Abstract
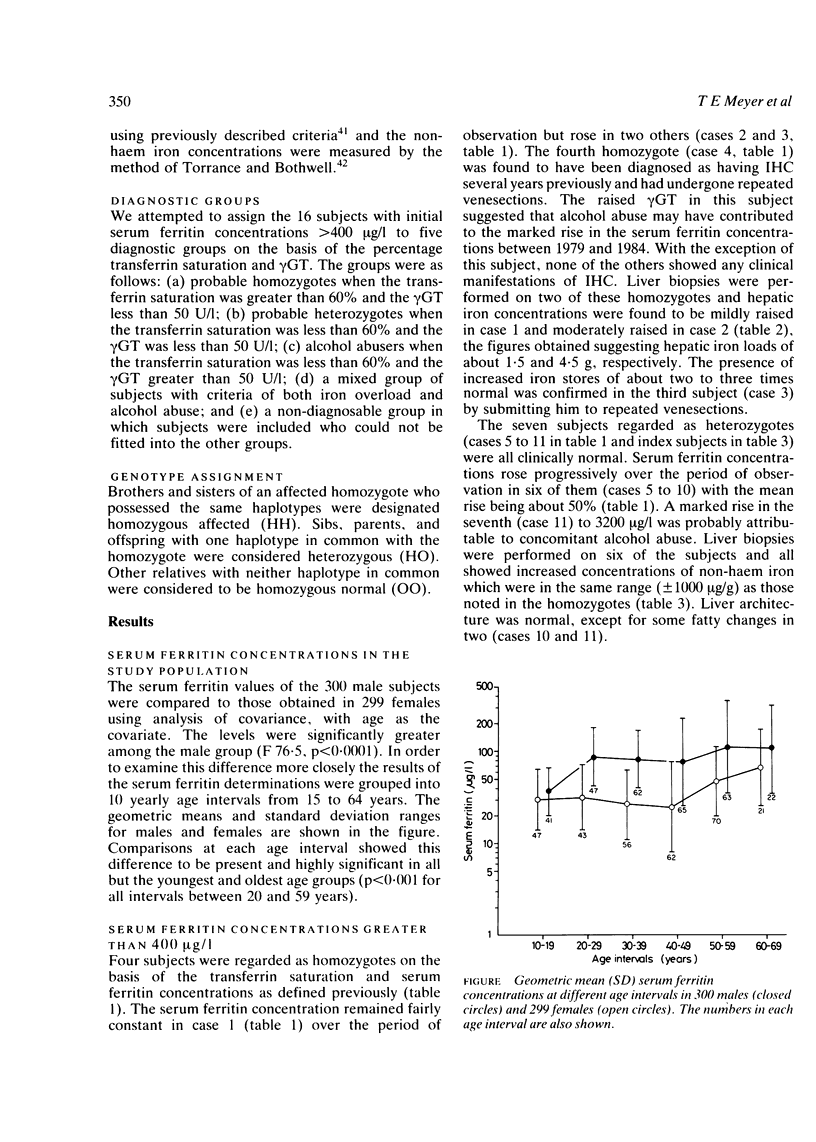
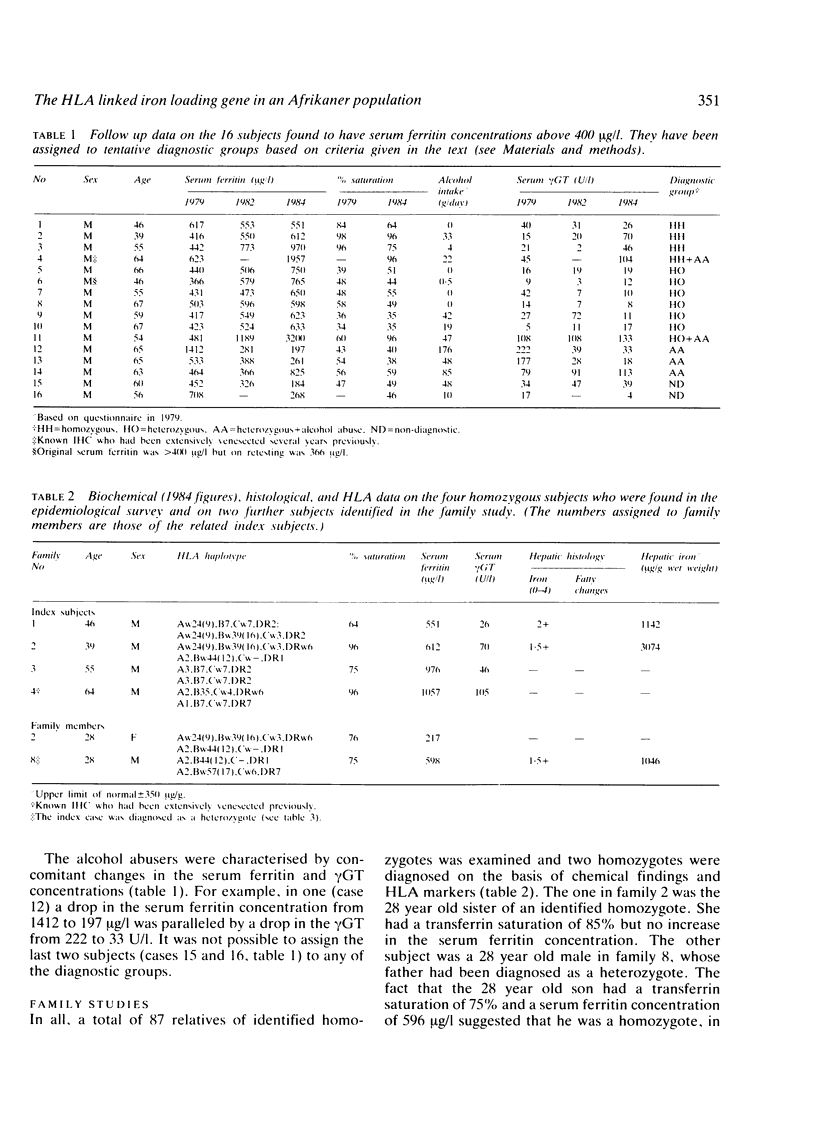
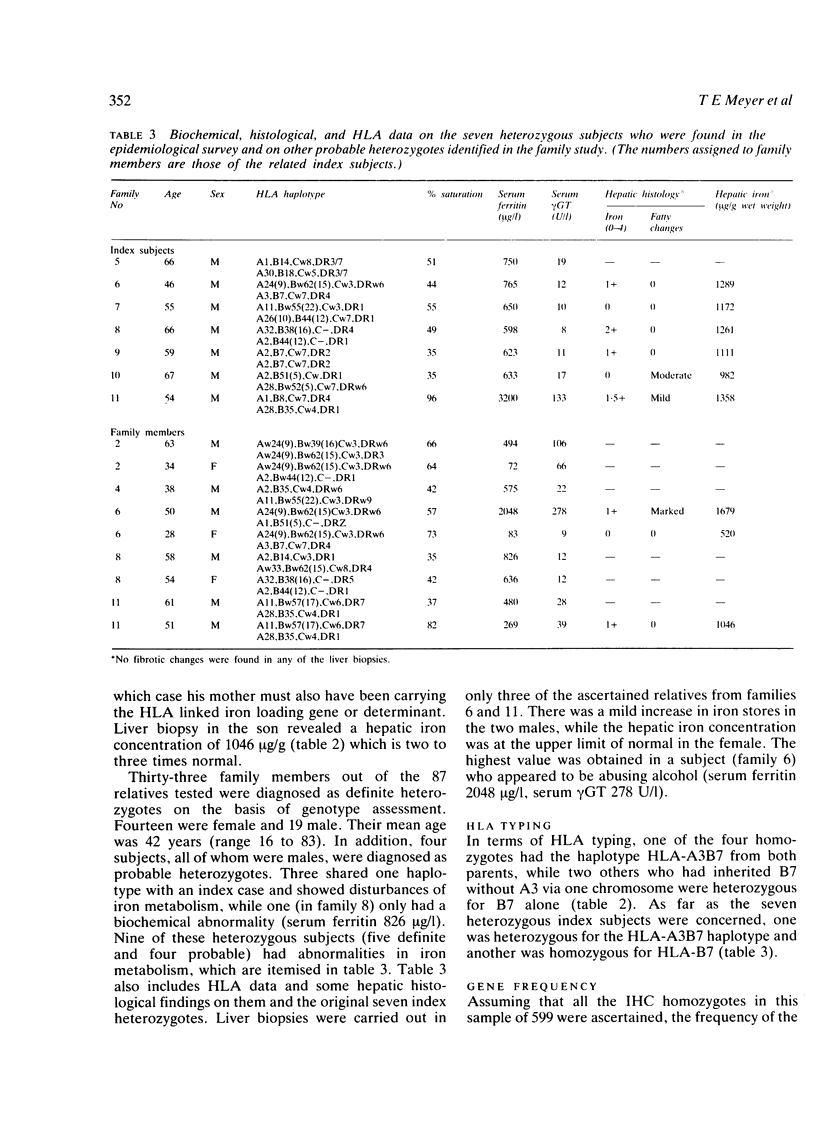
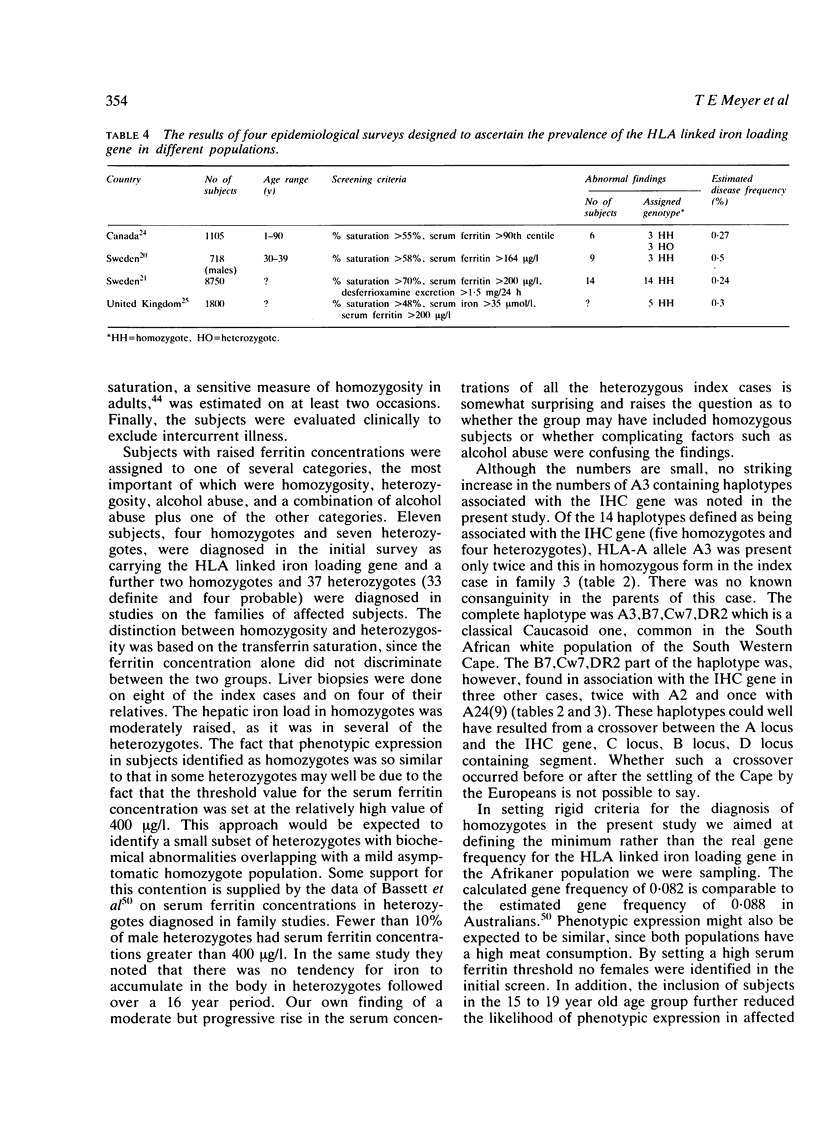
The serum ferritin concentration was used as a screening test to identify the presence of iron overload in 599 Afrikaans subjects (300 males and 299 females) living in the South Western Cape, South Africa. Seventeen of the males with concentrations greater than 400 micrograms/l were reevaluated three and five years later. Serum ferritin concentrations were measured again and further diagnostic procedures were carried out. These included an assessment of alcohol intake and measurements of serum gamma glutamyltransferase, the percentage saturation of transferrin, and HLA-A,-B,-C, and -DR loci typing on the subjects as well as their families. Liver biopsies were performed on some affected subjects. Of the original 16 index subjects, four were diagnosed as homozygous for the HLA linked iron loading gene which is responsible for the clinical disease idiopathic haemochromatosis. Six appeared to be heterozygotes, three were heterozygotes who were also abusing alcohol, and two did not fit into any of the diagnostic groups. The calculated gene frequency was 0.082, with an expected heterozygote frequency of 0.148. The fact that no females were identified in the study suggested that the diagnostic criteria for homozygosity (serum ferritin greater than 400 micrograms/l and % saturation greater than 60%) were set too high. The data were therefore recalculated for the 300 males; when this was done the gene frequency was 0.115 and the heterozygote frequency 0.024. Two subjects were diagnosed as homozygotes in the study of family members and 37 as heterozygotes (33 definite and four probable). Both the homozygotes and nine of the heterozygotes showed mild to moderate disturbances of