Abstract
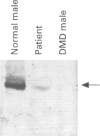
A Becker muscular dystrophy patient was found to have a single base substitution at the 5' end of intron 54. This single base substitution disrupts the invariant GT dinucleotide within the 5' donor splice site and was shown to cause an out of frame deletion of exon 54 during mRNA processing. This is predicted to produce a truncated dystrophin protein which is more consistent with a DMD phenotype. However, small quantities of normal mRNA are also transcribed and these are sufficient to produce a reduced amount of normal molecular weight dystrophin and give rise to a milder BMD phenotype. This indicates that a single base substitution at an invariant dinucleotide of the splice site consensus sequence may still allow read through of the message and allow the production of some normal protein. This shows that there are a greater number of possible intronic mutations that can lead to a mild phenotype and it also underlines the importance of performing cDNA analysis when screening for small gene alterations in the BMD patient population.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darras B. T., Blattner P., Harper J. F., Spiro A. J., Alter S., Francke U. Intragenic deletions in 21 Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)/Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) families studied with the dystrophin cDNA: location of breakpoints on HindIII and BglII exon-containing fragment maps, meiotic and mitotic origin of the mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):620–629. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillard E. F., Chamberlain J. S., Murphy E. G., Duff C. L., Smith B., Burghes A. H., Thompson M. W., Sutherland J., Oss I., Bodrug S. E. Molecular and phenotypic analysis of patients with deletions within the deletion-rich region of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):507–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara Y., Nishio H., Kitoh Y., Takeshima Y., Narita N., Wada H., Yokoyama M., Nakamura H., Matsuo M. A novel point mutation (G-1 to T) in a 5' splice donor site of intron 13 of the dystrophin gene results in exon skipping and is responsible for Becker muscular dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Jan;54(1):53–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Fischbeck K. H., Brown R. H., Johnson M., Medori R., Loike J. D., Harris J. B., Waterston R., Brooke M., Specht L. Characterization of dystrophin in muscle-biopsy specimens from patients with Duchenne's or Becker's muscular dystrophy. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 26;318(21):1363–1368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805263182104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu X. Y., Ray P. N., Murphy E. G., Thompson M. W., Worton R. G. Duplicational mutation at the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus: its frequency, distribution, origin, and phenotypegenotype correlation. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):682–695. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson I. J. A reappraisal of non-consensus mRNA splice sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3795–3798. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C. J., Coovert D. D., Bulman D. E., Ray P. N., Mendell J. R., Burghes A. H. Somatic reversion/suppression in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD): evidence supporting a frame-restoring mechanism in rare dystrophin-positive fibers. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 May;50(5):950–959. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liechti-Gallati S., Koenig M., Kunkel L. M., Frey D., Boltshauser E., Schneider V., Braga S., Moser H. Molecular deletion patterns in Duchenne and Becker type muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;81(4):343–348. doi: 10.1007/BF00283688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Bertelson C. J., Liechti-Gallati S., Moser H., Kunkel L. M. An explanation for the phenotypic differences between patients bearing partial deletions of the DMD locus. Genomics. 1988 Jan;2(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior T. W., Bartolo C., Pearl D. K., Papp A. C., Snyder P. J., Sedra M. S., Burghes A. H., Mendell J. R. Spectrum of small mutations in the dystrophin coding region. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jul;57(1):22–33. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. G., Gardner R. J., Bobrow M. Searching for the 1 in 2,400,000: a review of dystrophin gene point mutations. Hum Mutat. 1994;4(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380040102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. G., Passos-Bueno M. R., Bobrow M., Vainzof M., Zatz M. Point mutation in a Becker muscular dystrophy patient. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jan;2(1):75–77. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. B., Carvalho M., Derse D., O'Brien S. J., Dean M. Detecting single base substitutions as heteroduplex polymorphisms. Genomics. 1992 Feb;12(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90377-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilton S. D., Johnsen R. D., Pedretti J. R., Laing N. G. Two distinct mutations in a single dystrophin gene: identification of an altered splice-site as the primary Becker muscular dystrophy mutation. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jun 15;46(5):563–569. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]