T., Kidd K. K., Conte G. Re-evaluation of the linkage relationship between chromosome 11p loci and the gene for bipolar affective disorder in the Old Order Amish. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):238–243. doi: 10.1038/342238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan M., Tsilfidis C., Sabourin L., Shutler G., Amemiya C., Jansen G., Neville C., Narang M., Barceló J., O'Hoy K. Myotonic dystrophy mutation: an unstable CTG repeat in the 3' untranslated region of the gene. Science. 1992 Mar 6;255(5049):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1546325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInnis M. G., McMahon F. J., Chase G. A., Simpson S. G., Ross C. A., DePaulo J. R., Jr Anticipation in bipolar affective disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):385–390. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon C. D. Genetic linkage studies in bipolar disorder: a review. Psychiatr Dev. 1989 Summer;7(2):143–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendlewicz J., Rainer J. D. Adoption study supporting genetic transmission in manic--depressive illness. Nature. 1977 Jul 28;268(5618):327–329. doi: 10.1038/268327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice J., Reich T., Andreasen N. C., Endicott J., Van Eerdewegh M., Fishman R., Hirschfeld R. M., Klerman G. L. The familial transmission of bipolar illness. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1987 May;44(5):441–447. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1987.01800170063009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley R. M., Frith C. D., Crow T. J., Conneally P. M. Anticipation in Huntington's disease is inherited through the male line but may originate in the female. J Med Genet. 1988 Sep;25(9):589–595. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.9.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. G., MacMillan J. C., Cheadle J. P., Fenton I., Lazarou L. P., Davies P., MacDonald M. E., Gusella J. F., Harper P. S., Shaw D. J. Relationship between trinucleotide repeat expansion and phenotypic variation in Huntington's disease. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):393–397. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winokur G., Tsuang M. T., Crowe R. R. The Iowa 500: affective disorder in relatives of manic and depressed patients. Am J Psychiatry. 1982 Feb;139(2):209–212. doi: 10.1176/ajp.139.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]