iron metabolism. There was considerable overlap between the phenotype expression in these nine heterozygotes and the homozygotes, probably as a result of setting the threshold for the serum ferritin concentrations at the relatively high value of 400 microgram/ml. By doing this a small subset of heterozygotes with biochemical abnormalities was identified. The results of the present pilot study suggest a high frequency of the HLA linked iron loading gene in the Afrikaner population of South Western Cape.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOTHWELL T. H., BRADLOW B. A. Siderosis in the Bantu. A combined histopathological and chemical study. Arch Pathol. 1960 Sep;70:279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOTHWELL T. H., ISAACSON C. Siderosis in the bantu. A comparison of incidence in males and females. Br Med J. 1962 Feb 24;1(5277):522–524. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5277.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett M. L., Doran T. J., Halliday J. W., Bashir H. V., Powell L. W. Idiopathic hemochromatosis: demonstration of homozygous-heterozygous mating by HLA typing of families. Hum Genet. 1982;60(4):352–356. doi: 10.1007/BF00569217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett M. L., Halliday J. W., Ferris R. A., Powell L. W. Diagnosis of hemochromatosis in young subjects: predictive accuracy of biochemical screening tests. Gastroenterology. 1984 Sep;87(3):628–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassett M. L., Halliday J. W., Powell L. W. HLA typing in idiopathic hemochromatosis: distinction between homozygotes and heterozygotes with biochemical expression. Hepatology. 1981 Mar-Apr;1(2):120–126. