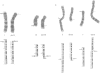Abstract
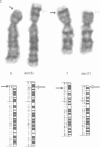
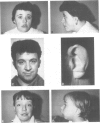
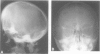
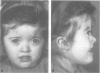
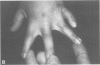
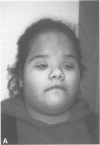
We describe three families segregating different reciprocal chromosome translocations, t(7;18)(p21.2;q23), t(2;7)(q21.1;p21.2), and t(5;7)(p15.3;p21.2). A total of seven apparently balanced carriers have been identified and all manifest features of the Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, although only two have overt craniosynostosis. In one family the carriers are immediately recognisable by their unusual ears, and clefts of the hard or soft palate are present in all three families. These observations extend previous linkage and cytogenetic evidence that a locus for Saethre-Chotzen syndrome resides in band 7p21.2.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brueton L. A., van Herwerden L., Chotai K. A., Winter R. M. The mapping of a gene for craniosynostosis: evidence for linkage of the Saethre-Chotzen syndrome to distal chromosome 7p. J Med Genet. 1992 Oct;29(10):681–685. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.10.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. O., Till K., Fraser V., Coffey R. A family study of craniosynostosis, with probable recognition of a distinct syndrome. J Med Genet. 1982 Aug;19(4):280–285. doi: 10.1136/jmg.19.4.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. M., Hanson J. W., Graham C. B., Smith D. W. Saethre-Chotzen syndrome: a broad and variable pattern of skeletal malformations. J Pediatr. 1977 Dec;91(6):929–923. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80892-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green E. D., Idol J. R., Mohr-Tidwell R. M., Braden V. V., Peluso D. C., Fulton R. S., Massa H. F., Magness C. L., Wilson A. M., Kimura J. Integration of physical, genetic and cytogenetic maps of human chromosome 7: isolation and analysis of yeast artificial chromosome clones for 117 mapped genetic markers. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Mar;3(3):489–501. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.3.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurczynski T. W., Casperson S. M. Auralcephalosyndactyly: a new hereditary craniosynostosis syndrome. J Med Genet. 1988 Jul;25(7):491–493. doi: 10.1136/jmg.25.7.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legius E., Fryns J. P., Van den Berghe H. Auralcephalosyndactyly: a new craniosynostosis syndrome or a variant of the Saethre-Chotzen syndrome? J Med Genet. 1989 Aug;26(8):522–524. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.8.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewanda A. F., Cohen M. M., Jr, Jackson C. E., Taylor E. W., Li X., Beloff M., Day D., Clarren S. K., Ortiz R., Garcia C. Genetic heterogeneity among craniosynostosis syndromes: mapping the Saethre-Chotzen syndrome locus between D7S513 and D7S516 and exclusion of Jackson-Weiss and Crouzon syndrome loci from 7p. Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):115–119. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantke O. A., Cohen M. M., Jr, Witkop C. J., Jr, Feingold M., Schaumann B., Pantke H. C., Gorlin R. J. The Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(2):190–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., McManus S. P., Summers D., Winter R. M. Cytogenetic evidence that the Saethre-Chotzen gene maps to 7p21.2. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Oct 1;47(5):633–636. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon W., Winter R. M. Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. J Med Genet. 1994 May;31(5):393–396. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.5.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid C. S., McMorrow L. E., McDonald-McGinn D. M., Grace K. J., Ramos F. J., Zackai E. H., Cohen M. M., Jr, Jabs E. W. Saethre-Chotzen syndrome with familial translocation at chromosome 7p22. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Oct 1;47(5):637–639. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinow M., Sorauf T. J. Acrocephalopolysyndactyly, type Noack, in a large kindred. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(5):99–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose C. S., King A. A., Summers D., Palmer R., Yang S., Wilkie A. O., Reardon W., Malcolm S., Winter R. M. Localization of the genetic locus for Saethre-Chotzen syndrome to a 6 cM region of chromosome 7 using four cases with apparently balanced translocations at 7p21.2. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1405–1408. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. M., Baraitser M., Hayward R. D. Parietal foramina in Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. J Med Genet. 1984 Oct;21(5):369–372. doi: 10.1136/jmg.21.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji K., Narahara K., Kikkawa K., Murakami M., Yokoyama Y., Ninomiya S., Seino Y. Craniosynostosis and hemizygosity for D7S135 caused by a de novo and apparently balanced t(6;7) translocation. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Jan 1;49(1):98–102. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320490119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. D., Harper P. S. An unusual form of familial acrocephalosyndactyly. J Med Genet. 1982 Aug;19(4):286–288. doi: 10.1136/jmg.19.4.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. D., Swift P. G. Parietal foramina in the Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. J Med Genet. 1985 Oct;22(5):413–414. doi: 10.1136/jmg.22.5.413-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Herwerden L., Rose C. S., Reardon W., Brueton L. A., Weissenbach J., Malcolm S., Winter R. M. Evidence for locus heterogeneity in acrocephalosyndactyly: a refined localization for the Saethre-Chotzen syndrome locus on distal chromosome 7p--and exclusion of Jackson-Weiss syndrome from craniosynostosis loci on 7p and 5q. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Apr;54(4):669–674. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]