Abstract
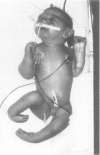
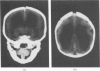
Ergotamine exposure during pregnancy has been suggested to cause birth defects which have a vascular disruptive aetiology. The present case provides additional support for the possible adverse fetal effects of exposure to ergotamine, caffeine, and propranolol during the first four months of pregnancy. At birth the infant showed evidence of early arrested cerebral maturation and paraplegia. The nature of these defects suggests a primary vascular disruptive aetiology. We hypothesise that ergotamine, acting either alone or in synergy with propranolol and caffeine, produced fetal vasoconstriction resulting in tissue ischaemia and subsequent malformation. This case raises the possibility that fetal malformation may result from concomitant use of multiple vasoconstrictive agents during pregnancy.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- David T. J. Nature and etiology of the Poland anomaly. N Engl J Med. 1972 Sep 7;287(10):487–489. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197209072871004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. D., Golbus M. S. The value of case reports in human teratology. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Mar;154(3):479–482. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90585-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. M., Jr, Marin-Padilla M., Hoefnagel D. Jejunal atresia associated with Cafergot ingestion during pregnancy. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1983 Mar;22(3):226–228. doi: 10.1177/000992288302200313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyme H. E., Higginbottom M. C., Jones K. L. Vascular etiology of disruptive structural defects in monozygotic twins. Pediatrics. 1981 Feb;67(2):288–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOYER J. H., TASHNEK A. B., MILLER S. I., SNYDER H., BOWMAN R. O. The effect of theophylline with ethylenediamine (aminophylline) and caffeine on cerebral hemodynamics and cerebrospinal fluid pressure in patients with hypertensive headaches. Am J Med Sci. 1952 Oct;224(4):377–385. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195210000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P., Yakovlev P. I. Development of the corpus callosum and cavum septi in man. J Comp Neurol. 1968 Jan;132(1):45–72. doi: 10.1002/cne.901320103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena P. R., de Vlaam-Schluter G. M. Role of some biogenic substances in migraine and relevant mechanism in antimigraine action of ergotamine--studies in an experimental model for migraine. Headache. 1974 Jan;13(4):142–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1974.hed1304142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinzel A. A., Smith D. W., Miller J. R. Monozygotic twinning and structural defects. J Pediatr. 1979 Dec;95(6):921–930. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80278-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber T. J. Amniocentesis and selective abortion. Pediatr Ann. 1981 Oct;10(10):31–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinhoj E., Paulson O. B. The mechanism of action of aminophylline upon cerebral vascular disorders. Acta Neurol Scand. 1970;46(2):129–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1970.tb05612.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DEN BERGH R. L'influence de quelques médicaments usuels sur la vasomotricité carotidienne; etude artériographique expérimentale. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1956 Jul;56(7):459–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale J. A., Jefferys D. B. Peripheral gangrene complicating beta-blockade. Lancet. 1978 Jun 3;1(8075):1216–1216. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter C. P., Joubert P. H., Buys A. C. Severe peripheral ischaemia during concomitant use of beta blockers and ergot alkaloids. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Aug 4;289(6440):288–289. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6440.288-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WECHSLER R. L., KLEISS L. M., KETY S. S. The effects of intravenously administered aminophylline on cerebral circulation and metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1950 Jan;29(1):28–30. doi: 10.1172/JCI102230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainscott G., Sullivan F. M., Volans G. N., Wilkinson M. The outcome of pregnancy in women suffering from migraine. Postgrad Med J. 1978 Feb;54(628):98–102. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.54.628.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]