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven M. A. Histamine (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 1;294(1):30–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601012940108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borwein S. T., Ghent C. N., Flanagan P. R., Chamberlain M. J., Valberg L. S. Genetic and phenotypic expression of hemochromatosis in Canadians. Clin Invest Med. 1983;6(3):171–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conradie J. D., Mbhele B. E. Quantitation of serum ferritin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). S Afr Med J. 1980 Feb 23;57(8):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadone M. M., Kushner J. P., Edwards C. Q., Bishop D. T., Skolnick M. H. Hereditary hemochromatosis. Analysis of laboratory expression of the disease by genotype in 18 pedigrees. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Aug;78(2):196–207. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. Q., Cartwright G. E., Skolnick M. H., Amos D. B. Homozygosity for hemochromatosis: clinical manifestations. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Oct;93(4):519–525. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-4-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCH S. C., FINCH C. A. Idiopathic hemochromatosis, an iron storage disease. A. Iron metabolism in hemochromatosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1955 Dec;34(4):381–430. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195512000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller E. R., Pont A., Wands J. R., Carter E. A., Foster G., Kourides I. A., Isselbacher K. J. Familial hemochromatosis. Physiologic studies in the precirrhotic stage of the disease. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 23;296(25):1422–1426. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706232962501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliday J. W., Russo A. M., Cowlishaw J. L., Powell L. W. Serum-ferritin in diagnosis of haemochromatosis. A study of 43 families. Lancet. 