Abstract
The p13E-11 probe has been shown to detect DNA rearrangements in sporadic and familial cases of FSHD. Its use, however, has been hampered by the fact that it detects at least two pairs of EcoRI alleles, one derived from the 4q35 region (D4F104S1), the other from 10q26 (D10F104S2). We have cloned p13E-11 EcoRI fragments from the 4q35 and 10q26 subtelomeric regions and shown the presence of several restriction site differences within the KpnI tandem repeat units. The two loci present a different distribution of restriction sites for the enzyme BlnI which allows differential cleavage of the KpnI units derived from 10q26, leaving intact the 4q35 pair of alleles. This method of differential restriction greatly facilitates the interpretation of Southern blots obtained from affected and unaffected subjects, with an important improvement in reliability for diagnosis and genetic counselling. In addition, this method can be used to investigate the molecular mechanism of the 4q35 rearrangement implicated in the disease and to ascertain whether the rearrangement is because of interchromosomal exchange between 4qter and 10qter KpnI repeats.
Full text
PDF


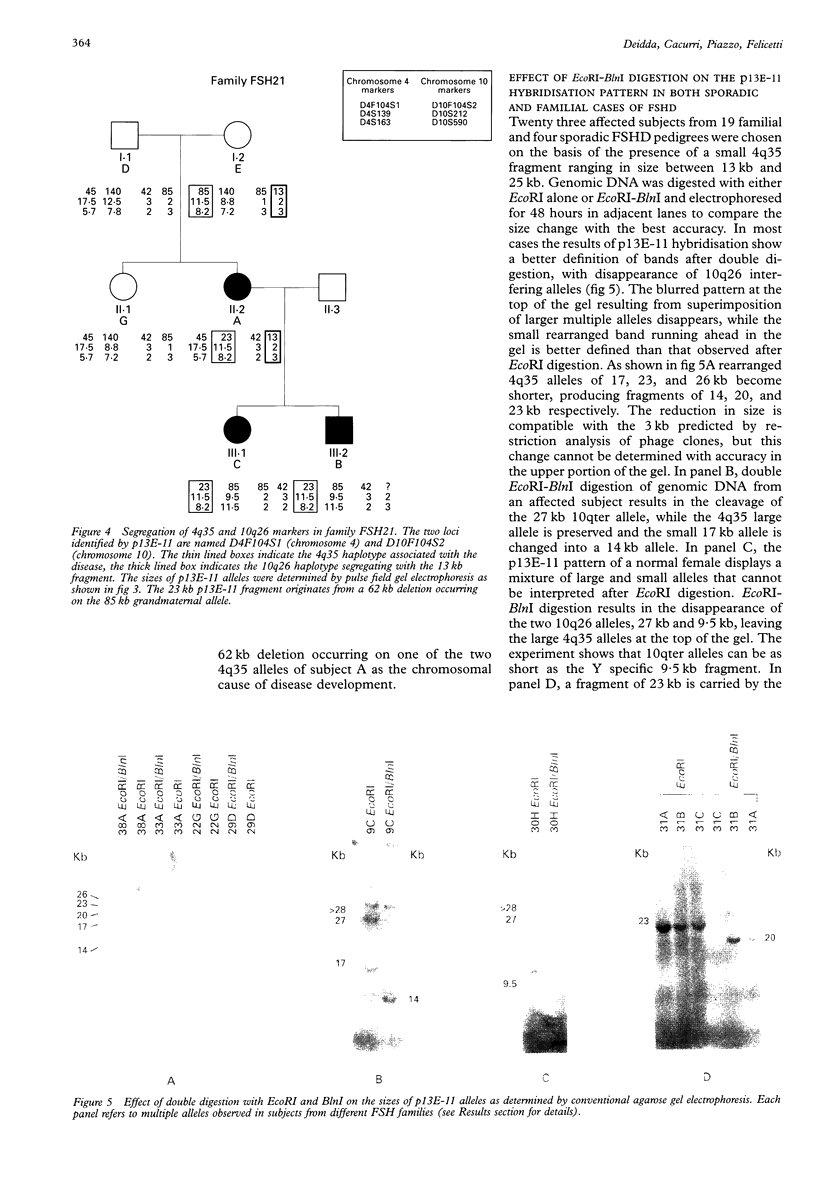

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cacurri S., Deidda G., Piazzo N., Novelletto A., La Cesa I., Servidei S., Galluzzi G., Wijmenga C., Frants R. R., Felicetti L. Chromosome 4q35 haplotypes and DNA rearrangements segregating in affected subjects of 19 Italian families with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;94(4):367–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00201595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deidda G. C., Cacurri S., La Cesa I., Scoppetta C., Felicetti L. 4q35 molecular probes for the diagnosis and genetic counseling of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 1994 Jul;36(1):117–118. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deidda G., Cacurri S., Grisanti P., Vigneti E., Piazzo N., Felicetti L. Physical mapping evidence for a duplicated region on chromosome 10qter showing high homology with the facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy locus on chromosome 4qter. Eur J Hum Genet. 1995;3(3):155–167. doi: 10.1159/000472291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. R., Stajich J. M., Wall S., Carter S. C., Qiu H., Vance J. M., Stewart C. S., Speer M. C., Pufky J., Yamaoka L. H. Evidence for heterogeneity in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD). Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Aug;53(2):401–408. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt J. E., Lyle R., Clark L. N., Valleley E. M., Wright T. J., Wijmenga C., van Deutekom J. C., Francis F., Sharpe P. T., Hofker M. Analysis of the tandem repeat locus D4Z4 associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Aug;3(8):1287–1295. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.8.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfarazi M., Wijmenga C., Upadhyaya M., Weiffenbach B., Hyser C., Mathews K., Murray J., Gilbert J., Pericak-Vance M., Lunt P. Regional mapping of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy gene on 4q35: combined analysis of an international consortium. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Aug;51(2):396–403. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijmenga C., Hewitt J. E., Sandkuijl L. A., Clark L. N., Wright T. J., Dauwerse H. G., Gruter A. M., Hofker M. H., Moerer P., Williamson R. Chromosome 4q DNA rearrangements associated with facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1992 Sep;2(1):26–30. doi: 10.1038/ng0992-26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijmenga C., van Deutekom J. C., Hewitt J. E., Padberg G. W., van Ommen G. J., Hofker M. H., Frants R. R. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of the D4F104S1 locus reveals the size and the parental origin of the facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD)-associated deletions. Genomics. 1994 Jan 1;19(1):21–26. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deutekom J. C., Wijmenga C., van Tienhoven E. A., Gruter A. M., Hewitt J. E., Padberg G. W., van Ommen G. J., Hofker M. H., Frants R. R. FSHD associated DNA rearrangements are due to deletions of integral copies of a 3.2 kb tandemly repeated unit. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2037–2042. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]