1977 Sep 24;2(8039):621–624. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92495-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs A., Miller F., Worwood M., Beamish M. R., Wardrop C. A. Ferritin in the serum of normal subjects and patients with iron deficiency and iron overload. Br Med J. 1972 Oct 28;4(5834):206–208. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5834.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins T., Nicholls E., Gordon E., Mendelsohn D., Seftel H. C., Andrew M. J. Familial hypercholesterolaemia--a common genetic disorder in the Afrikaans population. S Afr Med J. 1980 Jun 7;57(23):943–947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristenson H., Fex G., Trell E. Serum ferritin, gammaglutamyl-transferase and alcohol consumption in healthy middle-aged men. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1981 Aug;8(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0376-8716(81)90085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipschitz D. A., Cook J. D., Finch C. A. A clinical evaluation of serum ferritin as an index of iron stores. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 30;290(22):1213–1216. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405302902201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhail A. P., Simon M. O., Torrance J. D., Charlton R. W., Bothwell T. H., Isaacson C. Changing patterns of dietary iron overload in black South Africans. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jun;32(6):1272–1278. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.6.1272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. E., Kassianides C., Bothwell T. H., Green A. Effects of heavy alcohol consumption on serum ferritin concentrations. S Afr Med J. 1984 Oct 13;66(15):573–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson K. S., Ritter B., Rosén U., Heedman P. A., Staugård F. Prevalence of iron overload in central Sweden. Acta Med Scand. 1983;213(2):145–150. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1983.tb03706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persijn J. P., van der Slik W. A new method for the determination of gamma-glutamyltransferase in serum. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1976 Sep;14(9):421–427. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1976.14.1-12.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossouw J. E., Du Plessis J. P., Benadé A. J., Jordaan P. C., Kotzé J. P., Jooste P. L., Ferreira J. J. Coronary risk factor screening in three rural communities. The CORIS baseline study. S Afr Med J. 1983 Sep 17;64(12):430–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saddi R., Feingold J. Idiopathic haemochromatosis: an autosomal recessive disease. Clin Genet. 1974;5(3):234–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb01688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Alexandre J. L., Bourel M., Le Marec B., Scordia C. Heredity of idiopathic haemochromatosis: a study of 106 families. Clin Genet. 1977 May;11(5):327–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Alexandre J. L., Fauchet R., Genetet B., Bourel M. The genetics of hemochromatosis. Prog Med Genet. 1980;4:135–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrance J. D., Bothwell T. H. A simple technique for measuring storage iron concentrations in formalinised liver samples. S Afr J Med Sci. 1968 Apr;33(1):9–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worwood M. Serum ferritin. CRC Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 1979;10(2):171–204. doi: 10.3109/10408367909147133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



